ON THE FINITE MELLIN TRANSFORM IN QUANTUM CALCULUS AND APPLICATION∗
Bochra NEFZIKamel BRAHIM Ahmed FITOUHI
Faculty of Sciences of Tunis,University of Tunis El Manar,Tunisia
E-mail:asimellinbochra@gmail.com;kamel.brahim@ipeit.rnu.tn;ahmed. fitouhi@fst.rnu.tn
Abstract The aim of the present paper is to introduce and study a new type of q-Mellin transform[11],that will be called q- finite Mellin transform.In particular,we prove for this new transform an inversion formula and q-convolution product.The application of this transform is also earlier proposed in solving procedure for a new equation with a new fractional differential operator of a variational type.
Key words q-Mellin transform; finite Mellin transform;fractional q-integral;fractional q-differential equation
1 Introduction
Quantum calculus is the modern name for the investigation of the calculus without limits.The first formulae,which is well known as q-calculus,was obtained by Euler in the eighteenth century.In 1910,Jackson[13]introduced the notion of the definite q-integral and q-derivative,citing that he was the first to develop q-calculus in a systematic way.In the second half of the twentieth century there was a significant increase of activity in the area of the q-calculus due to its applications in mathematics,number theory and combinatorics[2].In addition,there was a great deal of interest in the study of quantum algebra and quantum group in connection with several physical fields[4].Beside the mathematical aspect and specially in view of physical meaning,the q-calculus plays a crucial role in the representation of quantum groups(see[6,18]).Today,and according to Ernst[9,10],the majority of scientists who use q-calculus are physicists,and he cites Jet Wimp[22].
The field has expanded explosively,due to the fact that applications of basic hypergeometric series to the diverse subjects of combinatorics,quantum theory,number theory,statistical mechanics,are constantly being uncovered.
During the last decade and within the harmonic analysis group,Fitouhi et al were interested to q-analogue of Mellin transform while remaining faithful the technique and the rigour of Titchmarsh.In fact,q-Mellin transform[11]is frequently applied when solving q-integral and q-differential equations especially q-differential equations of fractional order(see[1,3,5,7]).
Historically,the first occurrence of the Mellin transform is found in a memoir by Riemann in which he used it to study the famous Zeta function.However,it is the Finnish mathematician,Mellin(1854–1933),who was the first to give a systematic formulation of the transformation and its inverse.In short,the Mellin transform has many interesting applications in several areas of mathematics and mathematical sciences such as in field theory,special functions,differential equations,hypergeometric series,physical sciences,engineering.
In order to extend the applicability of the classical Mellin transform,Naylor(1963)introduced set of eight integral transforms that are suited to solve intial and boundary-value problems involving Laplace’s operator on regions bounded by the natural coordinate surfaces of cylindrical or spherical coordinate systems.Naylor[20]called these transforms the finite Mellin-type integral transforms since they are extensions of the classical Mellin integral transform.Recently,these transforms were the subject of several works(see[8,15–17]).
In the present paper,we start with the study of the q-analogue of the finite Mellin transform studied earlier in[15],that will be called q- finite Mellin transform.We also discuss its properties and we give its inversion formula.In the other hand,our purpose is the introduction of a new concepts of q-fractional quantum calculus by defining a new fractional q-integral and qderivative.New definitions of Riemann-Liouville fractional q-integral and q-difference are given and their basic properties are discussed.As application,we will apply the q- finite Mellin transform and its properties to solve a new class of fractional q-differential equation.
The paper is organized as follows:we summarize in Section 2,preliminaries and notations about some main properties of the q-theory.In Section 3,we introduce the q- finite Mellin transform,discuss its definition domain,its properties,and we give some examples.Special attention is devoted to the inversion formula of the q- finite Mellin transform and its convolution product.Section 4 is devoted to define a new fractional q-integral and q-derivative.We discuss some properties and their relations.Finally,the procedure of solving the new fractional qdifferential equation is explained in detail.
2 Preliminaries
Throughout this paper N,Z,R+,R and C will denote the set of natural numbers,integers,non-negative real numbers,real numbers and complex numbers,respectively.
We recall that
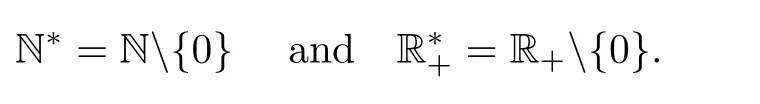
In what follows,we will fix q∈]0,1[and we write
•Rq,+={qn,n∈Z}.
• For b>0 and a=bqn,n=1,2,···,∞,
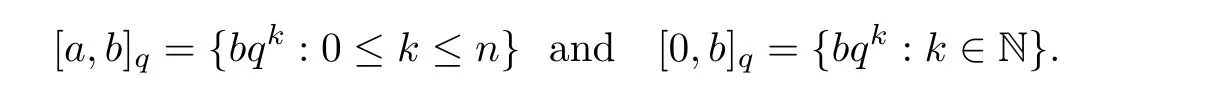
We refer to[12],[14]and[19]for the definitions,notations,properties of the q-shifted factorials,the Jackson’s q-derivative and the Jackson’s q-integrals.
Let a∈C,the q-shifted factorials are defined by
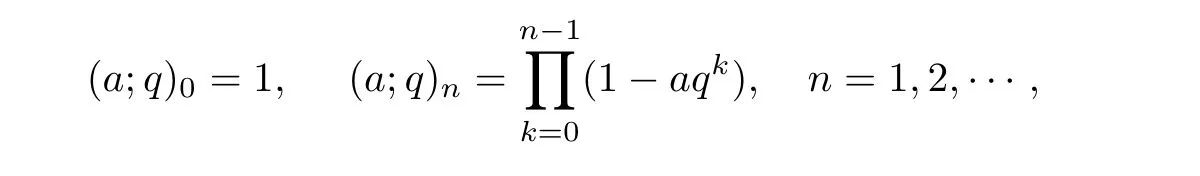
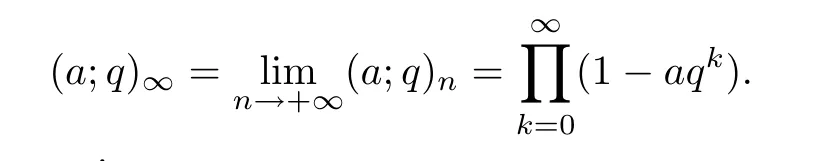
For negative subscripts,we write
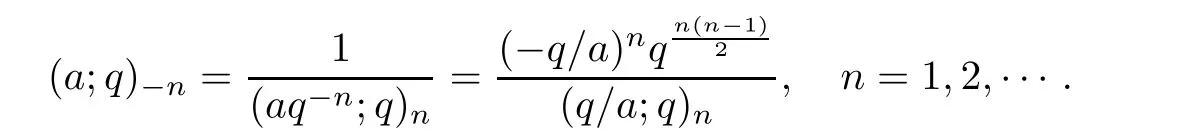
We note for a1,a2,···,ap∈ C,

