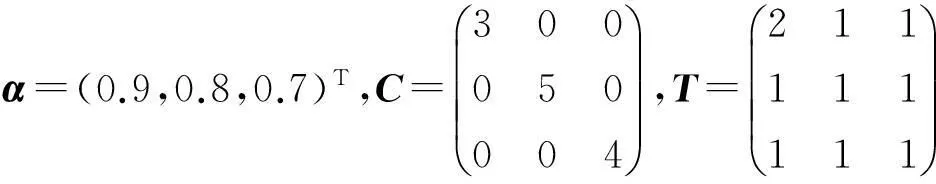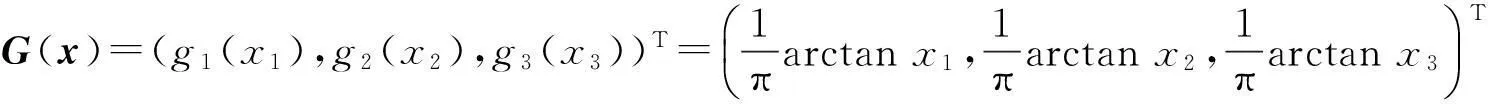一类非自治共振二阶系统的多重周期解
一类非自治共振二阶系统的多重周期解

张环环
(西北民族大学数学与计算机科学学院,甘肃 兰州 730030)
摘要:研究了非自治共振二阶系统周期解的存在性问题.在非线性项次线性增长时,将这类系统的周期解转化为定义在一个适当空间上泛函的临界点,然后利用临界点理论建立了此类系统周期解的存在性结果.
关键词:非自治二阶系统;临界点理论;周期解;共振;临界点
文章编号:1007-2985(2015)05-0016-05
收稿日期:2015-01-14
基金项目:数学天元基金资助项目(11326100);中央高校基本科研业务费专项资助项目(31920130010)
作者简介:张环环(1980—),女,甘肃静宁人,西北民族大学数学与计算机科学学院讲师,产要从事非线性泛函分析研究.
中图分类号:O175.12 文献标志码:A
DOI:10.3969/j.cnki.jdxb.2015.05.004
DOI:10.3969/j.cnki.jdxb.2015.05.005

1 问题的提出
考虑非自治二阶系统
(1)
其中m为非负整数,F∈C1(R×RN,R),且关于t是2π周期的.
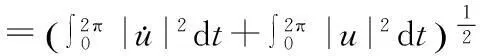
则φ连续可微,且
(F(t,u(t)),v(t))dt.
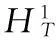
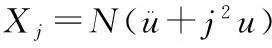
许多重要的数学模型都可以归结为非自治二阶系统的周期解,利用临界点理论研究非自治二阶系统周期解的存在性一直是人们关注的问题[1-11].文献[1]中研究了超二次条件下非自治二阶系统周期解的存在性;在具有部分周期位势时,文献[2-3,9,11]中得到了非自治二阶系统多重周期解的存在性;在非线性项F(t,u)有界时,文献[4]中得到了问题(1)周期解的存在性;在非线性项在无穷远处线性增长时,文献[5]中得到了非自治二阶系统周期解的存在性.
次线性条件指[9],存在f,g∈L1(0,T;R+),0≤α<1 ,使得
|F(t,x)|≤f(t)|x|α+g(t),
(2)
对所有x∈RN和a.e.t∈[0,2π]成立.
称问题(1)是共振的,指
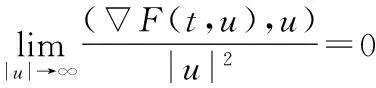
(3)
对t∈[0,2π]一致成立.在(2)式成立时,(3)式也成立,故此时称问题(1)是共振的.
当m=0时,在具有次线性非线性项时,文献[6]中得到了问题(1)周期解的存在性;文献[7]将文献[6]中结果推广为m不恒等于0的情形;文献[8]中讨论了次线性非自治一阶Hamiltonian系统周期解的存在性;文献[6-8]中均假设核空间上Ahmad-Lazer-Paul型强制性条件成立,即

