第五代移动通信技术(5G)
第五代移动通信技术(5G)
·编者按·
第五代移动通信技术(5th generation mobile networks 或 5th generation wireless systems,简称5G),是继4G之后,新一代的移动通信技术,该技术的研究方兴未艾,目前还没有电信公司或者标准制定组织在官方文件中提到这一概念。随着技术的发展,人们对通信网络的需求呈现爆炸式增长,推动在传输速率和资源利用率等方面大大优于4G的移动通信技术加快研发,按照预想,5G网络将达到五大性能目标:传输速率达到10 GB/s;频谱效率提高10倍;业务时延小于5 m/s;网络容量提升1000倍;能量效率提升10倍;并能提供更多的应用和更好的用户体验。
2013年初,欧盟在第7框架计划启动了面向5G研发的METIS(Mobile and Wireless Communications Enablers for the Twenty-Twenty(2020)Information Society)项目,韩国和中国分别成立了5G技术论坛和IMT-2020(5G)推进组。我国863计划也分别于2013年6月和2014年3月启动了5G重大项目一期和二期研发课题。2014年5月8日,日本电信营运商NTT DoCoMo正式宣布与其他厂商共同合作,测试超过现有4G网络1000倍网络承载能力的高速5G网络。2015年3月1日,英国《每日邮报》报道,英国已成功研制5G网络,并称于2018年投入公众测试,2020年正式投入商用。2015年9月7日,美国移动运营商Verizon无线公司宣布,将从2016年开始试用5G网络,2017年在美国部分城市全面商用。我国5G技术研发试验将在2016—2018年进行,分为5G关键技术试验、5G技术方案验证和5G系统验证三个阶段实施。
目前,世界各国正就5G的发展愿景、应用需求、候选频段、关键技术指标等进行广泛的研讨,5G在无线传输技术和网络技术方面的关键技术主要有超密集异构网络、自组织网络、D2D(device