绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫流行病学及分型研究进展
董 辉,陆瑶瑶,杨玉荣
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2017.09.014
绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫流行病学及分型研究进展
董 辉,陆瑶瑶,杨玉荣1
动物住肉孢子虫病可引起畜牧养殖业的经济损失,影响食品质量安全,威胁人类健康。国际上已确定的绵羊(Ovisaries)住肉孢子虫有4种:S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea、S.medusiformis,山羊(Caprahircus)住肉孢子虫有3种:S.capracanis、S.hircicanis、S.moulei。本文综述绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的生活史、国内和国际的流行情况、致病性、形态学特点和诊断方法,以期为中国绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的生物学特征研究及其诊断分型提供有力基础依据。
住肉孢子虫;绵羊;山羊;流行病学;形态学;分型; 分子生物学
住肉孢子虫(Sarcocystis)为顶复亚门,孢子虫纲,真球虫目,肉孢子虫科,孢子虫属的一种原生性细胞内寄生虫[1]。住肉孢子虫在世界分布广泛,人畜均会感染[2]。1843年Miescher第1次在鼠横纹肌中发现了白色线状的住肉孢子虫包囊[3-4],到目前为止在动物中一共发现有196种住肉孢子虫[5]。住肉孢子虫具有严格的宿主选择性,其生活史需要在中间宿主和终末宿主中完成,中间宿主多为草食动物或者杂食动物,终末宿主多为肉食动物[6-7]。住肉孢子虫可以在猪、牛和羊等中间宿主的肌肉形成包囊[8],住肉孢子虫虫型和感染数量的不同,其致病性也具有明显的差异,可引起家畜的厌食、流产、甚至死亡,人食用含住肉孢子虫的肉后,会引起胃肠道疾病。羊住肉孢子虫病可引起畜牧业经济损失,降低肉品质量,危害公共健康[9]。本文综述我国和国际上已确定的绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的流行情况、生活史、形态学特点和分型、致病性以及分子学诊断方法,为深入研究国内绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫生物学特征提供有力依据。
1 生活史
住肉孢子虫与哈蒙球虫、弓形虫和新孢子虫的[10-12]生活史十分相似,分为有性生殖和无性生殖。以S.tenalla的生活史为例解释绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的生活史[4]。当犬科动物食入含有S.tenella包囊的组织后,包囊在胃和小肠内消化释放出缓殖子,缓殖子在侵入小肠粘膜的过程中非常有活力,摄入包囊6 HPI(hours post inoculation),可以在杯状细胞内发现缓殖子。然后,缓殖子进入配子生殖阶段,发育为雌、雄配子,其数量比约为95∶5,雌配子和雄配子受精后产生合子,合子外分泌囊壁形成卵囊。卵囊在肠壁内进行孢子化,每个孢子化的卵囊内含有两个孢子囊,每个孢子囊内形成4个子孢子。孢子化的卵囊壁薄,易于破裂,游离的孢子囊会进入肠腔,随终末宿主的粪便排出到外界的环境中[1]。当中间宿主绵羊误食饲料和水中携带的S.tenella的卵囊,卵囊进入小肠后释放出的子孢子经肠系膜和肠系膜淋巴结动脉,进入全身动脉血管内皮细胞完成第一代裂殖生殖(9~21 DPI),然后进入全身毛细血管完成第二代裂殖生殖(16~40 DPI),虫血症时间为14~32 DPI,然后裂殖子进入中枢神经组织、心脏形成包囊。
2 流行病学
2.1 世界各国的感染情况 绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫病在世界分布广泛,文献统计绵羊住肉孢子虫病阳性率为31.42%~93.31%,山羊住肉孢子虫病阳性率为28.30%~83.69%。国际上广泛承认和确定的绵羊住肉孢子虫有4种,S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea、S.medusiformis。目前S.tenella、S.gigantea、S.arieticanis世界广泛分布,S.medusiformis只在澳大利亚、新西兰、伊朗和意大利有报道[7]。国际上广泛承认和确定的山羊住肉孢子虫有S.capracanis、S.hircicanis、S.moulei。山羊住肉孢子虫在欧洲和北美洲文献报道尚少。世界绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫感染和分布情况详见表1。
表1 世界绵羊及山羊住肉孢子虫病流行情况
Tab.1 Prevalence of Sarcocystis in sheep or goats from the world

宿主Host位置Location阳性率Positive%虫型Species参考文献References绵羊大洋洲93.31(990/1061)S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea、S.medusiformis[1]欧洲31.42(3158/10051)S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea、S.medusiformis[1,7][13]非洲54.67(621/1136)S.tenella、S.arieticanis[1]南美36.22(343/947)S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea[1,14][12,15]北美67.40(1141/1693)S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea[1]亚洲48.02(26061/54270)S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea、S.medusiformis[1,4,8,10,16-87]山羊大洋洲28.33(17/60)—[1]非洲76.80(907/1181)S.capracanis[1]南美83.69(585/699)S.capracanis[1,14]亚洲53.89(5522/10246)S.capracanis、S.hircicanis、S.moulei[1,5,6,8,20,26,33,50,51,61,73,80,84,88-91]