笔者将Ahmad-Lazer-Paul型强制性条件推广为
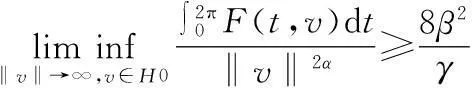
(4)

在此条件下,用临界点理论研究问题(1)的多重周期解,在非线性项满足次线性条件时,得到这类周期解个数的下界估计.
2 预备知识
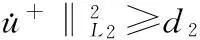
(5)
对所有u+∈H+和t∈[0,2π]成立.由文献[12],有
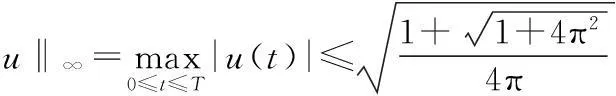
(6)
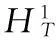
定义1 [9]设X为Banach空间,称泛函φ∈C1(X,R)满足(PS)条件是指对任何点列{un}⊂X,由{φ(un)}有界,φ′(un)→0蕴含{un}有收敛子列.
利用Z2不变群指标理论得到如下临界点定理:
引理1 [13]设φ∈C1(X,R)满足(PS)条件,又是偶函数,φ(0)=0.
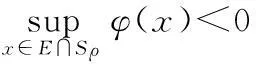

若m>j,则泛函φ至少有2(m-j)个不同的临界点.
3 主要结果
定理1设F满足(2),(4)式,F(t,0)=0且存在常数δ及整数k>m+1,使得
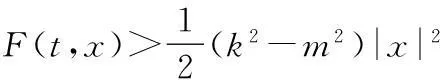
(7)
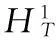
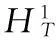
下文证明中用c表示常量.
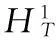
|φ(un)|≤c,φ′(un)→0n→∞,
(8)

由(2),(6)式,有
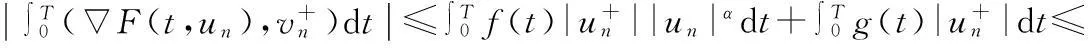
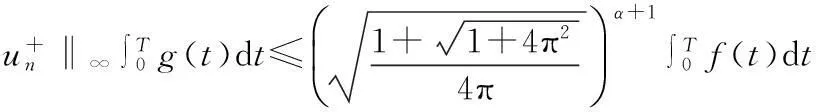

由(8)式,有
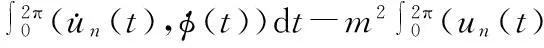

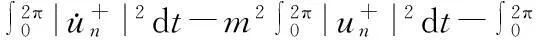
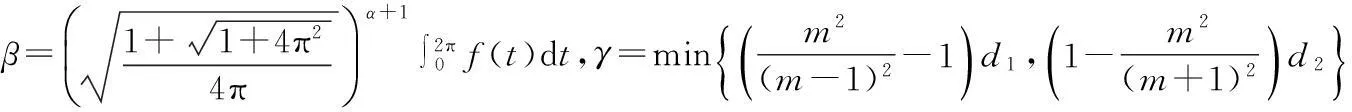

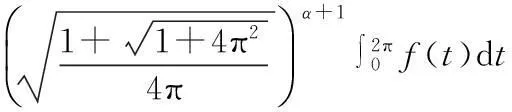
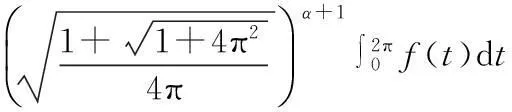
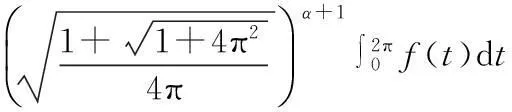
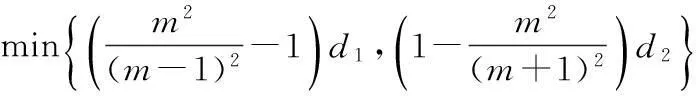
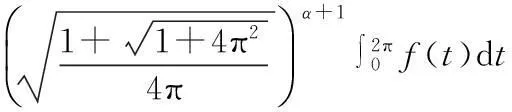
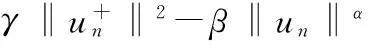
从而有

