种植手术同期根向复位瓣附着龈重建的临床研究
闫树伟
[摘要] 目的 探索一种简单高效的手术方法,用于增加种植体周围的附着龈宽度并且能缩短种植修复的疗程。探讨根向复位瓣附着龈重建术的效果。 方法 收集有种植修复需求的患者8例,但种植位点处附着龈宽度小于2 mm,行种植手术同期利用根向复位瓣技术进行附着龈重建。术后2周拆线。8周后常规种植上部修复并负荷。分别观察手术前、术后8周、修复完成即刻、修复完成1年时附着龈宽度的变化情况。 结果 所有患者种植体周围的附着龈宽度明显增加,修复完成1年后未见明显附着龈退缩。术后2 周拆线,除 1个种植位点在术后第2天因缝合线脱落致黏膜仍有炎症外,其余位点黏膜愈合良好。 结论 根向复位瓣附着龈重建术创伤小,并且同期种植手术可以缩短种植修复疗程,术后患者恢复效果较好。可以作为增加种植体周围附着龈宽度的简单高效的方法。
[关键词] 附着龈重建;种植修复;根向复位瓣;附着龈宽度
[中图分类号] R783 [文獻标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)03-0060-03
[Abstract] Objective To explore a simple and effective surgical method for increasing the width of attachment gingiva around the implant and shortening the course of implant restoration. Methods Eight patients required for planting repair were collected, whose attachment gingiva width at the implantation sites was less than 2 mm. The apically repositioned flap surgery for attachment gingiva reconstruction was performed during implantation. The suture was removed 2 weeks after surgery. After 8 weeks, the upper part of planting was routinely restored and loaded. The changes of the width of attachment gingiva were observed before surgery, at 8 weeks after surgery, immediately after the repair was completed, and 1 year after the repair was completed. Results The width of the attachment gingiva around the implants was significantly increased in all patients. After 1 year of repair, no obvious attachment gingiva retraction was observed. The suture was removed at 2 weeks after the operation, except for 1 planting site in which the mucosa still had inflammation on the 2nd day after surgery due to the suture detachment, and the mucosa of the other sites healed well. Conclusion The apically repositioned flap surgery for attachment gingiva reconstruction is less invasive, and the simultaneous implantation surgery can shorten the implantation and repair course. The recovery effect of the postoperative patients is better. It can be used as a simple and efficient method to increase the width of the attachment gingiva around the implant.
[Key words] Attachment gingiva reconstruction; Planting repair; Apically repositioned flap; Attachment gingiva width
