Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and Fdeoxyglucose positron emission computed tomography/computed tomography findings of alveolar soft part sarcoma with calcification in the thigh:A case report
Zeng-Jie Wu, Tian-Tian Bian, Xiao-Hong Zhan, Cheng Dong, Yan-Li Wang, Wen-Jian Xu
Zeng-Jie Wu, Cheng Dong, Wen-Jian Xu, Department of Radiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
Tian-Tian Bian, Breast Disease Center, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
Xiao-Hong Zhan, Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University,Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
Yan-Li Wang, Department of PET/CT, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University,Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
Abstract
Key words:Alveolar soft part sarcoma;Calcification;Magnetic resonance imaging;Positron emission computed tomography/computed tomography;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Alveolar soft part sarcoma (ASPS) is an extremely rare malignant sarcoma,constituting less than 1% of all soft-tissue sarcomas[1].ASPS was first described by Christophersonet al[2]in 1952, deriving its name from its histological appearance[1-3].The most common locations of ASPS are the lower extremities, head, and neck[4-6].Metastases are usually demonstrated in 20%-40% of the patients at the time of diagnosis, commonly involving the lung, bone, and brain[7,8].
Several cases of ASPS have been reported that discuss the characteristics of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings with hyperintensity on T1- and T2-weighted images and flow voids[8,9].However, these changes were not specific and may mimic arteriovenous malformations or hemangioma.Various studies explored the manifestations of multimodal imaging examinations, especially diffusion-weighted imaging and positron emission computed tomography/computed tomography(PET/CT).The present study reports a case of a 35-year-old female patient with calcification in the mass found on multimodal imaging [computed tomography (CT),diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), conventional sequence MRI, and PET/CT], which was confirmed to be ASPS using core needle biopsy.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 35-year-old woman complained of a palpable mass without pain in the left thigh for 1 year.The size of the mass increased suddenly, accompanied by pain starting from 3 wk ago.
History of present illness
The patient had no history of past illness and no family history of specific diseases.
Physical examination
The physical examination revealed a tender mass measuring 5.0 cm × 3.0 cm in the soft tissue of the left thigh without any obvious pulsation and local color change.
Laboratory examinations
Results of routine laboratory examinations, including routine blood tests, blood biochemistry, routine urine tests and serum tumor markers, were within normal levels.There were no valuable laboratory data.
Imaging examinations
MRI images taken in November 2017 showed a circumscribed mass measuring 5.4 cm× 3.4 cm with hyperintensity on T1- and T2-weighted images and high intensity on DWI images;numerous signal voids (intra-/extra-tumor) were also detected(Figure 1).The initial MRI examination was highly suggestive of hemangioma.Dynamic contrast enhancement of MRI was suggested for further diagnosis, but the patient discharged herself from the hospital against the advice of doctors.The patient was admitted for further treatment due to the enlargement of the mass in June 2018.Subsequent PET/CT examination was performed, and CT showed a slightly hypodense or isodense mass with patchy calcification (Figure 2B).Compared with the initial MRI images, the size of the mass had increased (6.0 cm × 4.1 cm).The PET/CT images showed increased F-deoxyglucose (FDG) uptake with the maximum standardized uptake value of 4.23 for both the mass and several pulmonary nodules,which was highly suggestive of malignant tumors and metastases (Figure 2C and D).
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
Core needle biopsy was performed 1 wk later.The tumor was diagnosed as ASPS according to the distinct histologic manifestation.The histopathological examination(Figure 3A) showed a pseudoalveolar pattern with nests of large granular cells separated by sinusoidal vascular channels.The immunohistochemical testing(Figure 3B) revealed that the tumor cells were positive for transcription factor binding to immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer 3 and negative for S-100 protein,cytokeratin, desmin, and CD56.
TREATMENT
The patient had missed the perfect opportunity of surgery and received six cycles of chemotherapy, including ifosfamide, doxorubicin, andSerratia marcescensvaccine for 6 mo.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
After chemotherapy, the patient had disease progression.MRI examination in December 2018 revealed an increase in the size (7.6 cm × 5.6 cm) of the tumor and brain metastases.Subsequent pulmonary CT showed multiple nodules and suggested metastases.The patient died 12 mo later.
DISCUSSION
ASPS is a distinct, malignant soft-tissue tumor characterized by a pseudoalveolar architecture associated with abundant sinusoidal vessels.Adolescents and young adults, aged 15–35 years with a male to female ratio of 1:2, are more likely to be affected[1-3].ASPS often develops in the lower extremities for adults;however, the head and neck are more frequently involved in children[4-6].The prognosis of ASPS depends on the presence of metastasis, tumor size, and patient age at the time of diagnosis[7,8].In the present case, the patient had lung and brain metastasis in the follow-up period and also poor prognosis.
