光通信
光通信
·编者按·
光通信(Optical Communication)是以光波为载波的通信方式。光波和无线电波同属电磁波,但光波的频率比无线电波的频率高,波长比无线电波的波长短。因此,它具有传输频带宽、通信容量大和抗电磁干扰能力强等优点。光通信按传输媒介的不同,可分为有线光通信和无线光通信(也叫大气光通信)。常用的光通信有:大气激光通信、光纤通信、蓝绿光通信、紫外线通信等。
自1972年我国开始光通信技术的研究至今,已经经历了40年的历程。从1982年第一个光通信实用化工程算起,也有了30年的发展。经过几代光通信技术人员的不懈努力,目前光通信已成为我国与国际先进水平差距最小的科技领域之一。我国现网的光通信技术应用水平已经站到了国际前列;从产业的角度看,我国也成为光通信产品的生产大国,当然还难以说是强国;在光通信前沿技术的研究方面,与国际先进水平却有着较大的差距。光纤通信技术目前仍处在高速发展期,我国在光纤通信技术方面取得了很大进步,但与国际水平的差距正被逐步拉大。我们正面临严峻的挑战,重担落在各位同仁肩上。我相信,只要大家共同努力,一定会在光纤通信技术方面不断有新的突破,攀登到世界光通信技术之巅。
本专题得到了柯熙政教授(西安理工大学光电工程技术研究中心)、陈林教授(湖南大学信息科学与工程学院)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年12月20日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“光通信(Optical Communication)、光通信技术(Optical Communication Technology)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为3379与22728条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“光通信(Optical Communication)、光通信技术(Optical Communication Technology)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“光通信(Optical Communication)、光通信技术(Optical Communication Technology)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
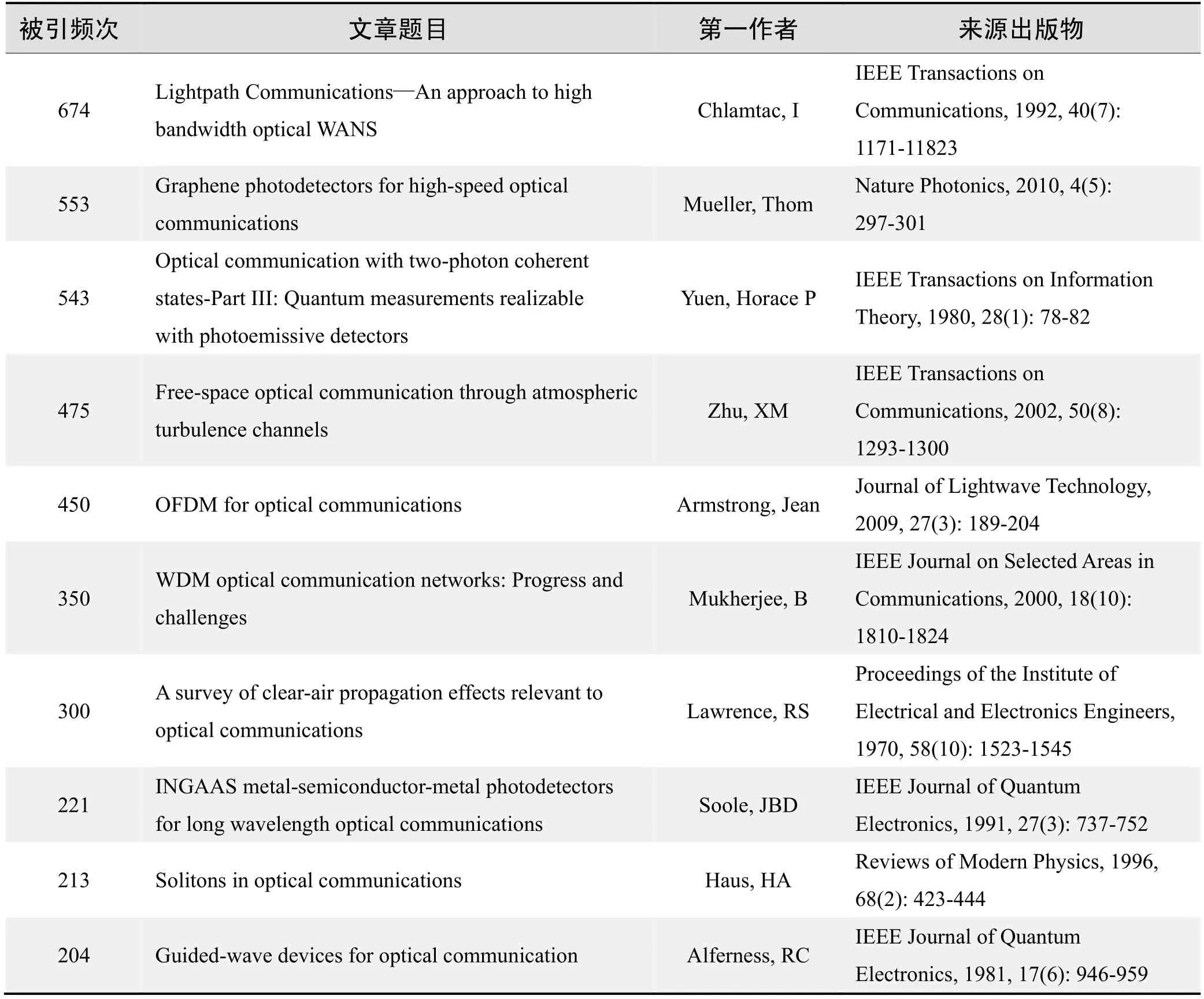
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 30文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
Free-space optical communication through atmospheric turbulence channels
Zhu,XM; Kahn JM
Abstract:In free-space optical communication links,atmospheric turbulence causes fluctuations in both the intensity and the phase of the received light signal,impairing link performance.In this paper,we describe several communication techniques to mitigate turbulence-induced intensity fluctuations,i.e.,signal fading.These techniques are applicable in the regime in which the receiver aperture is smaller than the correlation length of fading and the observation interval is-shorter than the correlation time of fading.We assume that the receiver has no knowledge of the instantaneous fading state.When the receiver knows only the marginal statistics of the fading,a symbol-by-symbol NIL detector can be used to improve detection performance.If the receiver has knowledge of the joint temporal statistics of the fading,maximum-likelihood sequence detection (MLSD) can be employed,yielding a further performance improvement,but at the cost of very high complexity.Spatial diversity reception with multiple receivers can also be used to overcome turbulence-induced fading.We describe the use of NIL detection in spatial diversity reception to reduce the diversity gain penalty caused by correlation between the fading at different receivers.In a companion paper,we describe two reduced-complexity implementations of the MLSD,which make use of a single-step Markov chain model for the fading correlation in conjunction with per-survivor processing. Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is a modulation technique which is now used in most new and emerging broadband wired and wireless communication systems because it is an effective solution to intersymbol interference caused by a dispersive channel.Very recently a number of researchers have shown that OFDM is also a promising technology for optical communications.This paper gives a tutorial overview of OFDM highlighting the aspects that are likely to be important in optical