机器人手术
Telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic right and sigmoid colectomies for benign disease
Weber,PA; Merola,S; Wasielewski,A; et al.
Assessment of intraoperative safety in transoral robotic surgery
Hockstein,NG; O'Malley,BW; Weinstein,GS; et al.
Transoral robotic surgery
Weinstein,GS; O'Malley,BW; Snyder,W; et al.
外科手术机器人发展及其应用*
龚朱,杨爱华,赵惠康
(同济大学附属同济医院,上海200065)
医疗机器人发展概况综述
杜志江,孙立宁,富历新
热点追踪
机器人手术
·编者按·
机器人手术系统是集自动机械技术、远程通讯和计算机技术等多项现代高科技手段于一体的综合系统,属于涉及医学、生物力学、机械力学、材料学、计算机图形学、微电子学、数学分析等诸多学科的交叉研究领域,是当前医疗器械信息化、程控化、智能化的一个重要发展方向,在临床微创手术以及战地救护、地震海啸救灾等方面有着广泛的应用前景。尤其是以da Vinci(达芬奇)为代表的手术机器人,以其全新的理念和前所未有的技术优势将手术精确度和可行性提升到一个全新的高度,引领了外科发展史上的一次新革命。
机器人首次协助手术治疗始于1978年,Victor Scheinmann研制的基于工业机器人平台的Puma560(Programmable Universal Manipulation Arm,PUMA)。到目前为止,获得美国食品药品监督管理局认证,并且比较有影响力的机器人手术系统主要有三代产品。第一代是美国Computer Motion公司1994年研制的持镜机器人伊索(AESOP),包括AESOP-1000、AESOP-2000、AESOP-3000三个阶段的产品;第二代是Computer Motion公司1995年研制的遥控机器人宙斯(ZEUS),分为Surgeonside系统和Patient-side系统;第三代为美国Intuitive Surgical公司研制的达芬奇机器人手术系统,达芬奇系统是现在最为先进、成熟和应用最广泛的机器人手术系统。达芬奇机器人手术系统由医生操作系统、床旁机械臂系统、成像系统3部分组成。其中,医生操作系统是达芬奇系统的控制核心,由计算机系统、监视器、操作手柄及输出设备等组成;床旁机械臂系统装有一系列的内置机械手腕装置,每一个机械手腕装置都有一个特定的手术功能,例如钳夹、缝合或组织处理;影像系统装配高清的3D内镜、图像加工装置和图像监视器。达芬奇机器人手术系统具有微创,术后恢复较快以及操作精细稳定,可以在某种程度上降低手术风险的优点。同时,也存在着无触觉,缺乏握力及压力反馈系统,无线通讯易受到干扰以及手术成本较高等不足之处,患者需要承担一定的安全风险。尽管机器人手术存在问题,但毕竟智能手术机器人正式应用于临床研究只不过十余年的时间,就已经极大地提高了手术的精度和准度,并且在实际应用中取得了不小的成果。截至2014年底,达芬奇机器人手术系统的全球装机总量为3266台,其中,中国大陆地区为29台,应用达芬奇机器人外科手术系统共完成手术11471例。有专家认为,随着医学和科技的进步,机器人手术中存在的问题将得到逐步解决,未来外科领域中的各种手术操作都将可以通过手术机器人系统完成,机器人辅助手术、机器人远程手术将会像普通手术一样平常。
本专题得到了田利国编审(《中国实用外科杂志》编辑部)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2015年6月15日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以机器人手术为词条检索到的期刊文献分别为1506与4795条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)

研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)

作者发文数量排名(WOS)
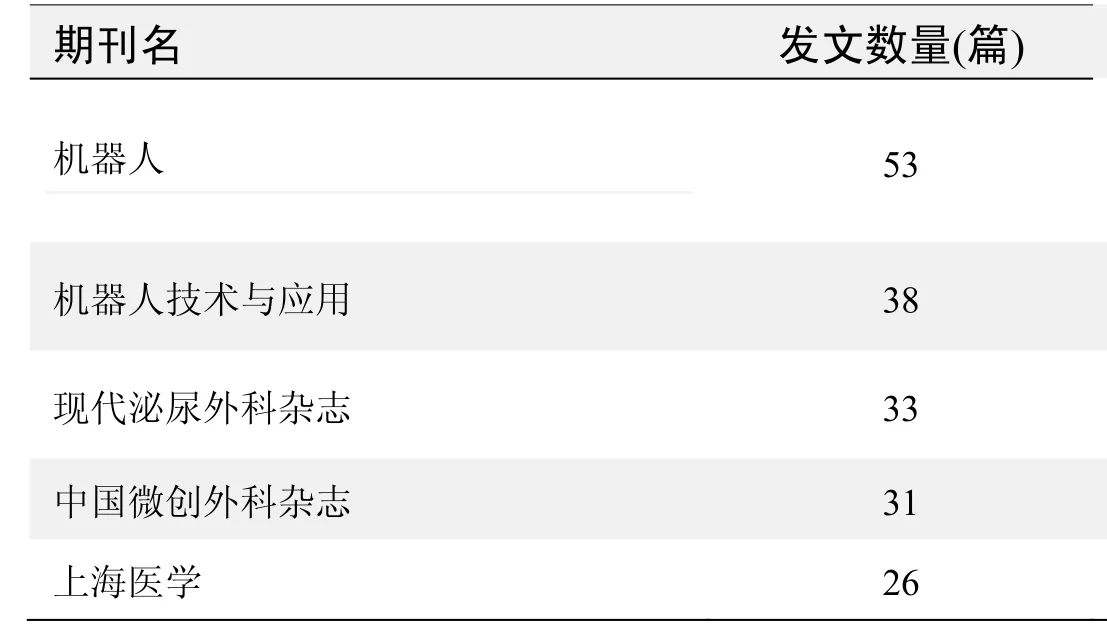
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)

期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以机器人手术为词条检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以机器人手术为词条检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 50文献作为节点进行分析,并结合专家意见得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物:Journal of Urology,2001,165(6): 1964-1966
Telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic right and sigmoid colectomies for benign disease
Weber,PA; Merola,S; Wasielewski,A; et al.
Abstract: PURPOSE: Telerobotic surgical systems attempt to provide technological solutions to the inherent limitations of traditional laparoscopic surgery. In this article,we present the first two reported cases of telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic colectomies performed on March 6 and 8,2001. METHODS: In the first patient we performed a telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy for diverticulitis. In the second patient,we accomplished a telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic right hemicolectomy for cecal diverticulitis. The Da Vinci telerobotic surgical system was used in both cases to mobilize the bowel. The mesenteric division,bowel transection,and anastomoses were accomplished with standard laparoscopic-assisted techniques. Both operations were completed with a three-trocar technique. RESULTS:We found that the Da Vinci system adequately replaced the camera holder. The three-dimensional virtual operative field helped to maintain the surgeon's orientation during the operation. The combination of three-dimensional imaging and the hand-like motions of the telerobotic surgical instruments facilitated dissection. The Da Vinci console offered an ergonomically comfortable position for the surgeon. Operative times for the sigmoid colectomy was 340 minutes and for the right hemicolectomy 228 minutes. Telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic colectomy is feasible,but required a longer operative time than our standard laparoscopic-assisted technique. CONCLUSION:Telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic colectomy is feasible and warrants further investigations in controlled trials.
Keywords: robots; telerobots; robotic surgery; telerobotic surgery; telepresence surgery; surgical technique; laparoscopic colectomy;diverticulitis
来源出版物:Diseases of the Colon & Rectum,2002,45(12): 1689-1694
Assessment of intraoperative safety in transoral robotic surgery
Hockstein,NG; O'Malley,BW; Weinstein,GS; et al.