We recall that
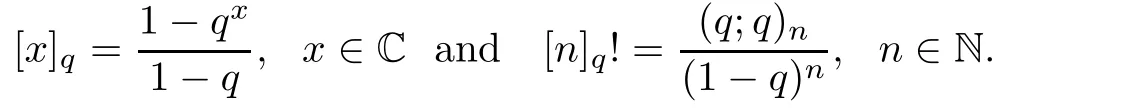
The q-analog of the power(a−b)kis(see[21])

Natural extensions is given for real α by

Note that

where
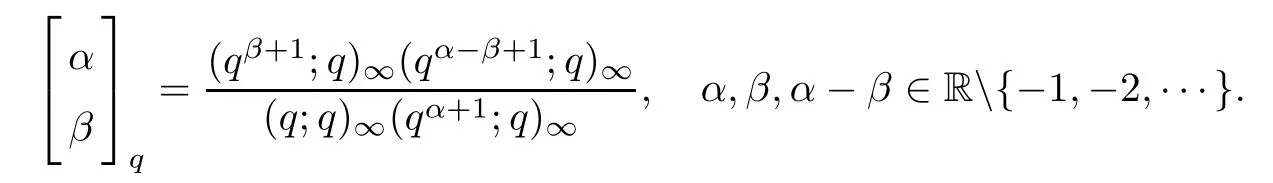
Lemma 2.1(see[21]) The following identities are true

The q-hypergeometric functions are defined by
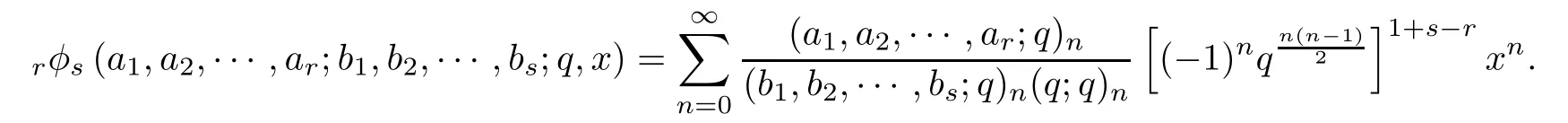
The q-derivatives Dqf and D+qf of a function f are given by

