Protective effects of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu Formula on hippocampal neurons in rats of diabetes complicated with depression via the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway
LING Ji,LIU Jin,JIN Shi,ZOU Mnshu,d,e,JIANG Yjie,WANG Yuhong,d,e*
a. Institute of Innovation and Applied Research in Chinese Medicine,Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
b. Center for Medical Research and Innovation,The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410007,China
c. Drug Inspector Center,Jiangxi Provincial Drug Administration,Nanchang,Jiangxi 330029,China
d. Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory for the Prevention and Treatment of Depressive Diseases with Traditional Chinese Medicine,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
e. Hunan Key Laboratory of Power and Innovative Drugs State Key Laboratory of Ministry Training Bases,Changsha,Hunan 410208,China
ABSTRACT Objective To explore the protective effects and mechanism of Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu Formula (左归降糖解郁方,ZGJTJYF) on hippocampal neurons in rats of diabetes complicated with depression (DD) via the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway.Methods (i) In vivo experiments: 60 specified pathogen free (SPF) grade male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomly divided into six groups with 10 rats in each groups: control,DD model,positive (1.8 mg/kg fluoxetine + 0.18 g/kg metformin),high-dose ZGJTJYF (ZGJTJYFH,40.500 g/kg ZGJTJYF),middle-dose ZGJTJYF (ZGJTJYF-M,20.250 g/kg ZGJTJYF),and lowdose ZGJTJYF (ZGJTJYF-L,10.125 g/kg ZGJTJYF) groups. Except for the control group,other groups were established DD model by high-fat emulsion intake with single tail vein streptozotocin (STZ) and four weeks of chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS). All drug administration groups were treated by gavage during CUMS modeling,and the control and model groups were given equal amount of distilled water. After four weeks,the serum levels of blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin were measured to determine the hypoglycemic effect of ZGJTJYF. Moreover,the open field test and Morris water maze test were performed to evaluate the antidepressant effect of ZGJTJYF. Changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) level were detected via high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection(HPLC-ECD); the levels of tryptophan (TRP),kynurenine (KYN),and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) in the hippocampus were detected using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA); the protein expression levels of synaptophysin (SYN) and postsynaptic density material-95 (PSD-95) were detected via immunohistochemistry (IHC); and the protein expression levels of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NR) 2A and NR2B were detected using Western blot. (ii) In vitro experiments: five SPF grade SD pregnant rats (E16 - 18) were used to obtain primary hippocampal neurons (Ne),six SD new-born rats were used to collected primary astrocytes (As) and microglia (MG),and to establish a Ne-As-MG co-culture system.All co-culture systems were divided into six groups: control (PBS),model [150 mmol/L glucose + 200 μmol/L corticosterone (G&P) + PBS],blank (G&P + blank serum),positive (G&P + positive drug-containing serum),ZGJTJYF (G&P + ZGJTJYF serum),and 1-methyl-D-tryptophan (1-MT,IDO inhibitor) (G&P + 1-MT) groups. After 18 h of intervention by corresponding treatment,immunofluorescence was used to analyze the protein expression levels of SYN,PSD-95,NR2A,and NR2B; ELISA was performed to measure the levels of interleukin(IL)-1β,IL-6,tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α ,and TRP/KYN metabolic pathway-related factors[TRP,KYN,kynurenine acid (KYNA),quinolinic acid (QUIN)].Results (i) In vivo experimental results showed that ZGJTJYF-M and ZGJTJYF-L significantly improved the elevated blood glucose state of DD rats (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05,respectively);ZGJTJYF-H,ZGJTJYF-M,and ZGJTJYF-L increased their autonomous activity,learning,and memory ability (P < 0.01,P < 0.01,and P < 0.05,respectively). Moreover,the levels of 5-HT and TRP were significantly increased (P < 0.01),and the levels of KYN and IDO were significantly decreased in the hippocampus (P < 0.01) of rats after ZGJTJYF-M treatment. The protein expression levels of SYN and PSD-95 were significantly upregulated in hippocampal neurons (P < 0.01),while the abnormal activation of NR2A and NR2B was markedly inhibited in hippocampus (P < 0.05) of rats after ZGJTJYF-M treatment. (ii) In vitro experimental results showed that ZGJTJYF-containing serum significantly increased the protein expression levels of SYN and PSD-95 in hippocampal neurons (P < 0.01),decreased the levels of IL-1β(P < 0.01),IL-6 (P < 0.05),TNF-α (P < 0.01),IDO (P < 0.05),KYN (P < 0.05),and QUIN (P <0.01),and increased the levels of TRP and KYNA (P < 0.01) in the simulated DD state. ZGJTJYF also had an significantly inhibitory effect on the abnormal activation of NR2A and NR2B in neurons (P < 0.05) in a stimulated DD state.Conclusion ZGJTJYF can effectively improve 5-HT deficiency in the hippocampus of rats by inhibiting IDO expression and regulating the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway,and it has a favorable protective effect on hippocampal neuron injury caused by DD. Therefore,ZGJTJYF is an effective potential therapeutic drug for the prevention and treatment of DD.
Keywords Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu Formula (左归降糖解郁方,ZGJTJYF) Diabetes Depression Diabetes complicated with depression TRP/KYN metabolic pathway Hippocampal neurons Neuroprotection 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)
1 Introduction
As of 2021,there were approximately 537 million diabetes cases worldwide[1]. With an aging population and unhealthy diet structure,the incidence of diabetes has increased rapidly and achieved an alarming global proportion[1]. An estimated 6.70 million adults died from diabetes or its complications in 2021,equivalent to one person dying of diabetes every five seconds[1]. Surprisingly,38.75% of patients with type 2 diabetes suffer from depression,and 48.38% of those have moderate depression[2]. Clinical researches have discovered that the quality of life and treatment compliance of patients suffering from diabetes complicated with depression (DD)are significantly declined,which is extremely harmful to the treatment and rehabilitation of both these diseases[3,4]. Therefore,the prevention and treatment of DD are urgently needed.