Abstract: Introduction: Robotic technology has been safely integrated into thoracic and abdominopelvic surgery,and the early experience has been very promising with very rare complications related to robotic device failure. Recently,several reports have documented the technical feasibility of transoral robotic surgery(TORS)with the daVinci Surgical System. Proposed pharyngeal and laryngeal applications include radical tonsillectomy,base-of-tongue resection,supraglottic laryngectomy,and phonomicrosurgery. The safety of transoral placement of the robotic endoscope and instruments has not been established. Potential risks specific to the transoral use of the surgical robot include facial skin laceration,tooth injury,mucosal laceration,mandible fracture,cervical spine fracture,and ocular injury. We hypothesize that these particular risks of transoral surgery are similar with robotic assistance compared with conventional transoral surgery. Methods: To test this hypothesis,we attempted to intentionally injure a human cadaver with the daVinci Surgical System by impaling the facial skin and pharyngeal and laryngeal mucosa with the robotic instruments and endoscope. We also attempted to extract or fracture teeth and fracture the cadaver's mandible and cervical spine by applying maximal pressure and torque with the robotic arms. Experiments were documented with still and video photography. Results: Impaling the cadaver's skin and mucosa resulted in only superficial lacerations. Tooth,mandible,and cervical spine fracture could not be achieved. Conclusions: Initial experiments performing TORS on a human cadaver with the daVinci Surgical System demonstrate a safety profile similar to conventional transoral surgery. Additionally,we discuss several strategies to increase patient safety in TORS.
Keywords: robotic; endoscopic; minimally invasive surgery; microsurgery; larynx; partial laryngectomy; laryngeal cancer; DaVinci;transoral robotic surgery(TORS); complications
来源出版物:Laryngoscope,2006,116(2): 165-168
Transoral robotic surgery
Weinstein,GS; O'Malley,BW; Snyder,W; et al.
Abstract: Objective: To describe and show the feasibility of a new surgical technique for transoral robotic surgery(TORS)radical tonsillectomy. Design: A prospective,phase 1 clinical trial. Setting: Academic,tertiary referral center. Patients: A total of 27 participants were prospectively selected using a volunteer sample. All eligible patients agreed to participate in the study. Interventions: Patients underwent TORS radical tonsillectomy for previously untreated invasive squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsillar region without free-flap reconstruction,staged neck dissection,and adjuvant therapy. Main Outcome Measures: Outcome measures included final pathologic margin status,need for short-and long-term tracheotomy tube placement,and need for gastrostomy tube feedings among patients with a minimum 6-month follow-up. The incidence of significant postoperative complications was recorded. Results: No mortality occurred. Final margins found to be negative for cancer were achieved in 25 of 27 patients(93%). Surgical complications included I case each of postoperative mucosal bleeding,delirium tremens,unplanned tracheotomy for temporary exacerbation of sleep apnea,and hypernasality and 2 cases of moderate trismus. Twenty-six of 27 patients(96%)were swallowing without the use of a gastrostomy. Conclusions: Radical tonsillectomy using TORS is a new technique that offers excellent access for resection of carcinomas of the tonsil with acceptable acute morbidity. Future reports will focus on long-term oncologic and functional outcomes.
Keywords: squamous-cell carcinoma; selective neck dissection; locally advanced head; lateral oropharyngectomy; tonsillar region;chemotherapy; cancer
来源出版物:Archives of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery,2007,133(12): 1220-1226
·推荐综述·
外科手术机器人发展及其应用*
龚朱,杨爱华,赵惠康
(同济大学附属同济医院,上海200065)
摘编自《海洋环境科学》2014年28卷3期:273-277页,图、表、参考文献已省略。
外科手术机器人是集临床医学、生物力学、机械学、材料学、计算机科学、微电子学、机电一体化等诸多学科为一体的新型医疗器械,是当前医疗器械信息化、程控化、智能化的一个重要发展方向,在临床微创手术以及战地救护、地震海啸救灾等方面有着广泛的应用前景。
进入新世纪以来,外科手术微创化,微创手术精细化、立体化,如同一股新浪潮席卷全球的外科学界,并渗透到普通外科、心脏外科、胸外科、泌尿外科、脑外科、骨科等各临床专科,动摇着并逐渐替代已沿用百余年之久的经典的传统外科手术方式。微创外科不仅引发了外科学领域的一场新技术革命,而且正在结合自动机械技术、远程通讯和计算机技术,开创一个机器人外科的新时代[1]!
1外科手术机器人概况及其应用
1.1达芬奇机器人微创外科手术系统
达芬奇机器人微创外科手术系统(da Vinci Si HDSurgical System)是目前世界范围应用广泛的一种智能化手术平台,2000年获得美国食品与药品监督管理局(FDA)批准,成为进入临床外科的智能内窥镜微创手术系统。适合普腹外科、泌尿外科、心血管外科、胸心外科、妇科、五官科、小儿外科等进行遥控微创手术。该系统的手术操作部分已可完成7个自由度的操作,由外科医师在远程工作站进行遥控,具有整合三维成像、触觉反馈和宽带远距离控制等功能[2]。
