白皮锦鸡儿黄酮醇类化合物及其抗菌和抗氧化活性
高海峰,郑兵兵,王蓟花,单体江,赵思峰,周立刚*
1石河子大学农学院,石河子832003;2中国农业大学农学与生物技术学院,北京100193
白皮锦鸡儿黄酮醇类化合物及其抗菌和抗氧化活性
高海峰1,2,郑兵兵2,王蓟花2,单体江2,赵思峰1,周立刚2*
1石河子大学农学院,石河子832003;2中国农业大学农学与生物技术学院,北京100193
从豆科植物白皮锦鸡儿(Caragana leucophloea Pojark.)地上部分分离到3个黄酮醇类化合物,经理化和波谱分析鉴定为3-O-甲基山奈酚(1)、3-O-甲基槲皮素(2)和槲皮素(3)。活性测定表明,1表现出较强的抗细菌活性,对大肠杆菌和番茄疮痂病菌的半抑制浓度分别为9.00 μg/mL和7.42 μg/mL,最低抑制浓度均为12.5 μg/mL;而2和3则表现出较强的抗氧化活性,对DPPH还原的半抑制浓度分别为14.39 μg/mL和13.64 μg/ mL;对β-胡萝卜素-亚油酸氧化的半抑制浓度分别为10.26 μg/mL和9.87 μg/mL。上述黄酮醇类化合物均为首次从白皮锦鸡儿中分离得到。
豆科;白皮锦鸡儿;黄酮醇类化合物;抗菌活性;抗氧化活性
Introduction
Caragana leucophloea Pojark.belongs to Leguminosae,and is mainly distributed in the Provinces of Xinjiang,Gansu and Inner Mongolia of Northwest China.It is also distributed in the surrounding countries such as Tajikistan,Kyrgyzstan,Kazakhstan,and Mongolia.It has been cultivated for dune-fixation,livestock forage,and biological resources for fuel energy and fiber production[1].The roots of C.leucophloea have been used to cure irregular menstruation,leucorrhea,numbness and pain caused by arthritis,edema due to the deficiency of spleen,lactation insufficiency and traumatic injury in traditional Chinese medicine[2].To the best of our knowledge,there are no reports on the metabolites of this plant species in the literature though some species in genus Caragana were reported to be rich with flavonoids,stilbenoids,terpenoids,and lectins[2].In our previous study,the crude ethanol extract of C.leucophloea exhibited obviously antioxidant activity[3].In this study,the ethyl acetate fraction of the crude ethanol extract was subjected to bioassay-guided fractionation leading to the isolation of three flavonol derivatives.The antimicrobial activity of these compounds was evaluated by testing their inhibitory ability on six bacterial and one fungal species.In addition their antioxidant activity was tested by using two complementary systems,namely the DPPH free radical-scavenging and β-carotene-linoleic acid bleaching assays.
Materials and Methods
General
Silica gel(100-200 and 200-300 mesh,Qingdao Marine Chemical Company,China),Sephadex LH-20 (Pharmacia),and C18 reversed-phasesilicagel (YMC)were used for column chromatography(CC).Thin layer chromatography(TLC)plates(Qingdao Marine Chemical Company,China)were coated with 0.5 mm layer of silica gel(GF254,300-400 mesh).Melting points were determined on an XT4-100B microscopic melting-point apparatus(Tianjin Tianguang Optical Instruments Company,China)and were uncorrected.NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker ARX-400(1H at 400 MHz and13C at 100 MHz)or a Bruker Avance DRX-500(1H at 500 MHz and13C at 125 MHz)spectrometer.ESI-MS spectra were recorded on a Bruker Esquire 6000 LC/MS spectrometer.A microplate spectrophotometer(PowerWave HT,BioTek Instruments,USA)was employed to measure the light absorption value.β-Carotene,carbendazim,streptomycin sulfate,and 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl(DPPH) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich(USA).Linoleic acid was obtained from Johnson Matthey(UK).3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide(MTT)was purchased from Amresco(USA).Butylated hydroxytoluene(BHT)and Tween-40 were from Beijing Chemical Company.All other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade.