-to-device)通信、M2M(machine-to-machine)通信、软件定义无线网络、信息中心网络、内容分发网络、移动云计算、软件定义网络/网络功能虚拟化和情景感知技术。
本专题得到孙震强(中国电信北京研究院高级工程师、北京邮电大学客座教授)、张治中(重庆邮电大学教授)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2016年1月8日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“5G”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为408与515条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
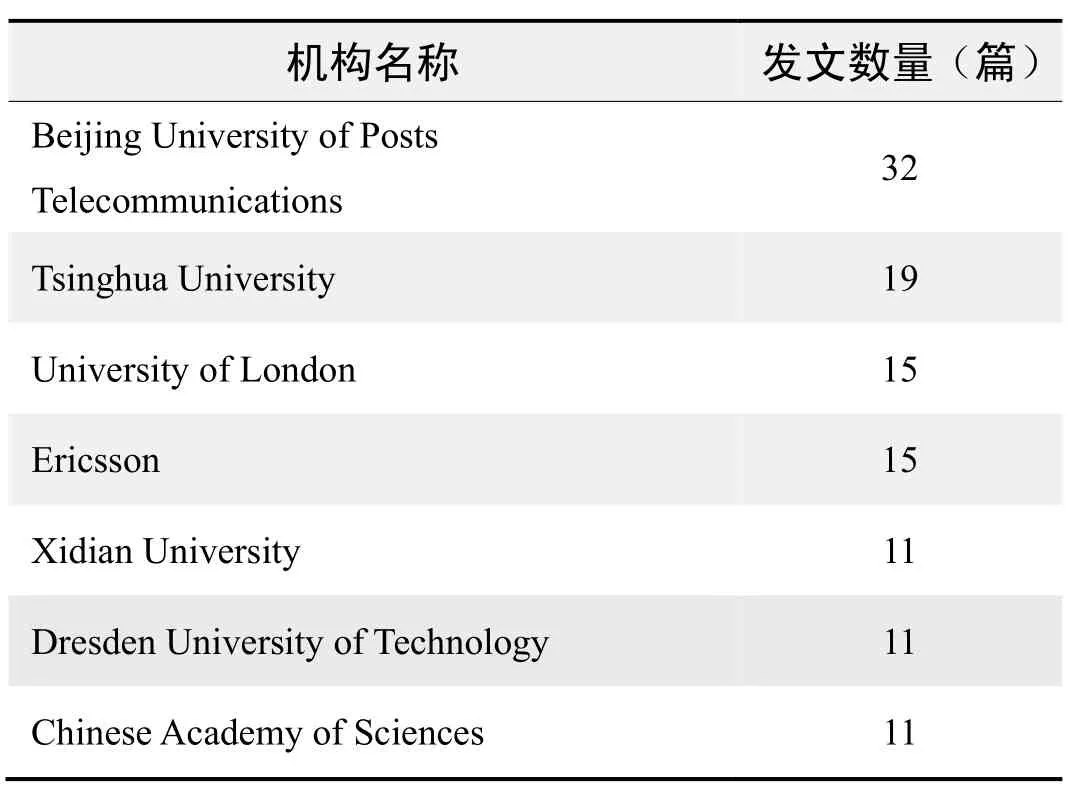
