Effect of tuina manipulations on blood pressure and its variability in hypertension patients
Shen Zhi-fang (沈志方), Bian Xiao-dong (边晓东), Gao Feng (高峰), Li Qiu-ju (李秋菊), Yuan Ju-ying (袁巨英)
Jiaxing Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang 314000, China
Effect of tuina manipulations on blood pressure and its variability in hypertension patients
Shen Zhi-fang (沈志方), Bian Xiao-dong (边晓东), Gao Feng (高峰), Li Qiu-ju (李秋菊), Yuan Ju-ying (袁巨英)
Jiaxing Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Zhejiang 314000, China
Objective:To observe the effect of tuina manipulations on blood pressure and its variability in hypertension patients.
Tuina; Massage; Meridians; Acupuncture Points; Hypertension; Blood Pressure
Hypertension is the most common cardiovascular disease, and has become a major global health issue. The 2004 National Nutrition and Health Status Survey showed that the prevalence of hypertension was 18.8% in Chinese people over 18 years old. Given the Chinese population size and structure in 2010, 0.2 billion people are estimated to have developed hypertension so far, i.e. 2 out 10 adults have hypertension, occupying 1/5 of global hypertension patients[1]. The increased fluctuation and circadian changes of blood pressure are closely related to the incidence and severity of the target-organ damage in hypertension, especially a significant increase in cardiocerebrovascular events in the morning and at night[2-3]. Therefore, it’s important to decrease the variability of blood pressure and turn the non-dipper type into dipper type to reduce the target-organ damage and complications while modulating blood pressure. We have adopted tuina manipulations to treat hypertension by tonifying kidney, promoting blood circulation, and unblocking collaterals. The observation is presented as follows.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
By referring to the2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension[1]: the systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mm Hg and/or the diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg without using any anti-hypertensive drugs measured 3 times in different days.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Hypertension grade 1-2, and low or moderate risk according to risk stratification; having signed the informed consent form.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Initial cerebrovascular accident; severe heart failure.
1.4 Drop-out criteria
Those who failed to finish the whole study; those who failed to cooperate in the study.
1.5 Statistical analysis
The SAS 6.12 and SPSS 10.0 software were adopted for data processing. The measurement data were expressed by mean ± standard deviationand the inter-group comparisons were analyzed by independent-samplet-test, while the intra-group comparisons were by pairedt-test.P<0.05 indicates a statistical significance.
1.6 General data
Totally 40 patients were recruited from our hospital. By coin flipping, they were divided into two groups, the front side to the observation group and the back side to the medication group. If the patient number reached 20 in one group, the rest would be enrolled into the other group. Finally, there were 20 subjects in each group. There were no between-group significant differences in comparing data of gender, age, and disease duration (P>0.05), indicating the comparability (Table 1).
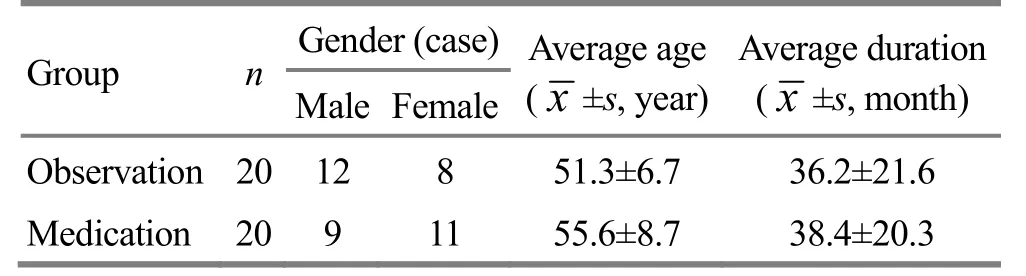
Table 1. Comparison of general data
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Observation group
2.1.1 Tuina manipulations of kidney-tonifying bloodcirculating and collaterals-unblocking
The following tuina manipulations were performed in order: An-pressing the three meridians on head (Figure 1), An-pressing the head with five fingers, Tui-pushing the occiput, Rou-kneading Fengchi (GB 20), (Figure 2), and Tui-pushing the neck on both sides. Each manipulation lasted 0.5 min, and it took about 3 min to finish all the manipulations.
It’s followed by Tui-pushing up the Governor Vessel (Figure 3), Gun-rolling bilateral Bladder Meridian (Figure 4), Rou-kneading Ganshu (BL 18) and Shenshu (BL 23), Na-grasping Jianjing (GB 21), (Figure 5), digital Rou-kneading Xueyadian (EX-HN 32) and Jiaji (EX-B 2) points. Each manipulation was performed for 0.5 min, 6 min in total.
Tui-pushing forehead, parting Mo-wiping forehead (Figure 6) and rim of the eyes, Yun-circular-pushing Taiyang (EX-HN 5), (Figure 7), Sao-sweeping Qiaogong (sternocleidomastoid), (Figure 8), Tui-pushing thenar, and deep An-pressing Jianjing (GB 21) were then performed in sequence, 0.5 min for each manipulation and 5 min in total.

