Consumers' Perception of Risks,Awareness of Products and Willingness to Pay:A Case Study of Organic Milk
Yingjun XU,Shijiu YIN,Mo CHEN,Yang GAO
1.School of Economics,Qufu Normal University,Rizhao 276826,China;2.School of Graphic Arts Qufu,Normal University,Rizhao 276826,China
As the material and cultural level is improved and the basic food and clothing problem is solved,China's consumers start to pay attention to improving the quality of life,and the proportion of dairy products in the residents' consumption structure has been increased greatly in recent years.Taking fresh milk for example,it was increased from 11.90 kg per capita in 2001 to 14.91 kg per capita in 2009[1].But there is still a large gap between this data and the Asian average or world average,and China's ranking of amount of milk possession is disproportionate to its status of the world's second largest economy.According to expert estimates,China's dairy consumption growth will remain at about6%by 2020.Empirical studies show that for every 1%increase in the income of residents,the urban residents' dairy consumption will grow 0.67%and rural residents' dairy consumption will increase 0.27%.With the sustained development of national economy and further improvement of urban and rural residents' income levels,the milk consumption is expected to continue to significantly increase[2].
With economic development and social progress,food safety has upgraded from quantity safety to quality safety.Organic food industry,as an important measure to improve food quality safety,has gradually attracted the world attention[3].Organic food production began slowly in the mid-twentieth century,and it began to accelerate from the late seventies of last century.The countries with rapid development of organic food production at present include Austria, Sweden, Finland, Denmark and the United States[4].China's organic food production started late,and in 1994,the State Environmental Protection Administration of China established the National Organic Food Development Center,beginning to engage in the research,development and extension of organic food.Organic vegetables and organic fruits have been actively developed firstly.The development of organic milk started late.On December 13,2005,Inner Mongolia Yunhai Qiulin Animal Husbandry Co.,Ltd.was approved as China's first certified organic milk corporate,and the domestic organic milk began to enter people's consumption ranges.Over two decades of development,China's organic food industry has been developed slowly.
Therefore,taking milk for example,we aim to understand consumers' perception of food safety risks and their awareness of organic food,and examine their willingness to pay and the influencing factors,which is of great reference significance to targeted marketing and management of organic food producers,and of positive reference value to the formulation of organic food development policy.
1 Data sources and sample description
1.1 Scope of the surveyThe research area is Shandong Province,a typical province in the eastern coastal areas of China.Shandong Province is a typical populous province and economically strong province.The sixth national census data show that the permanent population in Shandong Province was 957.931 million in 2010,and the born population was 0.84373 million,ranking third among the 34 first-level administrative regions of China[5].Moreover,the per capita GDP of Shandong Province reached$8224.07 in 2012,ranking tenth among the first-level administrative regions[6],so the per capita disposable income is higher.
In view of a huge number of annual births and relatively high per capita disposable income in Shandong Province,there will be bound to have an inevitable huge demand for organic milk,so we choose Shandong Province as a typical case to survey consumers' perception of organic food,perception of food safety risk,willingness to pay and the influencing factors.In this paper,we choose two cities from eastern,central and western parts of Shandong Province,respectively(East:Qingdao,Yantai;Central:Ji'nan,Tai'an;West:Dezhou,Heze).
1.2 Survey contentGiven the higher price of organic food,the survey object is urban consumers.Specifically it includes consumers' perception of food safety risks,awareness of organic food,purchase behavior and willingness to pay.
In addition,we survey consumers' individual characteristics,such as gender,income,education and health.The investigators are the undergraduate and graduate students from School of Economics,Qufu Normal University,who receive comprehensive and systematic training before the field survey.The field survey was conducted in the summer of 2013.In the survey,it was agreed to take the third consumer in sight as the survey object,in order to ensure the randomness of the sample selection[7].60 consumers were surveyed in each city with a response rate of 100%,and 11 copies of incomplete or incorrect questionnaires were excluded,so we finally got349 valid questionnaires and the proportion of valid questionnaires was 97%.
2 Descriptive statistical results
2.1 Basic characteristics of the consumersThe descriptive statistical results of the basic situation of consumers are shown in Table 1.From the survey data,we know that there are more women than men in consuming organic food,which is consistent with the fact that food is mostly purchased by women.From the age distribution,the 31-40 age group consumers are the most,possibly because they generally have infant or pursue fashion,so they are more likely to buy organic food;the small number of other age groups may be due to consumers' insufficient trust in organic food or low income.