达芬奇微创外科手术机器人高达1.8米,重达500公斤,由医师卧式操作控制台、立式机械手术臂、轮式标准仪器柜三大部分组成(如图1显示)。这种外科手术系统的最大特点是:采用了医师座式姿态(远程)遥控机器人系统进行手术,这样的手术方式突破了传统的手术方式,由“触觉外科”向“视觉外科”转变,标志着人类微创外科技术的革命性飞跃。
其核心技术是:
1.1.1DHD 高清手术视野(视觉)
该系统具有6-10倍的三维高清手术视野,可为医师提供身临其境的手术临场沉浸感,提供清晰细致的解剖组织结构图像与自然的深度感觉空间,还提供了无与伦比的术野视觉感[3]。
1.1.2EndoWrist 仿真机械手
该系统可提供比人手自由度更广泛的动作。具有7个自由度,包括臂关节上下、前后、左右运动与机械手的左右、旋转、开合、末端关节弯曲共7种动作。可作沿垂直轴360°和水平轴270°旋转,且每个关节活动度均大于90°。尤其在行深部操作时,机械手由于动作灵活,体积小巧,与开放手术的人手操作相比具有显著优势。EndoWrist仿真机械手配置了各类型手术器械,可满足抓持、钳夹、缝合等各项手术操作要求,也可满足胸心外科、普腹外科、泌尿外科、妇产科等各种手术的操作需求。各种类型手术器械手均有8 mm 和5 mm两种规格[3]。
1.1.3Intuitive 直觉运动控制技术
Intuitive 是达芬奇机器人独有的计算机辅助控制技术。眼—手协调、手—机械手端实时同步,使得医师可以凭借本能进行直觉式的操控机械手端。手术医师手指动作的运动行程与机械手端的运动行程比例可以调节,现有3种缩小比例,即5∶1、3∶1和11∶ 。该技术将术者手指动作的幅度自动缩小,使手术操作更加稳定精细。手术医师的手部抖动信号会被自动过滤[3]。
1.1.4达芬奇外科机器人手术系统临床应用
达芬奇机器人外科微创手术系统是21世纪微创外科技术、远程遥控手术技术的革命性标志,代表了当今世界最先进的外科医疗技术。
目前,在美国泌尿外科领域,有50%的病人选择达芬奇外科机器人手术。与常规泌尿外科腔镜手术比较,达芬奇机器人外科微创手术系统,提供3DHD高清晰度图像,6-10倍的放大倍率,自然的深度感觉,使手术医师能够精细处理解剖组织,尽可能不碰伤手术周围组织,如:在前列腺癌手术中不碰伤前列腺附近的神经血管束、副交感神经,等,以保全患者性功能。美国85%以上的前列腺癌根治术已使用达芬奇手术机器人完成。
另外,美国还采用达芬奇机器人打造新型战地医院。2005年3月28日,美国有关大学和斯坦福国际研究所(SRI International)与美国国防部签订了机器人医师的研制协议[4]。这项名为“外伤豆荚”的计划预计将耗资1200万美元、历时两年完成。机器人外伤救治体系是在达芬奇外科手术机器人系统基础上更进一步研究适用于战场的机器人手术医师。
2009年美国斯坦福国际研究所开发出流动“外伤救治舱”(Trauma Pod)[5],并将达芬奇机器人安装在改装的美军“布拉德利”(Bradley)装甲车上送往前线。医师护士远离战场,通过卫星联网,遥控达芬奇机械人给战场伤员注射麻醉剂,实施手术,挽救伤员生命,以减少美军官兵在战场上的伤亡人数。“外伤救治舱”遥控手术设计如图2所示: ①远离战场的外科医师(人):用声控监视器和遥感通过卫星连接遥控外伤救治舱(Trauma Pod)机器人;②机器人一个机械臂安置摄像机和内窥镜,另外两个机械臂可以是手术刀或者是手术钳和针;③手术床监视伤兵的重要信息并控制生命维持系统;④机器人器械柜放置各种手术用机械臂;⑤擦洗护士:声控的机械臂,从器械柜抓取机械臂,并提供给操作的机器人。
截止2013年3月31日,全球达芬奇外科手术机器人系统装机总数为2710台。其中,美国:1957台(占72.2%);欧洲:430台(占15.9%);亚洲:220台,(其中中国香港8台)(8.1%);其他地区:103台(占3.8%)[6]。2011年,全球各国完成达芬奇机器人手术共计为36万例,2012年为45万例,年手术量同比增长25%[3]。
1.1.5达芬奇机器人微创外科手术系统在我国的应用
2007年1月25日,解放军总医院心血管外科高长青运用达芬奇外科手术机器人“da Vinci S”,为一名女患者成功实施不开胸的心脏手术。这是我国首例全部由机器人完成的心脏病手术。2008年,解放军总医院引进中国第一台达芬奇(da Vinci S)机器人外科手术系统。2010年以来,以解放军总医院、第二炮兵总医院、上海复旦大学附属中山医院、上海交通大学附属瑞金医院为代表,在心胸外科、肝胆胰腺等领域应用达芬奇(da Vinci Si HD)机器人微创外科手术方面,已进入世界前列。
2010年1月20日,中国微创机器人心脏外科培训中心在解放军总医院正式成立。来自美、法等7个国家的200多名专家共同在该院观摩“da Vinci SiHD”机器人心脏手术实况演示。截止2013年该中心已实施500例达芬奇机器人心脏手术,手术种类世界第一[7]。
截止2012年底,中国大陆(港澳台除外)配置达芬奇手术机器人的有14家医院,共安装达芬奇机器人外科手术系统15台。这些医院在2011年完成各类达芬奇机器人手术808例,2012年完成1546例,年手术量同比增长91.3%。截止2012年底,国内历年累计完成达芬奇机器人手术3551例[6]。
1.2宙斯机器人手术系统
宙斯机器人手术系统(zeus robotic surgical system)是由美籍华裔王友仑先生于1998年在美国摩星有限公司研发成功。1999年获得欧洲市场认证,标志着真正的“手术机器人”进入全球医疗市场领域。进入中国市场的宙斯机器人手术系统包括:(aesop)声控内窥镜定位器、赫米斯(hermes)声控中心、宙斯(zeus)机器人手术系统(左右机械臂、术者操作控制台、视讯控制台)、苏格拉底(socrates)远程合作系统这几部分组成。
手术时,宙斯机器人三条机械臂固定在手术床滑轨上,医师坐在距离手术床2~5 m的控制台前,实时监视屏幕三维空间立体显示的手术野情况,用语音指示Aesop声控内视镜,另外两条宙斯黄绿机械臂则在医师遥控下执行手术操作,医师足部脚踏板控制超声波手术刀完成手术的烧灼、切割、电凝等工作。
宙斯机器人监控屏上手术画面能放大15~20倍,并可模拟医师的手部动作,宙斯手术抓持手是仿照人类手腕设计的机械手,能够做抛掷、推动、紧握等动作,可以使医师从5~8 mm的小切口进入病人体内进行微创手术。这给许多本来需要传统开放手术的患者无疑带来很大的福音。
1.2.1宙斯机器人手术系统应用—一次横跨大西洋的机器人辅助远程手术
2001年9月7日,美法两国医师实施了一次横跨大西洋的机器人辅助远程手术,由法国医师杰西奎·马雷斯科(MD. Jacques Marescaux)在纽约西奈山医院(Mount Sinai Hospital NY.)操纵着宙斯(Zeus)机器人(如图3所示),法国电信公司开通一条基于(asynchronous transfer mode,ATM)高速光纤专线(10 Mb/s),通过大西洋海底光缆链接到法国东部斯特拉斯堡大学医院远程遥控宙斯机器人3条机械臂,为一位68岁法国妇女作胆囊切除术(如图4所示)。这次手术用了54分钟,术后病人情况良好,48小时之后病人出院[8]。
越洋手术成功的一个关键是解决延时信号(Keyto oversea surgery-solution to signal delay)问题。纽约至法国斯特拉斯堡远程遥控手术视频图像信号传输相距14000公里,并且,穿越大西洋海底,法国电信公司开通一条基于ATM高速光纤专线(10 Mb/s),手术图像往返的传输几乎是瞬间完成的。也就是说,马雷斯科医师在纽约遥控斯特拉斯堡手术台上的3条宙斯机械臂的手术动作,几乎是即刻反馈在纽约的监控屏幕上,仅有约155毫秒的延迟,远远低于原来估计的330毫秒的安全延迟时限范围之内[8]。
为了此次越洋手术,医疗小组前后共进行了两年的时间准备,历经无数次的各种试验考验[8]。
1.2.2宙斯机器人手术系统在我国的应用
2004年4月,深圳市人民医院引进宙斯机器人手术系统,周汉新团队完成国内第一台宙斯机器人辅助胆囊切除术。该院温定国团队完成国内首例宙斯机器人辅助心脏搭桥术[9]。
1.3伊索机器人手术辅助系统
伊索声控机器人手术辅助系统Aesop 1000也是由王友仑先生所在的美国摩星公司于1994年10月研发成功,1996年11月第二代Aesop 2000研发成功。目前,在中国各大医院仍在使用的多为第四代Aesop 3000,重约17公斤。主要由机械手掌、机械臂、机械躯体和电脑语音识别系统几部分组成。Aesop实际上只是一种具有语言识别能力的内窥镜定位器声控自动装置。医师在手术前把各种指令记录在一张声卡上,手术时只需将这张声卡插入Aesop机器人的控制盒内,手术医师就能用声音直接控制Aesop内窥镜的各种动作。如:“move in(前进)、move back(后退)、move left(左移)、move right(右移),等,它能听懂几百条指令,常用指令约30条”。
1.4伊索机器人手术辅助系统在我国的应用
2001年起,Aesip 2000及Aesop 3000先后进入中国医疗领域,并先后完成以下手术,如:2001年6月,无锡四院子宫切除术和胆囊切除术;2002年3月,山东省胸科医院冠状动脉搭桥术;4月,复旦大学附属儿科医院3岁儿童的先天性室间隔缺损修复术;2003年6月,上海市第一人民医院心脏二尖瓣膜置换术;2005年7月,复旦大学附属中山医院的第10例7岁儿童房缺封堵术;2008年,湖南省儿童医院小儿巨结肠术。该院自投入300多万元从美国引进Aesop 3000运用,至今已行各种手术近千例[10]。2012年中国煤炭神马医疗集团总医院应用Aesop 3000机器人施行各种胆囊疾病微创手术418例的报道。Aesop声控机器人弥补了常规腹腔镜、胸腔镜光学内镜视角狭小、手持晃动引起头晕眼晃等不足,提高了微创手术的疗效。
2中国远程遥控机器人概况
2.1中国远程遥控机器人—“黎元BH-600”声控机器人
2001年,解放军海军总医院田增民神经外科团队与北京航空航天大学中国航天技术研究所合作,研发成功“黎元BH-600”声控机器人。并于2003年9月10日,在北京海军总医院通过互联网链接到相距600公里外的沈阳医学院附属中心医院手术室,为一位52岁的脑溢血患者实施微创手术,成功实施了国内第一例脑外科立体定向远程遥控手术(如图5所示)。
上午10点整,手术正式开始,田增民医师在北京手持鼠标发出指令,沈阳手术室里“黎元”机器人在一位脑溢血患者头部行校正、靶点定位后,钻出一个3 mm的小孔,将一根针管从小孔插到淤血里回抽出淤血。10点55分,手术圆满成功,病人的患肢肌力从二级提高到三级[11]。