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)
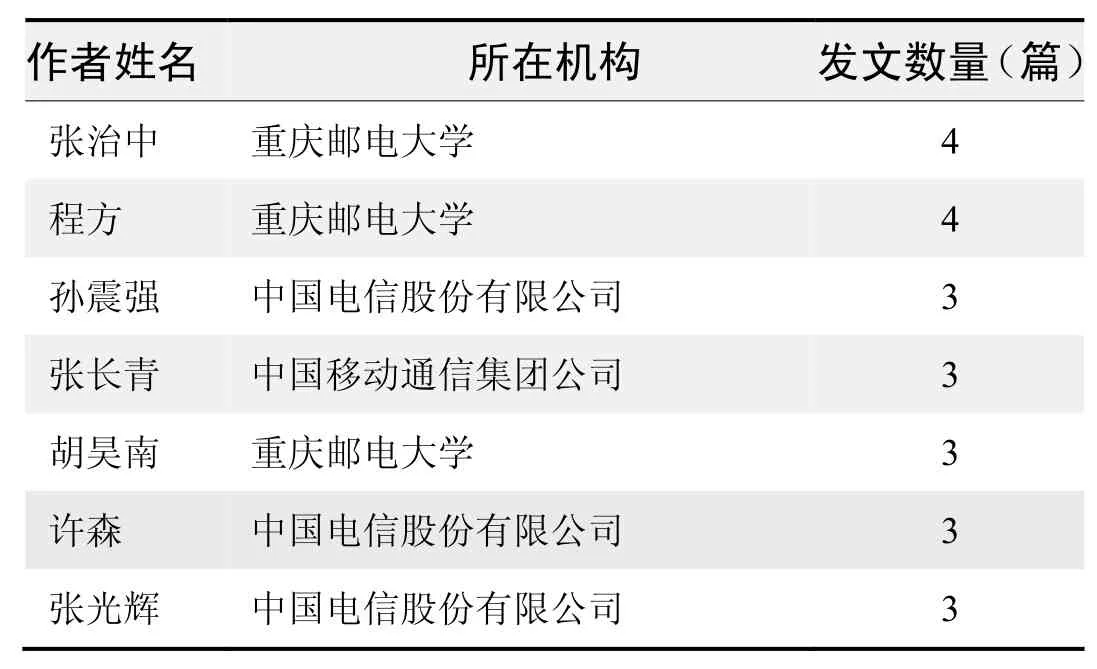
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
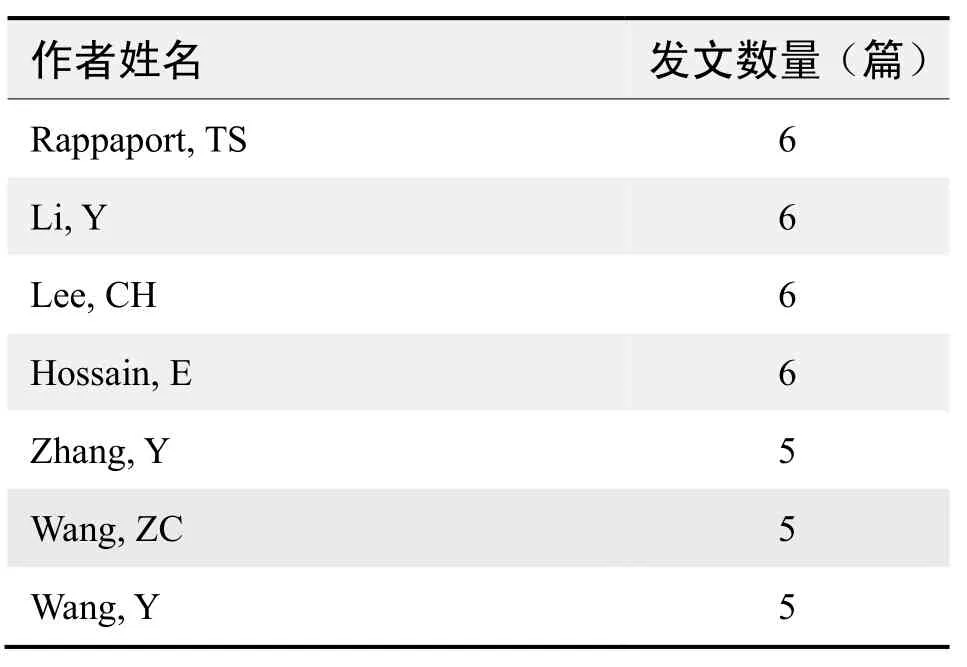
作者发文数量排名(WOS)
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
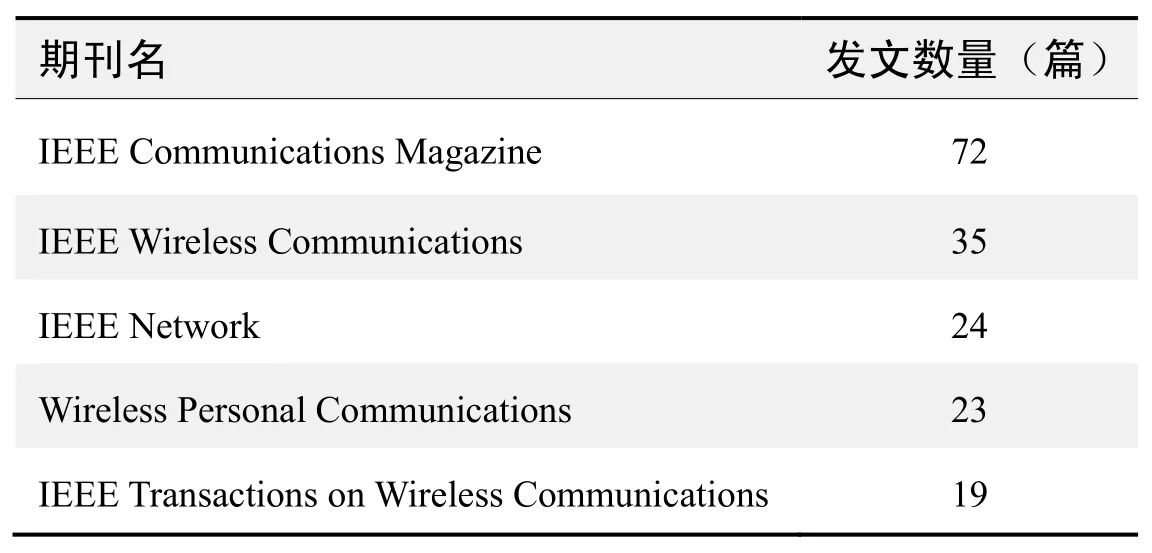
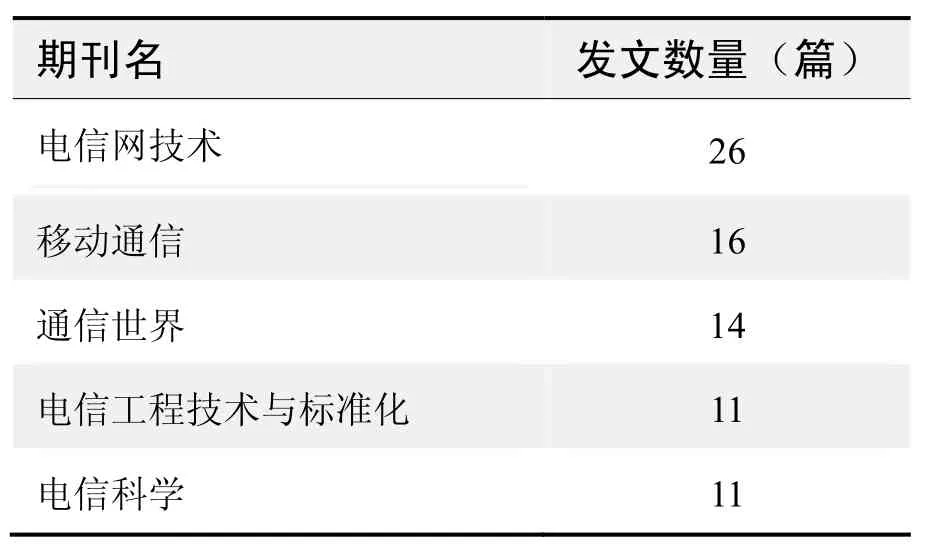
期刊发文数量排名(WOS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“5G”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