2.2 在我国的流行情况 我国已确定的绵羊住肉孢子虫有3种:S.tenella、S.arieticanis、S.gigantea,已确定的山羊住肉孢子虫有3种:S.hircianis、S.capracanis、S.moulei。绵羊住肉孢子虫病的阳性率在7.74%~100%,山羊住肉孢子虫病的阳性率在9.73%~77.94%。根据已报道的绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫病的流行病学调查,统计中国绵羊和山羊的住肉孢子虫病的分布情况,发现中国多地区羊感染住肉孢子虫,且感染率较高,见表2。
表2 中国绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫流行病学调查
Tab.2 Epidemiological investigation of Sarcocystis in sheep and goats of China
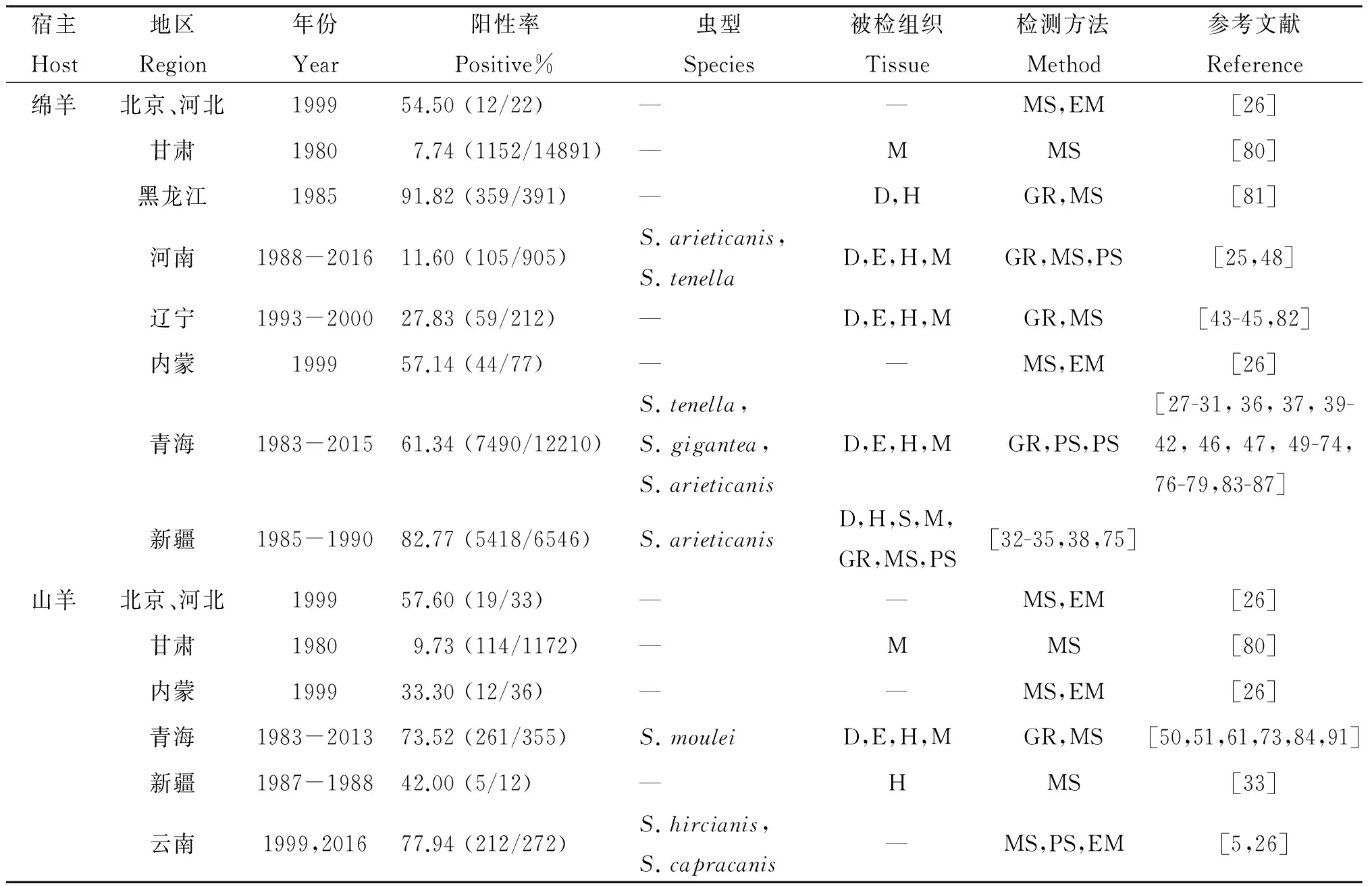
宿主Host地区Region年份Year阳性率Positive%虫型Species被检组织Tissue检测方法Method参考文献Reference绵羊北京、河北199954.50(12/22)——MS,EM[26]甘肃19807.74(1152/14891)—MMS[80]黑龙江198591.82(359/391)—D,HGR,MS[81]河南1988-201611.60(105/905)S.arieticanis,S.tenellaD,E,H,MGR,MS,PS[25,48]辽宁1993-200027.83(59/212)—D,E,H,MGR,MS[43-45,82]内蒙199957.14(44/77)——MS,EM[26]青海1983-201561.34(7490/12210)S.tenella,S.gigantea,S.arieticanisD,E,H,MGR,PS,PS[27-31,36,37,39-42,46,47,49-74,76-79,83-87]新疆1985-199082.77(5418/6546)S.arieticanisD,H,S,M,GR,MS,PS[32-35,38,75]山羊北京、河北199957.60(19/33)——MS,EM[26]甘肃19809.73(114/1172)—MMS[80]内蒙199933.30(12/36)——MS,EM[26]青海1983-201373.52(261/355)S.mouleiD,E,H,MGR,MS[50,51,61,73,84,91]新疆1987-198842.00(5/12)—HMS[33]云南1999,201677.94(212/272)S.hircianis,S.capracanis—MS,PS,EM[5,26]
D: diaphragm 膈肌; E: esophagus 食道肌; H: heart 心肌; M: skeletal muscle 骨骼肌; —:未报道;
EM: electron microscope 电子显微镜; GR: Gross 肉眼观察; MS: muscle squash 肌肉压片; PS: paraffin section 石蜡切片
3 致病性
绵羊住肉孢子虫S.tenella和S.arieticanis的终末宿主为犬科动物[7](表3)。S.tenella强致病性,绵羊感染后会出现厌食、体重减轻、贫血、产奶量降低、早产、流产、神经症状和死亡等[15,21]。S.arieticanis的致病性稍弱于S.tenalla[21],感染S.arieticanis可以引起绵羊腹泻、食欲下降、失去活动精神、毛发减少、虚弱等[4]。S.gigantea和S.medusiformis的终末宿主是猫科动物,对绵羊无致病性[7],当组织间寄生的住肉孢子虫包囊破裂时,引起肌肉的炎症反应将影响肉的品质[15]。山羊住肉孢子虫中,S.capracanis和S.hircicanis的终末宿主是犬科动物,S.capracanis致病性强于S.hircicanis,可以引起山羊体温升高、体重减轻、流产和死亡[6]。S.moulei的终末宿主是猫科动物,无致病性[6]。
绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫对中间宿主的致病性高于终末宿主,通过犬科动物传播的住肉孢子虫的致病性要强于通过猫科动物传播住的肉孢子虫(对比见表3)。对于强致病性的S.tenella和S.arieticanis引起的羊住肉孢子虫病,其感染严重程度与最初卵囊的摄入量、宿主的免疫状态及营养状态有关[4,7],但强致病性的绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫对人没有致病性。绵羊可以同时感染两种类型的住肉孢子虫(有致病性和无致病性的虫型)[7]。
4 形态学特征
4.1 光学显微镜下的形态结构 很难根据临床症状诊断住肉孢子虫病[21]。2016年,Damboriarena就报道了绵羊食道肌大量随机分布的白色椭圆形的S.gigantea包囊[15],因为绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的包囊通常寄生在肌肉组织。住肉孢子虫与肌纤维平行,形态呈纺锤形、圆柱形、卵圆型等,颜色呈灰白色、乳白色。S.gigantea和S.medusiformis包囊可以通过肉眼观察,S.tenella和S.arieticanis的包囊需要通过显微镜观察。山羊住肉孢子虫包囊均可以通过肉眼观察。
蛋白酶可以将肌组织和包囊壁消化破解,释放缓殖子,缓殖子呈月牙或香蕉型,通过光学显微镜可以检查住肉孢子虫的缓殖子[19,21];组织学压片技术可以观察到宿主肌肉组织中非肉眼可见的住肉孢子虫包囊[21],当住肉孢子虫的感染密度高时,组织学压片方法优于其它方法[14],住肉孢子虫对宿主选择和在组织器官内分布均有特异性,用光学显微镜观察H&E染色的切片可以判定住肉孢子虫包囊壁的薄厚并观察包囊壁内的缓殖子[21],所以结合组织学方法可以对住肉孢子虫进鉴别和分型[25]。比如绵羊住肉孢子虫中S.tenella是厚壁的住肉孢子虫,寄生于绵羊的心肌和舌肌,S.arieticanis是薄壁的住肉孢子虫,寄生于心肌,而S.gigantea和S.medusiformis为薄壁的住肉孢子虫未寄生于心肌。