Table 1 Descriptive statistical results of basic features of consumers
From the educational level,most of them have university degrees,which partly is a direct result of expanded university enrollment since the end of the last century,and partly is due to the fact that less educated consumers' awareness of organic food is low,and their income is generally low,and they are reluctant to pay a higher price to enjoy high quality of organic foods.The consumers with family members under the age of 12 years account for 22.35%;the consumers with family members over the age of60 years account for13.18%.The consumers' subjective evaluation of their health status affects their willingness to buy organic food.In this survey,68.19%of consumers believe that their health is better,while 31.81%of consumers believe that their health status is so-so or bad.
2.2 Consumers' perception of food safety risks and awareness of organic foodsThe question is set in the questionnaire,"How do you think about the China's current food safety risk?".It is measured using Likert Scale(1-5 representing"very small","small","so-so","large"and"very large",respectively).Most consumers choose"large"and"so-so",accounting for39%and 20%,respectively,indicating that consumers believe that China's current food security situation is not good enough,and they do not trust most food manufacturers.
Through the statistics of options on organic food awareness,consumers' awareness of organic food is low.The majority of consumers(51%)only have heard of organic food;34%of consumers know some about it;15%of consumers have a better under-standing of it.Therefore,the relevant government departments and manufacturers' promotion of organic foods has yet to be further strengthened.
3 Consumers' willingness to pay for organic foods
3.1 Variable definitionIn this paper,we use binary log it model to research the consumers' willingness to buy organic milk.The dependent variable yiis used to indicate whether consumers are willing to buy organic milk.When consumers choose"willing",yitakes value of 1,and when consumers choose"unwilling",the dependent variable yitakes value of0.
The independent variables are divided into three categories.The first category is to take the actual values,including the variables of age and years of education.The second category is the dummy variables,including the variables of gender,whether the family has the children under the age of12 and whether the family has the old man above the age of60.The third category uses Lik-ert Scale to measure,including the variables of health status self evaluation,awareness of organic food and perception of food safety risk.Variable definition and the related information are shown in Table 2.

Table 2 Variable definition,sample mean and the expected direction
In this paper,the binary logit model used is as follows[8]:
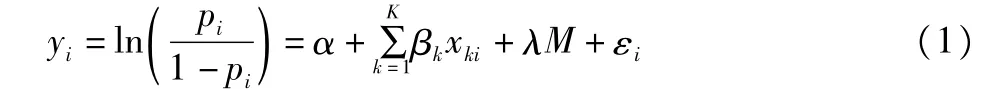
where piis the probability of consumers to buy organic milk;α is constant term;xkiis the variable influencing the willingness to buy organic food;M is the price that the consumers are willing to pay for the organic milk;εiis the error term.
Thus we get the average price that the consumers are willing to pay for the organic milk E(M)as follows:

So we can derive the average consumers' willingness to pay for the organic milk E(WTP)as follows:

where P0is the average price of organic milk.
3.2 Result analysis of consumers' willingness to pay for the organic m ilkThe regression results of formula(1)using EVIEWS 6.0 can be seen in Table 3.From the relevant data in Table 3,we know that the impact of gender on willingness to pay for organic milk is not significant.The survey results of Wang Ying et al(2008)on the Beijing consumers show that men are more willing to consume organic food[9],which may be related to the fact that this paper is to study based on specific organic milk while Wang Ying's paper is based on the organic food in a general sense.Age,educational level,whether the family has the children under the age of12,whether the family has the old man above the age of 60,health status self-evaluation,awareness of organic food and perception of food safety risk,have a significant impact on the consumers' willingness to buy organic milk.Younger consumers are more likely to buy organic milk,which may be due to the fact that such consumers generally have younger children.
Highly educated consumers are more willing to buy organic milk,because the consumers with higher level of education have a better understanding of organic milk,and they well know the benefits of organic milk to health and the contribution of organic milk to environmental protection,so they are more willing to pay premium for the organic milk.The studies of Yin Shijiu(2008)believe that the impact of age and educational level on consumers' willingness to buy organic food is not significant,which may be related to the fact that this paper is to study based on specific organic milk while Yin Shijiu's survey is based on the organic food in a general sense[10].
The consumers with children under the age of 12 or old man above the age of 60 in the family are more willing to consume organic milk for the sake of the children and the elderly's health,which is consistent with the research findings of Haghjou(2013)[11].The consumers with poor health status self-evaluation are more willing to buy organic milk from the perspective of protecting his body.The consumers with high awareness of organic food have a better understanding of organic milk,who believe that the organic milk industry is of great value to ensuring people's life security,reducing carbon emissions,and protecting the ecological environment and ecological diversity,so they are more willing to pay premium for organic milk.
The consumers with higher perception of food risk have not enough confidence in the ordinary food,but have a higher degree of trust in organic food,so they are more willing to pay premium for organic milk.The studies of Roitner-schobesberger et al(2008)on the Thai consumers' willingness to buy organic food also believe that the improvement in the awareness of organic food and perception of food safety risk plays a significant role in promoting the degree of consumers' willingness to buy organic food[12].