(9)

(10)
由(10)式可以推得

(11)
由(9),(11)式,有
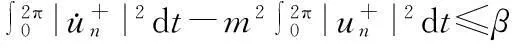
(12)
同理可证
(13)

(14)
由(12),(14)式,有
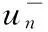
(15)
反设当n→∞时,‖un‖→∞,并注意到0≤α<1,由(15)式有
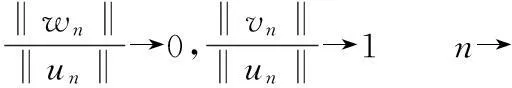
(16)
由(2),(6),(15)式,有
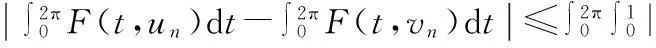
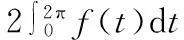


2β‖vn‖α‖wn‖+2β‖wn‖α+1+c‖wn‖≤
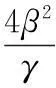
(17)
由(17)式可得
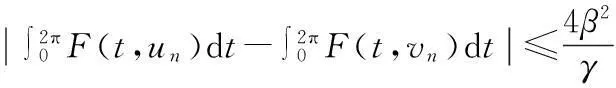
由(4)式,对∀ε>0,存在M>0,使‖vn‖≥M时有
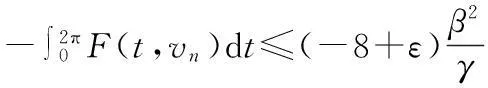
(18)
对所有‖vn‖≥M,由(13),(15),(18),(23)式,有
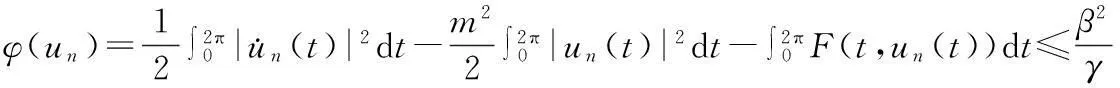
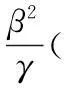
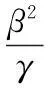
由ε的任意性及0≤α<1,由(16)式,当n→∞时,φ(un)→-∞,这与(8)式矛盾.
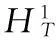
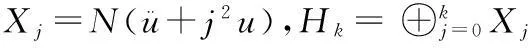
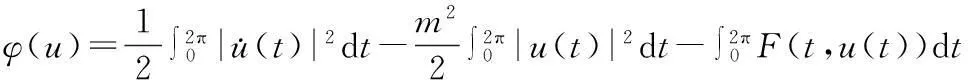
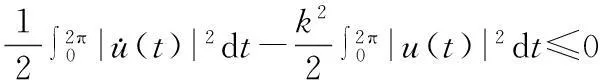
对所有的a.e.t∈[0,T],|u|≤C-1δ成立,其中C为Sobolev不等式‖u‖∞≤C‖u‖中的正常数.
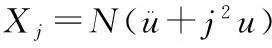
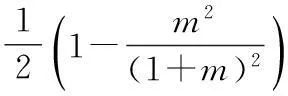
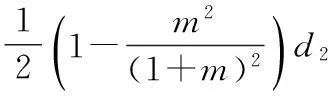
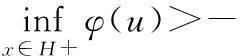