Figure 1. An-pressing the three meridians on head

Figure 2. Rou-kneading Fengchi (GB 20)

Figure 3. Tui-pushing up the Governor Vessel
It’s then followed by Mo-wiping the midline of chest with the palms, Shu-combing the intercostal spaces, Fen-parting abdominal yin and yang with fingers(Figure 9), Mo-rubbing Zhongwan (CV 12) and abdomen with both palms (Figure 10). Mo-rubbing Zhongwan (CV 12) took 2 min and 0.5 min for each of the rest manipulations, totally for 5 min.

Figure 4. Gun-rolling bilateral Bladder Meridian

Figure 5. Na-grasping Jianjing (GB 21)

Figure 6. Parting Mo-wiping forehead
The last group of manipulations included Roukneading Zusanli (ST 36), Sanyinjiao (SP 6), Fenglong (ST 40), and Xingjian (LR 2), 20 times for each point, and Rou-kneading Yongquan (KI 1) for 40 times, followed by Rou-kneading the anti-hypertensive groove on the back of the auricle for 1 min. Finally, it’s ended with Roukneading Binao (LI 14), Quchi (LI 11), Neiguan (PC 6), and Hegu (LI 4), 10 times for each point.

Figure 7. Yun-circular-pushing Taiyang (EX-HN 5)

Figure 8. Sao-sweeping Qiaogong (sternocleidomastoid)

Figure 9. Fen-parting abdominal yin and yang
The tuina manipulation was applied once a day, 1 month as a treatment course, for 3 courses in total.
2.1.2 Medication
Valsartan Capsule (Diovan) (Novartis, Beijing, China; China Food and Drug Administration approval number: H20040217) 80 mg, once a day, taken orally for 3 months.

Figure 10. Mo-rubbing Zhongwan (CV 12) and abdomen
2.2 Medication group
The medication group was only prescribed with the same medication, at same dose and for same duration.
3 Observation of Therapeutic Efficacy
3.1 24-hour mean SBP
There was no significant difference in comparing the 24-hour mean SBP between the two groups prior to the intervention (P>0.05). After 3-month treatment, the 24-hour mean SBP dropped significantly in both groups (P<0.05), and the decrease in the observation group was more marked than that in the medication group (P<0.05), (Table 2).
3.2 24-hour mean DBP
There was no significant difference in comparing the 24-hour mean DBP before the intervention (P>0.05). After 3-month treatment, the 24-hour mean DBP dropped significantly in both groups (P<0.05), and the decrease in the observation group was less significant than that in the mediation group (P<0.05), (Table 3).
3.3 24-hour blood pressure variability
There was no significant difference in comparing the 24-hour blood pressure variability between the two groups prior to the intervention (P>0.05). After 3-month treatments, the 24-hour blood pressure variability dropped in both groups, and the decrease in the observation group was more significant than that in the medication group (P<0.05), (Table 4).
Table 2. Comparison of 24-hour SBP

Table 2. Comparison of 24-hour SBP
Note: Compared with before treatment result in the same group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the medication group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 3-month treatments Difference between before and after treatment Observation 20 159.53±16.64 131.42±11.571) 28.11±13.422)Medication 20 156.47±13.74 139.42±16.211) 17.05±12.34
Table 3. Comparison of 24-hour DBP

Table 3. Comparison of 24-hour DBP
Note: Compared with before treatment result in the same group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the medication group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 3-month treatments Difference between before and after treatment Observation 20 95.61±11.26 84.17±8.531) 11.44±7.622)Medication 20 95.67±14.13 80.27±10.341) 15.40±9.78
Table 4. Comparison of 24-hour blood pressure variability