It is common to optimize traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prescriptions by combining disease characteristics in China. Zuogui Jiangtang Jieyu Formula (左归降糖解郁方,ZGJTJYF) is based on Zuogui Pill (左归丸) inComplete works of Jingyue(Jing Yue Quan Shu,《景岳全书》),which is often used in hypoglycemic therapy[5,6].ZGJTJYF consists of Shudihuang (Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata),Shanzhuyu (Corni Fructus),Gouqizi (Lycii Fructus),Huangqi (Astragali Radix),Tusizi (Cuscutae Semen),Niuxi (Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix),Duzhong(Eucommiae Cortex),Danshen (Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma),Mudanpi (Moutan Cortex),Guanyejinsitao (Hyperici Perforati Herba),and Jianghuang (Curcumae Longae Rhizoma). Previous studies have shown that ZGJTJYF could significantly improve cognitive learning,and memory function in DD rats,and has a regulatory effect on the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NR) expression and synaptic plasticity in hippocampal neurons[7,8]. Consequently,we believe that ZGJTJYF has great potential in the treatment of DD.
Kynurenine (KYN) is the core intermediate product of the essential amino acid tryptophan (TRP). Its main metabolites are quinolinic acid (QUIN) and kynurenine acid (KYNA),which directly act on the NR. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) is the pivotal limiting enzyme in the TRP/KYN pathway[9]. TRP is an important precursor of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT),a biomarker of depression[10]. Under physiological conditions,IDO activity is low. However,when the body is in a state of stress or inflammation,IDO’s activation can be induced by pro-inflammatory cytokines,such as interleukin (IL)-1βand tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α,promoting the production of TRP from the KYN metabolic pathway,which may result in the reduction of 5-HT level[11]. Previous studies have found that the level of 5-HT decreased,and the level of IDO increased in DD patients[12,13]. Hence,this study aimed to explore the underlying mechanism of the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway,and the protective effects of ZGJTJYF on hippocampus in DD rats.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Drug preparation
All crude drugs were provided by the pharmacy of The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine(China). ZGJTJYF consists of Guanyejinsitao (Hyperici Perforati Herba) (3 g),Jianghuang (Curcumae Longae Rhizoma) (9 g),Huangqi (Astragali Radix) (18 g),Tusizi(Cuscutae Semen) (9 g),Shudihuang (Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata) (15 g),Shanzhuyu (Corni Fructus) (12 g),Gouqizi (Lycii Fructus) (12 g),Niuxi (Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix) (9 g),Danshen (Salviae Miltiorrhizae Radix et Rhizoma) (12 g),Mudanpi (Moutan Cortex) (6 g),and Duzhong (Eucommiae Cortex) (9 g). All medicinal materials were extrcted and concentrated as for the reference[13]. The final yield was 42.8% of the total crude materials.
2.2 Experimental animals
Specified pathogen free (SPF) grade Sprague-Dawley(SD) rats,including 60 adult males (180 - 220 g),five pregnant females (E16 - 18) (350 - 450 g),six newborns (2 -3 days old),and 15 adult males (160 - 180 g),were purchased from Hunan Slake Jingda Laboratory Animal Company Limited (SCXK-2016-0002). All rats were kept in a SPF grade experimental animal center at The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine [SYXK(Xiang) 2015-0003],under a standard cycle of 12 h/12 h(light/darkness) at stable temperature (22 ± 2) °C,and humidity (55% - 65%). This study was supported by the Animal Experimental Ethical Inspection Committee of The First Hospital of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (HN-LL-KY-2016-004-01).
2.3 In vivo experiments
2.3.1 DD model establishment Sixty adult male SD rats(180 - 220 g) were randomly divided into six groups (10 rats in each group): control,DD model,positive,and high-,middle-,and low-dose ZGJTJYF (ZGJTJYF-H,-M,and -L) groups. Except for the control group,all groups were given the modeling treatment. The modeling operations were performed as follows.
The diabetic model was established as previous study[14]. Briefly,SD rats continuously received a high-fat emulsion for 14 d (i.g.,10 mL/kg). After overnight starvation on day 14,all animals were injected with fresh streptozotocin (STZ; Solarbio,China) (38 mg/kg),dissolved in 0.1 mol/L precooled citrate buffer (pH 4.5) through the caudal vein. On day 18,fasting blood glucose levels were assessed to determine whether the rats were in line with the standard diabetes model (fasting blood glucose ≥16.00 mmol/L) (Figure 1).
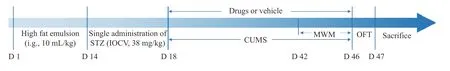
Figure 1 Schedule of the experiments
Based on the diabetes model,the depression model was established via single-cage feeding combined with chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) for 4 w,including placing in an ice bath for 5 min,tilting the cage at 45° for 24 h while feeding,reversing day and night cycles for 24 h,50 V electric shock for 1 min,tail clamping for 1 min,random noise stimulation for 8 h,and staying in wet litter (200 mL/cage) for 24 h[14]. During the CUMS period,one or two stimuli were selected and utilized on the rats every day so that the rats could not predict the stimulus. The same stimulus did not appear continuously within the four weeks.
2.3.2 Drug intervention During CUMS modeling,the rats in control and DD model groups were provided with distilled water; the positive group was administered a mixture of fluoxetine (1.8 mg/kg; Patheon,France) and metformin (0.18 g/kg; Yatai,China),and the rats in ZGJTJYF groups were treated with different concentrations of ZGJTJYF extracts,where the ZGJTJYF-H,-M,and -L groups received 40.500,20.250,and 10.125 g/kg ZGJTJYF,respectively. All drugs were administered once a day for four weeks.