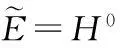
从而泛函φ至少有2(k-m-1)个不同的临界点,因此系统(1)至少有2(k-m-1)个周期解.
定理2设F满足(2),(7)式,且
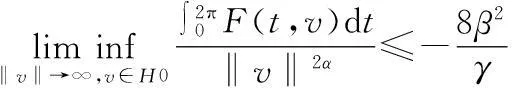
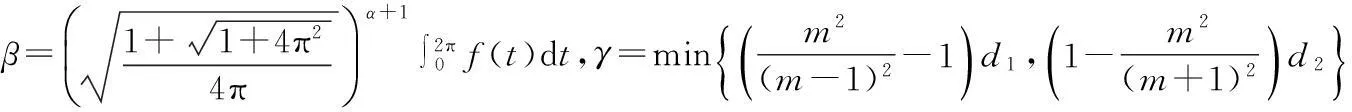
定理2证明方法与定理1类似,此省略.
参考文献:
[1]OUZengqi,TANGChunlei.PeriodicandSubharmonicSolutionsforaClassofSuperquadraticHamiltonianSystems[J].NonlinearAnalysisTMA,2004,58(3):245-258.
[2]TANGChunlei.ANoteonPeriodicSolutionsofSecondOrderSystems[J].Proc.Amer.Math.Soc.,2003,132:1 295-1 393.
[3]ZHANGXingyong,TANGXianhua.PeriodicSolutionsforanOrdinaryp-LaplacianSystem[J].TaiwaneseJournalofMathematics,2011,15(3):1 369-1 396.
[4]JEANMAWHIN.CriticalPointTheoryandHamiltonianSystems[M].NewYork:SpringerVerlag,1989.
[5]ZHAOFukun,WUXian.ExistenceofPeriodicSolutionsforNonautonmousSecondOrderSystemswithLinearNonlinearity[J].NonlinearAnal.,2005,60(7):325-335.
[6]TANGChunlei.PeriodicSolutionsforSecondOrderSystemswithSublinearNonlinearity[J].ProceedingsoftheAmericanMathematicalSociety,1998,126:3 263-3 270.
[7]韩志清.共振条件下的常微分方程组2π-周期解的存在性[J].数学学报,2000(4):639-644.
[8]HANZhiqing.ExistenceofPeriodicSolutionsofLinearHamiltonianSystemswithSublinearPerturbation[J].BoundaryValueProblems,2010,12:123-131.
[9]张申贵.非自治共振二阶离散Hamilton系统的周期解[J].贵州师范大学学报:自然科学版,2013,31(1):48-52.
[10]孟海霞,郭晓峰.一类共振二阶系统的多重周期解[J].华东师范大学学报:自然科学版,2006(1):40-44.
[11]张申贵.一类非自治二阶Hamilton系统的周期解的存在性[J].河北师范大学学报,2012,36(2):115-120.
[12]TANGXianhua,XIAOLi.HomoclinicSolutionsforaClassofSecondOrderHamiltonianSystems[J].NonlinearAnalsis,2009,71(3):1 140-1 151.
[13]CHANGKC.InfiniteDimensionalMorseTheoryandMultipleSolutionProblems[M].Boston:Birkhäuser,1993.
Multiplicity of Periodic Solution of a Class of Non-Automous
Second Order System at Resonance
ZHANG Huanhuan
(College of Mathematics and Computer Science,Northwest University for Nationalities,Lanzhou 730030,China)
Abstract:The existence of periodic solutions for non-automous second order systems at resonance is investigated.With the sub-linear increase of the non-linear term,the periodic solutions of the system are converted into the critical points of a functional defined on a proper space,and the existence of periodic solutions is proved through the critical point theory.
Key words:non-autonomous second order systems;critical point theory;periodic solutions;resonance;critical point
(责任编辑向阳洁)
Article ID:1007-2985(2015)05-0021-06
Mittag-Leffler Stability of a Class of Fractional
Order Hopfield Neural Networks
Received date:2014-11-26
Biography:LIU Xiaolei(1983—),male,was born in Weifang City,Shandong Province,master of science,lecture;research area are fractional order dynamic systems and neural networks.

LIU Xiaolei,MA Cuiling,HAO Shuyan
Abstract:In this paper,we investigate the Mittag-Leffler stability of a class of fractional order Hopfield neural network with Caputo derivative.By using the Mittag-Leffler function,we get some sufficient conditions to guarantee the existence and uniqueness of the equilibrium point and its Mittag-Leffler stability for the fractional order Hopfield neural networks.Finally,we use one numerical simulation example to illustrate the correctness and effectiveness of our results.
Key words:fractional order neural networks;Mittag-Leffler function;Mittag-Leffler stability
CLC number:O211.29Document code:A