Dqf(0)=f′(0)and D+qf(0)=q−1f′(0)provided f′(0)exists.Note that when f is differentiable at x,then Dqf(x)and D+qf(x)tends to f′(x)as q tends to 1−.
Definition 2.2(see[1,13]) Let f be a function,real or complex valued defined on a q-geometric set A,i.e.,a subset of R for which qt∈A whenever t∈A.
1.For a,b∈A such that a provided that the series at the right-hand side of(2.2)converges at x=a and at x=b. 2.If f is defined on Rq,+,the q-Jackson integral from 0 to∞is given by provided the series converges absolutely. We remark that for n∈N∗,we have The q-analogues of the exponential function are given by(see[11,12]) It is well known that The q-analogue of the Gamma function is defined by(see[13,19]and[21]) having the integral representation and the q-analogue of the fundamental formula is given by The q-Beta function is defined by Definition 3.1 Let a>0 and let f be a function defined on[0,a]q.We define the q- finite Mellin transform of f as provided the q-integral exists. Proposition 3.2 Let f be a function defined over[0,a]qand let uis bounded,then(f)(s)exists in the strip Notation In the rest of this paper,we denote by the strip in which Maq(f)(s)exists and is well defined. In the following subsection,we give some interesting properties of the q- finite Mellin transform. •(P1)For all b∈Rq,+,we have •(P2)If f(a)=0,then •(P3)If f(a)=0,then By induction,suppose that f(a)=Dqf(a)= ···=Dn−1qf(a)=0,then for all integer n ≥ 1,we have • (P4)Let f be a function defined on[0,aq−1]qsuch that f(q−1a)=0,then Let f be a function defined on[0,aq−n]q,n ∈ N∗.By induction,suppose that then • (P5)Given ρ >0.For every s ∈ C such that R(s)> ραqρ,f,we have •(P6)For all s∈C such that R(s)>max{0,αq,f−1},we get Indeed In this subsection,we give explicitly the q- finite Mellin transform of some functions such as the q-Exponential functions. By using(2.3),the above example can be modified as follows: This is the well known q-integral representation of the q-analogue of the Beta function. Example 3.5 Let f(x)=E−1/xq.Then for all s∈C,we have Theorem 3.9 Let f be a function defined over[0,a]qand give c∈]αq,f,∞[,then The interchange of series and integral are justified by the uniform convergence of the following series Definition 3.10 The q- finite Mellin convolution product of f and g is given by Proposition 3.11 If the q- finite Mellin convolution product of f and g exists,then Proof For n∈N,we have Then for all s∈ C such that R(s)>max{αq,f,αq,g},we obtain and the result follows. Proposition 3.12 1.Let f and g be two functions defined on[0,a]qsuch that the strip If;g=hαq,f,1−αq,gi is not empty.Then for every c∈R∩If;gwe have 2.Let f and g be two functions defined on[0,a]q.For all c′>max{αq,f;αq,g},we have Proof 1.To prove the first relation,let c∈ R∩If;gthen c∈]αq,f,∞[and 1−c∈]αq,g,∞[.We put From the q-inversion theorem,the Fubini’s theorem,the continuity of Maq(f)and the relation we obtain 2.To prove the second relation let c′∈]max{αq,f;αq,g},∞[.Then relation(3.13)and the q-inversion formula lead to the results for x=a. ? In[3]the authors introduced the Riemann-Liouville fractional operator and using the q-Mellin transform early deeply studied in[11]to solve some dual q-integral equations.It seems that this last approach can not be adopted when we restrict us with the set[0,a]q.To overcome this situation,we include in this section a new definition of fractional q-integral and q-derivative of q-fractional order and in general variable coefficients.We generalize their notions and we discuss some properties and their relations. Finally,the procedure of solving a new fractional q-differential equation with right-sided q-derivatives is explained in detail. In what follows,we assume that the function f is defined on[0,aq−1]q. Now,let us define the new fractional q-integral by Remark 4.1 1.Let n∈N.For x=aqn,the above q-integral can be expressed in its equivalent sum form 2.For α=1,the fractional q-integral(4.1)satisfies In the following lemma,we compute the q- finite Mellin transform of the fractional q-integral Lemma 4.2 For a suitable function f,we have Proof For R(s)>max{0,αq,f−α}, Lemma 4.3 For α>0,we have Proof Since the q-derivative over the variable t is and by using the q-integration by parts, We get Lemma 4.4 For α,β >0,we have Proof Using the following properties of Lemma 2.1,we have Theorem 4.5 Let α,β >0,the new q-fractional integration has the following semi-group property ProofBy Lemma 4.4,we have Then for all j∈N,we get In[21]it was proved that for µ,α and β ∈ R+, Then,we obtain Lemma 4.6 For α ∈ R∗+and λ ∈ (−1,+∞),we get We define the new fractional q-derivative by where[α]denotes the smallest integer greater than or equal to α. Lemma 4.7 For α ∈ RN∗,we have Proof We will consider three cases. 1.For α ≤ −1,according to relation(4.3)and Theorem 4.5,we have 2.In the case−1<α<0,i.e.,0<α+1<1,we have 3.For α>0,we have Theorem 4.8 For α ∈ RN∗,the following is valid Proof According to formulas(4.3),Theorem 4.5 and Lemma 4.6,we have for α<0, If α >0,there exists m ∈ N∗,such that α ∈ (m,m+1).Then,applying again the same procedure,we obtain Proposition 4.9 Let n∈N∗.Then the q-differential equation has a general solution in the form Proof We rely on the induction hypothesis.For n=1,thanks to formula(4.3),we get We assume that so Lemma 4.10 Let α ∈ R∗+and f be a function defined on[0,aq−1]q,then the following is valid Proof For α>0,we have Lemma 4.11 Let α ∈ R∗+and f be a function defined on[0,aq−1]q.Then,we have where where c1(a)and cα,k(a)do not depend on x. Proof 1.For α ∈(0,1),we have On other hand,by Theorem 4.5 and Lemma 4.3,we have Thus,we get 2.For α=1,we have 3.For α>1,we have On other hand,by using the q-integration by parts and relation(4.3),we have Then by Theorem 4.5,we get Next,using relation(4.17),we prove that By induction,we obtain Replacing g by H[α]−αq,af in the previous expression,we get Hence,for α>1 we have where Proposition 4.12 Let α ∈ R∗+.Then for R(s)>0,we have where fαis the function defined in Lemma 4.11. Proof 1.For α=1,we have 2.For α>1,by using relation(2.1),we have Then,by q-binomial Theorem(see[11]),we get This concludes the proof. Let us consider the following fractional q-differential equation where fαis the function defined in Lemma 4.11. Now,by applying the q- finite Mellin transform on(4.19),we obtain here we have put and denoting by Tα+βthe translation operator acting on functions of the complex variable as follows:Tα+βh(s):=h(s+α+β). Let n be an arbitrary natural integer.From equation(4.20),we have for R(s)>0 when R(α + β)>0. Summing the previous expression for n=0,···,j,we obtain From the d’Alembert test it follows that,the series is absolutely convergent for|λ| On the other hand,for R(s)>0 when R(α + β)>0,we have Let us discuss the more general situation when the function g is replaced by the product where hlis a function defined by Indeed,we have where thus G denotes the finite q-Mellin transform of the function h defined by Applying the inverse and the convolution formulas of the q- finite Mellin transform,we obtain the solution given as the series of h in the convolution with the stationary function multiplied by a power function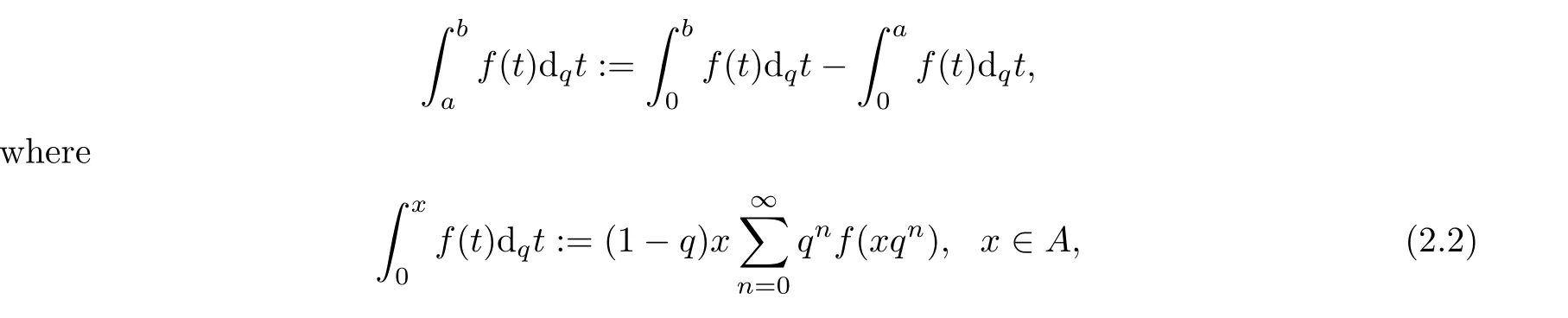
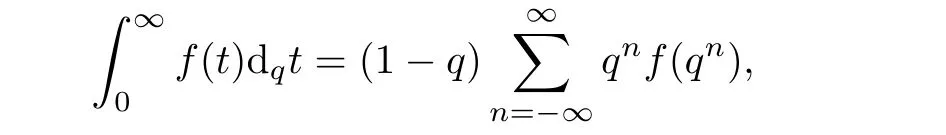
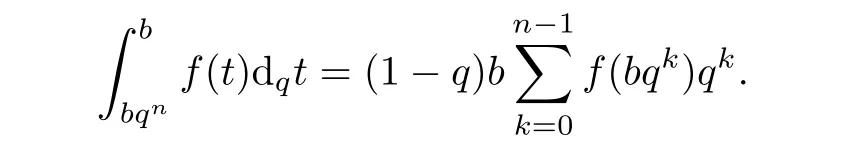
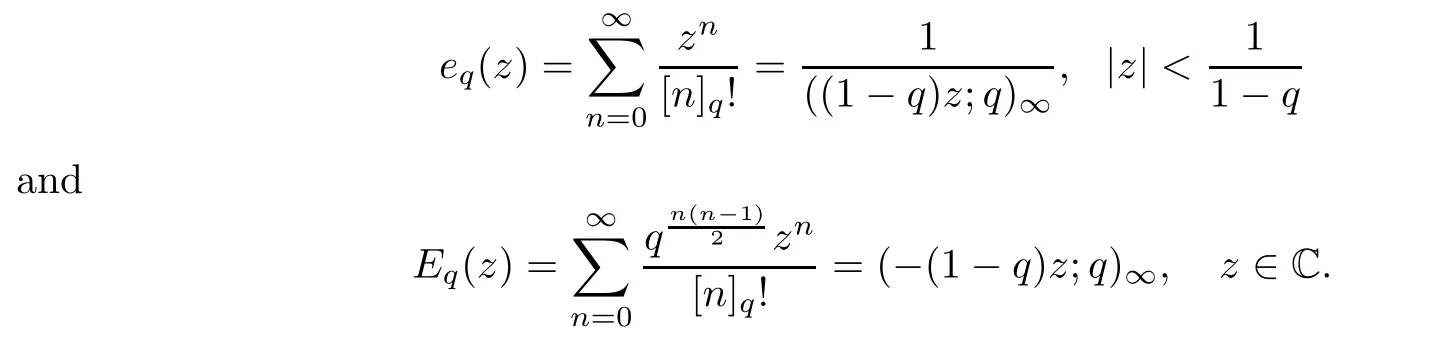