Plant material
The aerial parts of Caragana leucophloea Pojark.were collected in June 2008 at Kelamayi of Xinjiang Province of China,and was authenticated by Professor Pin Yan of Shihezi University of Xinjiang,where a voucher specimen of this plant was deposited.The plant materials were left to dry in the shade at room temperature to a constant weight.
Isolation and purification
The air-dried and powdered aerial parts(1.0 kg)of C.leucophloea were soaked in 95%ethanol(5 L)at room temperature for three times at an interval of 7 days(3×5 L).After the filtrate was combined and concentrated under vacuum at 50℃,the brown residue (95.5 g,9.55%w/w)was suspended in water and extracted with petroleum ether,then with ethyl acetate,and last with n-butanol.They were concentrated to yield petroleum ether fraction(32.0g,3.20%w/w),ethyl acetate fraction(13.1 g,1.31%w/w),n-butanol fraction(27.2 g,2.72%w/w),and aqueous fraction(20.5 g,2.05%w/w),respectively.The ethyl acetate extract,which was examined to show stronger antimicrobial and antioxidant activity than any other solvent fraction,was further subjected to silica gel column chromatography(CC)with CHCl3-MeOH-H2O (7∶1∶0.1,v/v)as an eluent,and four fractions(A,B,C,and D)were collected according to TLC examining.Fraction A was further chromatographed repeatedly over silica gel,Sephadex LH-20 and C18reverse phase silica gel CC to obtain compounds 1(100 mg),2(30 mg),and 3(10 mg).
Structural identification
3-O-Methylkaempferol(1)
was obtained as yellow amorphous powder(MeOH); mp.252-255℃;ESI-MS m/z 301[M+H]+;1H NMR (DMSO-d6,500 MHz)δ:3.77(3H,s,CH3O-3),12.67(1H,s,HO-5),6.19(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-6),10.81(1H,s,HO-7),6.42(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-8),7.92(H,d,J=7.0 Hz,H-2'),6.93(1H,d,J=7.0 Hz,H-3'),10.23(1H,s,HO-4'),6.93(1H,d,J= 7.0 Hz,H-5'),7.92(H,d,J=7.0 Hz,H-6');13C NMR(DMSO-d6,125 MHz)δ:155.6(C-2),137.6 (C-3),59.7(CH3O-3),177.9(C-4),161.2(C-5),98.5(C-6),164.1(C-7),93.7(C-8),156.3(C-9),104.2(C-10),120.5(C-1'),130.1(C-2'),115.6(C-3'),160.1(C-4'),115.6(C-5'),130.1(C-6').The structure was confirmed by comparison with literature data[4,5].
3-O-Methylquercetin(2) was obtained as yellow amorphous powder(MeOH); mp.256-257℃;ESI-MS m/z 315[M– H]–;1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400 MHz)δ:3.79(3H,s,CH3O-3),12.71(1H,s,HO-5),6.20(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-6),6.41(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-8),7.55(1H,d,J=2.2 Hz,H-2'),6.91(1H,d,J=8.5 Hz,H-5'),7.45(1H,dd,J=2.2,8.4 Hz,H-6');13C NMR(DMSO-d6,100 MHz)δ:155.6(C-2),137.7(C-3),59.7(CH3O-3),177.9(C-4),161.3(C-5),93.6(C-6),164.1(C-7),98.6(C-8),156.3(C-9),104.2(C-10),120.8(C-1'),115.4(C-2'),145.3(C-3'),148.7(C-4'),115.8(C-5'),120.6(C-6').The structure was confirmed by comparison with literature data[4,6].
Quercetin(3)
was obtained as yellow amorphous powder(MeOH); mp.314-315℃;ESI-MS m/z 303[M+H]+,301[MH]–;1H NMR(DMSO-d6,400 MHz)δ:9.37(1H,s,HO-3),12.49(1H,s,HO-5),6.18(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-6),6.40(1H,d,J=2.0 Hz,H-8),7.68(1H,d,J=2.2 Hz,H-2'),9.37(1H,s,HO-3'),9.37(1H,s,HO-4'),6.89(1H,d,J=8.5 Hz,H-5'),7.54(1H,dd,J=2.1,8.5 Hz,H-6');13C NMR(DMSO-d6,100 MHz)δ:147.7(C-2),135.8(C-3),175.9(C-4),160.8(C-5),98.4(C-6),163.9(C-7),98.2(C-8),156.2(C-9),103.0(C-10),122.0(C-1'),115.1(C-2'),145.1(C-3'),146.8(C-4'),115.6(C-5'),120.0(C-6').The structure was confirmed by comparison with literature data[6,7].