4.2 超微结构 住肉孢子虫包囊壁由两层构成,包囊外有囊壁和突起(Villar protrusions, VP),内壁向内延伸形成隔,将囊腔分成小室,小室内有大量香蕉状或肾形的缓殖子和母细胞。包囊壁的超微结构在不同类型的住肉孢子虫中具有明显的区别,目前为止住肉孢子虫包囊壁的种类至少已有82种[1]。不同住肉孢子虫包囊壁VP的类型有较大差别[1],所以通过电子显微镜对比超微结构的差异是对住肉孢子虫分型的一种有效方法[4],也是住肉孢子分类学中最为认可的手段[7]。绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫形态特征见表3[1,5]。
表3 绵羊及山羊住肉孢子虫形态特征
Tab.3 Morphology of the Sarcocystis in the sheep or goats

虫型Species宿主Host肉眼Gross包囊大小和壁厚度Cystssize(mm)andWal(μm)突起类型Villarprotrusions分布Distribution致病性Pathogenicity膈肌D心肌H中枢神经系统CNS绵羊或山羊SheeporGoat人Human终末宿主DefinitiveHostsS.gigantea绵羊可见7.5×5薄壁<2Type21:菜花状有无无无无家猫S.medusiformis可见8×0.2薄壁<2Type20:四边形有无无无无家猫S.tenella不可见最长0.7厚壁1~3Type14:栅栏状无有有强无家犬、狼、狐S.arieticanis不可见最长0.9薄壁<1Type7b:细丝状有有无较强无家犬S.capracanis山羊可见1×0.1厚壁2-3Type14:栅栏状有有有有无家犬、狼、狐S.hircicanis可见最长2.5薄壁<1Type7a:细丝状有有无无无家犬S.moulei可见17×7厚壁3~4Type21:菜花状有无无—无家猫
D: diaphragm 膈肌;H: heart 心肌;CNS: central nervous system 中枢神经系统;S: sheep 绵羊;G: goat 山羊;Hu: human 人;—: 未报道
5 分子生物学分型
近年来随着分子生物学技术的发展,关于住肉孢子虫基因序列的研究主要集中在分子流行病学调查、分型研究和种系发育。目前,通过核糖体小亚基(18S rRNA)、核糖体大亚基(28S rRNA)鉴别住肉孢子虫较为普遍[7]。内转录间隔区-ITS(Internal transcribed spacer)、线粒体细胞色素氧化酶Ⅰ-cox1(Cytochrome C oxidase subunit I)[5,93]也是良好的基因序列研究的选择。已报道的关于绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫PCR引物序列,见表4。
6 讨 论
国内对于住肉孢子虫病的研究多集中在黄牛[94]、水牛,关于绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫的研究多集中于流行病学方面的研究,关于其生活史和其它生物学特征尚未完全证实。研究住肉孢子虫,一方面是探究住肉孢子虫的整体感染情况、季节动态变化、地理区域分布,另一方面是明确我国存在的住肉孢子虫,对其分型,从而提高流行病学调查的信息多样性和准确性,确定是否会对畜牧业及人类的食品安全造成威胁并有效控制该病。
表4 绵羊和山羊住肉孢子虫PCR引物序列
Tab.4 Sequences of PCR primers of Sarcocystis in sheep or goats
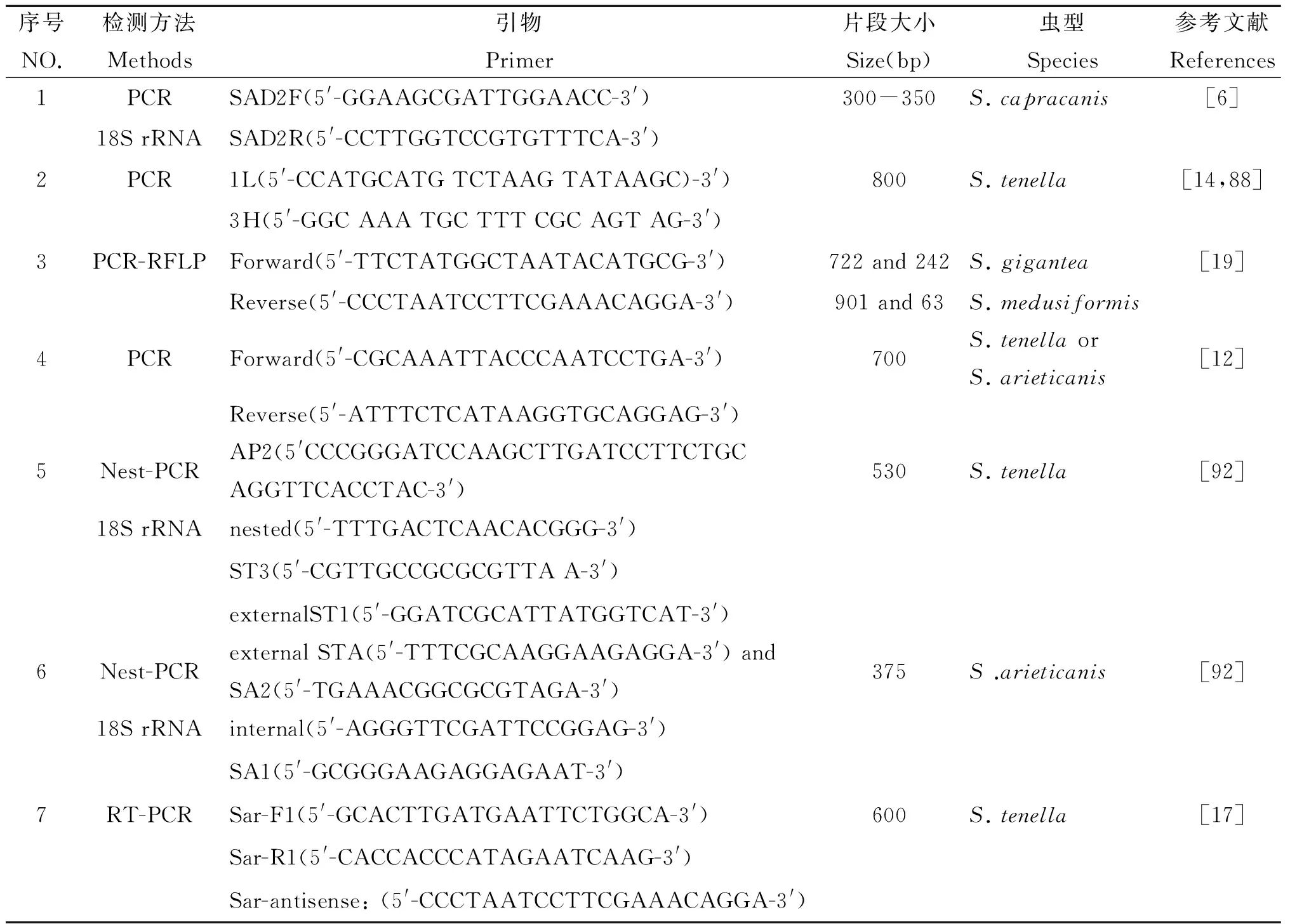
序号NO.检测方法Methods引物Primer片段大小Size(bp)虫型Species参考文献References1PCRSAD2F(5'-GGAAGCGATTGGAACC-3')300-350S.capracanis[6]18SrRNASAD2R(5'-CCTTGGTCCGTGTTTCA-3')2PCR1L(5'-CCATGCATGTCTAAGTATAAGC)-3')800S.tenella[14,88]3H(5'-GGCAAATGCTTTCGCAGTAG-3')3PCR-RFLPForward(5'-TTCTATGGCTAATACATGCG-3')722and242S.gigantea[19]Reverse(5'-CCCTAATCCTTCGAAACAGGA-3')901and63S.medusiformis4PCRForward(5'-CGCAAATTACCCAATCCTGA-3')700S.tenellaorS.arieticanis[12]Reverse(5'-ATTTCTCATAAGGTGCAGGAG-3')5Nest-PCRAP2(5'CCCGGGATCCAAGCTTGATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3')530S.tenella[92]18SrRNAnested(5'-TTTGACTCAACACGGG-3')ST3(5'-CGTTGCCGCGCGTTAA-3')externalST1(5'-GGATCGCATTATGGTCAT-3')6Nest-PCRexternalSTA(5'-TTTCGCAAGGAAGAGGA-3')andSA2(5'-TGAAACGGCGCGTAGA-3')375S.arieticanis[92]18SrRNAinternal(5'-AGGGTTCGATTCCGGAG-3')SA1(5'-GCGGGAAGAGGAGAAT-3')7RT-PCRSar-F1(5'-GCACTTGATGAATTCTGGCA-3')600S.tenella[17]Sar-R1(5'-CACCACCCATAGAATCAAG-3')Sar-antisense:(5'-CCCTAATCCTTCGAAACAGGA-3')
[1] Dubey JP, Calero BBR, Rosenthal BM, et al. Sarcocystosis of animals and humans[M]. 2nd. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2015.