3 The q-Finite Mellin Transform
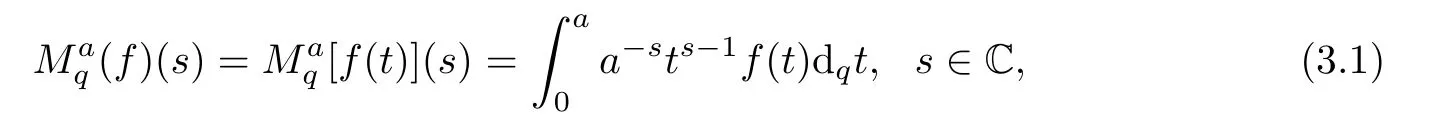
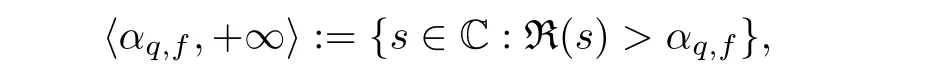
3.1 Properties
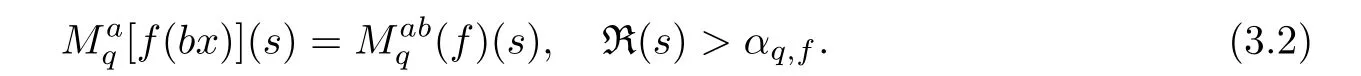

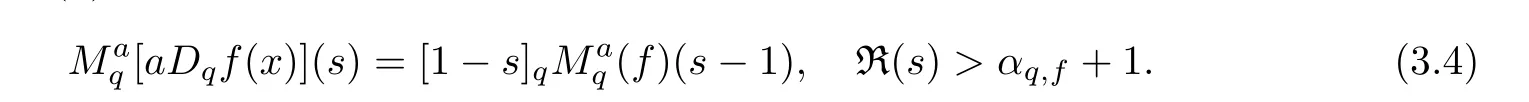
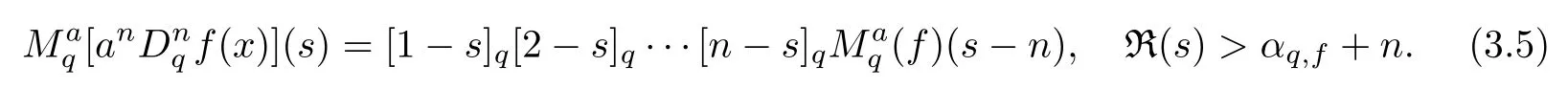
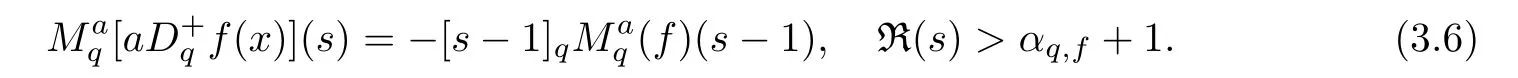





3.2 Examples

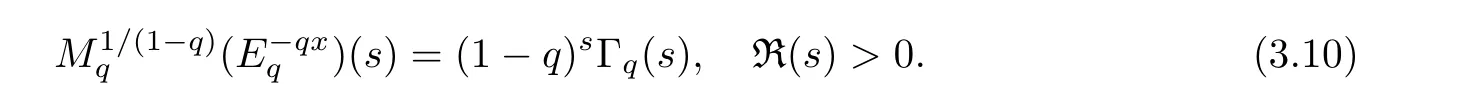


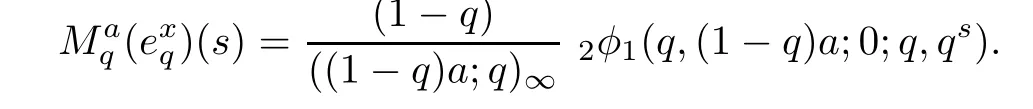
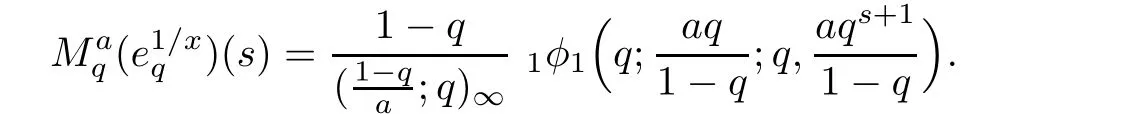

3.3 The q-Finite Mellin Inversion Formula


3.4 Finite q-Convolution Product
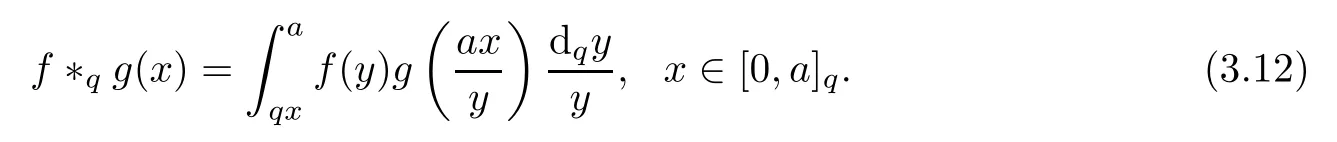

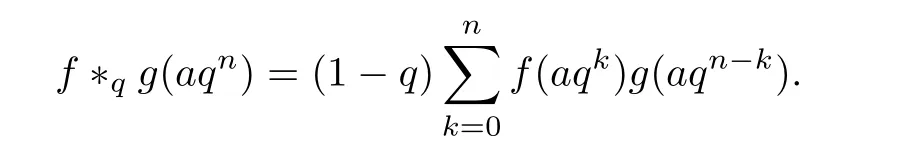
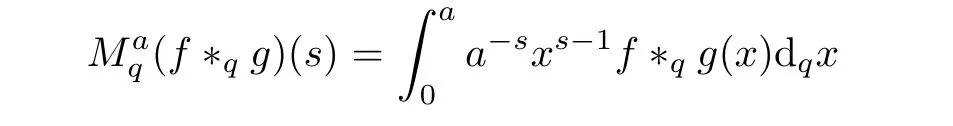


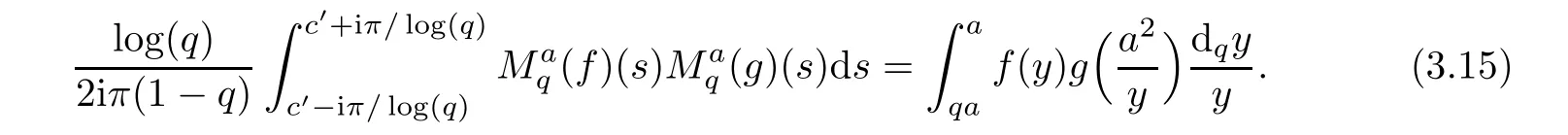
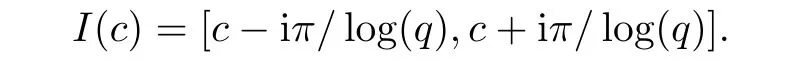


