建筑抗爆研究中超压的分布特征及确定方法
杨涛春 罗尧治

摘 要: 爆炸超压是描述爆炸荷载的重要指标,不同方法的超压计算结果具有较高的离散性。通过分析试验数据图表拟合确定入射超压与反射超压关系的反射系数计算式,搜集转化得到大量爆炸超压理论计算公式与爆炸试验数据,从而对爆炸超压在不同比例距离下的分布特征进行分析。研究结果表明:当比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压概率密度服从指数分布;当比例距离大于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压概率密度服从正态分布。当比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压变异系数达最大值1,比例距离在1.5~6.0 m/kg1/3之间时,变异系数较小,在0.13~0.2 m/kg1/3之间;反射超压变异系数较入射超压略大。依据不同比例距离下爆炸超压分布期望数据,拟合得到爆炸超压的计算公式与具有95%保证率条件下的爆炸超压分布范围计算公式。
关键词: 爆炸超压;比例距离;变异系数;分布特征
中图分类号:TU312 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2096-6717(2020)02-0115-10
Distribution characteristic and determination of overpressure for blast resistant study of buildings
Yang Taochun1,2, Luo Yaozhi1
(1.College of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027,P.R.China; 2.School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, University of Jinan, Jinan 250022, P.R.China)
Abstract: Explosion overpressure is an important indicator to describe blast load.And the results obtained by different methods have high discreteness.Based on this, the reflection coefficient formula of the relationship between incident overpressure and reflection overpressure is determined firstly by analyzing the experimental data chart fitting.Then a large number of theoretical calculation formulas and explosion test data were collected and transformed to analyze the distribution characteristics of explosion overpressure at different proportional distances.The results show that the probability density of explosion overpressure obeys exponential distribution when