2.2国内第一例长骨骨折髓内钉内固定远程遥控操作手术
2006年3月,北京积水潭医院与北京航空航天大学合作,利用小型模块化机器人,在北京和延安之间完成了国内第一例长骨骨折髓内钉内固定远程遥控操作手术,提出并实现了基于窄带网络的远程规划理念,从而在一定程度上降低了远程遥控外科对网络配置的要求[12]。
2.3我国自主研制成功首台微创外科手术机器人“妙手A”
“妙手A”系统是由天津大学、南开大学和天津医科大学总医院联合研制,是国家863计划和国家杰出青年科学基金重点支持项目。该系统主要用于腹腔微创手术,拥有多项技术创新和发明。如首次设计完成四自由度小型手术工具,可适应微创手术需求,并可完成复杂的缝合打结运动操作;采用多自由度丝传动技术,实现主、从操作手本体轻量化设计;基于异构空间映射模型,实现主、从遥操作控制;设计机器人系统与人体软组织变形仿真环境,实现主、从操作虚拟力反馈与手术规划;采用双路平面正交偏振影像分光法,研制成功微创外科手术机器人三维立体视觉系统[13]。
3外科手术机器人应用前景与启示
医用机器人是当今世界各国的研究热点。国际先进机器人计划(international advanced robotics program,IARP)在欧美、日本等国已召开过多届医用外科机器人研讨会。像IEEE robotics and automation,IEEE Eng,in medicine and biology society,IEEE system,man andcybernetics 等许多著名的国际会议,都将医用机器人与计算机辅助外科单独列为一个专题。
近年来,欧美诸国都进行专门立项投资,积极开展医用机器人方面的研究。2008年,美军在华尔特里德陆军医学中心(water reed army medical center,WRAMC)和约翰·霍普金斯医院(johns hopkins hospital,JHH)之间,两地相距64公里,采用达芬奇外科手术机器人系统,开展微创手术机器人远程外科项目。
目前,医用机器人技术在微创外科手术治疗、病人安全救援、无痛转运、康复护理、功能辅助及医院自动化服务等方面得到了广泛的应用,这不仅促进了传统医学的革命,也带动了新技术、新理论的发展。
如何将信息技术与数字化医学、3DHD和3D打印有机融入到自身的医学信息教育技术工作实践中去,将是当今每一位从事医学信息教育技术者所面临的新课题。
3D高清手术当前如火如荼地在全球医疗领域进行着,中国各大医院3D高清手术同样也是遍地开花。同济大学附属同济医院(临床医学院)从2009年起,至今已经连续举办了4届国家级3DHD高清手术转播系统学习班(2014年将举办第5届),2013年投入500万专项资金建设一套3DHD高清手术转播系统和3DHD远程医疗示教系统,用于3DHD高清手术临床实践与医学信息教育技术专业人才培养,并与松下电器(中国)有限公司合作,正式签署协议,建立上海乃至全国临床医疗领域第一家“3DHD高清手术转播系统和3DHD远程医疗示教系统上海基地”。
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:157
医疗机器人发展概况综述
杜志江,孙立宁,富历新
近年来,医疗机器人成为机器人领域研究热点之一。本文详细介绍了外科手术机器人、康复机器人、医院服务机器人等在国内外的研究及应用现状,并探讨了今后的发展方向。
外科手术机器人;康复机器人;医院服务机器人;生物机器人;纳米机器人
来源出版物:机器人,2003,25(2): 182-187
被引频次:83
微操作机器人系统的研究开发
毕树生,宗光华
摘要:介绍了国家自然科学基金资助课题“微动并联机器人的研制”、“面向生物工程及显微手术的微操作机器人系统”的部分研究成果,讨论了微操作机器人系统亟待解决的一些问题,阐述了在构筑微操作机器人过程中应特别注意的一些关键技术及理论。
关键词:微机械电气系统;微操作系统;机器人
来源出版物:中国机械工程,1999,10(9): 1024-1027
被引频次:81
基于虚拟现实的计算机辅助立体定向神经外科手术系统
王子罡,唐泽圣,王田苗,等
摘要:介绍了一个计算机辅助立体定向神经外科手术系统,该系统基于实时可视化绘制、机器人和虚拟现实技术,辅助医生完成立体定向神经外科手术系统首先利用患者脑部的扫描数据重构并绘制出患者脑部的三维组织结构,为医生调整和确定手术规划提供参照,系统采用了标记点的校准方法,在手术前和手术中分别进行脑部模型和患者的坐标校准。通过机械臂的导航,使机械臂达到手术规划规定的位置和姿态,医生利用安装在机械臂上的手术器械完成立体定向神经外科手术。通过虚拟现实设备,系统可以创造一个虚拟手术环境和虚拟病人。在这个虚拟环境中,医生可以进行虚拟手术,对医生以后的诊断和手术起到培训和教学的作用。
关键词:三维数据可视化;计算机辅助手术;立体定向神经外科手术;虚拟现实
来源出版物:计算机学报,2000,23(9): 931-937
被引频次:67
全方向蠕动机器人驱动内窥镜系统的研究
高立明,林良明,颜国正,等
摘要:微创外科手术是当前生物医学工程领域研究的一个主要目标和热点问题,而医用内窥镜是符合微创外科手术要求的一种典型医疗仪器。本文首先对医用内窥镜的现状和发展作了简短的评述,指出了传统内窥镜人为插入的不足之处;然后结合微型机电系统MEMS(micro Electro Me-chanical System)技术提出了新型全方向蠕动机器人驱动内窥镜系统的方案;最后就该系统的技术难点和应用前景提出了展望。
关键词:医用内窥镜;蠕动式机器人;微创外科手术
来源出版物:中国生物医学工程学报,1998,17(1): 36-41
被引频次:64
医疗机器人的研究与进展
张西正,侍才洪,李瑞欣,等
摘要:医疗机器人主要用于伤病员的救援、转运、手术和康复,是医疗卫生装备信息化、智能化的重要发展方向之一。通过对救援机器人、手术机器人和康复机器人等医疗机器人的研究现状及进展介绍,表明医疗机器人在军用和民用上有着广泛的应用前景,是目前机器人领域的一个研究热点。
关键词:医疗机器人;伤病员;救援;手术;康复
来源出版物:中国医学装备,2009,6(1): 7-12
被引频次:63
21世纪骨科领域新技术——微创外科
裴国献,任高宏
摘要:近年来,微创技术在骨科领域的应用日益广泛。骨折治疗的观念正在由生物力学向生物学微创固定转变,关节镜介导的微创技术在临床上的应用取得了惊人的发展,内镜介导的微创脊柱外科治疗技术显示了良好的发展前景,四肢和脊柱疾患的经皮微创技术取得了长足进步,计算机辅助的手术导航系统、手术模拟系统、远程会诊和远程机器人遥控手术等微创技术受到了广泛的关注,将微创技术应用于显微外科,已成为减少供区破坏、保存美观的有效手段。新的影像技术和介入放射技术的发展,为微创技术在骨科领域的应用提供了强有力的手段,激光、射频消融、微波、冷冻、聚焦超声等新的治疗手段和纳米技术、基因治疗的发展及组织工程研究的深入为骨科疾患的微创治疗拓展了更为广阔的发展空间。因此,21世纪的微创外科具有诱人的前景,可望成为骨科领域新的生长点。
关键词:微创;骨折;治疗;内镜;外科操作
来源出版物:中华创伤骨科杂志,2002,4(2): 89-95
被引频次:57
显微外科手术机器人——“妙手”系统的研究
王树新,丁杰男,贠今天,等
摘要:描述了一套显微外科手术机器人系统——“妙手(MicroHand)”。该系统采用主从遥操作方式,主从手为同构异型模式:主手是具有三维力感觉功能的PHANToM Desktop,从手是针对显微外科手术特点而设计的高精度关节型机器人。从手末端安装有六维力传感器Mini40,将检测到手术环境的力信息反馈给主手,从而使手术医生通过PHANToM,感受手术环境的三维力信息。本系统成功地对兔子颈部和腿部1毫米动脉进行了血管吻合手术操作,证明了它的有效性。
关键词:显微外科;手术机器人;血管吻合;主从操作;异构;力感觉
来源出版物:机器人,2006,28(2): 130-135
被引频次:51
面向脑外科微创手术的医疗机器人系统
丑武胜,王田苗
摘要:机器人为微创外科手术的实施提供了有利的技术支持。本文针对传统脑外科手术的不足,开发研制了一套机器人辅助脑外科微创手术系统,主要由5自由度机器人、手术规划和导航软件及基于标志点的标定模块组成,其中机器人系统不仅可用于系统标定和导航,而且可作为手术的支撑平台。该系统已应用到临床中,成功完成了大量的微创脑外科手术。
关键词:微创手术;医疗机器人
来源出版物:机器人技术与应用,2003(4): 18-21
被引频次:49
面向微创手术的医疗外科机器人构型综合
刘达,王田苗,张玉茹,等
摘要:在微创手术中医疗外科机器人可以辅助医生精确定位和提供稳定的手术平台,本文结合医疗外科机器人结构特点和手术适用范围,对适合微创手术的机器人结构进行了构型综合分析,并以此为依据,设计出一种适用于神经外科立体定向手术的机器人,系统已经应用于临床,取得了满意的效果。
关键词:医疗外科机器人;构型综合;微创手术
来源出版物:机器人,2003,25(2): 132-135
被引频次:47
全机器人不开胸房间隔缺损修补术
高长,杨明,王刚,等
摘要:以内腔镜与遥控技术为特征的机器人施行心脏手术始于上个世纪末期,旨在减轻手术创伤、提高治疗效果,是生物医学工程的重大成果。现在此项技术已由我国少数医院引进用于临床,这是一件可喜的事物,有利于对机器人心脏手术进一步探索发展。但到目前为止,机器人心脏手术技术不仅仅是花费昂贵,更重要的是此技术尚不十分完善,它的适应范围尚有一定局限性,其微创水平尚待不断提高,以房间隔缺损治疗为例已有多种微创方法可以选择。随着高科技发展,机器人技术必然会取得巨大进步。我国作为一个发展中国家,在医疗保健的投入尚不宽裕的情况下,少数有条件的单位开展机器人心脏手术的实践和研究是很有必要的,但在国内推广普及此技术还需慎重稳妥。心脏外科的微创技术是今后发展的大方向,但机器人能否代表这个大方向,目前下结论为时尚早,还需要今后不断的实践和研究。
关键词:房间隔缺损;心脏外科手术;机器人;达芬奇S系统
来源出版物:计算机学报,2002,25(11):1250-1256
被引频次:285
Alignment in total knee arthroplasty - A comparison of computer-assisted surgery with the conventional technique
Bathis,H; Perlick,L; Tingart,M; et al.