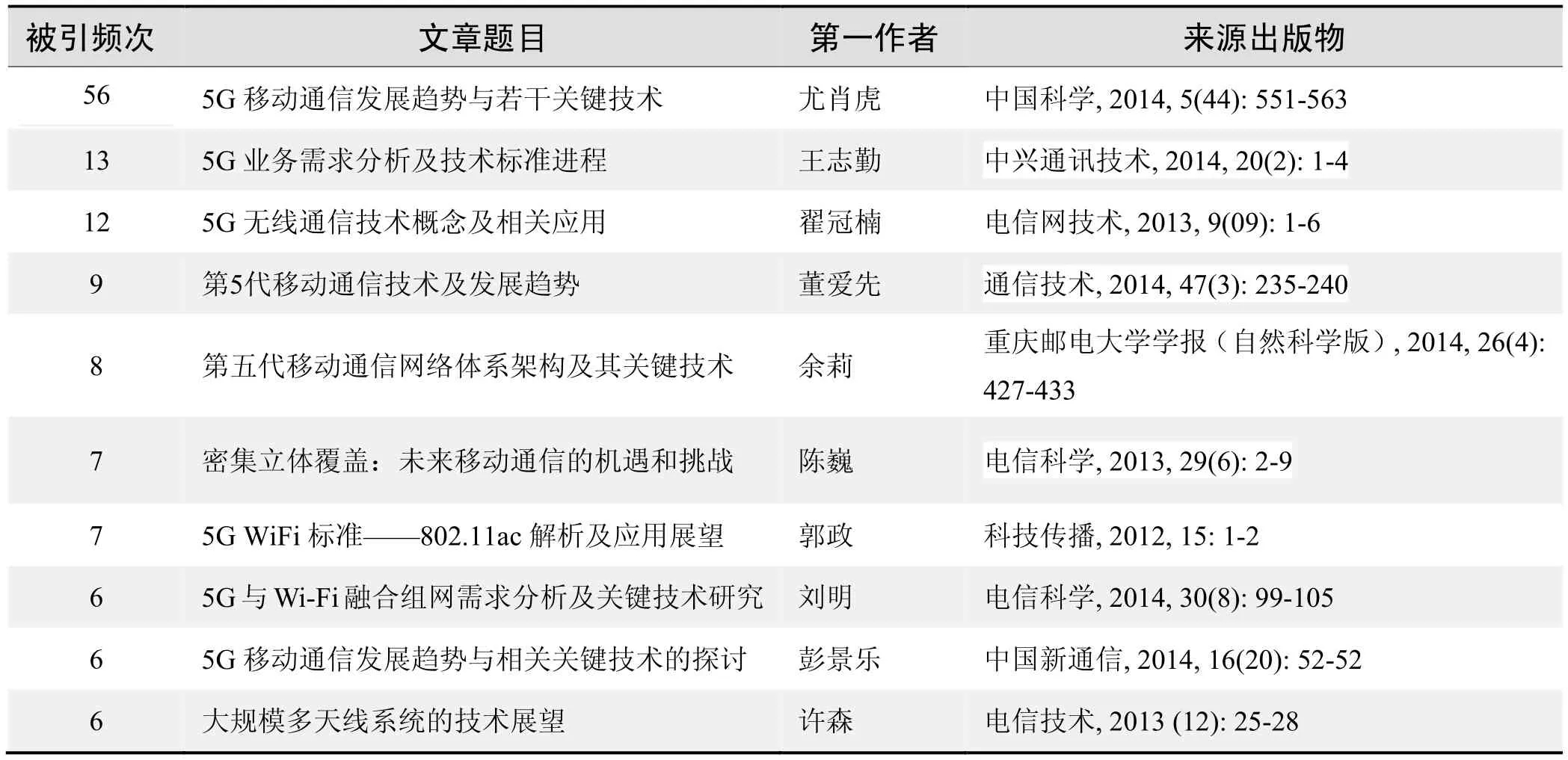
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“5G”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
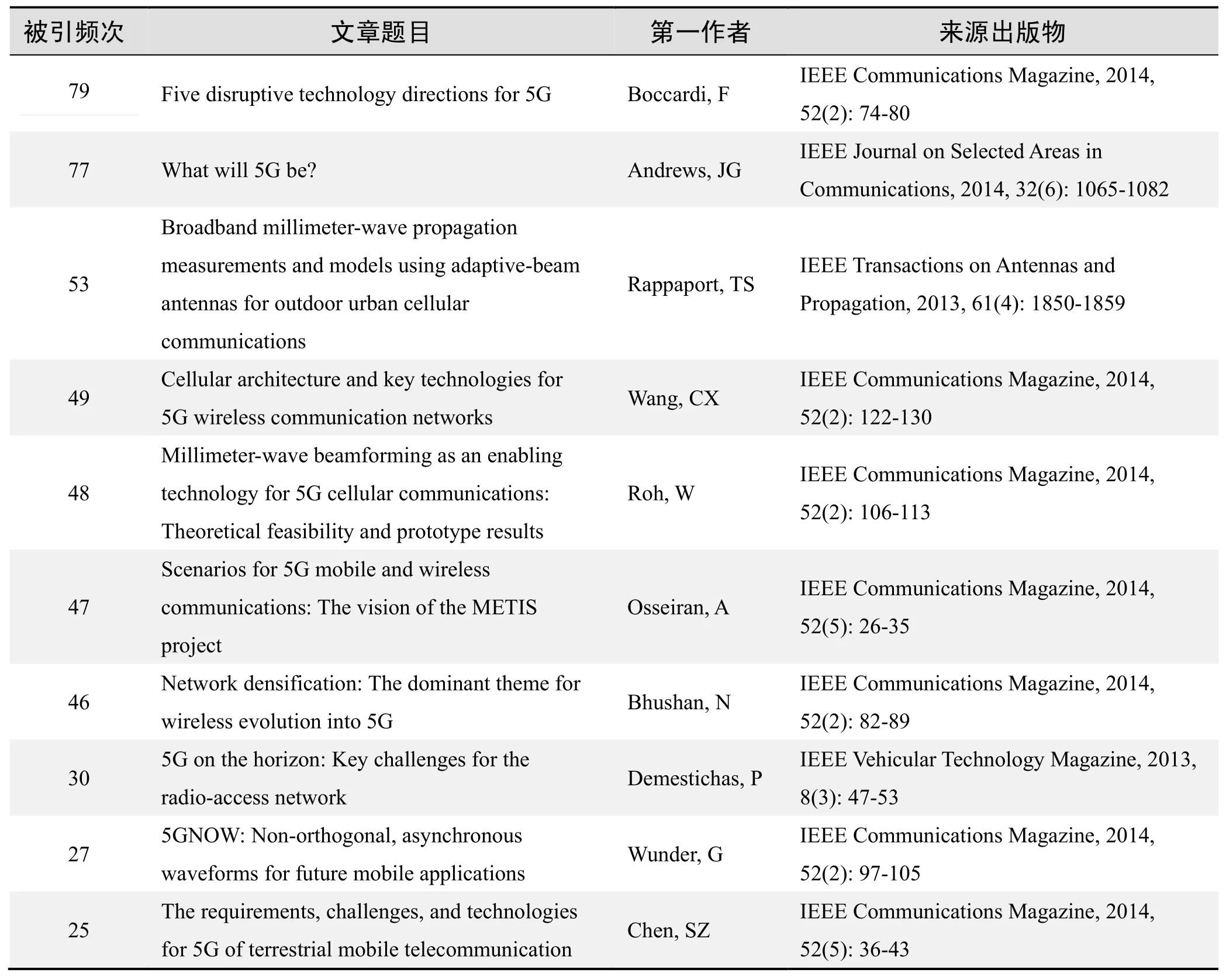
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 100文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
5G on the horizon: Key challenges for the radio-access network
Demestichas, P; Georgakopoulos, A; Karvounas, D; et al.