近年来,随着口腔种植修复技术和材料的不断发展,有关种植体骨结合的研究已经成熟,但是在保证种植体达到骨结合的基础上如何对种植体周围的软组织进行处理是近年来研究的热点。附着龈是自游离龈沟至牙槽黏膜的部分,与游离龈合称角化龈。附着龈在游离龈根方,紧密附着在牙槽嵴表面,具有保护牙周组织抵抗咀嚼食物、刷牙等刺激等作用[1-3]。临床上常见种植位点处的附着龈较窄甚至缺失。研究发现,种植体周围附着龈不足会导致种植体周围黏膜炎症加重、菌斑积聚增加[4-5]。因此,应采取必要措施来增加种植体周围附着龈的宽度,本研究通过探索一种简单高效的手术方法,用于增加种植体周围的附着龈宽度并且能缩短种植修复的疗程。目前临床对附着龈宽度进行重建,其中根向复位瓣术是常用方法,本研究旨在探讨根向复位瓣附着龈重建术的效果。现报道如下。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
收集有种植修复需求的患者8例,共10个种植位点,均位于下后牙区。采用Straumann SLAcive种植系统。
1.2 附着龈宽度的测量
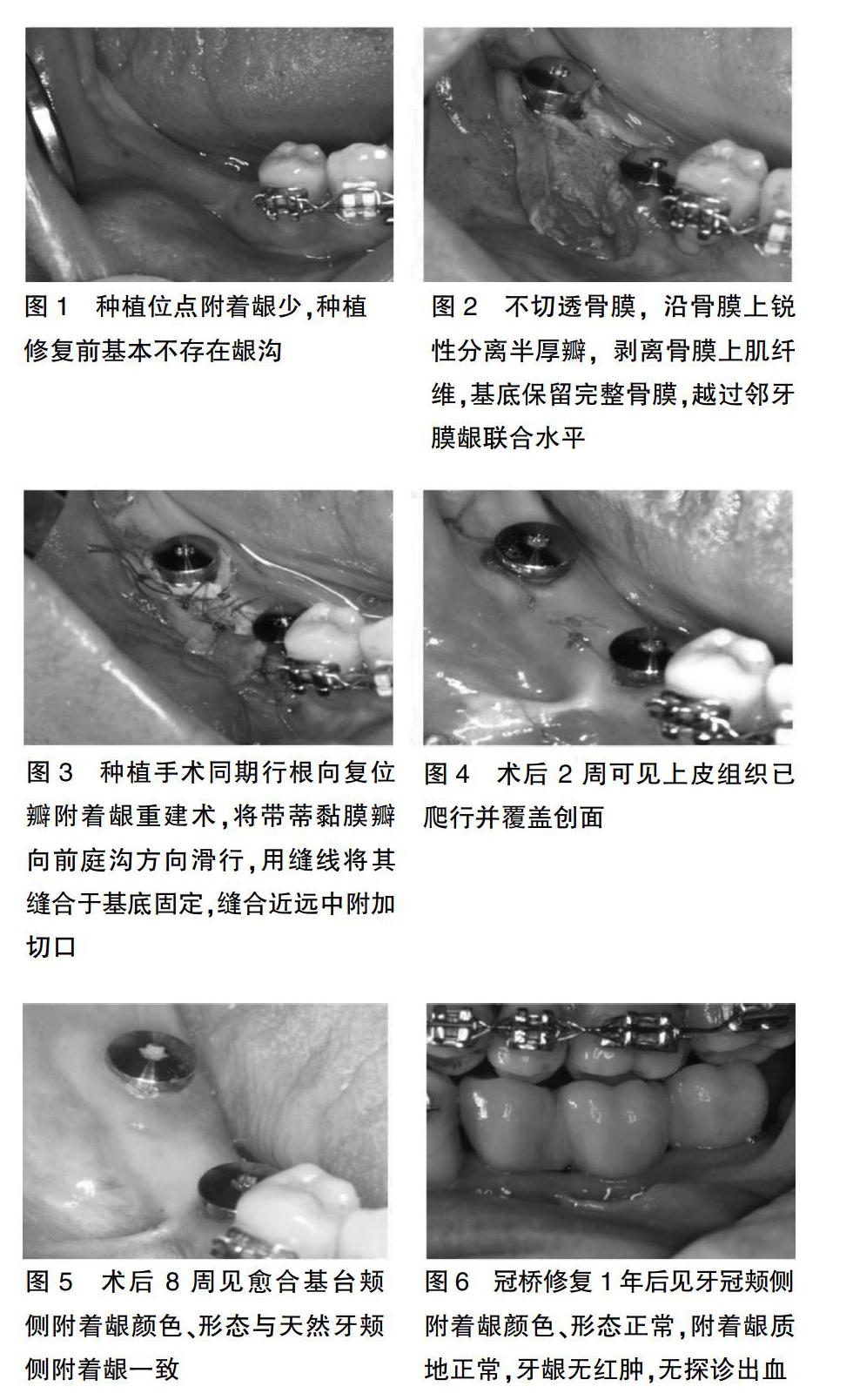
由于种植位点种植修复前基本不存在龈沟(图1),本研究中术前及术后8周附着龈的宽度被定义为膜龈联合处至牙槽嵴颊舌向中点连线的距离,而牙冠修复完成即刻及牙冠修复完成1年后附着龈的宽度被定义为膜龈联合处至牙冠颊侧边缘最低处的距离。
1.3 手术方法
从牙槽嵴顶偏舌侧作保留龈乳头的梯形切口,并使切口两侧均有角化牙龈。不切透骨膜,沿骨膜上锐性分离半厚瓣,剥离骨膜上肌纤维,基底保留完整骨膜,越过邻牙膜龈联合水平(图2)。球钻确定种植位点,环钻去除种植位点处骨膜,常规行种植手术,植入Straumann SLAcive植体,扭力均>25 N.cm,安放愈合基台。同期行根向复位瓣附着龈重建术,将带蒂黏膜瓣向前庭沟方向滑行,用缝线将其缝合于基底固定(图3)。
1.4 观察指标
患者冠修复1年后复诊,检查记录下列牙周指标。①改良菌斑指数(mPI):0-无菌斑;1-仅用探针尖轻划种植体表面可发现菌斑;2-肉眼可见菌斑;3-大量软垢。②探诊深度(PD):使用专用的牙周探针所测得的龈袋或牙周袋的深度,即龈缘至袋底或龈沟底的距离,是重要的牙周临床指标。③出血指数(BI):用鈍头探针轻探入龈沟或袋底,取出探针30 s后观察有无出血及出血程度,适用于牙龈炎症较重的人群观察治疗前后效果的临床研究。
2 结果
8例患者的10个种植位点进行了种植手术同期根向复位瓣附着龈重建术。术后2周拆线,除1个种植位点在术后第2天因缝合线脱落致黏膜仍有炎症外,其余位点黏膜愈合良好。术后 8周取印模时,即已形成正常的附着龈,膜龈联合的位置与邻牙处相协调。种植上部修复及复诊:术后2周可见上皮组织已爬行并覆盖创面(图4)。术后4周复诊,见术区已形成大量健康成熟的附着龈组织。术后8周见愈合基台颊侧附着龈颜色、形态与天然牙颊侧附着龈一致(图5)。常规采印,全瓷冠桥最终修复。冠桥修复1年后复诊,见牙冠颊侧附着龈颜色、形态正常,附着龈质地正常,牙龈无红肿,无探诊出血(图6)。
2.1 附着龈宽度的测量
附着龈宽度术前平均为(0.61±0.18)mm,术后 8周平均为(5.31±0.61)mm,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),平均增加 4.7 mm。附着龈宽度在冠修复即刻平均为(3.81±0.66)mm,1年后平均为(3.63±0.54)mm,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
2.2 牙周指标
冠修复1年后复诊结果显示患者口腔卫生情况基本良好,所有种植体均保持稳定,重建的附着龈无明显炎症并紧密贴合于全瓷冠。mPI平均为(0.38±0.17);PD平均为(1.61±0.52)mm,无深牙周袋;BI 平均为(0.64±0.12)。
3 讨论
3.1 附着龈重建的重要性
以往,口腔种植学先后经历了以外科为导向的种植理念和以修复为导向的种植理念。
目前以生物学为导向的种植理念被广泛认可与接受,对种植体和修复体的位置形态及种植牙周围软组织的位置形态要符合生物学规律。只有存在足够的角化黏膜区域才能维持软组织与种植体间较理想的功能状态。有研究显示,附着龈不足或缺失不利于种植体菌斑的控制及口腔卫生,甚至会产生许多并发症,建议种植修复牙冠颊侧最好有至少2 mm的附着龈[6-9]。因此,对于附着龈不足的患者,建议考虑附着龈的增量手术。
3.2根向复位瓣附着龈重建的方法评价
目前常用的附着龈重建方法包括:软组织瓣转移术、黏膜游离移植、结缔组织游离移植、脱细胞真皮基质移植、胶原基质或其他生物工程材料移植等,临床尚缺乏统一的方案[10]。根向复位瓣术是牙周常用的术式之一,其可以最大程度地消除牙周袋,增加附着龈。特别是在附着龈宽度较窄的牙位更加适合根向复位瓣手术。这项技术不仅用于牙周的附着龈增量,包括种植体周围的附着龈增量也是常用的一种基本技术。根向复位瓣术具有许多设计形式,可以单纯根向复位,也可以根据需要暴露适当宽度的骨膜带[11-13]。如 Carnio 等[14]提出的改良根向复位瓣术对多个邻牙采用单一的附着龈内水平切口。Thoma 等[15]的研究也证实了根向复位瓣术进行附着龈重建具有较好的效果。本研究使用的附着龈重建方法即是在根向复位瓣术基础上进行的改良,手术操作简便,减少了手术次数,缩短了种植修复的疗程。
