高能量Pilon骨折手术疗效的影响因素分析
尉俊民
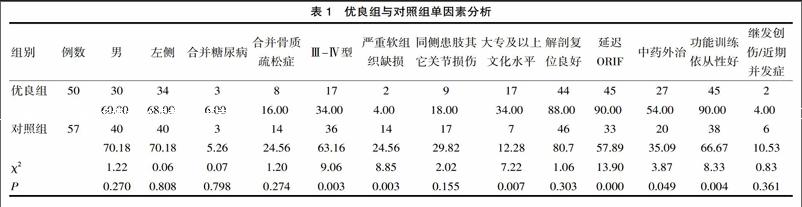
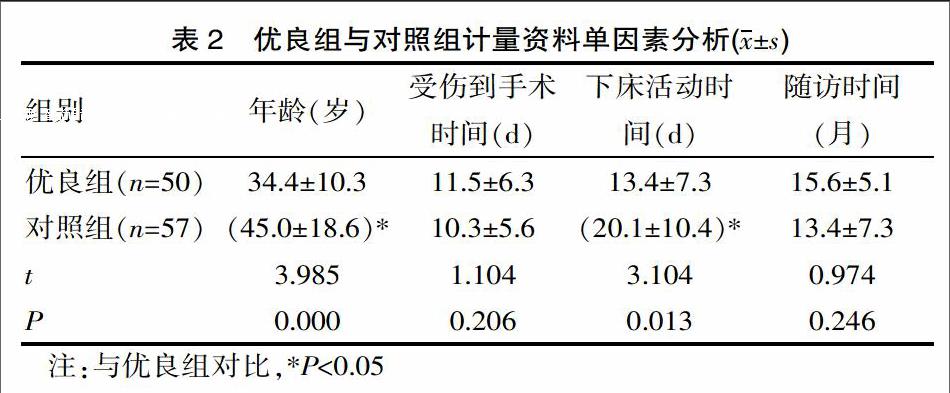
[摘要] 目的 分析高能量Pilon骨折手术疗效的影响因素。方法 方便选取2010年1月—2015年10月,山西省荣军医院治疗高能量Pilon骨折患者107例,恢复优良患者50例纳入优良组(Mazur踝关节评分≥87分),其余57例患者纳入对照组,进行因素分析。结果 患者末次随访Mazur踝关节评分(85.6±7.3)分;优良组Ⅲ-Ⅳ型、严重软组织缺损、大专及以上文化水平、延迟ORIF、中药外治、功能训练依从性好分别占34.00%、4.00%、34.00%、90.00%、54.00%、90.00%,对照组则为63.16%、24.56%、12.28%、57.89%、35.09%、66.67%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);延迟ORIF[OR=1.485,95%CI(1.189~10.763)]、功能锻炼依从性好[OR=1.310,95%CI(1.278~5.115)]成为保护因素,也是可控因素。结论 需科学的安排功能训练。
[关键词] Pilon骨折;手术疗效;高能量创伤;影响因素分析
[中图分类号] R683 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2017)03(b)-0086-03
[Abstract] Objective To analyze the influence factors of curative effect of high energy Pilon fracture surgery. Methods 107 cases of patients with high energy Pilon fracture surgery treated in our hospital from January 2010 to October 2015 were conveniently selected and divided into two groups, 50 cases of patients whose recovery was excellent and good (Mazur ankle joint score ≥87 points) were selected as the excellent and good group, while 57 cases of patients were include into the control group and were given the factor analysis. Results The final follow-up Mazur ankle joint score of patients was(85.6±7.3)points, and the difference in the ratio of Ⅲ-Ⅳ type, severe soft tissue defect, junior college or above, delayed ORIF, external treatment of traditional Chinese medicine and good compliance of functional training between the excellent and good group and control group had statistical significance(34.00%, 4.00%, 34.00%, 90.00%, 54.00%, 90.00% vs 63.16%, 24.56%, 12.28%, 57.89%, 35.09%, 66.67%)(P<0.05), and the delayed ORIF and good compliance of functional exercise became the protective factors and controllable factors. Conclusion We should scientifically arrange the functional training.
[Key words] Pilon fracture; Operative curative effect; High energy wound; Analysis of influence factors
Pilon骨折是指脛骨远端干骺端波及胫距关节面的骨折,是一种常见的关节内骨折,常伴有严重的软组织损伤,占胫骨骨折的3%~10%,占下肢骨折的1%[1]。Pilon骨折预后整体较差,特别是高能量创伤致骨折者,术后并发症发生率高,因关节软骨损伤,常伴有关节僵硬等远期并发症[2]。近年来,骨折手术治疗技术有了明显的进步,手术方式、时机、入路的选择研究较多,个体化治疗水平明显提高,但不同患者预后仍存在较大的差异。该次研究试2010年1月—2015年10月,山西省荣军医院治疗高能量Pilon骨折患者107例,分析手术疗效的影响因素,为手术治疗管理提供依据,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
采用回顾性分析方便选取该医院收治的高能量Pilon骨折患者作为研究对象。纳入标准:①高能量所致Pilon骨折;②明确外伤历史;③初次骨折,无原发性功能障碍;④手术治疗,Rured-AllgowerⅡ~Ⅲ;⑤年龄>18岁;④临床资料完整。排除标准:①合并严重的血管神经损伤,需进行神经重建等综合治疗;②不符合人入选标准;③二次骨折;④原发性严重的运动功能障碍。入选对象107例,其中男70例、女37例,年龄21~76岁,平均(40.4±10.2)岁。按照Mazur踝关节恢复情况,将恢复优良患者50例纳入优良组(Mazur踝关节评分≥87分),其余57例患者纳入对照组,进行因素分析。优良组患者50例,男32例,女18例,年龄21~74,平均年龄(39.8±8.7)岁;对照组患者57例,男38例,女19例,年龄22~76岁,平均年龄(41.7±11.3)岁。两组患者在病情、年龄、性别等方面,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。