2.3.3 Blood glucose measurement Blood glucose levels were measured at day 18 and day 46 using a one-touch blood glucose meter (LifeScan,OneTouch Ultra 2). The rats in each group were fasted for 8 h before test. On day 47,the rats were anesthetized,and blood samples were collected to obtain plasma and to detect glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) using enzymatic kits (Nanjing Jiancheng,China).
2.3.4 Behavioral examination Behavioral tests were performed 30 minutes after the last step of treatment administration of experimental rats.
(i) Morris water maze (MWM). The MWM test began on day 42 and was performed once a day for five consecutive days. The positioning navigation test was performed on the first four days,and the final exploration experiment was conducted on the 5th day. The maze pool was divided into four quadrants and filled with clean water (Figure 2).
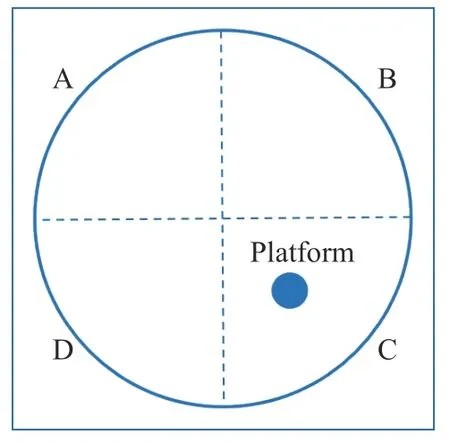
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of MWM
At the positioning navigation period (from day 42 to day 45),the rats were put into quadrant A to D of the pool in turn,one quadrant in each day,and the latency to climb onto the platform was recorded daily. If the rats could successfully climb the platform within 60 s,the latency was recorded as actual time spent. If not,the latency was recorded as 60 s. The average latency of four days was used as the learning threshold. At the exploration experiment (day 46),the rats were placed at quadrant A,and they were allowed to find the platform within 90 s. The search time was recorded as the space exploration time in the quadrant C,where the platform was located,to evaluate the memory ability of rats.
(ii) Open field test (OFT). The OFT was designed according to our previous study[15]. The test was performed on day 46. Briefly,the rats were placed in an open box(80 cm × 80 cm × 40 cm),which was placed in a fixed corner facing the wall. The rats were then given 30 s to adapt to the environment,and 4 min to explore the environment freely. All locomotor activities,including horizontal and vertical movements,were recorded for 4 min.
2.3.5 Samples collection After the behavioral test,the rats in each group were anesthetized. The blood samples were collected and centrifuged (4 °C,4 000 rpm,for 10 min). The supernatants were obtained and stored at- 80 °C for further analysis. The hippocampal tissues were quickly taken out and frozen in liquid nitrogen,then stored at - 80 °C. Whole brain tissues were collected and stored in 4% paraformaldehyde solution.
2.3.6 High-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD) of 5-HT HPLCECD (Agilent,1260) was used to evaluate the levels of monoamine transmitters. The hippocampal tissues were accurately weighed,with 0.01 mol/L perchloric acid being added at a ratio of 1∶3 (w/v),and homogenized on ice for 30 s. After centrifugation at 4 °C,12 000 rpm for 10 min,the supernatant was collected,purified,and loaded into a Quattro 3 C18 column (150 mm × 2.1 mm,3 μm). Mobile phase A is a solution containing 90 mmol/L sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate,50 mmol/L citric acid monohydrate,1.7 mmol/L sodium octane sulfonate,and 50 μmol/L Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid (EDTA); mobile phase B is methanol. The run parameters are as follows: ratio of A to B,93∶7; flow rate,0.2 mL/min; column temperature,30 °C; injection volume,20 μL.
2.3.7 Immunohistochemical (IHC) detection of synaptophysin (SYN) and postsynaptic density material-95 (PSD-95) Whole brain tissues were embedded in paraffin,cut into 4 μm-thick sections,and dehydrated in a graded ethanol series for 5 min. The sections were incubated with 3% H2O2at room temperature for 10 min,followed by antigen repair and blocking with 5% goat serum,then incubated with rabbit anti-SYN polyclonal antibody(1∶100; Proteintech,USA) and rabbit anti-PSD-95 polyclonal antibody (1∶100; Proteintech,USA) in a wet box at 4 °C overnight,followed by incubation with the secondary antibodies at 37 °C for 30 min. After staining with 3,3-N-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride and hematoxylin,the sections were digitally photographed under high magnification (IX73,Olympus).
2.3.8 Western blot analysis of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NR) 2A and NR2B protein expression Total protein was extracted from hippocampal tissues,detected using an ultraviolet spectrophotometer (BioDrop,μlite + ),separated on 8% polyacrylamide gels,and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes.The PVDF membranes were blocked with skim milk for 60 min,and incubated with rabbit anti-NR2A polyclonal antibody (1∶1 000; Abcam,UK),rabbit anti-NR2B polyclonal antibody (1∶1 000; Abcam,UK),and rabbit anti-GAPDH polyclonal antibody (1∶1 500; Cell Signaling Technology,USA) at 4 °C overnight. Afterward,the membranes were washed twice and incubated with second antibody (1∶3 000; Cell Signaling Technology,USA) at room temperature for 60 min. Finally,the protein expression levels were calculated using Image Lab software(Bio-Rad,ChemiDoc XRS + Imager).