1 Introduction
The subject of fractional calculus was planted over 300 years ago.In recent years,fractional calculus has played a significant role in many areas of science and engineering[1-3].The necessary and sufficient stability conditions for linear fractional differential equations (FDEs) and linear time-delayed FDEs have already been obtained in ref. [4-6].The stability of nonlinear fractional order system for Caputo’s derivative is studied in ref. [7-9].
Currently,some excellent results about fractional-order neural networks have been investigated[10-13].Particularly,Yu Juan et al[13]studiedα-stability andα-synchronization for fractional-order Hopfield neural networks as follows:
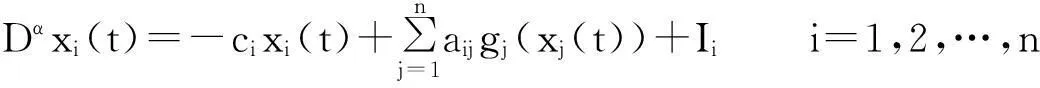
(1)
(1)
where 0<α<1,ncorresponds to the number of units in the neural networks;xi(t) corresponds to the state of theith unit at timet;gj(t) denotes the activation function of thejth neuron;aijdenotes the constant connection weight of thejth neuron on theith neuron;ci>0 represents the rate with which theith neuron will reset its potential to the resting state when disconnected from the network andIidenotes external inputs.
In this paper,by putting the systems translating into the nonlinear Volterra integral equation of the second kind,and making use of the existence and uniqueness Theorem of FDEs and a weakly singular discrete Gronwall inequality to prove the Mittag-Leffler stability of the Hopfield neural networks,which is the generation of the exponential stability.And when 0<α<1,the asymptotic rate of convergence for the system approaching the equilibrium point is faster than the exponential stability.
The remained of this paper is organized as follows:in section 2,some necessary definitions and lemmas are presented;in section 3,we give some sufficient conditions to guarantee the existence and uniqueness of the equilibrium point and its Mittag-Leffler stability for a class of fractional order Hopfield neural networks by using the Mittag-Leffler function;in section 4,one example and corresponding numerical simulation are used to illustrate the validity and feasibility of the results obtained in section 3.
2 Preliminaries
There are several definitions of a fractional derivative of orderα,which is the extended concept of integer order derivative.The commonly used definitions are Grunwald-Letnikov,Riemann-Liouville,and Caputo definitions.In this section,we will recall the definition of Caputo fractional derivative and the several important lemmas.
Definition 1[14]The Caputo fractional derivative of orderα∈R+of a functionx(t) is defined as

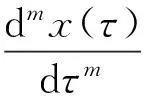
Consider the Cauchy problem of the following fractional differential equation:
(2)
where x=(x1,x2,…,xn)T∈Rn,0<α<1,and f:[0,+∞)×Rn→Rnis continuous int.
Definition 2[15]LetB⊂Rnbe a domain containing the origin.The zero solution of (2) is said to be Mittag-Leffler stable if
‖x(t)‖≤(m(x(t0))Eα(-λ(t-t0)α))b,
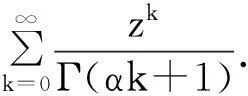
Definition 3[16]The constant x*is an equilibrium point of the Caputo fractional dynamic system (2) if and only iff(t,x*)=0 for anyt∈[0,+∞).
Lemma 1[17]Consider the following equation
(3)
The homotopy perturbation technique yields that the initial value problem (3) be equivalent to the nonlinear Volterra integral equation of the second kind