Antimicrobial activity assay
Five Gram-negative(Agrobacterium tumefaciens ATCC 11158,Escherichia coli ATCC 29425,Pseudomonas lachrymansATCC 11921,Ralstonia solanacearum ATCC 11696 and Xanthomonasvesicatoria ATCC 11633)and one Gram-positive(Bacillus subtilis ATCC 11562)bacteria were selected for antibacterial activity assay.They were grown in liquid LB medium(yeast extract 5 g/L,peptone 10 g/L,NaCl 5 g/L,pH 7.0) overnight at 28℃,and the diluted bacterial suspension (1×106cfu/mL)was ready for detection.A modified broth dilution-colorimetric assay by using the chromogenic reagent 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide(MTT)was employed to detect the antibacterial activity of the compounds according to our previous report[8].Rice blast fungus,Magnaporthe oryzae(strain P131)was maintained on the oatmeal-tomato agar medium(oatmeal 30 g/L,tomato juice 150 mL/L,and agar 20 g/L)at 25℃.The sporeswere prepared from 7-day-old cultures of M.oryzae.A modified spore germination assay was employed to detect the antifungal activity of the compounds according to our previous report[9].
Antioxidant activity assay
Both DPPH radical scavenging and β-carotene-linoleic acid bleaching assays were employed to determine antioxidant activity of the samples by a microplate spectrophotometric method according to our previous reports[10].All tests were carried out in triplicate.BHT was used as the positive control.
Results and Discussion
Elucidation of the purified flavonol derivatives
Three compounds(1-3)were isolated from the ethyl acetate fraction of the crude ethanol extract of the aerial parts of C.leucophloea based on the bioassay-guided fractionation.Aftercomparing theirphysicochemical and spectrometric data with those reported in literatures,they were known flavonol derivatives and confirmed as 3-O-methylkaempferol(1)[4,5],3-O-methylquercetin(2)[5,6],and quercetin(3)[6,7],respectively.
Antimicrobial activity
Three flavonol derivatives were tested for antimicrobial activities and the corresponding minimum inhibitory concentration(MIC)and median inhibitory concentration (IC50)values are summarized in Table 1.Compound 1 was the most active compound with the MIC values ranging from 12.5 μg/mL to 50 μg/mL,and IC50values from 7.42 μg/mL to 25.83 μg/mL on the test bacteria.Among the test bacteria,E.coli and R.solanacearum were the most sensitive to 1.The IC50values of the compounds 1-3 on the spore germination of M.oryzae were 56.56 μg/mL,76.61 μg/mL and 49.80 μg/mL,respectively.