2.4 In vitro experiments
2.4.1 Drug-containing serum collection Fifteen adult male SD rats (160 - 180 g) were randomly divided into three groups (five ratsin each group): TCM,blank,and positive groups. They were intragastrically administrated with 2.28 g/mL ZGJTJYF extract,distilled water,and(1.8 mg/kg fluoxetine + 10.8 mg/kg metformin) for 5 d,respectively . All the rats were sacrificed 1 h after the last administration. Blood was collected and centrifuged(1 000 rpm,10 min) to obtain the serum. All serum samples were collected,sterilized,and then stored at - 80 °C.
2.4.2 Cell culture According to previous studies[16-18],primary hippocampal neurons (Ne) was obtained from five pregnant female SD rats (E16 - 18),and astrocytes(As) and microglia (MG) were obtained from six newborn SD rats (2 - 3 days old) to estabilish a three-cell coculture system[19]. Briefly,sterile wax drops were added to form a triangular shape in a 12-well plate and incubated after sterilization. Then,the mixed glial cells were made into a single-cell suspension and inoculated into sterile wax drops for proliferation. Afterward,regions of neurons with rich networks were placed upside down on the wax drops. After continuing the co-culture in an incubator for 2 - 3 d,thein vitroMG-Ne-As co-culture system was established.
2.4.3 Model construction and drug intervention Thein vitroexperiment included six groups: control,model,blank,positive,ZGJTJYF,and 1-methyl-D-tryptophan (1-MT,IDO inhibitor) groups. Except for the control group,which was given an equivalent volume of culture medium,other groups were treated with 150 mmol/L glucose and 200 μmol/L corticosterone for 18 h to establish a DD environment[20]. The blank group was given 10% blank serum; the positive group was given 10% serum containing fluoxetine; the ZGJTJYF group was given 10%ZGJTJYF-containing serum,and the 1-MT group was administered 1-MT (MCE,USA) at a final concentration of 50 μmol/L. The control and model groups were administered the same volume of PBS.
2.4.4 Immunofluorescent detection of SYN,PSD-95,NR2A,and NR2B After treatment for 18 h,neurons were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min,treated with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 15 min,blocked in 5% bovine serum albumin for 30 min,and incubated with primary antibodies overnight in a wet box at 4 °C in the dark. The primary rabbit polyclonal antibodies were used [anti-SYN(1∶100),anti-PSD-95 (1∶100),anti-NR2A (1∶100),and anti-NR2B (1∶100)]. Then,the cells were incubated with a fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled secondary antibody(1∶400; Proteintech,USA) at 37 °C for 30 min,and the nuclei were counter stained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (1∶800; Abcam,UK) at room temperature in the dark for 15 min. Finally,a confocal microscope(Zeiss,LSM800) was used to analyze the protein expression of SYN,PSD-95,NR2A,and NR2B.
2.5 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection of TRP,KYN,IDO,KYNA,QUIN,IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α
The hippocampal tissues were weighed,mixed with PBS,homogenized at 4 °C,then centrifuged,and the supernatant was obtained. TRP,KYN,and IDO levels were measured using an ELISA kit (Shanghai Jingtian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China). The supernatant from the co-culture system was also collected after establishing thein vitroDD model. The levels of IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α,IDO,TRP,KYNA,KYN,and QUIN in the co-culture supernatant were measured using an ELISA kit (Shanghai Jingtian Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.6 Statistical analysis
SPSS 20.0 software was used for data analysis. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Indicators were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance. If the variance was homogeneous,the least significant difference (LSD) method was applied for pairwise comparison; otherwise,Dunnett’s T3 test was performed. Differences were considered statistically significant atP< 0.05.
3 Results
3.1 In vivo experiments
3.1.1 Effects of ZGJTJYF on blood glucose and HbA1c levels in DD rats A high-fat diet and STZ injection led to a typical diabetic syndrome characterized by hyperglycemia and high level of HbA1c[14]. The blood glucose increase in the rats was selected as the evaluation index.There was no obvious fluctuation in blood glucose levels in the control group throughout the experiment. Compared with the control group,the blood glucose level in DD model group was significantly higher (P< 0.01)(Figure 3A),and the blood HbA1c level also increased considerably (P< 0.01) (Figure 3B). Conversely,blood glucose levels decreased in the rats of positive,ZGJTJYF-H,and ZGJTJYF-M groups compared with the DD model group (P< 0.01) (Figure 3A),and the HbA1c level in treatment groups were lower than that in the DD model group (Figure 3B).

Figure 3 Changes of blood glucose and HbA1c content in each group rats
3.1.2 Effects of ZGJTJYF on depression-like behavior in DD model rats In the OFT,rats in the DD model group showed fewer autonomous activities than those in the control group (P< 0.01) (Figures 4A and 4B). After treatment with ZGJTJYF-H,ZGJTJYF-M,and ZGJTJYF-L,the number of horizontal autonomous activities of DD rats was significantly increased compared with the DD model group (P< 0.01,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively)(Figure 4A),meanwhile,rats in the positive and ZGJTJYF-H groups had a significantly increased number of vertical autonomous activities (P< 0.01 andP< 0.05,respectively) (Figure 4B). In the MWM,the spatial exploration time of rats in the DD model group was significantly shorter than that in the control group (P< 0.01),and escape latency was longer (D1:P> 0.05; D2:P< 0.05;D3:P< 0.01; D4:P< 0.01) (Figure 4C and 4D). Compared with the DD model group,rats in the positive,ZGJTJYF-H,and ZGJTJYF-M groups had significantly extended space exploration time (P< 0.05,P< 0.05,andP< 0.01,respectively) at the exploration period (Figure 4C); and rats in the positive,ZGJTJYF-H,ZGJTJYF-M and ZGJTJYF-L groups had significantly shortened the escape latency on day 4 (P< 0.01,P< 0.01,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively) at the positioning navigation period (Figure 4D).