(4)
In particular,if 0<α<1,then eq. (4) can be written in the following form

(5)
Lemma 2[18]Letx(t) be a continuous and nonnegative function ont∈[0,T].If

where 0≤α<1 andψ(t) is a nonnegative,monotonic increasing function ont∈[0,T],andMis a constant,then x(t)≤ψ(t)E1-α(MΓ(1-α)t1-α).
Lemma 3[14]Let 0≤α<1 andf(t,x):[0,+∞)×Rn→Rnbe a function such that,for allt∈[0,+∞) and for allx1,x2∈G⊂Rn,
|f(t,x1)-f(t,x2)|≤A|x1-x2|,
whereA>0 does not depend ont∈[0,+∞),then there exists a unique solution x(t) to the Cauchy problem in theC[0,+∞).
3 Mittag-Leffler Stability of a Class of Fractional Order Neural Networks
In this section,we suppose that the fractional order Hopfield neural networks satisfies the following conditions:
(A1)gj(j=1,2,…,n) are Lipschtiz-continuous on (-∞,+∞) with Lipschtiz constantsLj>0,i.e.,|gj(ξ)-gj(η)|≤Lj|ξ-η|,for allξ,η∈(-∞,+∞);
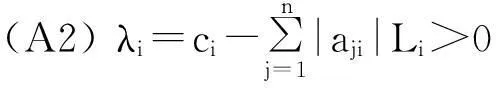
Letλ=min{λ1,λ2,…,λn},l=max{l1,l2,…,ln},then we haveλ>0,l<1.
Theorem 1Under the assumptions (A1) and (A2),system (1) has a unique equilibrium point.
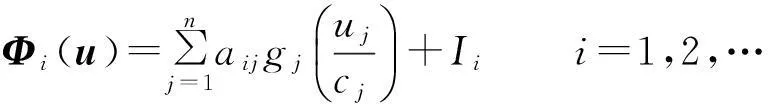
By the assumptions (A1) and (A2),we have
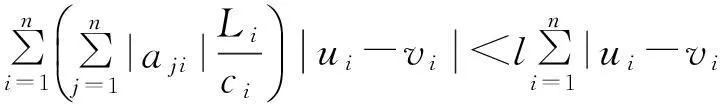
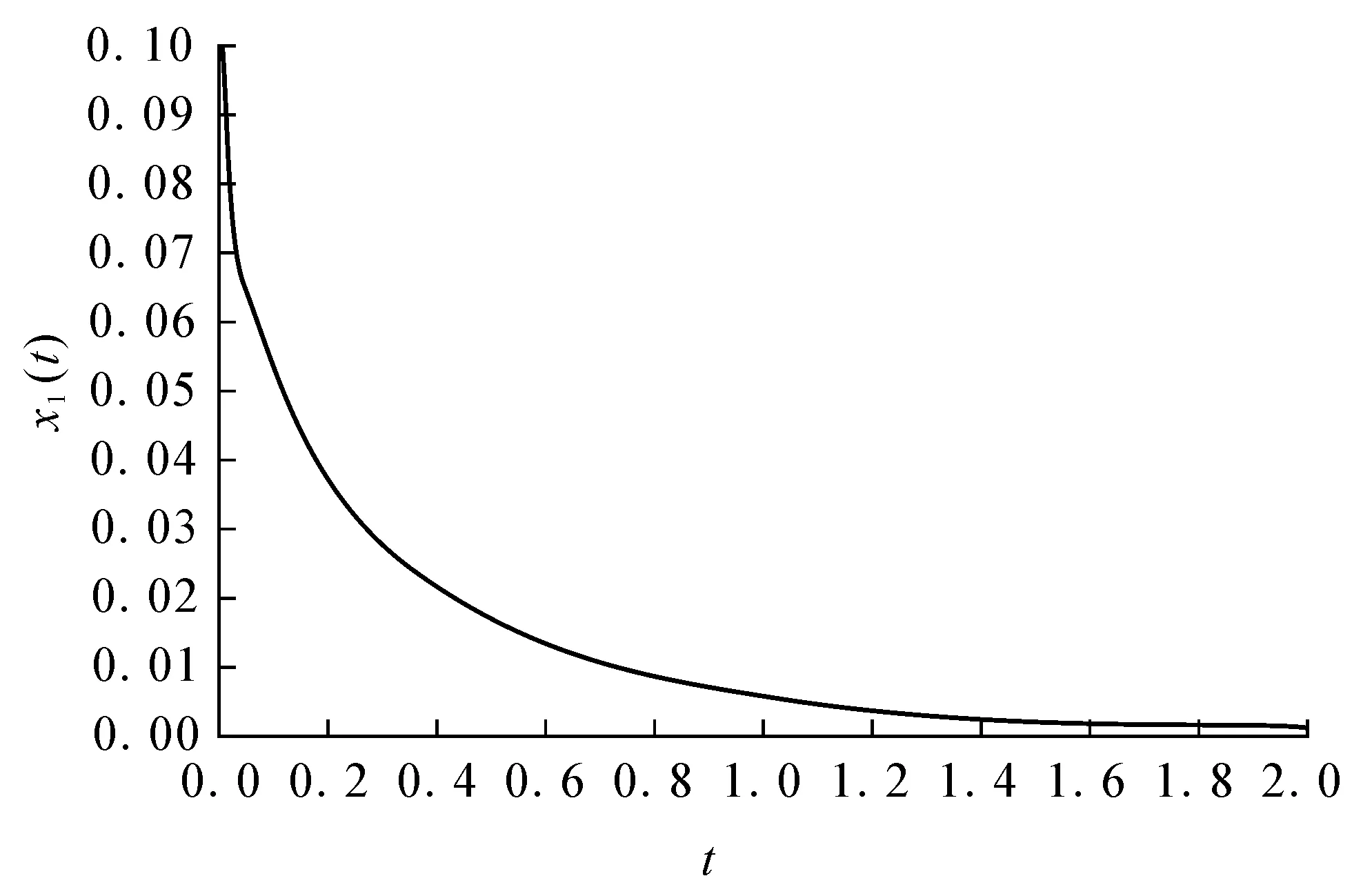
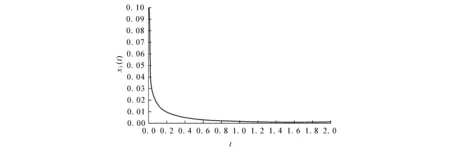
It shows that ‖Φ(u)-Φ(v)‖ So the conclusion of the theorem is correct. Theorem 2Under the assumptions (A1) and (A2),the unique equilibrium point of system (1) is Mittag-Leffler stable. (6) By the lemma 3 and the assumption (A1),the solution of the system (6) exists and is unique.It is easy to see thatei(t)≡0 is a solution of the system (6);therefore we haveei(t)ei(0)>0 fort∈[0,+∞).We divide our discussion into two cases. Case 1Ifei(0)>0,thenei(t)>0 fort∈[0,+∞).From (5) in lemma 1,we have Case 2Ifei(0)<0,thenei(t)<0 fort∈[0,+∞).It is similar to the case 1,we have Therefore, From case 1 and case 2,we get the inequality By lemma 2,we have which shows that the system (1) is Mittag-Leffler stable. In the system (1),let x(0)=(x1(0),x2(0),x3(0))T=(0.1,0.1,0.1)T, thenthesystem(1)satisfiestheconditionsoftheorem1andtheorem2;thereforeithastheuniqueMittag-Lefflerstableequilibriumpoint(seefig. 1). a x 1(t) plane b x 2(t) plane c x 3(t) plane Reference: [1] IGOR PODLUBNY.Geometric and Physical Interpretation of Fractional Integration and Fractional Differentiation[J].Fractional Calculus & Applied Analysis,2002,5(4):367-386. [2] J TENREIRO MACHADO,VIRGINIA KIRYAKOVA,FRANCESCO MAINARDI.Recent History of Fractional Calculus[J].Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul.,2011,16:1 140-1 153. [3] SAMKO G,KILBAS A A,MARICHEV O I.Fractional Integrals and Derivatives:Theory and Applications[M].Yverdon:Gordon & Breach,1993. [4] BONNET C,PARTINGTON J R.Coprime Factorizations and Stability of Fractional Differential Systems[J].Syst. Control Lett.,2000,41:167-174. [5] DENG Weihua,LI Changpin,LV Jinhu.Stability Analysis of Linear Fractional Differential System with Multiple Time-Delays[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2007,48(4):409-416. [6] LI Changpin,DENG Weihua.Remarks on Fractional Derivatives[J].Applied Mathematic and Computation,2007,187(2):777-784. [7] SADATI S J,BALEANU D,RANJBAR A,et al.Mittag-Leffler Stability Theorem for Fractional Nonlinear Systems with Delay[EB/OL].[2014-09-22].http:∥dx.doi.org/10.1155/2010/108651. [8] LIU L,ZHONG S.Finite-Time Stability Analysis of Fractional Order with Multi-State Time Delay[J].Word Acad. Sci.,Eng. Technol.,2011,76:874-877. [10] AREFEH BOROOMAND,MOHANMMAD B MENHAJ.Fractional-Order Hopfield Neural Networks[J].Lecture Notes in Computer Science,2009,5 506:883-890. [11] HADI DELAVARI,DUMITRU BALEANU,JALIL SADATI.Stability Analysis of Caputo Fractional-Order Nonlinear Systems Revisited[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2012,67(4):2 433-2 439. [12] CHEN Liping,CHAI Yi,WU Ranchao,et al.Dynamic Analysis of a Class of Fractional-Order Neural Networks with Delay[J].Neurocomputing,2013,111:190-194. [13] YU Juan,HU Cheng,JIANG Haijun.α-Stability andα-Synchronization for Fractional-Order Neural Networks[J].Neural Networks,2012,35:82-87. [14] ANATOLY A KILBAS,HARI M SRIVASTAVA,JUAN J TRUJILLO.Theory and Applications of Fractional Differential Equations[M].North-Holland:Elsevier,2006. [15] LI Yan,CHEN Yangquan,IGOR PODLUBNY.Mittag-Leffler Stability of Fractional Order Nonlinear Dynamic Systems[J].Automatica,2009,45:1 965-1 969. [16] HADI DELAVARI,DUMITRU BALEANU,JALIL SADATI.Stability Analysis of Caputo Fractional-Order Nonlinear Systems Revisited[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2012,67(4):2 433-2 439. [17] K SAYEVAND,A GOLBABAI,AHMET YILDIRIM.Analysis of Differential Equations of Fractional Order[J].Applied Mathematical Modelling,2012,36(9):4 356-4 364. [18] J A DIXON,S MCKEE.Weakly Singular Discrete Gronwall Inequalities[J].Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics:Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik,1986,66(11):535-544.
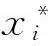
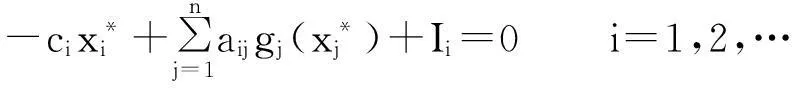