Abstract: Restoration of neutral alignment of the leg is an important factor affecting the long-term results of total knee arthroplasty(TKA). Recent developments in computer-assisted surgery have focused on systems for improving TKA. In a prospective study two groups of 80 patients undergoing TKA had operations using either a computer-assisted navigation system or a conventional technique. Alignment of the leg and the orientation of components were determined on post-operative long-leg coronal and lateral films. The mechanical axis of the leg was significantly better in the computer-assisted group(96%,within +/-3degrees varus/valgus)compared with the conventional group(78%,within +/-3degrees varus/valgus). The coronal alignment of the femoral component was also more accurate in the computer-assisted group. Computer-assisted TKA gives a better correction of alignment of the leg and orientation of the components compared with the conventional technique. Potential benefits in the long-term outcome and functional improvement require further investigation.
Keywords: femoral intramedullary guides; replacement; prosthesis; experience
来源出版物:Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery,British Volume,2004,86(5): 682-687
被引频次:282
Synthetic gecko foot-hair micro/nano-structures as dry adhesives
Sitti,M; Fearing,RS
Abstract: This paper proposes techniques to fabricate synthetic gecko foot-hairs as dry adhesives for future wall-climbing and surgical robots,and models for understanding the synthetic hair design issues. Two nanomolding fabrication techniques are proposed: the first method uses nanoprobe indented flat wax surface and the second one uses a nano-pore membrane as a template. These templates are molded with silicone rubber,polyimide,etc. type of polymers under vacuum. Next,design parameters such as length,diameter,stiffness,density,and orientation of hairs are determined for non-matting and rough surface adaptability. Preliminary micro/nano-hair prototypes showed adhesion close to the predicted values for natural specimens(around 100 nN each).
Keywords: biomimetic adhesives; pressure controlled dry adhesives; adhesion forces; polymer micro/nano-fabrication;micro/nano-robotics; nanoindentation; and nanomolding
来源出版物:Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology,2003,17(8): 1055-1073
被引频次:271
Image guided navigation system to measure intraoperatively acetabular implant alignment
DiGioia,AM; Jaramaz,B; Blackwell,M; et al.
Abstract: There has been little clinical research to examine the effects of patient positioning and pelvic motion on the alignment of the acetabular implant during total hip replacement surgery. Until now,no tools were capable of accurately measuring these variables during the actual procedure. As part of a broader program in medical robotics and computer assisted surgery,a clinical system has been developed that includes several enabling technologies. The hip navigation system(HipNav)continuously and precisely measures pelvic location and tracks relative implant alignment intraoperatively. HipNav technology is used to gauge current clinical practice and provide intraoperative feedback to surgeons with the goal of improving the precision and accuracy of acetabular alignment during total hip replacement. Thissystem provides surgeons with a new class of image guided measurement tools and assist devices. These tools successfully were introduced into the clinical practice of surgery with results showing the following:(1)There exist unpredictable and large variations in the initial position of patients' pelves on the operating room table and significant pelvic movement during surgery and during intraoperative range of motion testing;(2)current mechanical acetabular alignment guides do not account for these variations,and result in variable and in the majority of cases unacceptable acetabular alignment; and(3)press fitting oversized acetabular components influences the final cup orientation.
Keywords: total hip-arthroplasty; dislocation; replacement; reoperation
来源出版物:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research,1998,355: 8-22
被引频次:268
A prospective comparison of radical retropubic and robot-assisted
Tewari,A; Srivasatava,A; Menon,M
Abstract: To prospectively compare standard radical retropubic prostatectomy(RRP)and the robotically assisted Vattikuti Institute prostatectomy(VIP)in the management of localized prostate cancer. The study was a single-institution,prospective,unrandomized comparison of histopathological,and functional outcomes,at baseline and during and after surgery,in 100 patients undergoing RRP and 200 undergoing VIP. While the variables before surgery,the operative duration(163 vs 160 min)and pathological stages were comparable,there were significant differences in the measured outcomes. The blood loss was 910 and 150 mL for RRP and VIP,respectively,and transfusion was greater after RRP(67% vs none; both P < 0.001). There were four times as many complications after RRP(20% vs 5%,P <0.05),the haemoglobin level at discharge was lower(100 vs 130 g/L,P < 0.005)and the hospital stay longer(3.5 vs 1.2 days; P < 0.05). Most(93%)of VIP and none of the RRP patients were discharged within 24 h(P < 0.001); the duration of catheterization was twice as long after RRP(15.8 vs 7 days; P < 0.05). Positive margin was more frequent after RRP(23% vs 9%,P < 0.05). After VIP,patients achieved continence and return of erections more quickly than after RRP(160 vs 44,and 180 vs 440 days,both P < 0.5). The median return to intercourse was 340 days after VIP but after RRP half the patients have as yet not resumed intercourse at 700 days(P < 0.05). The VIP procedure appears to be safer,less bloody and requires shorter hospitalization and catheterization. The oncological and functional results were favourable in patients undergoing VIP.
Keywords: robotic surgery; prostate cancer; prostatectomy; outcome
来源出版物:BJU international,2003,92(3): 205-210
被引频次:265
Computer-assisted knee arthroplasty versus a conventional jig-based technique - A randomised,prospective trial
Chauhan,SK; Scott,RG; Breidahl,W; et al.
Abstract: We have compared a new technique of computer-assisted knee arthroplasty with the current conventional jig-based technique in 70 patients randomly allocated to receive either of the methods. Post-operative CT was performed according to the Perth CT Knee Arthroplasty protocol and pre- and post-operative Maquet views of the limb were taken. Intra-operative and peri-operative morbidity data were collected and blood loss measured. Post-operative CT showed a significant improvement in the alignment of the components using computer-assisted surgery in regard to femoral varus/valgus(p = 0.032),femoral rotation(p = 0.001),tibial varus/valgus(p = 0.047)tibial posterior slope(p = 0.0001),tibial rotation(p 0.011)and femorotibial mismatch(p = 0.037). Standing alignment was also improved(p 0.004)and blood loss was less(p = 0.0001). Computer-assisted surgery took longer with a mean increase of 13 minutes(p = 0.0001).
Keywords: replacement; alignment; prosthesis
来源出版物:Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery,British Volume,2004,86(3): 372-377
被引频次:263
Intraoperative brain shift and deformation: A quantitative analysis of cortical displacement in 28 cases
Roberts,DW; Hartov,A; Kennedy,FE; et al.