Some studies have demonstrated the imaging characteristics of ASPS.High intensity on T1-weighted images and the presence of numerous signal voids (intra-/extra-tumor) were often emphasized, and these were attributed to the slow-flowing blood and high vascularity[10].In the present case, the tumor showed similar characteristics on MRI compared with the previous study.The DWI findings of ASPS were rarely reported.ASPS showed the same signal on DWI, as revealed by Cuiet al[11].However, the present case demonstrated high signal intensity, which might be related to abundant cytoplasm and densely arranged cells, leading to the limited diffusion of water molecules.
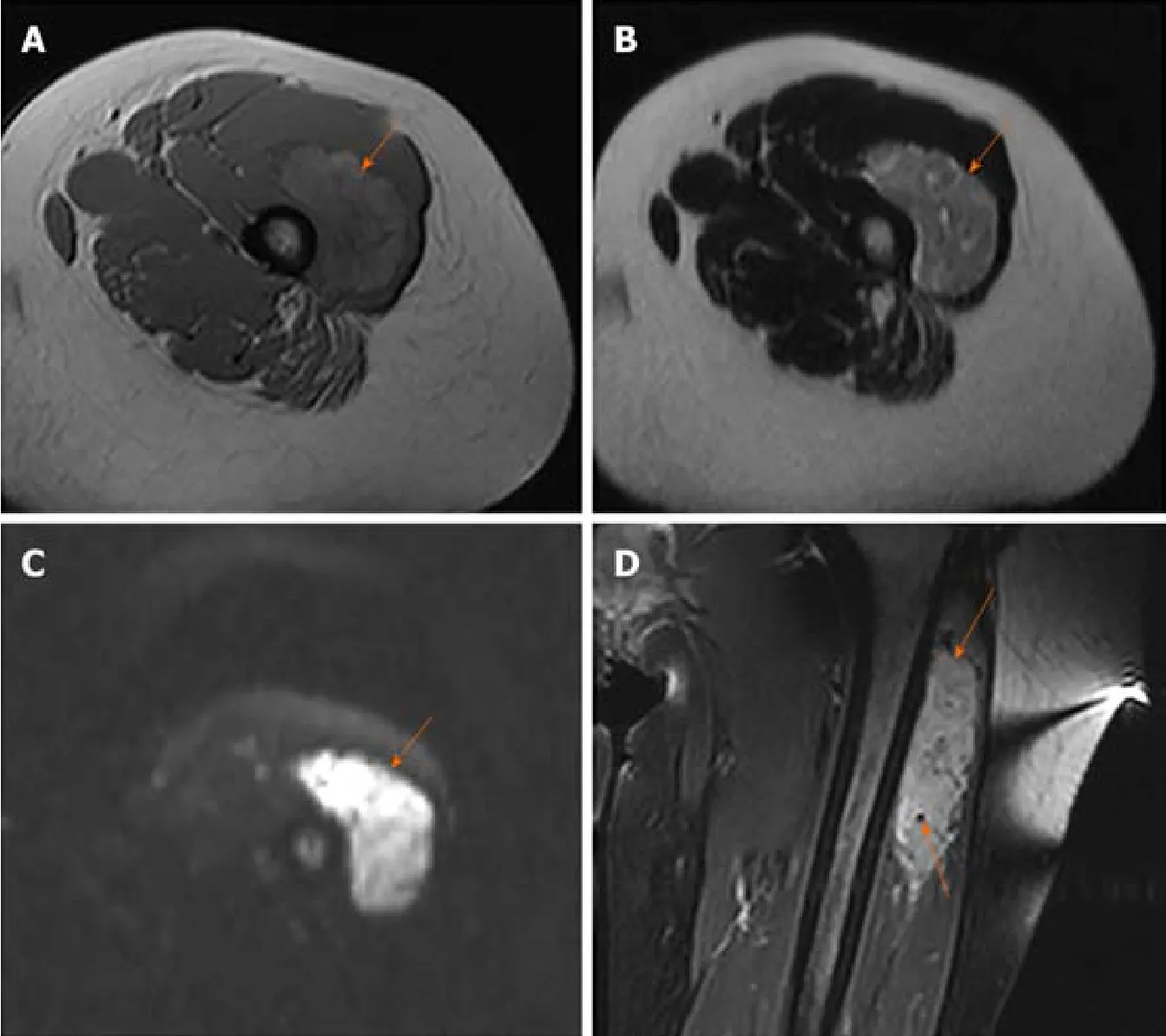
Figure 1 Alveolar soft part sarcoma in a 35-year-old woman.
CT findings are frequently overlooked, and FDG PET/CT findings were rarely reported earlier.No previous study reported calcification;however, some patchy calcification in the mass was detected in the present study, which was easily misdiagnosed as synovial sarcoma.The mechanism of calcification may be associated with calcium deposition caused by histiocytic ischemia and nutritional deficiency.The findings in the present case were consistent with previous findings that ASPS had high FDG uptake[12].Increased FDG uptake on PET/CT images can help distinguish between benign and malignant tumors[12].FDG PET/CT makes it possible to distinguish between hemangioma and ASPS more easily.PET/CT examination may also be used for detecting metastasis of the tumor.