the scaled distance less than 0.5 m/kg1/3.And obeys normal distribution when the scaled distance greater than 0.5 m/kg1/3.The variation coefficient reaches the maximum value 1 when the scaled distance less than 0.5 m/kg1/3.While variation coefficient is in the range of 0.13 to 0.2 when the scaled distance within the range of 1.5 m/kg1/3 to 6 m/kg1/3.The variation coefficient of reflect overpressure is a little bigger than that of incident overpressure.According to the expected data of explosion overpressure distribution at different proportional distances, the calculation formula of explosion overpressure and the calculation formula of explosion overpressure distribution range with 95% guarantee rate are obtained by fitting.
Keywords: explosion overpressure; scale distance; variation coefficient; distribution characteristic
隨着恐怖袭击事件和偶然爆炸事故的不断发生,建筑结构防爆、抗爆研究已成为土木工程领域的热点问题,特别是从“9·11”事件以来,世界多国学者已开展很多相关建筑结构的抗爆研究工作,如爆炸荷载、结构动力响应、破坏模式及简化计算、抗爆分析方法及抗爆加固措施等,得出很多非常有意义的结论,对指导工程结构防爆、抗爆安全有重要参考价值。
在搜集的试验数据中,既有垂直入射数据,也有非垂直入射数据,为分析数据的统一和严谨性,仅保留垂直入射的数据,即上述数据共计125组。而在这125组试验数据中,有的仅有入射超压,有的仅有反射超压,入射超压与反射超压同时存在的只有11组,对于同批试验,有22组数据存在较大差异,在分析中未考虑,因此,实际使用的试验统计数据有103组。
分析爆炸超压计算公式发现,入射超压的计算公式主要有两种形式,如式(4)、式(5)所示,在每个公式中,均存在3个待定系数。其中,式(4)通过爆炸力学理论求得,并通过试验确定相关系数,此方法在已有入射超压的计算公式中得到更多应用,式(5)主要通过试验数据拟合而得,在入射超压的计算公式中也有一定应用。对于统计的仅有入射超压或反射超压的试验数据,通过反射系数式(2)和入射超压计算公式可得到该组试验条件下的相关入射超压公式和反射超压相关数据,为分析得到爆炸超压的概率分布特征提供统计样本。
P0= a Z + b Z2 + c Z3 (4)
P0=d·Ze+f (5)
式中:Z为比例距离。
2 超压分布特征
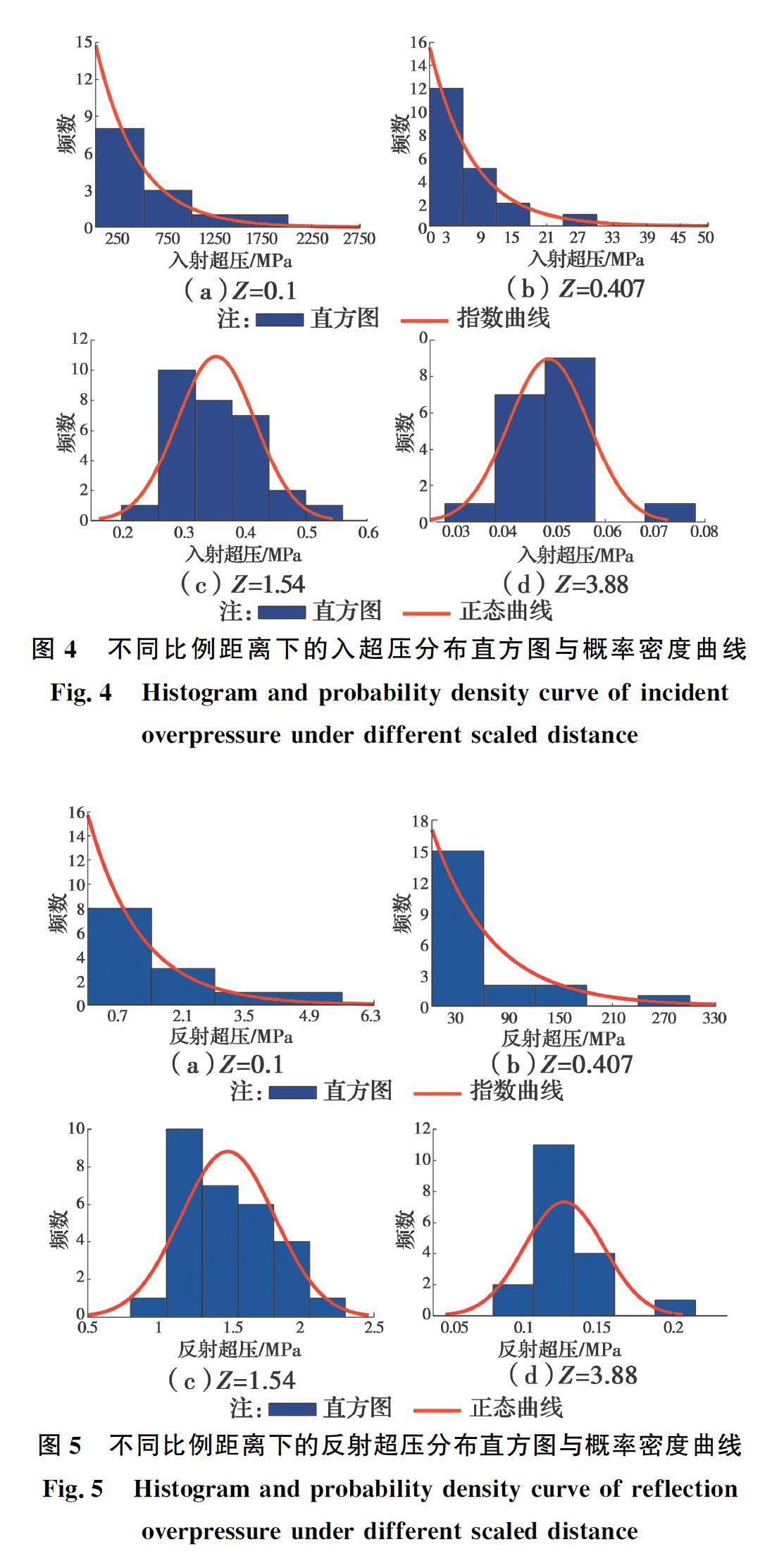