Abstract: OBJECTIVE: A quantitative analysis of intraoperative cortical shift and deformation was performed to gain a better understanding of the nature and extent of this problem and the resultant loss of spatial accuracy in surgical procedures coregistered to preoperative imaging studies. METHODS: Three-dimensional feature tracking and two-dimensional image analysis of the cortical surface were used to quantify the observed motion. Data acquisition was facilitated by a ceiling-mounted robotic platform,which provided a number of precision tracking capabilities. The patient's head position and the size and orientation of the craniotomy were recorded at the start of surgery. Error analysis demonstrated that the surface displacement measuring methodology was accurate to 1 to 2 mm. Statistical tests were performed to examine correlations between the amount of displacement and the type of surgery,the nature of the cranial opening,the region of the brain involved,the duration of surgery,and the degree of invasiveness. RESULTS: The results showed that a displacement of an average of 1 cm occurred,with the dominant directional component being associated with gravity. The mean displacement was determined to be independent of the size and orientation of the cranial opening. CONCLUSION: These data suggest that loss of spatial registration with preoperative images is gravity-dominated and of sufficient extent that attention to errors resulting from misregistration during the course of surgery is warranted.
Keywords: brain shift; computer-assisted surgery; image-guided surgery; stereotaxy
来源出版物:Neurosurgery,1998,43(4): 749-758
被引频次:254
Robotics in general surgery - Personal experience in a large community hospital
Giulianotti,PC ; Coratti,A; Angelini,M; et al.
Abstract: Hypothesis: Robotic technology is the most advanced development of minimally invasive surgery,but there are still some unresolved issues concerning its use in a clinical setting. Design: The study describes the clinical experience of the Department of General Surgery,Misericordia Hospital,Grosseto,Italy,in robot-assisted surgery using the da Vinci Surgical System. Results: Between October 2000 and November 2002,193 patients under-went a minimally invasive robotic procedure(74 men and 119 women; mean age,55.9 years[range,16-91 years]). A total of 207 robotic surgical operations,including abdominal,thoracic and vascular procedures,were performed;179 were single procedures,and 14 were double(2 operations on the same patient). There were 4 conversions to open surgery and 3 to conventional laparoscopy(conversion rate,3.6%; 7 of 193 patients). The perioperative morbidity rate was 9.3%(18 of 193 patients),and 6 patients(3.1%)required a reoperation. The postoperative mortality rate was 1.5%(3 of 193 patients). Conclusions: Our preliminary experience at a large community hospital suggests that robotic surgery is feasible in a clinical setting. Its daily use is safe and easily managed,and it expands the applications of minimally invasive surgery. However,the best indications still have to be defined,and the cost-benefit ratio must be evaluated. This report could serve as a basis for a future prospective,randomized trial.
Keywords: laparoscopic cholecystectomy; nissen fundoplication; feasibility; nephrectomy
来源出版物:Archives of Surgery,2003,138(7): 777-784
被引频次:253
Measurement of intraoperative brain surface deformation under a craniotomy
Hill,DLG; Maurer,CR; Maciunas,RJ; et al.
Abstract: OBJECTIVE: Several causes of spatial inaccuracies in image-guided surgery have been carefully studied and documented for several systems. These include error in identifying the external features used for registration,geometrical distortion in the preoperative images,and error in tracking the surgical instruments. Another potentially important source of error is brain deformation between the time of imaging and the time of surgery or during surgery. In this study,we measured the deformation of the dura and brain surfaces between the time of imaging and the start of surgical resection for 21 patients. METHODS: All patients underwent intraoperative functional mapping,allowing us to measure brain surface motion at two times that were separated by nearly an hour after opening the dura but before performing resection. The positions of the dura and brain surfaces were recorded and transformed to the coordinate space of a preoperative magnetic resonance image,using the Acustar surgical navigation system(manufactured by Johnson & Johnson Professional,Inc.,Randolph,MA)(the Acustar trademark and associated intellectual property rights are now owned by Picker International,Highland Heights,OH). This system performs image registration with bone-implanted markers and tracks a surgical probe by optical triangulation. RESULTS: The mean displacements of the dura and the first and second brain surfaces were 1.2,4.4,and 5.6 mm,respectively,with corresponding mean volume reductions under the craniotomy of 6,22,and 29 cc. The maximum displacement was greater than 10 mm in approximately one-third of the patients for the first brain surface measurement and one-half of the patients for the second. In all cases,the direction of brain shift corresponded to a "sinking" of the brain intraoperatively,compared with its preoperative position. Analysis of the measurement error revealed that its magnitude was approximately 1 to 2 mm. We observed two different patterns of the brain surface deformation field,depending on the inclination of the craniotomy with respect to gravity. Separate measurements of brain deformation within the closed cranium caused by changes in patient head orientation with respect to gravity suggested that less than 1 mm of the brain shift recorded intraoperatively could have resulted from the change in patient orientation between the time of imaging and the time of surgery. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that intraoperative brain deformation is an important source of error that needs to be considered when using surgical navigation systems.
Keywords: brain deformation; computer-assisted surgery; image-guided surgery; image registration; registration accuracy; stereotactic surgery
来源出版物:Neurosurgery,1998,43(3): 514-526
被引频次:249
Constitutive modelling of brain tissue: Experiment and theory
Miller,K; Chinzei,K
Abstract: Recent developments in computer-integrated and robot-aided surgery-in particular,the emergence of automatic surgical tools and robots-as well as advances in virtual reality techniques,call for closer examination of the mechanical properties of very soft tissues(such as brain,liver,kidney,etc.). The ultimate goal of our research into the biomechanics of these tissues is the development of corresponding,realistic mathematical models. This paper contains experimental results of in vitro,uniaxial,unconfined compression of swine brain tissue and discusses a single-phase,non-linear,viscoelastic tissue model. The experimental results obtained for three loading velocities,ranging over five orders of magnitude,are presented. The applied strain rates have been much lower than those applied in previous studies,focused on injury modelling. The stress-strain curves are concave upward for all compression rates containing no linear portion from which a meaningful elastic modulus might be determined. The tissue response stiffened as the loading speed increased,indicating a strong stress-strain rate dependence. The use of the single-phase model is recommended for applications in registration,surgical operation planning and training systems as well as a control system of an image-guided surgical robot. The material constants for the brain tissue are evaluated. Agreement between the proposed theoretical model and experiment is good for compression levels reaching 30% and for loading velocities varying over five orders of magnitude.
Keywords: brain tissue; mechanical properties; mathematical modelling; compression experiment
来源出版物:Journal of Biomechanics,1997,30(11): 1115-1121
被引频次:239
Radiosurgery for spinal metastases - Clinical experience in 500 cases from a single institution
Gerszten,PC; Burton,SA; Ozhasoglu,C; et al.
Abstract: Study Design: A prospective nonrandomized,longitudinal cohort study. Objective: To evaluate the clinical outcomes of single-fraction radiosurgery as part of the management of metastatic spine tumors. Summary of Background Data. The role of stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of spinal lesions has previously been limited by the availability of effective target immobilization and target tracking devices. Large clinical experience with spinal radiosurgery to properly assess clinical experience has previously been limited. Methods: A cohort of 500 cases of spinal metastases underwent radiosurgery. Ages ranged from 18 to 85 years(mean 56). Lesion location included 73 cervical,212 thoracic,112 lumbar,and 103 sacral. Results: The maximum intratumoral dose ranged from 12.5 to 25 Gy(mean 20). Tumor volume ranged from 0.20 to 264 mL(mean 46). Long-term pain improvement occurred in 290 of 336 cases(86%). Long-term tumor control was demonstrated in 90% of lesions treated with radiosurgery as a primary treatment modality and in 88% of lesions treated for radiographic tumor progression. Twenty-seven of 32 cases(84%)with a progressive neurologic deficit before treatment experienced at least some clinical improvement. Conclusions: The results indicate the potential of radiosurgery in the treatment of patients with spinal metastases,especially those with solitary sites of spine involvement,to improve long-term palliation.