[2] Mirzaei M, Rezaei H. A survey onSarcocystisspp. infection in cattle of Tabriz city, Iran[J]. J Parasit Dis, 2016, 40 (3): 648-651. DOI: 10. 1007/s12639-014-0551-2
[3] Fayer R, Esposito DH, Dubey JP. Human infections withSarcocystisspecies[J]. Clin Microbiol Rev, 2015, 28(2): 295-311. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00113-14
[4] Al Quraishy S, Morsy K, Bashtar AR, et al.Sarcocystisarieticanis(Apicomplexa: Sarcocystidae) infecting the heart muscles of the domestic sheep,Ovisaries(Artiodactyla: Bovidae), from K. S. A. on the basis of light and electron microscopic data[J]. Parasitol Res, 2014, 113(10): 3823-3831. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-014-4050-2
[5] Hu JJ, Liu TT, Liu Q, et al. Prevalence, morphology, and molecular characteristics ofSarcocystisspp. in domestic goats (Caprahircus) from Kunming, China[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(10): 1-9. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-016-5163-6
[6] Kutty MK, Latif B, Muslim A, et al. Detection of sarcocystosis in goats in Malaysia by light microscopy, histology, and PCR[J]. Trop Anim Health Product, 2015, 47(4): 751-756. DOI: 10.1007/s11250-015-0789-4
[7] Pipia AP, Varcasia A, Zidda A, et al. Cross-sectional investigation on sheep sarcosporidiosis in Sardinia, Italy[J]. Vet Parasitol, 2016, 3-4: 13-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.vprsr.2016.05.004
[8] Latif B, Kannan Kutty M, Muslim A, et al. Light microscopy and molecular identification ofSarcocystisspp. in meat producing animals in Selangor, Malaysia[J]. Trop Biomed, 2015, 32(3): 444-452.
[9] Blagojevic B, Antic D. Assessment of potential contribution of official meat inspection and abattoir process hygiene to biological safety assurance of final beef and pork carcasses[J]. Food Ctrl, 2014, 36(1): 174-182. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.08.018
[10] Rassouli M, Ahmadpanahi J, Alvandi A. Prevalence ofSarcocystisspp. andHammondiaspp. microcysts in esophagus tissue of sheep and cattle, emphasized on their morphological differences[J]. Parasitol Res, 2014, 113(10): 3801-3805. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-014-4047-x
[11] Feng Y, Lu Y, Wang Y, et al.ToxoplasmagondiiandNeosporacaninumin free-range chickens in Henan Province of China[J]. BioMed Res Intl, 2016, 2016: 8290536. DOI: 10.1155/2016/8290536
[12] Wang K, Feng YJ, Fu XY, et al. Virulence and pathogenicity ofToxoplasmagondiiToxoDB#17 strain oocysts in Kunming mice[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2017, 33(1): 49-52. (in Chinese)
王凯,冯永杰,付晓莹,等. ToxoDB# 17型弓形虫卵囊对昆明小鼠致病性的研究[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2017, 33(1): 49-52. DOI: 10. 3969/J. ISSN. 1002-2694. 2017. 01. 009.