基于统计的爆炸超压数据,对不同比例距离下的离散超压值进行分析,画出对应不同比例距离的超压分布直方图,结合超压直方图分布特征,并通过K-S检验和Lilliefors检验分别开展不同比例距离下的超压概率分布拟合优度检验。结果表明,当比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,入射超压和反射超压分布均服从指数分布,当比例距离大于0.5 m/kg1/3时,超压分布均服从正态分布。在确定概率分布模型基础上,计算得到不同比例距离条件下的超压均值和标准差的极大似然估计值,同时,得到超压均值在95%保证率条件下的置信区间,如表2、表3所示,从而得到不同比例距离下的超压分布概率密度曲线,如图4、图5所示(指数分布和正态分布各两组)。从表2、表3中可以看出,比例距离较小时,标准差最大,超压分布越分散。
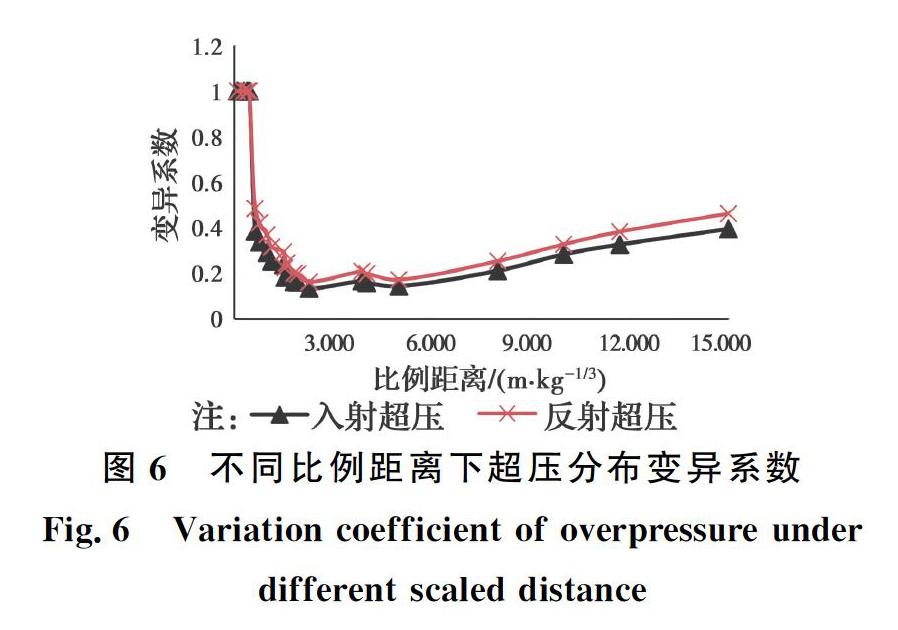
为对比不同比例距離条件下入射超压与反射超压的分散程度,通过表2、表3中超压期望和标准差的极大似然估计值得到超压分布的变异系数,如图6所示。从图6可以看出,比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,超压变异系数达到最大,为指数分布的常值1;当比例距离约在1.5~6 m/kg1/3之间时,得益于较多的试验数据,变异系数较小,在0.13~0.2之间,且反射超压的变异系数较入射超压略大。
3 爆炸超压公式确定
根据表2、表3中超压期望的极大似然估计值,可得到入射超压和反射超压95%置信区间上、下限随比例距离的变化关系,分别如图7、图8所示,因不同比例距离的超压值相差较大,故将比例距离分3段分别绘制,从图中也可看出超压分散程度随比例距离的变化趋势,比例距离越小,超压分布越分散。取比例距离和超压值的自然对数,再通过最小二乘法对自然对数超压进行多项式拟合,如图9、图10所示,入射超压和反射超压拟合曲线的回归系数均大于0.99,最终得到入射超压的计算公式为
ln P0=0.158 3ln2Z-2.342ln Z-0.097 7 (6)
入射超压95%置信区间上、下限的计算公式为
ln P0=0.214 9ln2Z-2.486 7ln Z+0.071 1(上限) (7)
ln P0=0.111 1ln2Z-2.242 8ln Z-0.250 6(下限) (8)
同理,可得到反射超压的计算公式为
ln Pr=0.208 7ln2Z-2.926 3ln Z+1.564 7 (9)
反射超压95%置信区间上、下限的计算公式为
ln Pr=0.264 3ln2Z-3.065 2ln Z+1.751 2(上限) (10)
ln Pr=0.162ln2Z-2.833 9ln Z+1.389 8(下限) (11)
其中,比例距离Z在0.1~15 m/kg1/3范围内。
4 结论
通过搜集文献获取大量爆炸超压的试验与理论数据,并从不确定性角度出发,研究了爆炸超压的概率分布特征,主要得到以下结论:
1)爆炸超压试验数据受炸药类型、当量、形状及试验环境等因素影响明显,超压分布具有较高的离散性,且试验数据多以小当量炸药为主,比例距离多集中于0.4~2.0 m/kg1/3之间。
2)基于试验数据,针对垂直入射情况拟合给出反射系数公式,并得到根据入射超压获取反射超压的计算公式。
3)比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压概率密度服从指数分布;比例距离大于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压概率密度服从正态分布。
4)比例距离小于0.5 m/kg1/3时,爆炸超压变异系数达最大值1;比例距离约在1.5~6 m/kg1/3间时,变异系数较小,在0.13~0.2之间;反射超压变异系数较入射超压略大。
5)根据不同比例距离下爆炸超压分布期望数据,拟合得到爆炸超压的计算公式与具有95%保证率条件下的超压分布范围计算公式。