Keywords: CyberKnife(R); image-guided surgery; robotic surgery; spine metastases; spine tumors; stereotactic radiosurgery
来源出版物:Spine,2007,32(2): 193-199
·推荐论文摘要·
机器人手术系统在胃癌治疗中的应用研究进展
汤玉成,王子卫
摘要:自1994年日本Kitano等首次报道腹腔镜辅助早期胃癌根治术以来,腹腔镜技术在胃癌中应用得到广泛普及和推广。与传统开腹手术相比,腹腔镜手术具有切口小、并发症少、术后恢复快、住院时间少等优点。但仍然存在二维图形、反向操作、医生体位不适等不足之处。因此,2000年机器人手术系统被引进用于克服传统微创外科的技术缺点。
关键词:机器人;胃肿瘤;外科手术;微创性;淋巴结切除术
来源出版物:重庆医学,2015,44(1): 120-122联系邮箱:王子卫,wangziwei571@sina.com
机器人手术系统行胰腺钩突肿瘤切除术疗效评价(附6例报告)
施昱晟,彭承宏,詹茜,等
摘要:目的:探讨机器人手术系统行胰腺钩突肿瘤切除术的临床疗效。方法:回顾性分析自2010年12月至2013年12月上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院完成的6例机器人手术系统辅助胰腺钩突肿瘤切除术的临床资料。结果:6例手术均顺利完成,无中转开腹。病人平均年龄51.7(40~64)岁,男性3例,女性3例。平均手术时间143.3(100~200)min;平均术中出血80(30~150)mL;平均术后住院天数23.8(13~44)d;术后2例出现B级胰瘘,1例出现C级胰瘘及肺部感染;无死亡病例。术后病理检查报告:4例为导管内乳头状黏液性肿瘤(IPMT),1例为胰岛素瘤,1例为实性假乳头状瘤(SPT)。术后常规随访:根据手术时间分别随访2个月至2年,术后均未因相关并发症再次入院,均未发现肿瘤复发。结论:机器人手术系统辅助胰腺钩突肿瘤切除术安全可行,成功率高,较传统开腹手术及腹腔镜手术,具有一定优势,但术后出现胰瘘等并发症概率仍较高。
关键词:胰腺钩突肿瘤;达芬奇机器人手术系统;局部切除术
来源出版物:中国实用外科杂志,2015,35(3): 308-312联系邮箱:彭承宏,chhpeng@188.com
中国达芬奇手术机器人临床应用
金振宇
摘要:达芬奇手术机器人引领着微创外科技术的发展,使用达芬奇手术机器人进行微创手术给医生带来诸多优势。我国自2008年起,先后由北京、上海等地14家医院逐步开展达芬奇机器人手术,至2012年底已经累计完成达芬奇机器人手术3551例,涵盖普外科、泌尿外科、心血管外科、胸外科、妇产科、五官科等各学科多种手术术式,取得了瞩目的成就。
关键词:达芬奇手术系统;外科手术;微创性;机器人
来源出版物:中国医疗器械杂志,2014,38(1): 47-49联系邮箱:金振宇,satyraga@sina.com
达芬奇机器人直肠癌根治术的学习曲线
兰远志,曾冬竹,张超,等
摘要:目的:探讨达芬奇机器人直肠癌根治术的学习曲线。方法:回顾分析我院微创胃肠外科中心2010年3月—2012年5月完成的60例达芬奇机器人直肠癌根治术的临床资料,按手术先后顺序分成A、B、C 3组,每组20例,比较各组机器人安装时间、手术时间、出血量、淋巴结清扫数目、并发症、术后住院时间。结果:A组机器人安装时间(66±6)min,显著长于B组(35±5)min和C组(32±4)min(q=27.365,P<0.05;q=30.013,P<0.05),B、C 2组无统计学差异(q=2.648,P>0.05)。3组手术时间无统计学差异(F=1.28,P=0.286),总手术时间差异(F=8.82,P=0.000)主要由于机器人安装时间差异,机器人直肠癌根治术学习曲线为20例。3组出血量、淋巴结清扫数目、并发症、术后住院时间无显著性差异(P>0.05)。结论:对于熟练掌握腹腔镜直肠癌根治术的外科医生,达芬奇机器人直肠癌根治术学习曲线约为20例。
关键词:直肠癌;达芬奇机器人手术系统;学习曲线
来源出版物:中国微创外科杂志,2014,14(6): 490-493联系邮箱:余佩武,yupeiwu01@sina.com
达芬奇机器人手术系统与电视胸腔镜在胸内纵隔疾病手术治疗中的对比研究
丁仁泉,童向东,许世广,等
摘要:背景与目的:近年来达芬奇机器人手术系统(da Vinci robot system)应用于治疗胸内纵隔疾病日趋成熟。本研究通过总结沈阳军区总医院近3年来在纵隔疾病中行手术治疗的临床病例资料,探讨达芬奇机器人手术系统在手术中的疗效;并比较其与电视胸腔镜在纵隔手术中的优缺点,展望达芬奇机器人手术系统在纵隔手术中的应用前景。方法:选择2010年1月—2013年11月沈阳军区总医院行达芬奇机器人手术及电视胸腔镜下(含胸腔镜辅助小切口)手术的胸内纵隔疾病患者共203例。对两组的手术时间、术中失血量、术后3天内引流总量、术后拔管时间、术后住院时间、手术费用进行比较,结果:应用SPSS 19.0进行相关分析。结果:两组共203例患者均顺利完成手术。术后恢复良好,无围手术期死亡病例。手术时间机器人组为82(20-320)min,电视胸腔镜组89(35-360)min,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术中出血量:机器人组为10(1-100)mL,电视胸腔镜组50(3-1,500)mL;术后72 h引流量:机器人组215(0-2,220)mL,电视胸腔镜组350(50-1,810)mL;术后拔管时间:机器人组3(0-10)d,电视胸腔镜组5(1-18)d;术后住院天数:机器人组7(2-15)d,电视胸腔镜组9(2-50)d;手术费用:机器人组(18,983.6±4,461.2)元,电视胸腔镜组(9,351.9±2,076.3)元,以上指标两组比较差异均具有统计学意义(P<0.001)。结论:达芬奇机器人手术与电视胸腔镜手术在胸内纵隔疾病的手术时间相当,在手术安全性以及术后快速恢复上均优于胸腔镜手术,但手术费用也比胸腔镜手术明显增加。
关键词:达芬奇机器人手术系统;纵隔疾病;微创手术
来源出版物:中国肺癌杂志,2014,17(7): 557-562联系邮箱:王述民,sureman2003congo@163.com
达芬奇机器人在小儿外科手术中的应用(附20例报告)
黄格元,蓝传亮,刘雪来,等
摘要:目的:达芬奇机器人手术系统具有独特的优势,是当前微创外科手术的前沿领域。本文通过回顾分析和总结我中心在机器人辅助下完成小儿外科手术资料,为今后深入开展机器人小儿外科手术提供经验和参考。方法:2007—2012年,我中心累积采用机器人辅助完成小儿外科手术20例(男女各10例;平均年龄10.7岁)。手术包括9例胃底折叠术、5例肾盂成形术、2例胆总管囊肿切除术、2例食管部分切除术、1例输尿管膀胱再植术和1例可控性尿流改道术。结果:9例胃底折叠平均手术时间为220.1 min,5例肾盂成形平均手术时间为204.2 min。1例胆总管囊肿术中因组织分离困难而中转开腹。1例先天性食管狭窄伴食管气管瘘行食管部分切除术后2周复发,经二次手术治愈。结论:机器人手术是小儿微创外科治疗的有效手段。仍需对患儿长期随访,以进一步评估机器人手术的远期效果。
关键词:机器人系统;小儿外科;手术
来源出版物:中国微创外科杂志,2013,13(1): 4-8联系邮箱:黄格元,kkywong@hku.hk
达芬奇手术机器人与腹腔镜行远端胃癌根治术近期疗效对照研究
赵坤,潘华峰,王刚,等
摘要:目的:对比分析达芬奇手术机器人系统(以下简称机器人)和腹腔镜行胃癌根治术远端胃大部切除病人术中、术后恢复情况。方法:选取2012年1月至2012年5月南京军区南京总医院普外科60例远端胃癌根治术的病人,随机分为机器人组和腹腔镜组行远端胃癌根治术,每组各30例,比较两组病人手术时间、术中出血、术后恢复情况、术后并发症情况。结果:机器人组术中出血、手术切口长度、术后3 d切口疼痛及术后首次进食时间优于腹腔镜组(P<0.05),但在淋巴结清扫及术后并发症方面两者差异无统计学意义。结论:机器人组除价格昂贵外较腹腔镜远端胃癌根治术病人手术创伤更小,术后恢复快,值得推广和应用。
关键词:达芬奇机器人;腹腔镜;远端胃癌
来源出版物:中国实用外科杂志,2013,33(4): 325-327联系邮箱:江志伟,surgery34@163.com
Robotic management of genitourinary injuries from obstetric and gynaecological operations: a multi-institutional report of outcomes
Gellhaus,PT; Bhandari,A; Monn,MF; et al.