Figure 4 Changes of the depression-like behavior in each group rats
3.1.3 Effects of ZGJTJYF on TRP,5-HT,IDO,and KYN in DD rats TRP is an essential amino acid for humans,which can be metabolized into KYN and 5-HT,a vital biomarker of depression. The results of HPLC-ECD and ELISA showed that the levels of TRP and 5-HT were significantly reduced (P< 0.01) in the DD model group(Figure 5A and 5B),and the levels of IDO (P< 0.05) and KYN (P< 0.01) increased significantly (Figure 5C and 5D)compared with the control group. Compared with the DD model group,rats in the positive,ZGJTJYF-H,and ZGJTJYF-M groups had significantly increased levels of TRP and 5-HT (P< 0.01) (Figure 5A and 5B),and the positive and ZGJTJYF-H groups had decreased levels of IDO and KYN (P< 0.01 andP< 0.05,respectively) (Figure 5C and 5D).
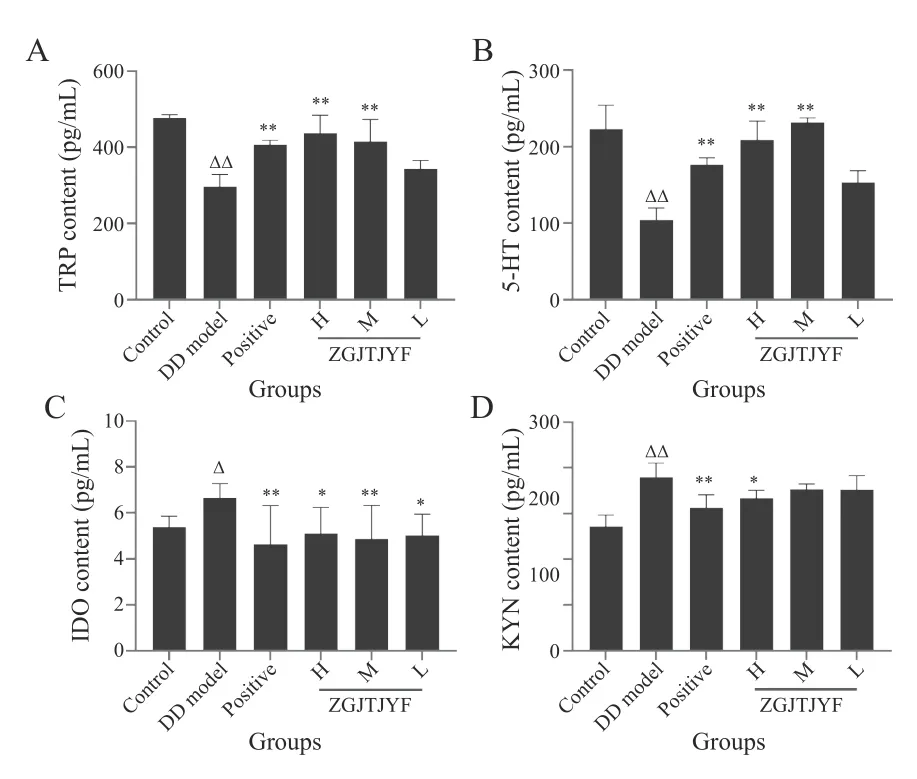
Figure 5 TRP,5-HT,IDO,and KYN contents in hippcampus of each group rats
3.1.4 Effects of ZGJTJYF on the expression of SYN and PSD-95 in DD rats SYN and PSD-95 are fundamental proteins on the synapses of neurons,which are located on the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes,respectively. IHC results showed that the expression of SYN and PSD-95 was significantly lower in the DD model group than that in the control group (P< 0.01) (Figure 6).Compared with the DD group,rats in the positive,ZGJTJYF-H,and ZGJTJYF-M groups had an increased expression levels of SYN (P< 0.01) and PSD-95 (P< 0.05).
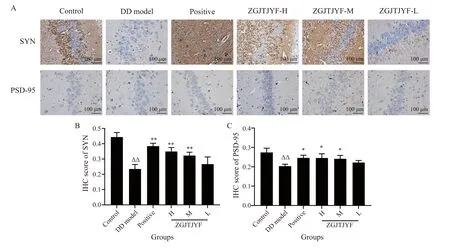
Figure 6 Changes in the expression of SYN and PSD-95 in the hippocampus of each group rats
3.1.5 Effects of ZGJTJYF on the expression of NR2A and NR2B in DD rats NR is a major indicator of synaptic plasticity,whose common functional subtypes include NR2A and NR2B. Western blot results showed that the protein expression levels of NR2A (P< 0.01) (Figure 7A)and NR2B (P< 0.05) (Figure 7B) sharply increased in the DD model group,compared with the control group.Compared with the DD group,the protein expression levels of NR2A and NR2B reduced in the positive,ZGJTJYF-H,and ZGJTJYF-M groups (P< 0.01,P<0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively).
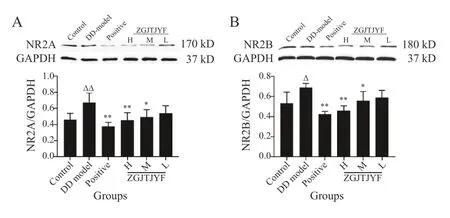
Figure 7 Protein expression levels of NR2A and NR2B in the hippocampus of each group rats
3.2 In vitro experiments
3.2.1 Neuroprotective effects of ZGJTJYF in hippocampal neurons The immunofluorescence assay results showed that the neurons in the model group were seriously injured,as evidenced by the broken neural network connections. Compared with the control group,the average fluorescence intensity of SYN and PSD95 decreased significantly (P< 0.01) (Figure 8). Compared with the model group,ZGJTJYF-containing serum and positive drug-containing serum protected neurons to a certain extent,repairing the breakage or disappearance of neural network connections. Moreover,after being treated with drug-containing serum,the average fluorescence intensity of SYN and PSD95 increased significantly (P< 0.01).Moreover,the IDO inhibitor (1-MT) increased the expression of SYN (P< 0.05) and PSD95 (P< 0.01). The average fluorescence intensity was directly proportional to protein expression.