[13] Bacci C, Vismarra A, Passeri B, et al. Detection ofToxoplasmagondiiandSarcocystistenellain indigenous Cornigliese sheep in Italy using serological and molecular methods[J]. Small Ruminant Res, 2016, 135: 13-16. DOI: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2015.12.025
[14] Bittencourt MV, Meneses ID, Ribeiro-Andrade M, et al.Sarcocystisspp. in sheep and goats: frequency of infection and species identification by morphological, ultrastructural, and molecular tests in Bahia, Brazil[J]. Parasitol Res, 2016, 115(4): 1683-1689. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-016-4909-5
[15] Damboriarena PA, Silveira CS, Morais RM, et al. Natural Sarcocystis gigantea infection in sheep from Southern Brazil[J]. Cienc Rural, 2016, 46(7): 1229-1232. DOI: 10.1590/0103-8478cr20151183
[16] Mirzaei M, Rezaei H. The role of sheep in the epidemiology ofSarcocystisspp. in Tabriz area northwest of Iran[J]. J Parasit Dis, 2016, 40(2): 1-4. DOI: 10.1007/s12639-014-0495-6
[17] Salehi M, Bahari P, Vatanchian M. First molecular identification of Sarcocystis ovicanis (Protozoa, Apicomplexa) in the brain of sheep in Iran[J]. Iranian J Parasitol, 2014, 9(2): 286-291.
[18] Bahari P, Salehi M, Seyedabadi M, et al. Molecular identification of macroscopic and microscopic cysts of sarcocystis in sheep in north Khorasan province, Iran[J]. Intl J Mol Cellular Med, 2014, 3(1): 51-56.
[19] Farhang PF, Yakhchali M, Mardani K. Molecular determination of abundance of infection with sarcocystis species in slaughtered sheep of Urmia, Iran[J]. Vet Res Forum, 2014, 5(3): 181-186.
[20] Elbadre MA, Osman FA, Hussien SM. Studies on sarcocystis in sheep and goats using serological survey in New Valley governorate, Egypt[J]. Intl J Agro Vet Med Sci, 2014, 5(8): 150-153.
[21] Gokpinar S, Yildiz K, Gurcan IS. Prevalence and concentration of Sarcocystis spp. microscopic cysts in sheep muscles using percoll gradient centrifugation[J]. Israel J Vet Med, 2014, 69(1): 16-19.
[22] Hajimohammadi B, Zohourtabar A, Bafghi AF, et al. Occurrence and distribution of sarcocystis parasite isolated from sheep in Yazd province, Iran[J]. J Commun Health Res, 2014, 3(3): 204-209.
[23] Ayoub IA, Anas H, Faisal A. Molecular identification and phylogeny of microscopic sarcocystis sheep in Baghdad Province[J]. Intl J Mol Cellular Med, 2016, 3(11): 200-205.
[24] Arash O, Sadaf S, Saeed N. Alterations of some acute phase proteins, and antioxidant status in sheep following natural infection with some metacestodes, andSarcocystisspp[J]. Sci Parasitol, 2016, 17(1-2): 16-25.
[25] Dong H, Lu YY, Wang YH, et al. Histopathological and typing the Sarcocystis in myocardium of cattle and sheep [J]. Chin J Vet Sci, 2018, 38(1). Article in press. (in Chinese)
董辉, 陆瑶瑶, 王英华, 等. 牛和羊心肌住肉孢子虫包囊病理组织学及分型研究[J]. 中国兽医学报,2018,38(1). 待发表.
[26] Wang M, Ma JH, Zhang CG, et al. A survey of Sarcocystis infection in domestic animals[J]. Chin J Vet Med, 1999, 25(12): 11-12. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.1999.12.004 (in Chinese)
汪明, 马俊华, 张长弓, 等. 家畜住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 1999, 25(12):11-12.
[27] Li O, Xu TD, Li W, et al. Survey on sarcosporidosis of sheep in Qinghai Province[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1989(2): 12-13. (in Chinese)
李欧, 徐天德, 李伟,等. 青海省绵羊肉孢子虫病调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1989(2):12-13.
[28] Li W, Li O, Li ZN, et al. Investigation on the sarcosporidosis in a sheep breeding farm o f Qinghai Province[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1991(1):18-19. (in Chinese)
李伟, 李欧, 李志宁, 等. 青海省某种羊场绵羊肉孢子虫病调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1991(1):18-19.
[29] Han XM. Survey on sarcosporidosis of slaughter livestocks in Xining, Qinghai[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2001, 31(3):27-28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2001.03.016 (in Chinese)
韩秀敏. 青海省西宁市屠宰牲畜住肉孢子虫病的调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2001, 31(3):27-28.
[30] Ma WS, Wang HY. Survey on parasites of locally organs of sheep in Qingshiju[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1996, 26(1): 31-32. (in Chinese)
马维胜, 王海英. 青石咀地区绵羊局部脏器寄生虫调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1996, 26(1):31-32.
[31] Fei YM. A survey of Sarcocystis infection in sheep of Wulan County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2002, 32(1):35-35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2002.01.014 (in Chinese)
费延梅. 乌兰县羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2002, 32(1):35.
[32] Wang GL, Xu M, Nusilaiti, et al. Survey on the pathogen of Sarcocystis infection in sheep of Urumqi city[J]. Xinjiang Anim Husb, 1990(5): 9, 27. (in Chinese)
王光雷, 徐敏, 努斯来提,等. 乌鲁木齐市绵羊住肉孢子虫病病原的调查研究[J]. 新疆畜牧业, 1990(5): 9, 27.
[33] Liu JR, Wang HJ. Epidemiological investigation on the Sarcocystis of sheep in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agri Sci, 1989, (3): 39-40. (in Chinese)
刘继荣, 王宏江. 新疆绵羊住肉孢子虫流行病学调查[J]. 新疆农业科学, 1989(3): 39-40.
[34] Jiang YP, Liu JR, Miao LW, et al. Survey on the epidemic situation of sarcosporidosis in sheep in Shihezi, Xinjiang[J]. Chin Vet Sci, 1985(12): 18-20. DOI: 10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.1985.12.012 (in Chinese)
姜悦平, 刘继荣, 缪礼维,等. 新疆石河子地区绵羊住肉孢子虫病流行情况的调查[J]. 中国兽医科学, 1985(12):18-20.