applications.To achieve good performance in optical systems OFDM must be adapted in various ways.The constraints imposed by single mode optical fiber,multimode optical fiber and optical wireless are discussed and the new forms of optical OFDM which have been developed are outlined.The main drawbacks or OFDM are its high peak to average power ratio and its sensitivity to phase noise and frequency offset.The impairments that these cause are described and their implications for optical systems discussed. Recent theoretical work has shown that novel quantum states,called two-photon coherent states (TCS),have significant potential for improving free-space optical communications.The first part of a three-part study of the communication theory of TCS radiation is presented.The issues of quantum-field propagation and optimum quantum-state generation are addressed.In particular,the quantum analog of the classical paraxial diffraction theory for quasimonochromatic scalar waves is developed.This result,which describes the propagation of arbitrary quantum states as a boundary-value problem suitable for communication system analysis,is used to treat a number of quantum transmitter optimization problems.It is shown that,under near-field propagation conditions,a TCS transmitter maximizes field-measurement signal-to-noise ratio among all transmitter quantum states; the performance of the TCS system exceeds that for a conventional (coherent state) transmitter by a factor of Ns+1,where Nsis the average number of signal photons (transmitter energy constraint).Under far-field propagation conditions,it is shown that use of a TCS local oscillator in the receiver can,in principle,attenuate field-measurement quantum noise by a factor equal to the diffraction loss of the channel,if appropriate spatial mode mixing can be achieved.These communcation results are derived by assuming that field-quadrature quantum measurement is performed.In part II of this study,photoemissive reception of TCS radiation will be considered; it will be shown therein that homodyne detection of TCS fields can realize the field-quadrature signal-to-noise ratio performance of part I.In part III,the relationships between photoemissive detection and general quantum measurements will be explored.In particular,a synthesis procedure will be obtained for realizing all the measurements described by arbitrary TCS. Although silicon has dominated solid-state electronics for more than four decades,a variety of other materials are used in photonic devices to expand the wavelength range of operation and improve performance.For example,gallium-nitride based materials enable light emission at blue and ultraviolet wave-lengths(1),and high index contrast silicon-on-insulator facilitates ultradense photonic devices(2,3).Here,we report the first use of a photodetector based on graphene(4,5),a two-dimensional carbon material,in a 10 Gbit s-1optical data link.In this interdigitated metal-graphene-metal photodetector,an asymmetric metallization scheme is adopted to break the mirror symmetry of the internal electric-field profile in conventional graphene field-effect transistor channels(6-9),allowing for efficient photo-detection.A maximum external photoresponsivity of 6.1 mA W-1is achieved at a wavelength of 