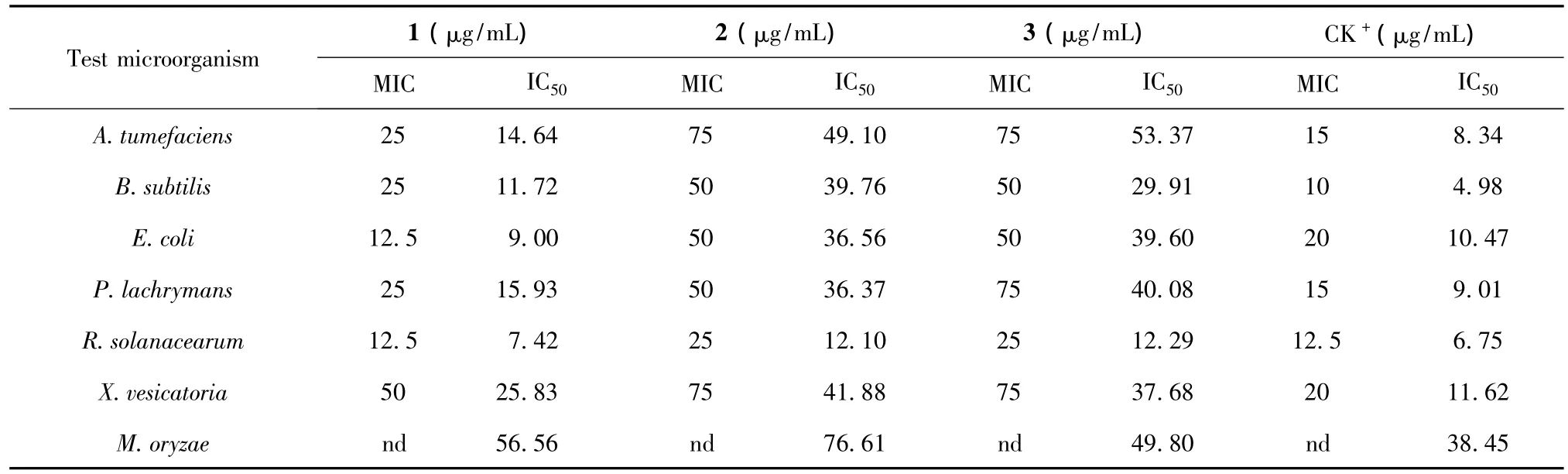
Table 1 Antimicrobial activity of the flavonol derivatives from C.leucophloea
Antioxidant activity
Both the radical scavenging on DPPH reduction and βcarotene-linoleic acid bleaching assays were employed to evaluate antioxidant activity of the compounds.The IC50values of the compounds are summarized in Table 2.By using radical scavenging assay,the IC50values of the compounds 1-3 as well as the positive control (BHT)were 471.52,14.39,13.64 μg/mL,and 25.66 μg/mL,respectively.Similarly,by using β-carotene-linoleic acid bleaching assay,their IC50values were 322.47,10.26,9.87 μg/mL,and 31.46 μg/mL,respectively.Both 2 and 3 showed stronger antioxidant activity than 1 and BHT by using two antioxidant assays.1 was reported to exhibit antipoliovirus activity[11].Both 2 and 3 were reported to have a variety of bioactivities such as antimicrobial[12,13],antioxidant[14],immunomodulatory[15],and anti-inflammatory[16]properties.
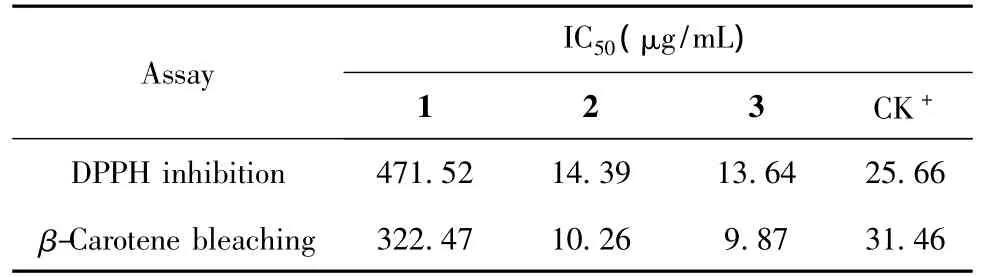
Table 2 Antioxidant activity of the flavonol derivatives from C.leucophloea
In conclusion,three flavonol derivatives(1-3)were first isolated from C.leucophloea to exhibit antimicrobial and antioxidant activities in this study.Compound 1 was also first isolated from the genus Caragana.These flavonol derivatives may be the main bioactive components in the aerial parts of C.leucophloea though other metabolites should be further isolated.The results could provide additional data for future development and utilization of C.leucophloea.In addition,both 2 and 3 have been found in the genus Caragana[2],which comprises more than 100 species native to arid and semiarid areas of the temperate zones of Asia and Eastern Europe[1].They may be chemotaxonomic markers for C.leucophloea though more research is needed to confirm this.
1 Niu XW.The distribution and description of Caragana Fabr.in China.Acta Bot Boreal-Occid Sin,1999,19:107-133.
2 Meng Q,Niu Y,Niu XW,et al.Ethnobotany,phytochemistry and pharmacology of the genus Caragana used in traditional Chinese medicine.J Ethnopharmacol,2009,124:350-368.
3 Gao H,Wang J,Zhao S,et al.Antioxidant activity of the extracts and fractions of Caragana acanthophylla,Caragana leucophloea and Halimodendron halodendron.Nat Prod Res Dev,2010,22:S191-193.