[35] Chen YM, Wang GL, Wei T, et al. Survey of sarcocystis infection in sheep of Urumqi County, Xinjiang[J]. J Trad Chin Vet Med, 1991(2): 9-10. DOI: 10.13823/j.cnki.jtcvm.1991.02.004 (in Chinese)
陈亚民, 王光雷, 魏珽,等. 新疆乌鲁木齐县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况的调查[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 1991(2):9-10.
[36] Peng JX, Nanlaji. Survey ofSarcocystisinfection in sheep of Xunhua County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2010, 31(7): 65. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1733.2010.07.042 (in Chinese)
彭金霞, 南拉吉. 循化县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 畜牧兽医山东, 2010, 31(7): 65.
[37] Zhang HB, Cangnianggai, Hou HM, et al. Survey ofSarcocystisinfection in cattle and sheep diaphragm of Zeku County[J]. Anim Husb Vet Med, 2014, 46(7): 138-138. (in Chinese)
张洪波, 仓娘盖, 侯洪梅,等. 泽库县牛羊膈肌住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2014, 46(7):138.
[38] Wang GL, Wei T, Wang XY, et al. Morphological study onS.arieticanis[J]. Xinjiang Anim Husb, 1989, (5): 37-38. (in Chinese)
王光雷, 魏珽, 王兴亚,等. 白羊犬住肉孢子虫的形态学研究[J]. 新疆畜牧业, 1989(5): 37-38.
[39] Han ZC, Li X, Yang WC. Survey on parasites of sheep in Guinan County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2000, 30(5): 29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2000.05.017 (in Chinese)
韩占成, 李昕, 杨文才. 贵南县绵羊寄生虫区系调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2000, 30(5): 29.
[40] Caigejia, Li YH. Survey ofSarcocystisinfection in sheep of Maying town in Guinan County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2006, 36(4): 28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2006.04.014 (in Chinese)
才格加, 李元海. 贵南县过马营镇绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2006, 36(4): 28.
[41] Yin H. To test the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in Xunhua County[J]. Chin J Anim Infect Dis, 2004, 12(3):64. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6422.2004.03.034 (in Chinese)
尹辉. 检验循化县绵羊胴体住肉孢子虫感染情况[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2004, 12(3): 64.
[42] Ma SG, Guo W, Dong ZS. Survey on sarcosporidosis infection in sheep of Ledu County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2003, 33(1): 17. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2003.01.011 (in Chinese)
马生贵, 郭伟, 董泽生. 乐都县绵羊住肉孢子虫病感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2003, 33(1): 17.
[43] Wang SQ, Wang K, Bi CM, et al. Survey on main parasitic flora of sheep in Western Liaoxing[J]. Meat Thyg, 2002, (9): 38-39. (in Chinese)
王书全,王坤, 毕聪明,等. 辽西地区绵羊主要寄生虫区系调查[J]. 肉品卫生, 2002, (9): 38-39.
[44] Liu XG, Zhu R, Yu JL, et al. A case ofSarcocystisinfection in the whole body muscle of sheep[J]. Meat Thyg, 1997, 24(3): 22. (in Chinese)
刘孝刚, 朱瑞, 于金玲,等. 绵羊全身肌肉感染住肉孢子虫一例[J]. 肉品卫生, 1997, 24(3): 22.
[45] Liu XG, Yu JL, Zhu R, et al. Survey onSarcocystisin sheep[J]. Meat Thyg, 1996(10): 10-11. (in Chinese)
刘孝刚, 闫宝贵. 绵羊住肉孢子虫的调查[J]. 肉品卫生, 1996(10):10-11.
[46] Zhong WD. Survey ofSarcocystisinfection in sheep in the market of Minhe County[J]. Chin Anim Health Inspec, 2009, 26(9): 50. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2009.09.025 (in Chinese)
钟卫东. 民和县各市场羊酮体住肉孢子虫感染调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2009, 26(9):50.
[47] Yang GS. Survey onSarcocystisinfection in sheep slaughtering in Minhe County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2014, 44(1): 30. (in Chinese)
杨更善. 民和县屠宰环节绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2014, 44(1):30.
[48] Gong GX. Investigation report onSarcocystisof cattles and sheep[J]. Meat Thyg, 1997, (6): 13-14. (in Chinese)
龚广学. 牛羊肉孢子虫的调查报告[J]. 肉品卫生, 1997(6):13-14.
[49] Xu CF. Survey onSarcocystisinfection in sheep of Pingan County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2005, 35(4): 4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2005.04.015 (in Chinese)
徐春芳. 平安县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2005, 35(4):4.
[50] Zhou WY. Sampling investigation and analysis of sarcosporidosis of Commercial Livestock in Lenghu, Qinghai[J]. Chin Anim Health Inspec, 2011, 28(9):51-52. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2011.09.023 (in Chinese)
周伟业. 青海冷湖地区商品牲畜肉孢子虫病抽样调查与分析[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2011, 28(9):51-52.
[51] Li SS. Survey onSarcocystisinfection in sheep of Qingshizui, Qinghai[J]. Chin Vet Sci, 2014, 50(10): 41-42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2014.10.014 (in Chinese)
李世双. 青海青石嘴羊住肉孢子虫感染情况的调查[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2014, 50(10):41-42.
[52] Guo ZP. Test report on sarcosporidosis of sheep in Dulan County, Qinghai Province[J]. Chin Anim Health Inspec, 2011, 28(12): 44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2011.12.020 (in Chinese)
郭正朴. 青海省都兰县羊胴体肉孢子虫病检验报告[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2011, 28(12):44.
[53] Li CH, Cai JZ. Epidemiological investigation of sarcosporidosis in yak and sheep in parts of Qinghai Province[J]. Chin Vet Sci, 2009,(9): 33-35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-6005.2009.09.014 (in Chinese)
李春花, 蔡进忠. 青海省部分地区牦牛和绵羊住肉孢子虫病流行病学调查[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2009(9):33-35.
[54] Chen YM, Wang XY, Wei T. Survey onSarcocystisinfection in Tibetan Sheep in Gangcha County, Qinghai Province[J]. J Trad Chin Vet Med, 1989, (5): 13-15. DOI: 10.13823/j.cnki.jtcvm.1989.05.007 (in Chinese)
陈亚民, 王兴亚. 青海省刚察县藏系绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况的调查[J]. 中兽医医药杂志, 1989(5):13-15.
[55] Li Y, Kang M, Li YJ, et al. Survey on diaphragmatic muscle of sheep infected withSarcocystisin Huzhu County, Qinghai Province[J]. Anim Husb Feed Sci, 2009, 30(9): 152-153. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5190.2009.09.073 (in Chinese)
李英, 康明, 李永坚,等. 青海省互助县绵羊膈肌住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学, 2009, 30(9): 152-153.