Table 3 The regression results of consumers' willingness to buy organic milk
3.3 The price that the consumers are willing to pay for the organic milkAccording to formula(2),the price that the consumers are willing to pay for the organic milk E(M)is 16 yuan per liter.Therefore,the average consumers' willingness to pay for the organic milk E(WTP)is as follows:

where P0is10 yuan per liter,namely the price of ordinary milk is 10 yuan per liter.
Thus we know that the consumers are willing to pay the premium of 6 yuan per liter for the good quality organic milk,which is60%of the price of ordinary milk.The current market price of organic milk is about three times the price of the ordinary milk.
Therefore,there is still a gap between consumers' willingness to pay for organic milk and the market price.The possible reasons are as follows:(i)The consumers' awareness of organic food is low,having not the correct understanding of difference in the costs and scarcity between organic food and ordinary food;(ii)In recent years,some negative news has been exposed,eroding the consumers' confidence in organic food that has not been effectively established.
4 Conclusions and policy recommendations
4.1 ConclusionsOn the basis of the survey data on consumers in Ji'nan City and other five cities of Shandong Province,this paper carries out the statistical analysis of consumers' perception of food safety risk and awareness of organic food,and taking organic milk for example,uses binary logit regression model to analyze the main factors influencing consumers' willingness to buy organic food,and calculate the consumers' willingness to pay for the organic milk.
The results show that the consumers have high perception of food safety risk but low awareness of organic food;the impact of age on consumers' willingness to pay for the organic milk is not significant;for the well educated consumers,or the consumers with children under the age of 12 years in the family,or the consumers with old man above the age of 60 years in the family,or the consumers with poor health status self-evaluation,or the consumers with high awareness of organic food or the consumers with high perception of food safety risk,they are more willing to buy organic milk.The calculation results show that the consumers are willing to pay 60%of premium for the organic milk.
4.2 Policy recommendations
4.2.1Timely disclosing information to enhance consumer trust.In view of the important significance of food safety to people's health and security,the relevant government departments should timely release the food safety status systematically,comprehensively and authoritatively on relevant websites,to deny various rumors and avoid the phenomenon of food safety scares;establish the incentive mechanism to promote organic food production enterprises to truthfully disclose the food safety information for consumers,trying to improve the level of consumer trust.
4.2.2Increasing the organic food publicity efforts to improve consumers' awareness of organic food.Organic food industry in China has been developed for more than twenty years,but there has been no substantive progress.We find in the survey that consumers' awareness of organic food is low.Government departments at all levels should step up efforts to increase the public welfare publicity of positive contribution of organic food to health and the environment,such as television public service ads and public service broadcasting.We can film a documentary with the brief development history of China's food as the theme,to make people better learn organic food industry.There is a need to give preferential policies for the publishing of organic food-related books;in the elective course in college,it is necessary to increase organic food-related courses.
4.2.3Increasing the business publicity to seize the opportunity.Currently,organic food is still a new thing to the vast majority of consumers who know little about it.Thus,the relevant enterprises can take this opportunity to increase publicity,gain the initiative,and get first-strike advantage to win organic food battle victory.
[1]LIU CG.China dairy yearbook,2010[M].Beijing:China Agriculture Press,2010.(in Chinese).
[2]News release of organic milk's successful verification by Inner Mongolia Qiulin Corporation[EB/OL].[2011-06-07](2013-09-01)http://www.yhql.net/Article/HTML/6.htm.(in Chinese).
[3]YANG YG.Chinese organic products development and agriculture industrialization[J].China Population Resources and Environment,1998,8(2):75-77.(in Chinese).
[4]MIAO AQ.Discussion on the status quo and development countermeasures of organic products in China[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2002,(4):480-482.(in Chinese).
[5]The data from China's census of 2010[EB/OL].http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/pcsj/rkpc/6rp/indexch.htm.(in Chinese).
[6]China statistical uyearbook,2012[EB/OL].http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2012/indexch.htm.(in Chinese).
[7]WU LH,XU LL,ZHU D,et al.Factors affecting consumer willingness to pay for certified traceable food in Jiangsu Province of China[J].Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics,2012,(60):317-333.
[8]WANG ZG,QIAN CJ,ZHOU YG.Willingness to pay for traceable pork:Evidence from Beijing,China[J].Journal of Hunan Agricultural University(Social Sciences),2013,14(3):7-13.(in Chinese).
[9]WANG Y,LIU D,TIAN XC.Analysis on consumer willingness to pay for organic food[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2008,36(33):14827-14828.(in Chinese).
[10]YIN SJ,WU LH,CHENM.Analysis on the needs for organic food based on willingness to pay[J].Journal of Agrotechnical Economics,2008,(5):81-88.(in Chinese).
[11]Hajhjou M.,Hayati B.,Pishbahar E.,etal.Factors affecting consumers' potential willingness to pay for organic food products in Iran:case study of abriz[J].Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2013,159(2):191-202.
[12]Roitner-schobesberger Birgit,Darnhofer Ika,Somsook Suthichai,Vogl Christian R.Consumer perceptions of organic foods in Bangkok,Thailand[J].Food Policy,2008(33):112-121.
 Asian Agricultural Research2014年1期
Asian Agricultural Research2014年1期
- Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Study on Performance of Development of Sports Industry in China-Based on DEA Nonlinear Estimation
- Comparative Analysis of the Purchase Price of Raw M ilk in the World
- The Chinese Urban-rural Dual Economic Structure Model and Analysis
- Study on the Supply Efficiency of Rural Public Service in China Based on Three-stage DEA M odel
- Research on the Peanut Leaf Etiolation Prevention and Film M ulching Effect in Hubei Province
- Com parative Research of Residents'Effect Perception and Participation Capacity and Willingness on Pro-poor Tourism