参考文献:
[1] Department of the Army. Fundamentals of protective design for conventional weapons:TM 5-855-1 [M]. Department of the Army, Washington, DC, USA, 1986.
[2] Department of the Army. Structures to resist the effects of accidental explosion:TM 5-1300 [M]. Department of the Army, 1969.
[3] Department of Defense Explosives Safety Board. Structures to Resist the Effects of Accidental Explosions:UFC 3-340-02 [M]. Department of Defense Explosives Safety Board (DDESB), 2008.
[4] Design and assessment of buildings subjects to blast loads:CSA/S 850-12 [S]. Ontario, Canada:Canadian Standards Association, 2012.
[5] 爆破安全规程:GB 6722—2014 [S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2014.
Safety regulations for blasting:GB 6722-2014 [S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[6] 人民防空地下室设计规范:GB 50038—2005 [S]. 北京:中国计划出版社, 2005.
Code for design of civil air defence basement:GB 50038-2005 [S]. Beijing:China Planning Press, 2014. (in Chinese)
[7] LOW H Y, HAO H. Reliability analysis of reinforced concrete slabs under explosive loading [J]. Structural Safety, 2001, 23(2):157-178.
[8] BOGOSIAN D, FERRITTO J, SHI Y J. Measuring uncertainty and conservatism in simplified blast models [C] // 30th Explosives Safety Seminar, August 2002, Atlanta, Georgia, USA.
[9] 李忠献,路建辉,师燕超,等. 不确定爆炸荷载作用下钢梁的可靠度分析[J]. 工程力学, 2014, 31(4):112-118, 133.
LI Z X, LU J H, SHI Y C, et al. Reliability analysis of steel beam under uncertain blast loads [J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(4):112-118, 133. (in Chinese)
[10] 路建辉. 不确定爆炸荷载作用下钢梁的可靠度分析[D]. 天津:天津大学, 2012.