4 A New Fractional q-Differential Equation
4.1 A New Fractional q-Integral

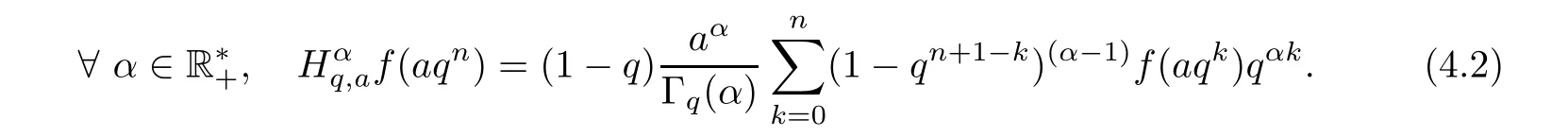





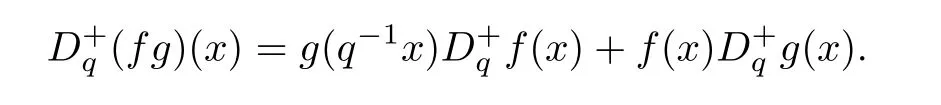
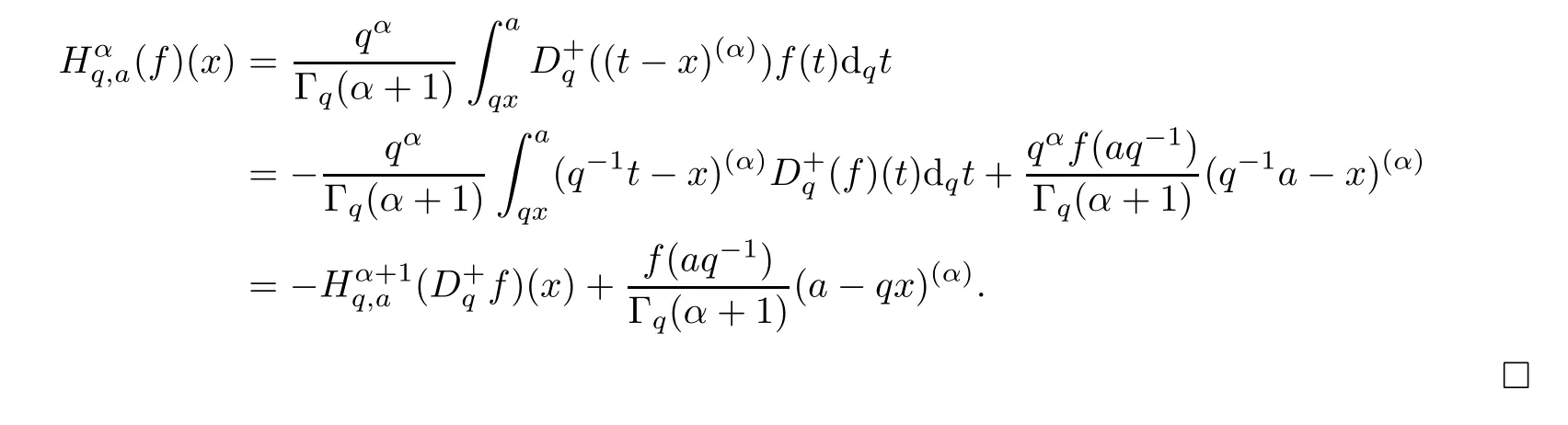
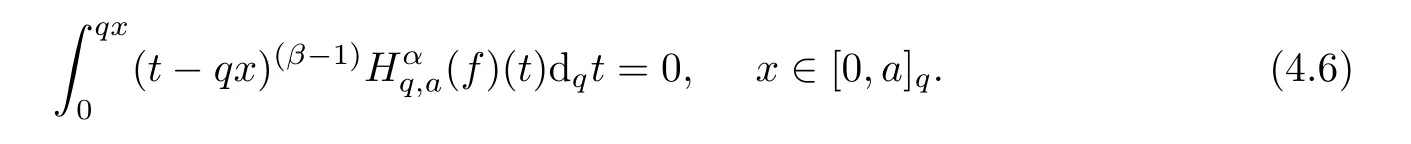
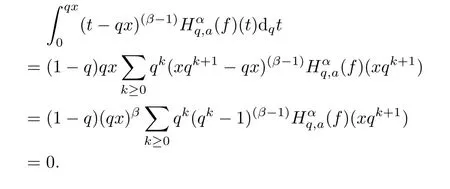

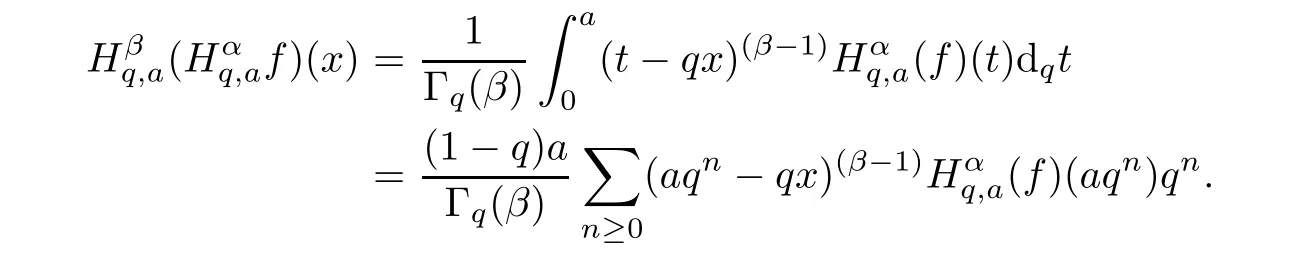
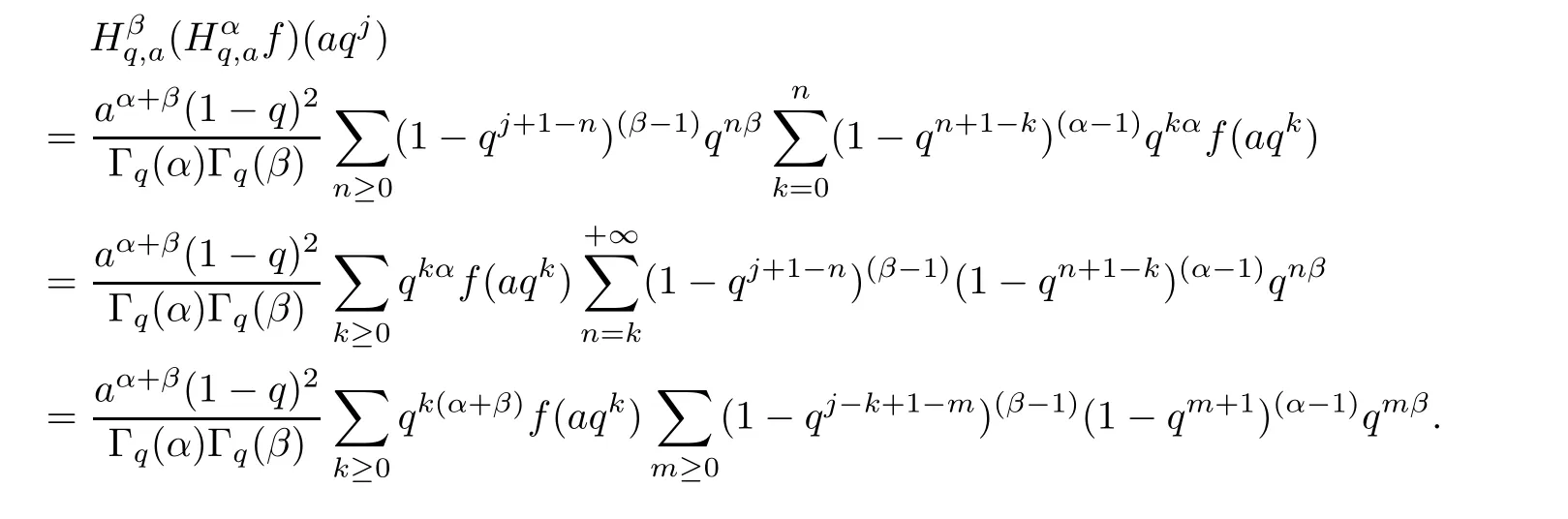
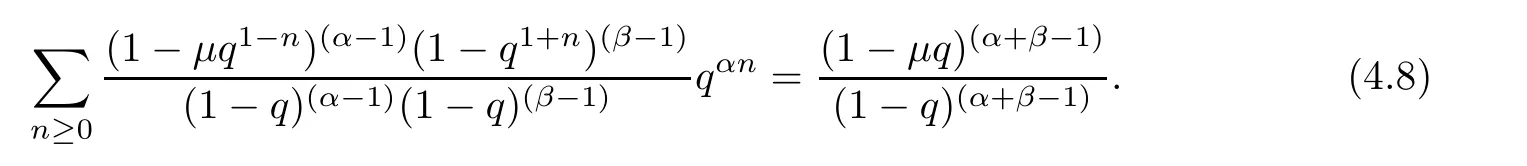