[56] Han L, Yan ZL. Survey on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep of six counties in Qinghai Province[J]. Chin Anim Health Inspec, 2005, 22(9): 41. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2005.09.027 (in Chinese)
韩乐, 严作良. 青海省六县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2005, 22(9): 41.
[57] Li CH, Cai JZ. Epidemiological investigation on the sarcosporidosis of yak and sheep in Qinghai Province[C]. Chin Vet Pub Heal Assoc Caav, 2008: 641-644. (in Chinese)
李春花, 蔡进忠. 青海省牦牛和绵羊住肉孢子虫病流行病学调查[C]. 中国畜牧兽医学会兽医公共卫生学分会成立大会暨第一次学术研讨会论文集. 2008: 641-644.
[58] Shi KL, Wang SL. Survey on the situation ofSarcocystisin sheep in Huangzhong[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2003, 33(5): 20. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2003.05.011 (in Chinese)
史可琳, 汪生林. 湟中地区绵羊住肉孢子虫情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2003, 33(5):20.
[59] Chen G, Ji HZ, Luo JZ, et al. Observation on morphology ofSarcocystisin Sheep of Huangyuan County[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1992, (5): 19-20. (in Chinese)
陈刚, 纪辉宗, 罗建中,等. 湟源县绵羊住肉孢子虫形态观察[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1992, 22(5): 19-20.
[60] Zha X, Jia HZ, Ma YC et al. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in some areas of Huangnan Prefecture[J]. Chin Qinghai J of Ani and Vet Sci, 2008, 38(4): 37-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2008.04.019 (in Chinese)
扎西, 贾海珍, 马玉春, 等. 黄南州部分地区绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2008, 38(4): 37-38.
[61] Wu YCQK. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin Sheep and Qaida Cashmere Goat in Butoula region[J]. Ani Breeding and Feed, 2012, (5): 56-57. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-427X.2012.05.033 (in Chinese)
乌英才其克. 不头他拉地区绵羊及柴达木绒山羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 养殖与饲料, 2012(5): 56-57.
[62] Zhang CW. Investigation on the infection of meatSarcocystisin cattle and sheep of Huilong county[J]. Mod Agricultural Sci Technol, 2009, (3): 217, 222. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2009.03.152 (in Chinese)
张超舞. 化隆县牛羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查研究[J]. 现代农业科技, 2009(3): 217, 222.
[63] Wang CJ. Investigation onSarcocystisof Sheep in Hualong county[J]. Chin J Anim Quarant, 2000, (5): 41. (in Chinese)
王春景. 化隆县绵羊住肉孢子虫调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2000(5): 41.
[64] Ren XR, Zhang K. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep of Hualong county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2012, 42(4): 38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2012.04.028 (in Chinese)
任旭荣, 张奎. 化隆县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2012, 42(4): 38.
[65] Ren XR, Li JQ, Zhang K. Investigation on partial organ parasites in sheep of Huilong county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2006, 36(5): 25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2006.05.014 (in Chinese)
任旭荣, 李坚强, 张奎. 化隆县绵羊部分脏器寄生虫区系调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2006, 36(5): 25.
[66] Kang M, Li Y, Shi WH, et al. Study on the infection ofSarcocystisin the livestock diaphragmatic muscle in Huilong County[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sci, 2013, 41(3): 1154-1156. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2013.03.083 (in Chinese)
康明, 李英, 石文辉,等. 化隆县家畜膈肌住肉孢子虫感染情况研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(3): 1154-1156.
[67] Zhang K, Wei SM, Du CM. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in eastern of Hualong county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2005, 35(5): 54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2005.05.017 (in Chinese)
张奎, 魏生明, 杜常明. 化隆县东部地区绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2005, 35(5): 54.
[68] Zhao YL, Xie XF. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin commercial mutton[J]. Chin J Anim Husb Vet Med, 2011, 41(4): 84-85. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2011.05.040 (in Chinese)
赵玉莲, 谢先福. 互助县商品羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国畜牧兽医文摘, 2011, 41(4): 84-85.
[69] Zhang XJ. Investigation and pathological observation ofSarcocystisin sheep heart of Hainan province[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1988, (2): 27-29. (in Chinese)
张旭静. 海南州绵羊心肌肉孢子虫的调查及病理学观察[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1988(2): 27-29.
[70] Chu RP. Investigation on partial organ parasites of sheep in Dawu area[J]. Chin J Anim Quarant, 2008, 25(3): 34-35. (in Chinese)
褚荣鹏. 果洛州大武地区绵羊局部脏器寄生虫调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2008, 25(3): 34-35.
[71] Chen HX, Cui J. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in Guinan area[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2002, 21(1): 29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2001.05.014 (in Chinese)
陈红霞, 崔俊. 贵南地区绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2002, 32(1): 29.
[72] Duan QH. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep of Golmud[J]. Chin Livestock Poult Breed, 2013, 9(7): 26. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4556.2013.07.015 (in Chinese)
段青河. 格尔木市绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2013, 9(7): 26.
[73] Yan QL, Niang JX, Chen SP, et al. Investigation on sarcocystosis of Tibetan Lamb[J]. Chin Vet Sci, 1985, (6): 25-26. DOI: 10.16656/j.issn.1673-4696.1985.06.008 (in Chinese)
阎启礼, 娘吉先, 陈世平,等. 高原藏羊肉孢子虫病的调查[J]. 中国兽医科学, 1985(6): 25-26.
[74] A RZ, Tan SK. Investigation on the infection of Tibet sheepSarcocystisin Gangcha county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2004, 34(2): 19. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2004.02.019 (in Chinese)
阿仁增, 谭生魁. 刚察县藏羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2004, 34(2): 19.
[75] Ding ZT, Yu NK. A preliminary investigation on theSarcocystisof frozen mutton[J]. Meat Hyg, 1992, (3): 9-10. (in Chinese)
丁仲田, 于念科. 关于冻绵羊肉肉孢子虫的初步调查[J]. 肉品卫生, 1992(3): 9-10.
[76] Wei YM. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin Gonghe county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2000, 30(6): 35. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2000.06.021 (in Chinese)
魏有梅. 共和县羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2000, 30(6): 35.
[77] Liu YL. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep of Gonghe county[J]. Chin J Anim Husb Vet Med, 2014, 30(12): 88. (in Chinese)
刘永兰. 共和县绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国畜牧兽医文摘, 2014, 30(12): 88.
[78] Yuan ZY. Investigation on parasite flora of sheep in Gonghe county[J]. Shandong J Anim Sci Vet Med, 2016, 37(5): 45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1733.2016.05.031 (in Chinese)
袁志芸. 共和县绵羊寄生虫区系调查[J]. 山东畜牧兽医, 2016, 37(5): 45.