LU J H. Reliability analysis of steel beam under uncertain blast loads [D]. Tianjin:Tianjin University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[11] 李忠献, 任其武, 师燕超, 等. 重要建筑结构抗恐怖爆炸设计爆炸荷载取值探讨[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2016, 37(3):51-58.
LI Z X, REN Q W, SHI Y C, et al. Research on blast load value in design of important building structures against terrorist explosions [J]. Journal of Building Structures, 2016, 37(3):51-58. (in Chinese)
[12] MILLS C A. The design of concrete structure to resist explosions and weapon effects [C] // Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Concrete for Hazard Protections, Edinburgh, UK:1987:61-73.
[13] BRODE H L. Blast wave from a spherical charge [J]. Physics of Fluids, 1959, 2(2):217.
[14] BRODE H L. Numerical solutions of spherical blast waves [J]. Journal of Applied physics. 1955, 26(6):766-775.
[15] BRODE H L. A calculation of the blast wave from a spherical charge of TNT [M]. Austin:University of Texas at Austin, 1961.
[16] HENRYCH J. 爆炸動力学及其应用[M]. 熊建国. 译. 北京:科学出版社, 1987.
HENRYCH J. The Dynamics of explosion and its use [M]. Translated by XIONG J G. Beijing:Science Press, 1987. (in Chinese)
[17] HENRYCH J, ABRAHAMSON G R. The dynamics of explosion and its use [M]. Amsterdam and New York:Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co., 1979.
[18] KINNEY G F, GRAHAM K J. Explosive shocks in air [M]. Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1985.
[19] NEWMARK N M, HANSEN R J. Design of blast resistant structures [M]. New York:Shock and Vibration Handbook. Harris and Crede. McGraw-Hill, 1961:3.
[20] BAKER W E, COX P, WESTINE P, et al. Explosion hazards and evaluation [M]. Amsterdam:Elsevier Scientific Pub. Co., 1983.
[21] WU C Q, HAO H. Modeling of simultaneous ground shock and airblast pressure on nearby structures from surface explosions [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2005, 31(6):699-717.
[22] NAUMYENKO I A, PETROVSKY I G. The shock wave of a nuclear explosion [M]. Moscow:вoен. издат. мии. сборокы СССР, 1956:183-184.
[23] SADOVSKII M A. Mechanical effects of air shock waves from explosions according to experiments [M]. Moscow:физика взрыва, No.1, AH СССР, 1952.
[24] 葉晓华. 军事爆破工程[M]. 北京:解放军出版社,1999.
YE X H, Military blasting engineering [M]. Beijing:the Peoples Liberation Army Press,1999.(in Chinese)
[25] SIDDIQUI J I, AHMAD S. Impulsive loading on a concrete structure [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Structures and Buildings, 2007, 160(4):231-241.
[26] AHMAD S, ELAHI A, IQBAL J, et al. Impulsive loading on reinforced concrete wall [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Structures and Buildings, 2013, 166(3):153-162.
[27] IQBAL J, AHMAD S. Improving safety provisions of structural design of containment against external explosion [C] // International Conference on Opportunities and Challenges for Water Cooled Reactors in the 21st Century, International Atomic Energy Agency(IAEA), 2011.
[28] HELD M. Blast waves in free air [J]. Propellants, Explosives, Pyrotechnics, 1983, 8(1):1-7.
[29] GHANI RAZAQPUR A, TOLBA A, CONTESTABILE E. Blast loading response of reinforced concrete panels reinforced with externally bonded GFRP laminates [J]. Composites Part B:Engineering, 2007, 38(5/6):535-546.
[30] WANG H W, WU C Q, ZHANG F R, et al. Experimental study of large-sized concrete filled steel tube columns under blast load [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 134:131-141.
[31] LI J, WU C Q, HAO H, et al. Post-blast capacity of ultra-high performance concrete columns [J]. Engineering Structures, 2017, 134:289-302.
[32] 金何伟,刘中宪,刘申永,等. 钢管超高强钢纤维混凝土柱抗爆性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2016, 46(4):45-49.