4.2 A New Fractional q-Derivative

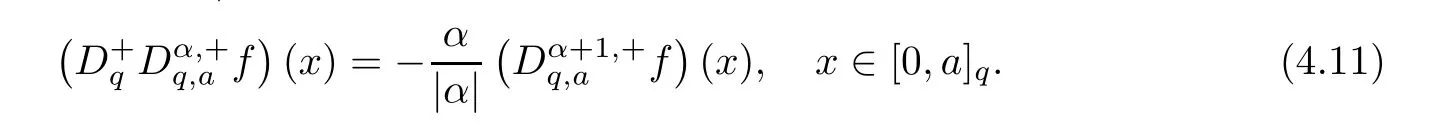
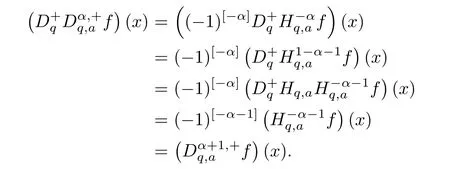






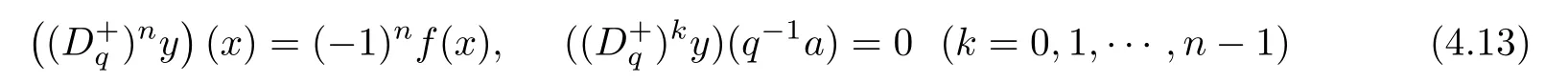
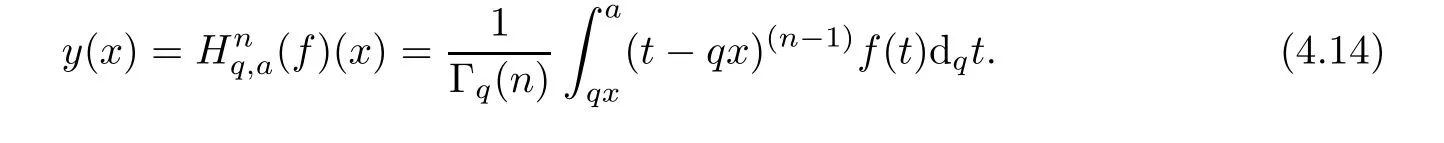

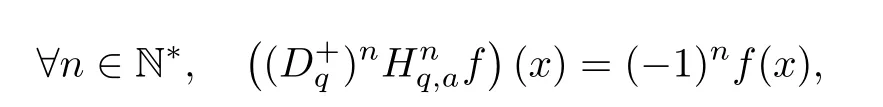

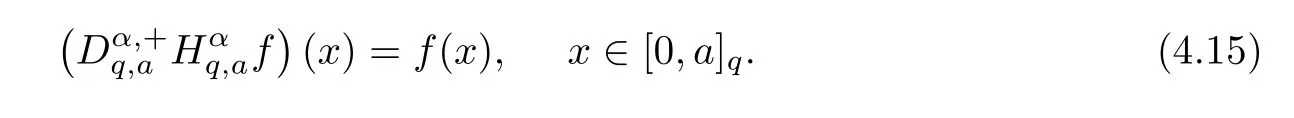
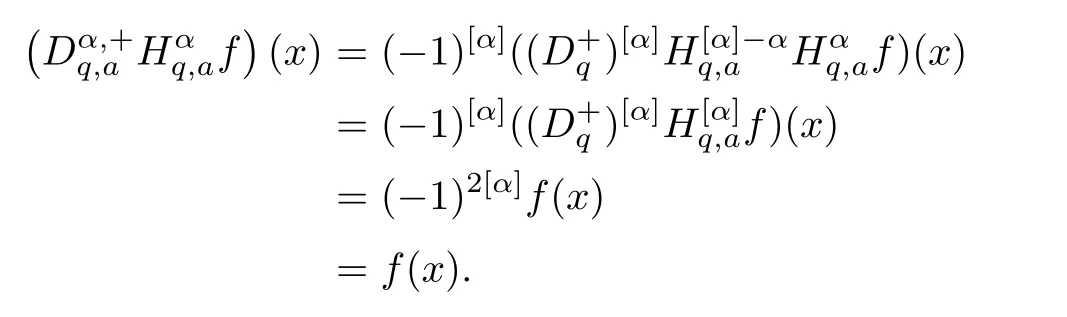
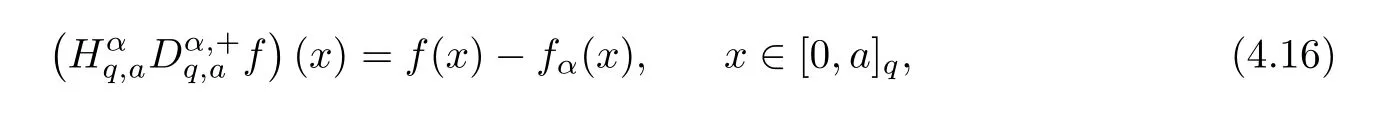

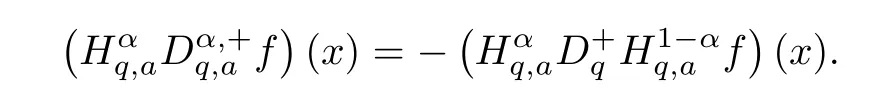
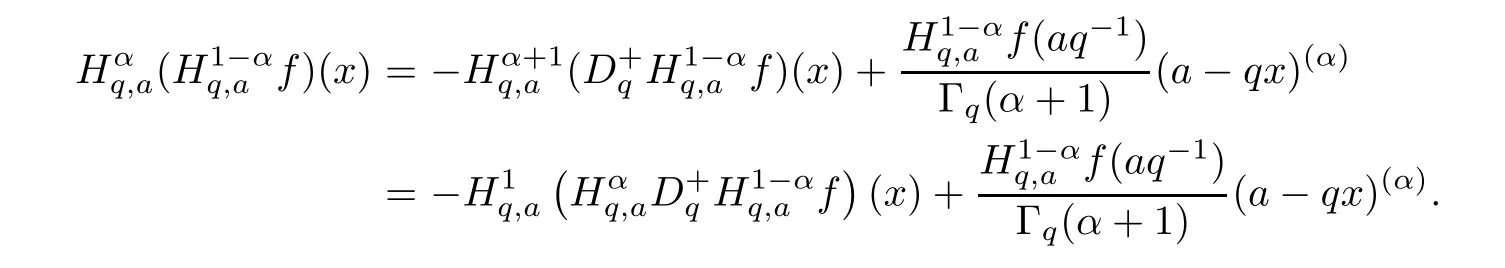