Table 4. Comparison of 24-hour blood pressure variability
Note: Compared with before treatment result in the same group, 1) P<0.05; compared with the medication group, 2) P<0.05
Group n Before treatment After 3-month treatments Difference between before and after treatment Observation 20 44.32±7.18 27.14±6.641) 17.18±5.262)Medication 20 46.24±8.47 34.35±8.721) 11.89±9.21
4 Discussion
In traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), hypertension belongs to the scopes of headache, vertigo, and wind stroke[4], caused by deficiency of the liver and kidney, disharmony between qi and blood and imbalance between yin and yang resulting from emotional disturbances, improper diet or dysfunctions of Zang-fu organs. It’s mainly associated with the heart, liver and kidney.
The heart dominates blood vessels. The heart qi promotes blood circulation, and regulates the beating of heart and dilation of vessels, keeping the vessels unblocked and a smooth blood circulation. The vessels house blood, working as both container and channels to transport blood. The heart, vessels, and blood together form up the blood circulation system, and thus we say the heart governs blood and vessels. The liver stores blood and maintains free flow of qi. A normal liver function guarantees regular qi activity and blood circulation. The kidney stores essence and dominates water and absorbs qi. Kidney yin and kidney yang can promote and harmonize the yin-yang of Zang-fu organs. Kidney qi governs and regulates the metabolism ofbody fluids, not only modulating the Zang-fu organs involved in the metabolism, but also adjusting the production and discharge of urine. Nan Jing (Classic of Difficult Issues) holds that expiration depends on the function of the heart and lung, while inspiration depends on the function of the liver and kidney[5]. It’s believed in Western medicine that heart pumping blood, circulating blood volume, and vascular resistance are three basic components for blood pressure and also three key factors that influence blood pressure, corresponding to the physiological functions of heart, liver, and kidney. Meanwhile, the liver and kidney share the same origin. Liver is the son and kidney is the mother. This is also to say that essence and blood share the same origin. Storing and discharging interact with each other and yin and yang reinforce and restrict each other. Therefore, this study took tonifying kidney, promoting blood circulation, and unblocking vessels as the general treatment principle.
The results showed that the two methods can both improve the blood pressure and its variability, either with tuina plus medication or with medication alone. However, the effect of tuina plus medication is more significant than medication alone, especially on improving blood pressure variability. It’s also confirmed the long-term effect of tuina manipulations on blood pressure and its variability by tonifying kidney, promoting blood circulation, and unblocking vessels. By working on specific points, tuina manipulations work to tonify liver and kidney, supplement yin and balance yang, relax tendons and unblock collaterals, and promote blood circulation. Modern studies indicate that tuina manipulations modulate blood pressure by the following four aspects. First, it regulates the nervous system, activating vagus, inhibiting sympathetic nerves, and adjusting autonomic nerves in both ways, and further dilating capillaries and reducing the resistance of peripheral blood vessels[6]. Second, the manipulations can relax major muscle groups, release vascular spasm, increase vascular bed, and improve blood flow in peripheral vessels[7]. Third, it stimulates the carotid baroreceptor to excite the vagus, reduce heart rate and pumping blood volume, inhibit vasomotor neurons, dilate blood vessels, and decrease the resistance of peripheral blood vessels[8]. Four, the manipulations can also reduce symptoms such as pressure and anxiety[9-10]. It’s also found that the blood pressure variability is associated with the target-organ damage in hypertension patients[11-12]. The tuina manipulations of kidney-tonifying blood-circulating and collaterals-unblocking can produce a significant effect on anti-hypertension and improving blood pressure variability, and it can effectively reduce the target-organ damage in hypertension and benefit the prognosis. Moreover, it’s safe and causes no adverse effects. Therefore, this method is worth to promote in clinical application.
Conflict of Interest
There was no conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Project of Zhejiang Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (浙江省中医药管理局项目, No. 2012zb154).