Figure 8 Protein expression levels of SYN and PSD-95 in hippocampal neurons of each group rats
3.2.2 Effects of ZGJTJYF on the levels of pro-inflammatory factors and IDO activation in hippocampal neurons Pro-inflammatory factors can lead to the excessive activation of IDO. Compared with the control group,the contens of IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α,and IDO in the supernatant in the model group increased significantly (P<0.01,P< 0.05,P< 0.05,andP< 0.01,respectively)(Figure 9). Compared with the model group,the levels of IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α,and IDO decreased in the ZGJTJYF group (P< 0.01,P< 0.05,P< 0.01,andP< 0.05,respectively),and the level of IDO decreased in the 1-MT group(P< 0.05) .

Figure 9 Contents of IL-1β,IL-6,TNF-α,and IDO in the supernatant of hippocampal neurons
3.2.3 Effects of ZGJTJYF on the regulation of the KYN metabolic pathway in hippocampal neurons QUIN and KYNA are metabolites of KYN and intermediate metabolites of TRP. Compared with the control group,the contents of TRP and KYNA in the supernatant in the model group decreased significantly (P< 0.01),whereas,the concentrations of KYN and its metabolite QUIN increased significantly (P< 0.01) (Figure 10). Compared with the model group,the contents of TRP and KYNA increased in the ZGJTJYF group (P< 0.01),but decreased the concentrations of KYN and QUIN (P< 0.05 andP<0.01,respectively) ,meanwhile,1-MT increased TRP level(P< 0.01) and decreased the levels of KYN (P< 0.01) and QUIN (P< 0.05).
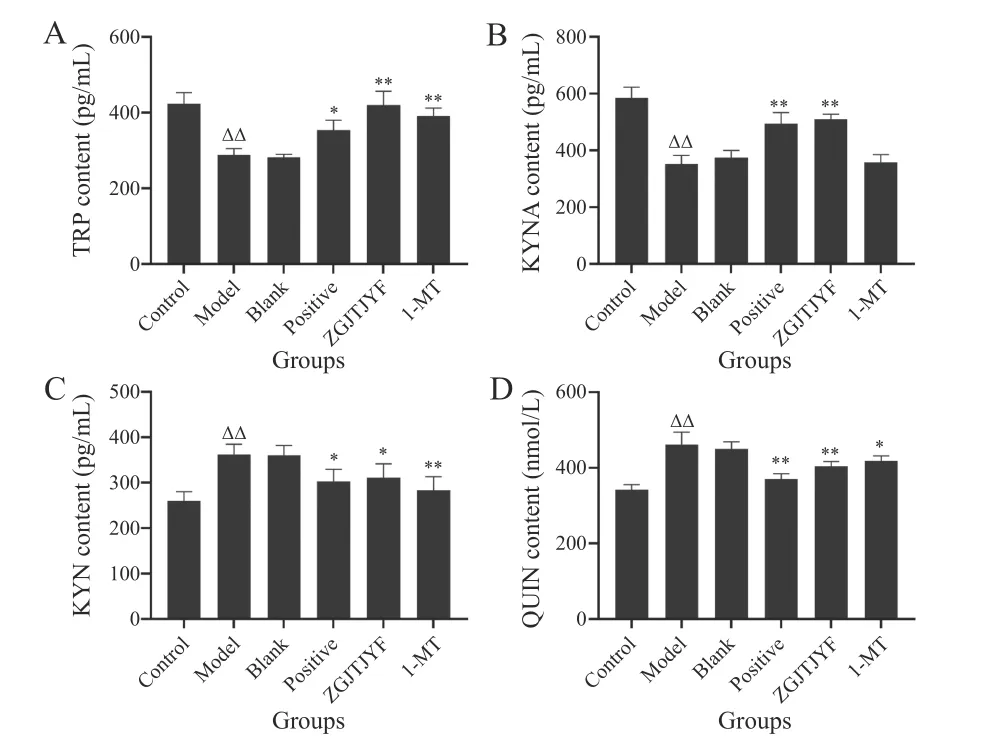
Figure 10 Contents of TRP,KYNA,KYN,and QUIN in the supernatant of nippocampal neurons
3.2.4 Effects of ZGJTJYF on the protein expression levels of NR2A and NR2B in hippocampal neurons Compared with the control group,the average fluorescence intensity of NR2A and NR2B significantly increased in hippocampal neurons of rats in the model group (P<0.01) (Figure 11). Compared with the model group,the average fluorescence intensity of NR2A and NR2B in hippocampal neurons decreased in ZGJTJYF and 1-MT groups (P< 0.05).