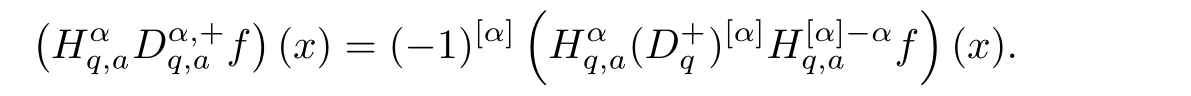
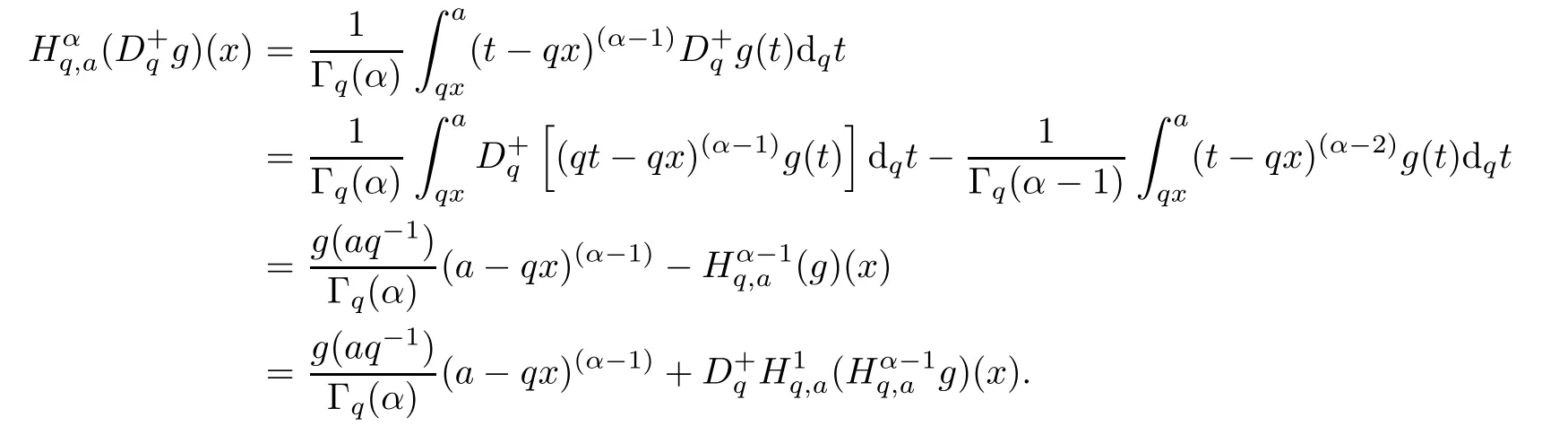





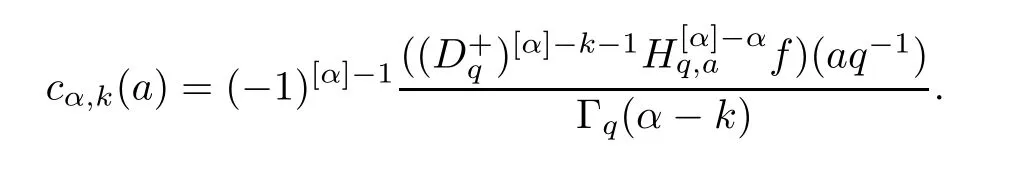
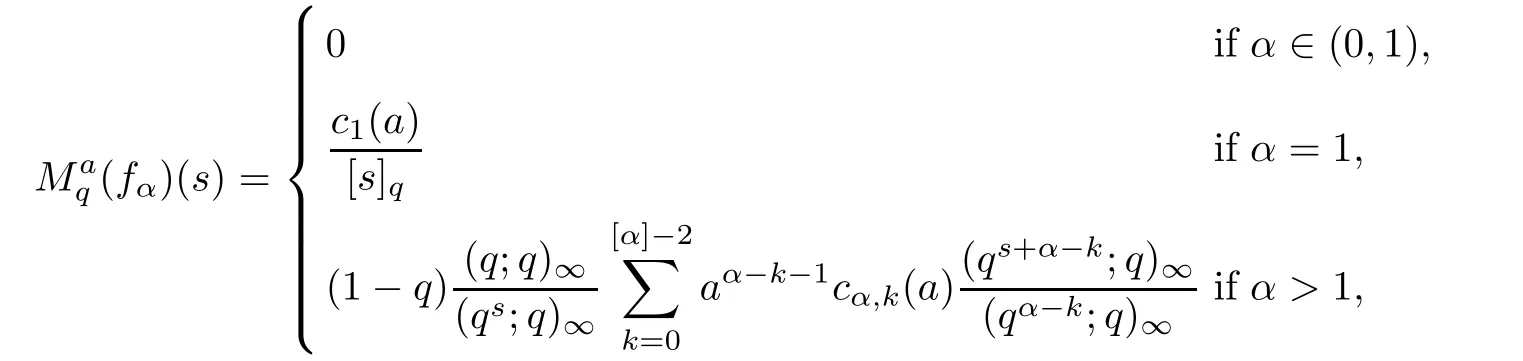
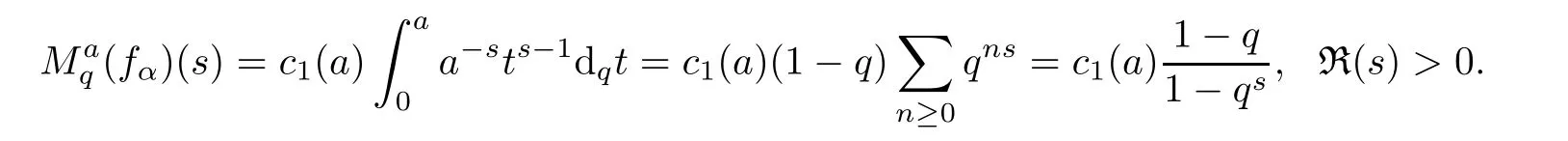