JIN H W, LIU Z X, LIU S Y, et al. Experimental study of ultra-high performance fiber reinforced concrete filled steel tube columns under blast loading [J]. Building Structure, 2016, 46(4):45-49. (in Chinese)
[33] LIANG X X, WANG Z Q, WANG R N. Deformation model and performance optimization research of composite blast resistant wall subjected to blast loading [J]. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2017, 49:326-341.
[34] 李國强,瞿海雁,杨涛春,等. 钢管混凝土柱抗爆性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2013, 34(12):69-76.
LI G Q, QU H Y, YANG T C, et al. Experimental study of concrete-filled steel tubular columns under blast loading [J].Journal of Building Structures, 2013, 34(12):69-76. (in Chinese)
[35] KIM J H J, KIM S B, CHOI J K. Experiment study on blast loading response of FRP-retrofitted RC slab structures [C] // The Second Official International Conference of International Institute for FRP in Construction for Asia-Pacific Region, 2009.
[36] BARBHUIYA S, AHMAD S, ELAHI A, et al. Experimental study of masonry wall exposed to blast loading [J]. Materiales de Construcción, 2014, 64(313):e007.
[37] RITCHIE C B, PACKER J A, SEICA M V, et al. Behavior of steel rectangular hollow sections subject to blast loading [J]. Journal of Structural Engineering, 2017, 143(12):04017167.
[38] AUNE V, FAGERHOLT E, HAUGE K O, et al. Experimental study on the response of thin aluminium and steel plates subjected to airblast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 90:106-121.
[39] TABATABAEI Z S, VOLZ J S, BAIRD J, et al. Experimental and numerical analyses of long carbon fiber reinforced concrete panels exposed to blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2013, 57:70-80.
[40] CHOI J H, CHOI S J, CHO C M, et al. Experimental evaluation of Bi-directionally unbonded prestressed concrete panel blast resistance behavior under blast loading scenario [J]. Journal of the Korea Concrete Institute, 2016, 28(6):673-683.
[41] CHOI J H, CHOI S J, KIM J H J, et al. Evaluation of blast resistance and failure behavior of prestressed concrete under blast loading [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2018, 173:550-572.
[42] SAFARI H, ZAMANI J, KHALILI R, et al. Experimental, theoretical, and numerical studies on the response of square plates subjected to blast loading [J]. The Journal of Strain Analysis for Engineering Design, 2011, 46(8):805-816.
[43] ZHANG F R, WU C Q, ZHAO X L, et al. Experimentalstudy of CFDST columns infilled with UHPC under close-range blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 93:184-195.
[44] HAO Y F, HAO H, SHI Y C, et al. Field testing of fence type blast wall for blast load mitigation [J]. International Journal of Structural Stability and Dynamics, 2017, 17(9):1750099.
[45] JACINTO A C, AMBROSINI R D, DANESI R F. Experimental and computational analysis of plates under air blast loading [J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2001, 25(10):927-947.
[46] 崔瑩,赵均海,张常光,等. 爆炸冲击波在钢管混凝土柱表面压力分布试验研究及数值模拟[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2014(12):1828-1836.
CUI Y, ZHAO J H, ZHANG C G, et al. Research on pressure distribution of blast wave on the surface of CFST column based on explosion test and numerical simulation [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2014, 40(12):1828-1836. (in Chinese)
(编辑 胡玥)
收稿日期:2019-05-15
基金项目: 国家自然科学基金(51608229);山东省高校科研发展计划(J18KA206)
作者简介: 杨涛春(1983- ),男,副教授,博士,主要从事爆炸灾害分析评估研究,E-mail:yangtaochun@126.com。
Received: 2019-05-15
Foundation items: National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.51608229); Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (No. J18KA206).
Author brief: Yang Taochun (1983- ), associate professor, PhD, main research interest: anlysis and assessment of explosion disaster, E-mail: yangtaochun@126.com.