Abstract:Toward the fifth generation (5G) of wireless/mobile broadband, numerous devices and networks will be interconnected and traffic demand will constantly rise. Heterogeneity will also be a feature that is expected to characterize the emerging wireless world, as mixed usage of cells of diverse sizes and access points with different characteristics and technologies in an operating environment are necessary. Wireless networks pose specific requirements that need to be fulfilled. In this respect, approaches for introducing intelligence will be investigated by the research community. Intelligence shall provide energy and cost-efficient solutions at which a certain application/service/quality provision is achieved. Particularly, the introduction of intelligence in heterogeneous network deployments and the cloud radio-access network (RAN) is investigated. Finally, elaboration on emerging enabling technologies for applying intelligence will focus on the recent concepts of software-defined networking (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV). This article provided an overview for delivering intelligence toward the 5G of wireless/mobile broadband by taking into account the complex context of operation and essential requirements such as QoE, energy efficiency, cost efficiency, and resource efficiency. Self-interference cancellation invalidates a long-held fundamental assumption in wireless network design that radios can only operate in half duplex mode on the same channel. Beyond enabling true in-band full duplex, which effectively doubles spectral efficiency, self-interference cancellation tremendously simplifies spectrum management. Not only does it render entire ecosystems like TD-LTE obsolete, it enables future networks to leverage fragmented spectrum, a pressing global issue that will continue to worsen in 5G networks. Self-interference cancellation offers the potential to complement and sustain the evolution of 5G technologies toward denser heterogeneous networks and can be utilized in wireless communication systems in multiple ways, including increased link capacity, spectrum virtualization, any-division duplexing (ADD), novel relay solutions, and enhanced interference coordination. By virtue of its fundamental nature, self-interference cancellation will have a tremendous impact on 5G networks and beyond. METIS is the EU flagship 5G project with the objective of laying the foundation for 5G systems and building consensus prior tobook=14,ebook=18standardization. The METIS overall approach toward 5G builds on the evolution of existing technologies complemented by new radio concepts that are designed to meet the new and challenging requirements of use cases today's radio access networks cannot support. The integration of these new radio concepts, such as massive MIMO, ultra dense networks, moving networks, and device-to-device, ultra reliable, and massive machine communications, will allow 5G to support the expected increase in mobile data volume while broadening the range of application domains that mobile communications can support beyond 2020. In this article, we describe the scenarios identified for the purpose of driving the 5G research direction. Furthermore, we give initial directions for the technology components (e.g., link level components, multinode/multi-antenna, multi-RAT, and multi-layer networks and spectrum handling) that will allow the fulfillment of the requirements of the identified 5G scenarios. New research directions will lead to fundamental changes in the design of future fifth generation (5G) cellular networks. This article describes five technologies that could lead to both architectural and component disruptive design changes: device-centric architectures, millimeter wave, massive MIMO, smarter devices, and native support for machine-to-machine communications. The key ideas for each technology are described, along with their potential impact on 5G and the research challenges that remain. The ever growing traffic explosion in mobile communications has recently drawn increased attention to the large amount of underutilized spectrum in the millimeter-wave frequency bands as a potentially viable solution for achieving tens to hundreds of times more capacity compared to current 4G cellular networks. Historically, mmWave bands were ruled out for cellular usage mainly due to concerns regarding short-range and non-line-of-sight coverage issues. In this article, we present recent results from channel measurement campaigns and the development of advanced algorithms and a prototype, which clearly demonstrate that the mmWave band may indeed be a worthy candidate for next generation (5G) cellular systems. The results of channel measurements carried out in both the United States and Korea are summarized along with the actual free space propagation measurements in an anechoic chamber. Then a novel hybrid beamforming scheme and its link-and system-level simulation results are presented. Finally, recent results from our mmWave prototyping efforts along with indoor and outdoor test results are described to assert the feasibility of mmWave bands for cellular usage.
来源出版物:IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2013, 8(3): 47-53
Applications of self-interference cancellation in 5G and beyond
Hong, S; Brand, J; Il Choi, J; et al.
来源出版物:IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 114-121
Scenarios for 5G mobile and wireless communications: The vision of the METIS project
Osseiran, A; Boccardi, F; Braun, V; et al.
来源出版物:IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(5): 26-35
Five disruptive technology directions for 5G
Boccardi, F; Heath, RW; Lozano, A; et al.
来源出版物:IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 106-113
·推荐综述·
来源出版物:IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 74-80
Millimeter-wave beamforming as an enabling technology for 5G cellular communications: Theoretical feasibility and prototype results
Roh, W; Seol, JY; Park, J; et al.
文献编号本领域经典文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 5G on the horizon: Key challenges for the radio-access network Demestichas, P IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2013, 8(3): 47-53 2Applications of self-interference cancellation in 5G and beyond Hong, S IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 114-121 3 Scenarios for 5G mobile and wireless communications: The vision of the METIS project Osseiran, A IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(5): 26-35 4Five disruptive technology directions for 5G Boccardi, F IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 74-80 5 Millimeter-wave beamforming as an enabling technology for 5G cellular communications: Theoretical feasibility and prototype results Roh, W IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 106-113