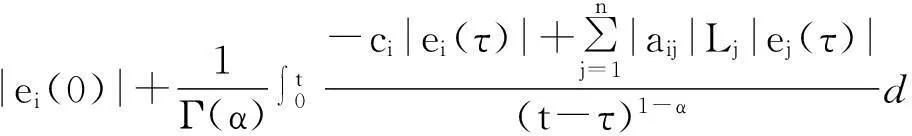
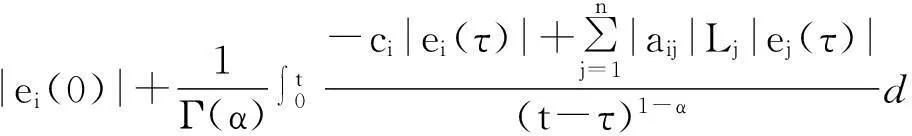

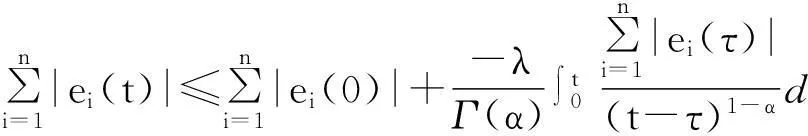
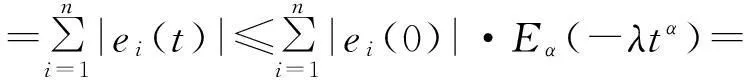
4 Illustrative Examples