1.55 mu m.Owing to the unique band structure of graphene(10,11)and extensive developments in graphene electronics(12,13)and wafer-scale synthesis(13),graphene-based integrated electronic-photonic circuits with an operational wavelength range spanning 300 nm to 6 μm (and possibly beyond) can be expected in the future. Free-space optical communications (FSO) propagated over a clear atmosphere suffers from irradiance fluctuation caused by small but random atmospheric temperature fluctuations.This results in decreased signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and consequently impaired performance.In this paper,the error performance of the FSO using a subcarrier intensity modulation (SIM) based on a binary phase shift keying (BPSK) scheme in a clear but turbulent atmosphere is presented.To evaluate the system error performance in turbulence regimes from weak to strong,the probability density function of the received irradiance after traversing the atmosphere is modelled using the gamma-gamma distribution while the negative exponential distribution is used to model turbulence in the saturation region and beyond.The effect of turbulence induced irradiance fluctuation is mitigated using spatial diversity at the receiver.With reference to the single photodetector case,up to 12 dB gain in the electrical SNR is predicted with two direct detection PIN photodetectors in strong atmospheric turbulence.
Keywords:atmospheric turbulence; free-space optical communication; MLSD; spatial diversity reception modulation; orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM); optical communication atmospheric turbulence; diversity; free-space optics (FSO); gamma-gamma distribution; negative exponential distribution; subcarrier modulation
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Communications,2002,50(8):1293-1300
OFDM for Optical Communications
Armstrong,Jean
来源出版物:Journal of Lightwave Technology,2009,27(3):189-204
Optical communication with two-photon coherent states—Part I:Quantum-state propagation and quantum-noise
Yuen,Horace P.; Shapiro,J.H.
来源出版物:IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,1978,24(6):657-668
Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications
Mueller,Thomas; Xia,Fengnian; Avouris,Phaedon
来源出版物:Nature Photonics,2010,4(5):297-301
来源出版物:Journal of Lightwave Technology,2009,27(8):967-973
·推荐综述·
BPSK subcarrier intensity modulated free-space optical communications in atmospheric turbulence
Popoola,Wasiu O.; Ghassemlooy,Zabih
文献编号本领域经典文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 Free-space optical communication through atmospheric turbulence channels Zhu,XM IEEE Transactions on Communications,2002,50(8):1293-1300 2OFDM for optical communications Armstrong,Jean Journal of Lightwave Technology,2009,27(3):189-204 3 Optical communication with two-photon coherent states—Part I:Quantum-state propagation and quantum-noise Yuen,Horace P IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,1978,24(6):657-668 4 Graphene photodetectors for high-speed optical communications Mueller,Thomas Nature Photonics,2010,4(5):297-301 5 BPSK subcarrier intensity modulated freespace optical communications in atmospheric turbulence Popoola,Wasiu O Journal of Lightwave Technology,2009,27(8):967-973