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Received: 10 August 2014/Accepted: 18 October 2014
[1] Writing Group of 2010 Chinese Guidelines for the Management of Hypertension. 2010 Chinese guidelines for the management of hypertension. Zhonghua Xinxueguan Zazhi, 2011, 39(7): 579-616.
[2] Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E, O'Brien E, Dobson JE, Dahlöf B, Sever PS, Poulter NR. Prognostic significance of vist-to-vist variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet, 2010, 375(9718): 895-905.
[3] Zhang YM, Cheng N. Relationship between ambulatory blood pressure and carotid artery atherosclerosis as well as left ventricular hypertrophy. Zhonghua Gaoxueya Zazhi, 2008, 16(8): 749-750.
[4] Zhang BY. Internal Chinese Medicine. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 1985: 198-208.
[5] Sun GR. Basic Theory of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 104-128.
[6] Liu P, Chen YF, Liu K, Liu J, Cao DW. Clinical efficacy of tuina treatment for 71 hypertension. Zhongguo Minkang Yixue, 2010, 22(21): 2771.
[7] Hao F. Tuina treatment for 60 hypertension. Anmo Yu Kangfu Yixue, 2011, 2(9): 35-36.
[8] Wang CH, Ran MS. Clinical observation of traditional Chinese tuina on the management of essential hypertension. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2010, 28(7): 1546-1549.
[9] Xu L, Chen YQ. Discussion of Tuiqiaogong in the treatment of essential hypertension. Zhongyi Xuebao, 2013, 28(1): 146-147.
[10] Low XF. Clinical comparison of head and facial massage and Qiaogong point massage as adjuvant therapy of hypertension. Zhejiang J ITCWM, 2009, 19(4): 209-211.
[11] Wang DQ, Wang SX. Research progress of blood pressure variability. J Jining Med Univ, 2013, 8(4): 292-294.
[12] Ma PR. Application value of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in the elderly hypertension combined with target organ damage. Zhongguo Yiyao Kexue, 2013, 3(23): 177-178.
Translator:Hong Jue (洪珏)
推拿手法对高血压患者血压及血压变异性的影响
目的:观察推拿手法对高血压患者的血压及血压变异性的影响。方法:选取高血压患者40例, 将其随机分为观察组和药物组, 每组 20例。观察组在常规药物治疗基础上予以“益肾活血通脉”推拿手法治疗, 药物组仅采用与观察组相同的常规药物治疗。分别于治疗前及治疗3个月后行24-hour动态血压监测, 比较两组患者血压及血压变异性的变化。结果:治疗前两组患者的血压及血压变异系数组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05); 治疗3个月后, 两组患者血压及血压变异系数均较本组治疗前显著改善(P<0.05); 观察组改善情况优于对照组, 两组间差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:“益肾活血通脉”推拿手法结合常规药物对高血压患者的血压及血压变异性改善情况优于单纯常规药物治疗, 且操作方便, 无毒副作用, 适宜临床推广应用。
推拿; 按摩; 经络; 穴位; 高血压; 血压
R244.1 【
】A
Author: Shen Zhi-fang, bachelor, attending physician of traditional Chinese medicine.
E-mail: shenzf08@163.com
Methods:Forty hypertension patients were randomized into an observation group and a medication group, 20 cases in each group. The observation group was intervened by tuina manipulations of kidney-tonifying blood-circulating and collateralsunblocking in addition to regular medication, while the medication group was by the same medication. The 24-hour blood pressure monitoring was performed before intervention and after 3-month intervention. The blood pressure and its variability were observed and compared.
Results:There were no significant differences in comparing the blood pressure and blood pressure variability between the two groups before intervention (P>0.05); after 3-month intervention, the blood pressure and its variability were significantly improved in both groups (P<0.05); the improvements in the observation group were more significant than those in the control group (P<0.05).
Conclusion:Tuina manipulations of kidney-tonifying blood-circulating and collaterals-unblocking plus medication can produce a better effect than regular medication in promoting blood pressure and its variability, and this method is worth applying in clinic as it’s easy-to-operate and has no adverse effect.
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2015年3期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2015年3期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Anti-depression effects of electroacupuncture through up-regulating serum E2and BDNF and expression of BDNF in hippocampus in chronic depression rats
- Effects of wrist-ankle acupuncture on associated factors in uterus tissue and serum in rats with primary dysmenorrhea
- Clinical study on acupuncture combined with low-frequency electric stimulation for scissor gait in children with spastic cerebral palsy
- Observation on therapeutic effect of half puncture plus transcutaneous acupoint electric stimulation for infantile facial paralysis
- Tuina combined with needling distal points for pseudo-myopia in adolescents
- Clinical observation on regulating Conception Vessel and unblocking Governor Vessel by acupuncture combined with tuina for cerebral infarction