4 Lee EH,Kim HJ,Song YS,et al.Constituents of the stems and fruits of Opuntia ficus-indica var.saboten.Arch Pharm Res,2003,26:1018-1023.
5 Wang Y,Hamburger M,Gueho J,et al.Antimicrobial flavonoids from Psiadia trinervia and their methylated and acetylated derivatives.Phytochemistry,1989,28:2323-2327.
6 Wang J,Gao H,Zhao J,et al.Preparative separation of phenolic compounds from Halimodendron halodendron by highspeed counter-current chromatography.Molecules,2010,15: 5998-6007.
7 Fossen T,Pedersen AT,Andersen OM.Flavonoids from red onion(Allium cepa).Phytochemistry,1998,47:281-285.
8 Wang J,Liu H,Zhao J,et al.Antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of the root bark essential oil of Periploca sepium and its main component 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde.Molecules,2010,15:5807-5817.
9 Liu H,Wang J,Zhao J,et al.Isoquinoline alkaloids from Macleaya cordata active against plant microbial pathogens.Nat Prod Commun,2009,4:1557-1560.
10 Wang J,Zhao J,Liu H,et al.Chemical analysis and biological activity of the essential oils of two valerianaceous species from China:Nardostachys chinensis and Valeriana officinalis.Molecules,2010,15:6411-6422.
11 Robin V,Irurzun A,Amoros M,et al.Antipoliovirus flavonoids from Psiadia dentata.Antivir Chem Chemoth,2001,12:283-291.
12 Lee KA,Moon SH,Kim K T,et al.Antimicrobial effects of various flavonoids on Escherichia coli 157∶H7 cell growth and lipopolysaccharide production.Food SciBiotechnol,2010,19:257-261.
13 Lall N,Hussein AA,Meyer JJM.Antiviral and antituberculous activity of Helichrysum melanacme constituents.Fitoterapia,2006,77:230-232.
14 Haraguchi H,Hashimoto K,Yagi A.Antioxidative substances in leaves of Polygonum hydropiper.J Agric Food Chem,1992,40:1349-1351.
15 Okoko T,Oruambo IF.Inhibitory activity of quercetin and its metabolite on lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of macrophage U937 cells.Food Chem Toxicol,2009,47:809-812.
16 Kim JY,Lim HJ,Ryu JH.In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of 3-O-methyl-flavones isolated from Siegesbeckia glabrescens.Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2008,18:1511-1514.
April 25,2011;Accepted August 3,2011
This work was co-financed by the grants from the Hi-Tech R&D Program of China(2011AA10A202),and the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest of China(nyhyzx07-022 and 200903052).
Flavonol Derivatives from Caragana leucophloea and Their Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities
GAO Hai-feng1,2,ZHENG Bing-bing2,WANG Ji-hua2,SHAN Ti-jiang2,ZHAO Si-feng1,ZHOU Li-gang2*1College of Agronomy,Shihezi University,Shihezi 832003,China;2College of Agronomy and Biotechnology,China Agricultural University,Beijing 100193,China
Three flavonol derivatives have been isolated from the aerial parts of Caragana leucophloea Pojark.(Leguminosae).By means of physicochemical and spectrometric analysis,they were identified as 3-O-methylkaempferol(1),3-O-methylquercetin(2),and quercetin(3).Among them,1 exhibited the strongest antibacterial activity with its median inhibitory concentration(IC50)values on Escherichia coli and Ralstonia solanacearum as 9.00 μg/mL and 7.42 μg/ mL,respectively,and minimum inhibitory concentration(MIC)values on these two bacteria equally as 12.5 μg/mL.Either 2 or 3 showed stronger antioxidant activity than 1.The IC50values of 2 and 3 on DPPH reduction were 14.39 μg/mL and 13.64 μg/mL,respectively,and those on β-carotene-linoleic acid oxidation were 10.26 μg/mL and 9.87 μg/mL,respectively.These flavonol derivatives were isolated from this plant species for the first time.
Leguminosae;Caragana leucophloea;flavonol derivatives;antimicrobial activity;antioxidant activity
1001-6880(2011)05-0853-05
*Corresponding author Tel:86-10-62731199;E-mail:lgzhou@cau.edu.cn
Q946.8;S541
A