ASPS should be distinguished from hemangioma, liposarcoma, and synovial sarcoma.Hemangioma mimicking ASPS may show high signal intensity on T1-weighted images and marked enhancement.However, high FDG uptake on PET/CT image is rarely detected, and DWI usually shows low signal intensity.Although some primary malignant tumors, including liposarcoma and soft-tissue tumors, have high FDG uptake, the characteristic signal intensity on MRI images or density on CT images may be useful in differentiation.Differentiating ASPS with calcification from synovial sarcoma on CT and PET/CT images is difficult, but synovial sarcoma often showed no signal voids on MRI[1,9,13].Therefore, the combination of these three examinations can provide more clues for the differential diagnosis of ASPS.
CONCLUSION
In summary, this case highlighted the importance of multimodal imaging examinations in diagnosing ASPS.The possibility of ASPS should be considered when a mass is detected in the soft tissue of the extremities, with hyperintensity and numerous signal voids on T1-weighted, T2-weighted, and DWI images and intense FDG uptake on PET/CT.
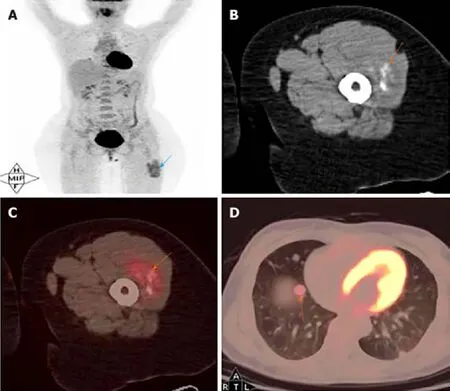
Figure 2 Positron emission computed tomography/computed tomography findings of the same patient.
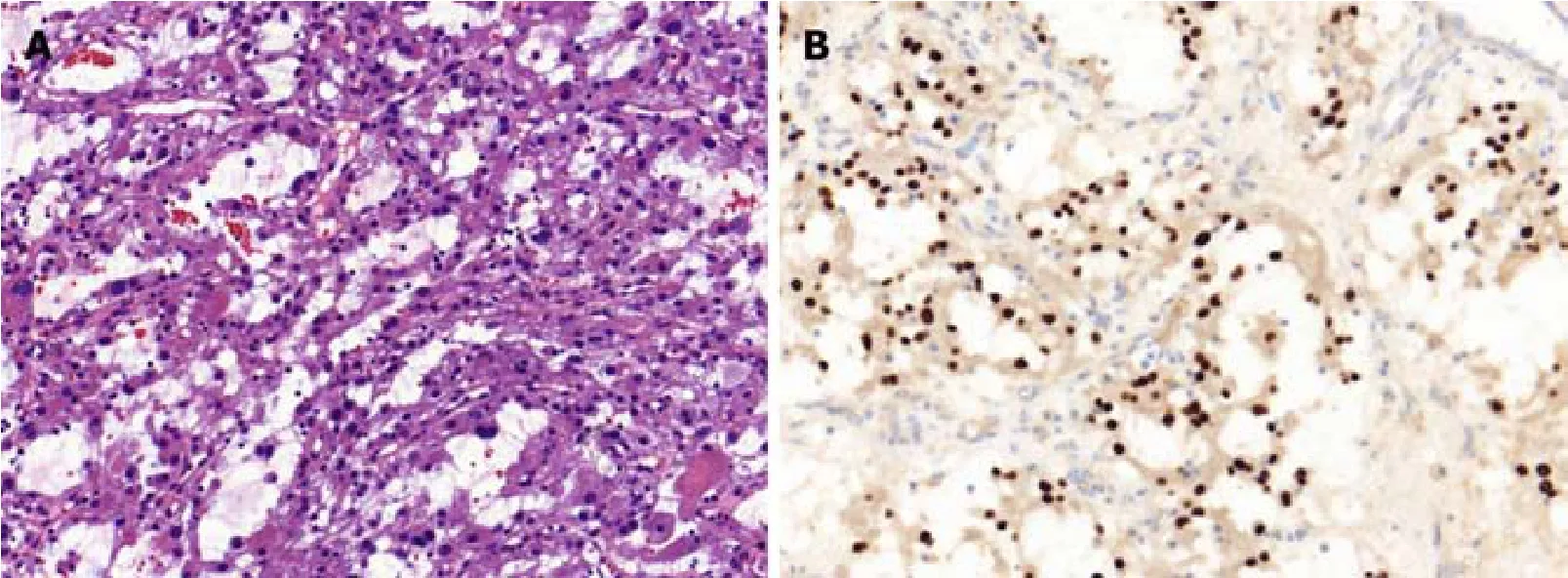
Figure 3 Histopathological examination of the same patient.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年15期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年15期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Impacts and challenges of United States medical students during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Recent advances in the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- Medical research during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Progress of intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted imaging in liver diseases
- Typical and atypical COVID-19 computed tomography findings
- Review of possible psychological impacts of COVID-19 on frontline medical staff and reduction strategies