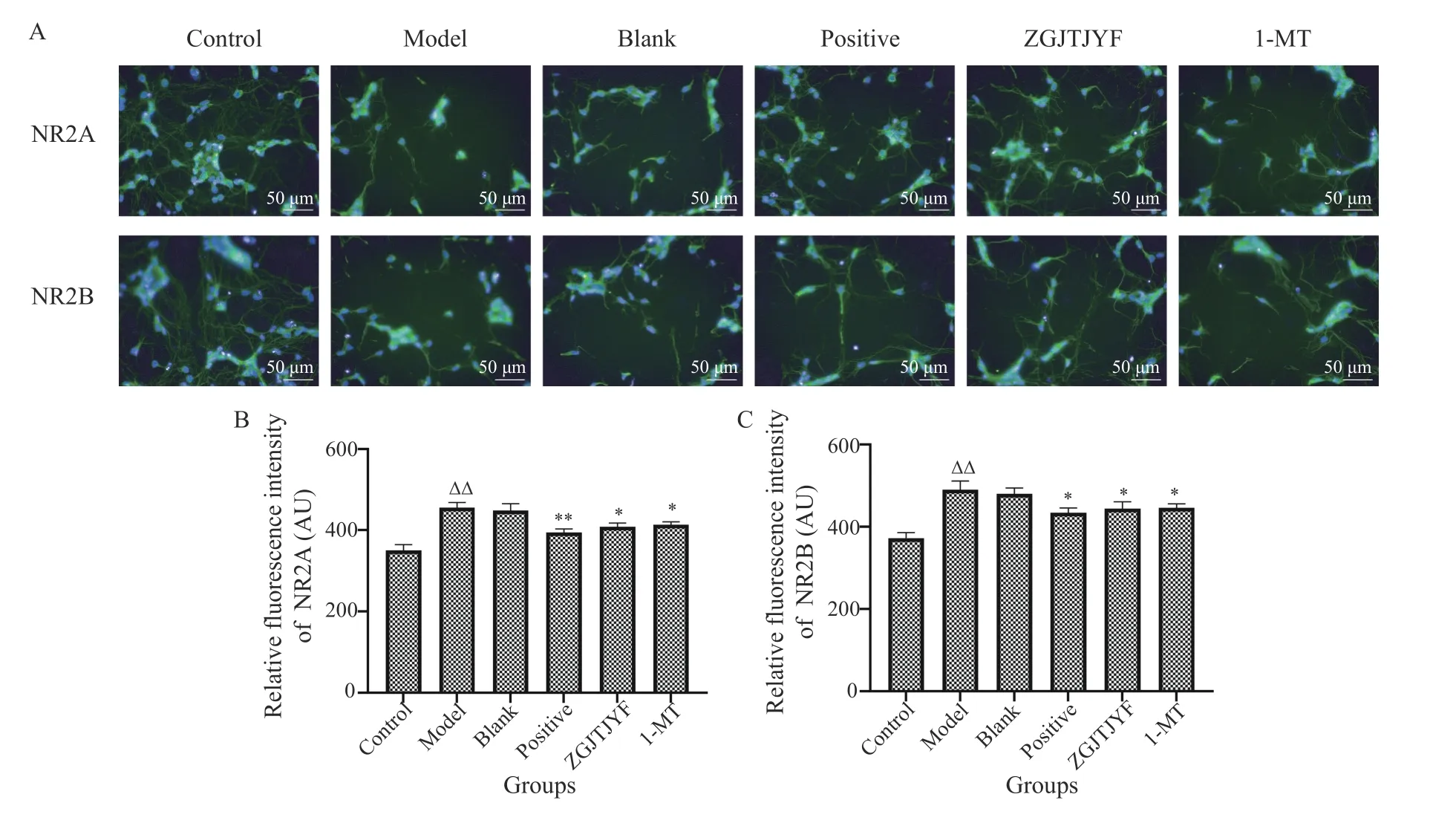
Figure 11 Protein expression levels of NR2A and NR2B in hippocampal neurons of each group rats
4 Discussion
TCM has a curative effect on several diseases and has low toxicity,which attracts worldwide attention[21,22]. In this study,ZGJTJYF,which consists of 11 Chinese herbs,is used to intervene DD model rats. The wholeprescription has effects of tonifying Yin,promoting Qi,removing blood stasis,and resolving depression. Modern pharmacological research has shown that astragaloside IV in Huangqi (Astragali Radix) can play a hypoglycemic role by regulating the AMPK/SIRT1 pathway[23],and 20-hydroxyecdysone from Niuxi (Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix) can stimulate survivingβ-cells to release more insulin[24]. Meanwhile,it has been proven that curcumin,the main active substance of Jianghuang (Curcumae Longae Rhizoma),can play an antidepressant role by increasing the levels of monoamines and brain-derived neurotrophic factors[25]. Hypericum perforatum has become a vital herbal medicine component of antidepressants in Europe and the United States. Its main constituents include hyperforin and hyperoside[26],which may play an antidepressant role by inhibiting the activity of monoamine oxidase,inhibiting the reuptake of monoamine transmitters,and regulating zinc levels[27,28]. This study confirmed that ZGJTJYF could control the increase in blood glucose; it could significantly improve autonomous activity,learning,and memory; and it may have hypoglycemic and antidepressant effects on DD rats.
The hippocampus is a crucial brain region responsible for learning and memory; therefore,hippocampal injury is important in studying emotional diseases such as depression[29]. Since hippocampal neurons are interconnected through synapses,and synaptic plasticity guarantees normal hippocampal function[29]. SYN is a calcium-binding protein in the membranes of synaptic vesicles,which is related to the formation of neuronal synapses. In addition,the localization and quantification of SYN staining can accurately reflect the distribution and density of synapses and can reveal the number and proliferation of synapses[30]. Postsynaptic density material(PSD),a layer of dense,specialized material in the postsynaptic membrane,contains various enzymes and proteins. Changes in its thickness can affect the transmission efficiency of synapses[31]. In particular,PSD-95,a representative scaffold protein in the PSD,is often regarded as a molecular marker of neuronal remodeling since it can play a synaptic regulatory role by integrating NR-mediated signal transduction[32]. Interestingly,this study showed that ZGJTJYF also had a regulatory effect on the synaptic proteins SYN and PSD-95.