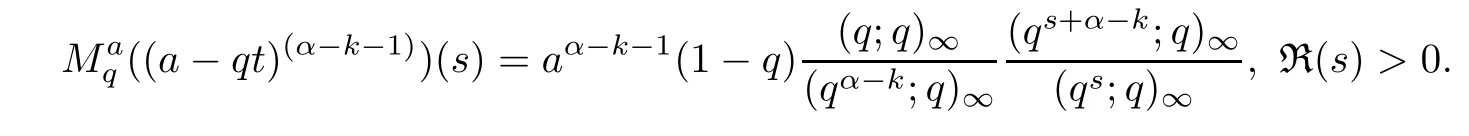
4.3 Application


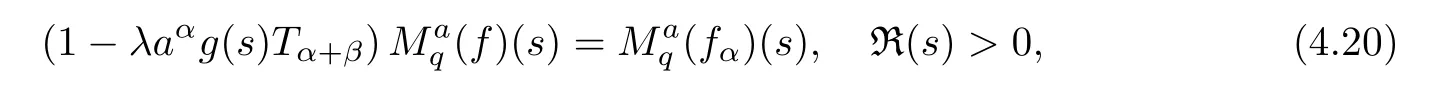



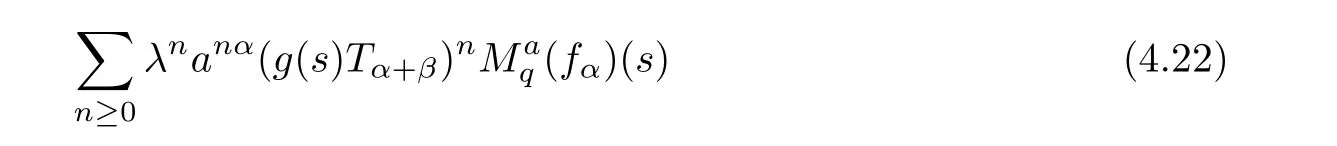
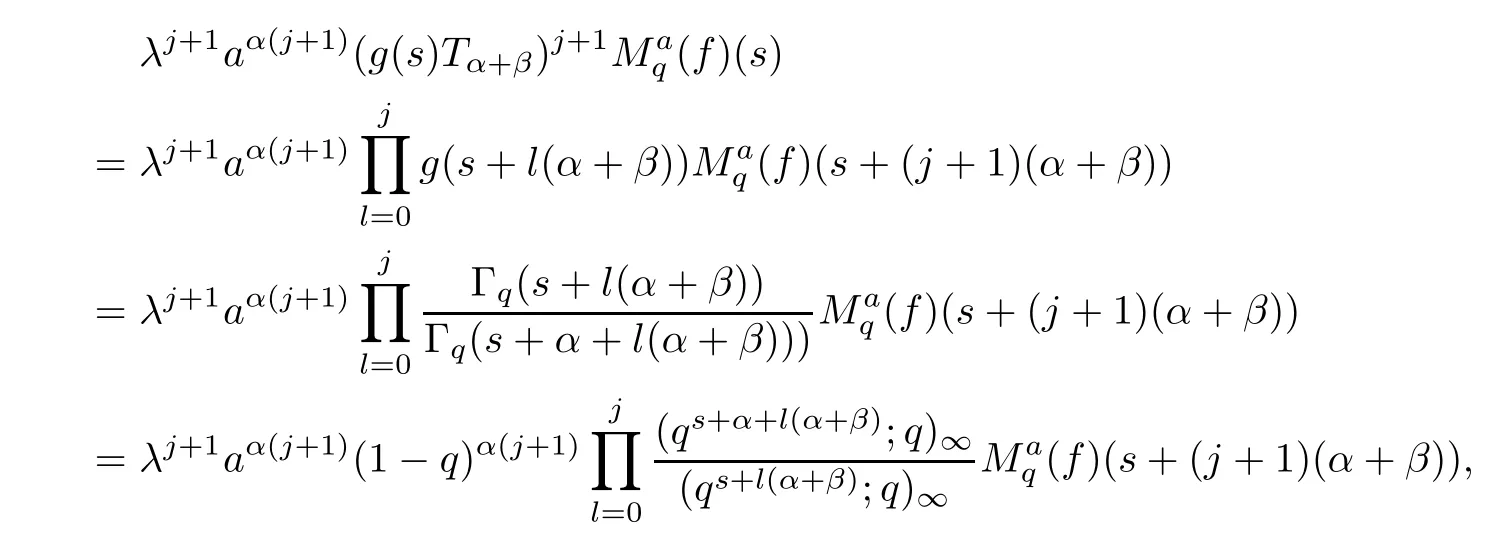

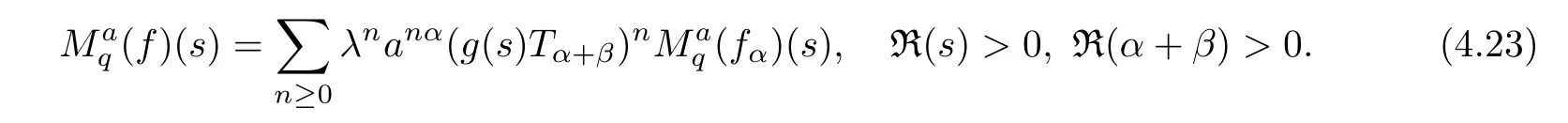


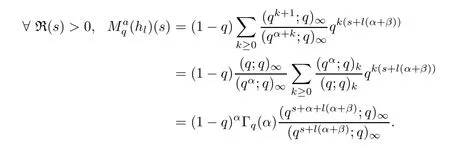



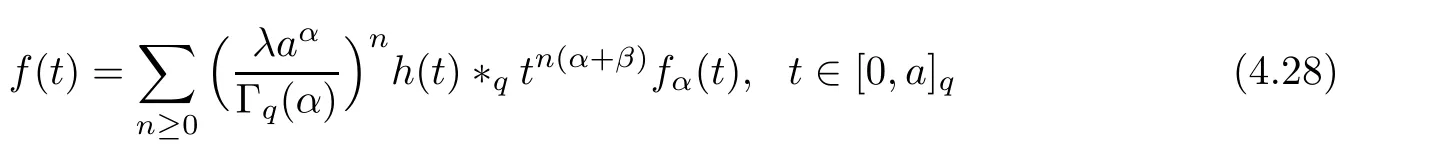
 Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2018年4期
Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)2018年4期
- Acta Mathematica Scientia(English Series)的其它文章
- PRODUCTS OF WEIGHTED COMPOSITION AND DIFFERENTIATION OPERATORS INTO WEIGHTED ZYGMUND AND BLOCH SPACES∗
- A NOTE ON THE UNIQUENESS AND THE NON-DEGENERACY OF POSITIVE RADIAL SOLUTIONS FOR SEMILINEAR ELLIPTIC PROBLEMS AND ITS APPLICATION∗
- SOLUTIONS TO THE SYSTEM OF OPERATOR EQUATIONS AXB=C=BXA∗
- BURKHOLDER-GUNDY-DAVIS INEQUALITY IN MARTINGALE HARDY SPACES WITH VARIABLE EXPONENT∗
- CHAIN CONDITIONS FOR C∗-ALGEBRAS COMING FROM HILBERT C∗-MODULES∗
- SINGULAR LIMIT SOLUTIONS FOR 2-DIMENSIONAL ELLIPTIC SYSTEM WITH SUB-QUADRTATIC CONVECTION TERM∗