Abstract: Objective: To evaluate the utility of robotic repair of injuries to the ureter or bladder from obstetrical and gynaecological(OBGYN)surgery. Patients and Methods: A retrospective review of all patients from four different high-volume institutions between 2002 and 2013 that had a robot-assisted(RA)repair by a urologist after an OBGYN genitourinary injury. Results: Of the 43 OBGYN operations,34 were hysterectomies: 10 open,10 RA,nine vaginally,and five pure laparoscopic. Nine patients had alternative OBGYN operations:three caesarean sections,three oophorectomies(one open,two laparoscopic),one RA colpopexy,one open pelvic cervical cerclage with mesh and one RA removal of an invasive endometrioma. In all,49 genitourinary(GU)injuries were sustained: ureteric ligation(26),ureterovaginal fistula(10),ureterocutaneous fistula(one),vesicovaginal fistula(VVF; 10)and cystotomy alone(two). In all,10 patients(23.3%)underwent immediate urological repair at the time of their OBGYN RA surgery. The mean(range)time between OBGYN injury and definitive delayed repair was 23.5(1-297)months. Four patients had undergone prior failed repair: two open VVF repairs and twoballoon ureteric dilatations with stent placement. In all,22 ureteric re-implants(11 with ipsilateral psoas hitch)and 15 ureteroureterostomies were performed. Stents were placed in all ureteric cases for a mean(range)of 32(1-63)days. In all,10 VVF repairs and two primary cystotomy closures were performed. Drains were placed in 28 cases(57.1%)for a mean(range)of 4.1(1-26)days. No case required open conversion. Two patients(4.1%)developed ureteric obstruction after RA repair requiring dilatation and stenting. The mean(range)follow-up of the entire cohort was 16.6(1-63)months. Conclusions: RA repair of GU injuries during OBGYN surgery is associated with good outcomes,appears safe and feasible,and can be used successfully immediately after injury recognition or as a salvage procedure after prior attempted repair. RA techniques may improve convalescence in a patient population where quick recovery is paramount.
Keywords: robotic surgery; gynaecology injury; ureteroneocystostomy; vesicovaginal fistula; ureterovaginal fistula
来源出版物:BJU International,2015,115(3): 430-436联系邮箱:Boris,RS; rboris@IUHealth.org
Randomised Controlled Trial Comparing Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Radical Prostatectomy
Porpiglia,F; Morra,I; Chiarissi,ML; et al.
Abstract: Background: The advantages of robot-assisted radical prostatectomy(RARP)over laparoscopic radical prostatectomy(LRP)have rarely been investigated in randomised controlled trials. Objective: To compare RARP and LRP in terms of the functional,perioperative,and oncologic outcomes. The main end point of the study was changes in continence 3 mo after surgery. Design,setting,and participants: From January 2010 to January 2011,120 patients with organ-confined prostate cancer were enrolled and randomly assigned(using a randomisation plan)to one of two groups based on surgical approach: the RARP group and the LRP group. Intervention: All RARP and LRP interventions were performed with the same technique by the same single surgeon. Outcome measurements and statistical analysis:The demographic,perioperative,and pathologic results,such as the complications and prostate-specific antigen(PSA)measurements,were recorded and compared. Continence was evaluated at the time of catheter removal and 48 h later,and continence and potency were evaluated after 1,3,6,and 12 mo. The student t test,Mann-Whitney test,chi(2)test,Pearson chi(2)test,and multiple regression analysis were used for statistics. Results and limitations: The two groups(RARP: n = 60; LRP: n = 60)were comparable in terms of demographic data. No differences were recorded in terms of perioperative and pathologic results,complication rate,or PSA measurements. The continence rate was higher in the RARP group at every time point: Continence after 3 mo was 80% in the RARP group and 61.6% in the LRP group(p = 0.044),and after 1 yr,the continence rate was 95.0% and 83.3%,respectively(p = 0.042). Among preoperative potent patients treated with nerve-sparing techniques,the rate of erection recovery was 80.0% and 54.2%,respectively(p = 0.020). The limitations included the small number of patients. Conclusions: RARP provided better functional results in terms of the recovery of continence and potency. Further studies are needed to confirm our results.
Keywords: prostate cancer; laparoscopy; robotic surgery; continence; potency
来源出版物:European Urology,2013,63(4): 606-614联系邮箱:Porpiglia,F; porpiglia@libero.it
250 Robotic Pancreatic Resections Safety and Feasibility
Zureikat,AH; Moser,AJ; Boone,BA; et al.
Abstract: Background and Objectives: Computer-assisted robotic surgery allows complex resections and anastomotic reconstructions to be performed with nearly identical standards to open surgery. We applied this technology to a variety of pancreatic resections to assess the safety,feasibility,versatility,and reliability of this technology. Methods: A retrospective review of a prospective database of robotic pancreatic resections at a single institution between August 2008 and November 2012 was performed. Perioperative outcomes were analyzed. Results: A total of 250 consecutive robotic pancreatic resections were analyzed; pancreaticoduodenectomy(132),distal pancreatectomy(83),central pancreatectomy(13),pancreatic enucleation(10),total pancreatectomy(5),Appleby resection(4),and Frey procedure(3). Thirty-day and 90-day mortality was 0.8% and 2.0%. Rate of Clavien 3 and 4 complications was 14% and 6%. The International Study Group on Pancreatic Fistula grade C fistula rate was 4%. Mean operative time for the 2 most common procedures was 529 +/- 103 minutes for pancreaticoduodenectomy and 257 +/- 93 minutes for distal pancreatectomy. Continuous improvement in operative times was observed over the course of the experience. Conversion to open procedure was required in 16 patients(6%)(11 with pancreaticoduodenectomy,2 with distal pancreatectomy,2 with central pancreatectomy,1 with total pancreatectomy)for failure to progress(14)and bleeding(2). Conclusions: This represents to our knowledge the largest series of robotic pancreatic resections. Safety and feasibility metrics including the low incidence of conversion support the robustness of this platform and suggest no unanticipated risks inherent to this new technology. By defining these early outcome metrics,this report begins to establish a framework for comparative effectiveness studies of this platform.
Keywords: minimally invasive surgery; pancreatic cancer; pancreatic; pancreaticoduodenectomy; robotic surgery
来源出版物:Annals of Surgery,2013,258(4): 554-562联系邮箱:Zeh,HJ; zehxhx@upmc.edu
编辑:王微
Purpose: Robotics in surgery is a recent innovation. This technology offers a number of attractive features in laparoscopy. It overcomes the difficulties with fixed port sites by restoring all 6 degrees of freedom at the instrument tips,provides new possibilities for miniaturization of surgical tasks and allows remote controlled surgery. We investigated the applicability of remote controlled robotic surgery to laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Materials and Methods: Our previous experience with laparoscopic prostatectomy served as a basis for adapting robotic surgery to this procedure. A surgeon at a different location who activated the tele-manipulators of the da Vinci* robotic system performed all steps of the intervention. A scrub nurse and second surgeon who stood at patient side had limited roles to port;and instrument placement,exposure of the operative field,assistance in hemostasis and removal of the operative specimen. Our patient was a 63-year-old man presenting with a T1c tumor discovered on 1 positive sextant biopsy with a 3+3 Gleason score and 7 ng./ml. preoperative serum prostate specific antigen. Results: The robot provided an ergonomic surgical environment and remarkable dexterity enhancement. Operating time was 420 minutes,and the hospital stay lasted 4 days. The bladder catheter was removed 3 days postoperatively,and 1 week later the patient was fully continent. Pathological examination showed a pT3a tumor with negative margins. Conclusions: Robotically assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy is feasible. This new technology enhances surgical dexterity. Further developments in this field may have new applications in laparoscopic tele-surgery.
robotics; feasibility studies; laparoscopy; prostatectomy; prostatic neoplasms
典
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with a remote controlled robot Abbou,CCJournal of Urology,2001,165(6):1964-1966 2(12): 1689-1694 3Assessment of intraoperative safety in transoral robotic surgery Telerobotic-assisted laparoscopic right and sigmoid Weber,PA Diseases of the Colon & Rectum,2002,45 colectomies for benign disease Hockstein,NGLaryngoscope,2006,116(2): 165-168 4 Transoral robotic surgery Weinstein,GS Archives of Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery,2007,133(12): 1220-1226
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with a remote controlled robot
Abbou,CC; Hoznek,A; Salomon,L; et al.