A deficiency in 5-HT is a classic depression hypothesis; most common antidepressant medicines play a role in increasing the level of 5-HT. Nevertheless,there are no definitive conclusions yet regarding the causes of 5-HT deficiency. It is well known that TRP is an essential precursor of human 5-HT[10]. However,another metabolic pathway associated with TRP,the KYN metabolic pathway,is activated in the inflammatory state,which may result in the competitive antagonism of 5-HT biosynthesis[33]. Some clinical studies found that the urinary level of TRP declined significantly in patients with depression,while the urinary level of KYN increased significantly,leading to a reduction in the TRP/KYN ratio[34,35]. Hence,TRP degradation and IDO activity are increased in patients with depression[35]. This study found that ZGJTJYF could significantly increase the concentrations of 5-HT and TRP,decrease the levels of IDO and KYN,and decrease the levels of IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-α.
IDO is the first rate-limiting enzyme in the TRP metabolism pathway to KYN. The specific IDO inhibitor 1-MT can effectively improve depression-like behavior mediated by excessive levels of pro-inflammatory factors and significantly reduce the expression of IDO in the mouse brain[36,37]. Therefore,this inhibitor was used for reverse validationin vitro. The results showed that 1-MT treatment had a remarkable inhibitory effect on IDO activity.
NR2A and NR2B play important roles in neurogenesis,neuronal survival,and synaptic plasticity,among other biological processes[38]. Interestingly,KYN can produce two active products,QUIN and KNYA,with opposite functions under the action of different enzymes. QUIN,an NR agonist,can selectively bind NR and cause excitatory neurotoxicity,meanwhile,KYNA is an NR antagonist and has a neuroprotective effect[39,40]. A study has shown that when QUIN level increases and KYNA level decreases,they synergistically increase the expression of NR in the postsynaptic membrane,which can damage hippocampal synaptic plasticity[41]. This study showed that ZGJTJYF could significantly increase KNYA level,decrease QUIN level,and downregulate the expression of NR2A and NR2B. Furthermore,the effect of ZGJTJYF was consistent with that of 1-MT,indicating that ZGJTJYF may play a role in inhibiting the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway (Figure 12).
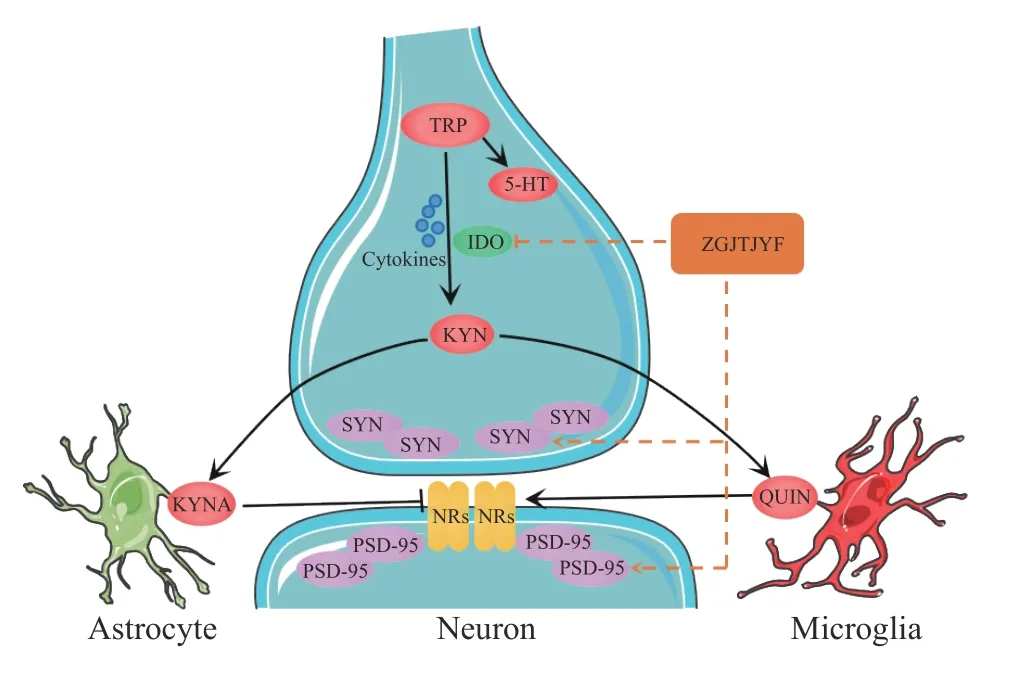
Figure 12 Graphic abstract of this study Cytokines represents IL-1β,IL-6,and TNF-ɑ.
5 Conclusion
In summary,our findings supported that ZGJTJYF could play a neuroprotective role by regulating the TRP/KYN metabolic pathway and the synaptic plasticity of hippocampal neurons. This study revealed promising molecular targets and strategies for the treatment of DD.However,this study did not consider the role of glial cells in the mechanism of ZGJTJYF activity,which will be the focus of future work.
Fundings
National Natural Science Foundation of China (81874464 and 82104793),and the Scientific Research Project of Education Department of Hunan Province (19K066).
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
 Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
Digital Chinese Medicine2022年2期
- Digital Chinese Medicine的其它文章
- Visualization analysis of the international standard ISO/TC 249 for traditional Chinese medicine
- MEDICLOUD: a holistic study on the digital evolution of medical data
- Ancient and modern medication laws of aromatic Chinese medicines in treating angina pectoris based on data mining
- Intra-set correlation analysis of medical records of thyroid cancer treated by traditional Chinese medicine Master ZHOU Zhongying
- Traditional Chinese medicine Master XIONG Jibo’s medication experience in treating arthralgia syndrome through data mining
- Screening influencing factors of blood stasis constitution in traditional Chinese medicine