[79] Feng CL, Liu YF. Investigation on the infection of meat andSarcocystisin slaughtered livestock in Gonghe area[J]. Prataculture Anim Hus, 2008, (9): 44-45. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8403.2008.09.016 (in Chinese)
冯成兰, 刘延芳. 共和地区屠宰牲畜住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 草业与畜牧, 2008, (9): 44-45.
[80] Sun YJ. Detection and pathogenicity of sarcocystosis in parts of Gansu province[J]. Gansu Anim Vet Sci, 1980, (3): 12-14. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1064/s.1980.03.004 (in Chinese)
孙映杰. 甘肃部分地区羊肉孢子虫病的检出及其病原特征[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 1980, (3): 12-14.
[81] Tian WF, Jia J, Liang SZ, et al. Investigation onSarcocystisin cattle and sheep in Gannan prefecture[J]. Gansu Anim Vet Sci, 1989, (2): 16. DOI: 10.15979/j.cnki.cn62-1064/s.1989.02.013 (in Chinese)
田维丰, 贾吉, 梁守泽,等. 甘南州牛羊住肉孢子虫调查[J]. 甘肃畜牧兽医, 1989, (2): 16.
[82] Bi CM, Wang K, Li B. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in Fuxin area[J]. Meat Hyg, 2000, (10): 11. (in Chinese)
毕聪明, 王坤, 李冰. 阜新地区绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 肉品卫生, 2000, (10): 11.
[83] Wang CX, Mao QY. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep of Delingha city[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2007, 37(4): 31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2007.04.020 (in Chinese)
王春香, 毛启元. 德令哈市绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2007, 37(4): 31.
[84] Zhan SX, Zhao CC, Qi HY, et al. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin sheep in Delingha region[J]. Chin J Ani Quarant, 2001, 18(1): 28-29. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2001.01.025 (in Chinese)
湛守新, 赵昌存, 祁海燕,等. 德令哈地区羊住肉孢子虫感染情况的调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2001, 18(1): 28-29.
[85] Zhong QH, Ma XB, Zhang YC, et al. Investigation on theSarcocystisof slaughtering sheep in Datong county[J]. Chin J Anim Quarant, 2002, 19(3): 37-38. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-944X.2002.03.035 (in Chinese)
仲青花, 马学宝, 张迎春,等. 大通县屠宰羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 中国动物检疫, 2002, 19(3): 37-38.
[86] Chen G, Luo JZ, Yang Z, et al. Investigation on theSarcocystisof sheep in the Chuankou farmer’s and market[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 1991, (3): 43. (in Chinese)
陈刚, 罗建中, 杨枝,等. 川口镇农贸市场绵羊肉孢子虫调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 1991, (3): 43.
[87] Li FY. Investigation on the infection ofSarcocystisin Angsiduo county[J]. Chin Qinghai J Anim Vet Sci, 2007, 37(4): 33. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7950.2007.04.022 (in Chinese)
李发英. 昂思多镇羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 青海畜牧兽医杂志, 2007, 37(4): 33.
[88] Kalantari N, Khaksar M, Ghaffari S, et al. Molecular analysis ofSarcocystisSpp. isolated from sheep (Ovisaries) in Babol Area, Mazandaran Province, Northern Iran[J]. Iranian J Parasitol, 2016, 11(1): 73-80.
[89] Abdel-Hafeez EH, Kamal AM, Abdelgelil NH, et al. Parasites transmitted to human by ingestion of different types of meat, El-Minia City, El-Minia Governorate, Egypt[J]. J Egyptian Soc Parasitol, 2015, 45(3): 671-680.
[90] Hong EJ, Sim C, Chae JS, et al. Ultrastructural and molecular identification ofSarcocystistenella(Protozoa, Apicomplexa) in naturally infected Korean native goats[J]. Veterinarni Medicina, 2016, 61(7): 374-381. DOI: 10.17221/93/2015-VETMED
[91] Zhao G. Investigation on the infection ofsarcocystisin Tibetan sheep in Xingka County[J]. Ani Husb Vet Med, 2012, 44(10): 106. (in Chinese)
赵刚. 兴海县河卡镇藏系绵羊住肉孢子虫感染情况调查[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2012, 44(10): 106.
[92] Heckeroth AR, Tenter AM. Development and validation of species-specific nested PCRs for diagnosis of acute sarcocystiosis in sheep[J]. Intl J Parasitol, 1999, 29(8): 1331-1349.
[93] Kolenda R, Schierack P, Zieba F, et al. First molecular characterization ofSarcocystistenellain Tatra chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra tatrica) in Poland[J]. Parasitol Res, 2015, 114(10): 3885-3892. DOI: 10.1007/s00436-015-4619-4
[94] Dong H, Lu YY, Yang YR. Species and hazard of sarcocystis in beef[J]. Chin J Zoonoses, 2017, 33(8): 88-94. DOI: 10.3969/j. issn.1002-2694.2017.08.001 (in Chinese)
董辉,陆瑶瑶,杨玉荣. 牛肉住肉包子虫的种类及危害研究进展[J], 中国人兽共患病学报, 2017, 33(8): 88-94.
EpidemiologyandclassificationofSarcocystisinsheepandgoat
DONG Hui, LU Yao-yao, YANG Yu-rong
(CollegeofAnimalScienceandVeterinaryMedicine,HenanAgriculturalUniversity,Zhengzhou450002,China)
Sarcocystiscould cause significant economic losses of animal husbandry, and threaten to public health and the quality of food safety.S.tenella,S.arieticanis,S.giganteaandS.medusiformisare four speciesSarcocystisin sheep (Ovisaries). WhileS.capracanis,S.hircicanisandS.mouleiare three species ofSarcocystisin goat (Caprahircus). The life cycle, epidemiological, pathogenicity, morphological characteristics and diagnostic methods of sheep and goats were reviewed in this paper. The research of biological characteristics ofSarcocystisprovides a powerful basis for diagnosis in sheep and goat in China.
Sarcocystis; sheep; goat; epidemiology; morphology; classification; molecular biology
Yang Yu-rong, Email: yangyu7712@sina.com
国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0500707),河南省高校科技创新人才支持计划(17HASTIT038)资助项目
杨玉荣, yangyu7712@sina.com
河南农业大学牧医工程学院, 郑州 450002
R382.3
:A
:1002-2694(2017)09-0828-09
2017-03-23编辑:刘岱伟
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFD0500707) and the Program for Science and Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (No. 17HASTIT038)