综上所述,根向复位瓣附着龈重建术创伤小,并且同期种植手术可以缩短种植修复疗程,术后患者恢复效果较好,可以作为增加种植体周围附着龈宽度的简单高效的方法。
[参考文献]
[1] Shepherd N,Greenwell H,Hill M,et al. Root coverage using acellular dermal matrix and comparing a coronally positioned tunnel with and without platelet-rich plasma:a pilot study in humans[J].Periodontol,2009,80(3):397-404.
[2] Bouri A Jr,Bissada N,Al -Zahrani MS,et al. Width of keratinized gingiva and the health status of the supporting tissues around dental implants[J]. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants,2008,23(2): 323-326.
[3] Chung DM,Oh TJ,Shotwell JL,et al. Significance of keratinized mucosa in maintenance of dental implants with different surfaces[J].J Periodontol,2006,77(8):1410-1420.
[4] Kim BS,Kim YK,Yun PY,et al. Evaluation of peri -implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa[J].Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod,2009,107(3):e24-e28.
[5] Agarwal Chitra,Tarun Kumar AB,Mehta Dhoom Singh. Comparative evaluation of free gingival graft and AlloDerm in enhancing the width of attached gingival:A clinical study[J]. Contemporary Clinical Dentistry,2015, 6(4):483-488.
[6] Kim Chang-Soon,Duong Hieu Pham,Park Jung-Chul,et al. Preservation of keratinized mucosa around implants using a prefabricated implant-retained stent:A case-control study[J]. Journal of Periodontal & Implant Science,2016,46(5):329-336.
[7] 李鵬,姜宝岐,兰晶,等. 角化龈重建在口腔种植修复中的应用[J]. 上海口腔医学,2013,22(2):214-218.
[8] Rusu Darian,Calenic Bogdan,Greabu Maria,et al. Evaluation of oral keratinocyte progenitor and T-lymphocite cells response during early healing after augmentation of keratinized gingiva with a 3D collagen matrix-a pilot study[J]. BMC Oral Health,2016,17(1):9.
[9] Karring T,Lang NP,L?觟e H. The role of gingival connective tissue in determining epithelial differentiation[J]. J Periodontal Res,1975,10(1):1-11.
[10] 徐守吉,刘倩倩.改良根向复位瓣术对种植二期手术患者实施附着龈重建治疗的临床修复效果观察[J]. 当代医学,2017,23(33):62-63.
[11] 李海霞.附着龈重建在口腔种植修复中的应用价值研究[J].中华全科医学,2016,(1):44-46.
[12] 杨沐. 附着龈重建在口腔种植修复中的应用研究[J]. 中国医药指南,2016,14(17):15-16.
[13] 孙瑾. 附着龈重建在口腔种植修复中的应用探索[J]. 中国美容医学,2014,23(16):1369-1371.
[14] Carnio J,Camargo PM,Passanezi E. Increasing the apico-coronal dimension of attached gingiva using the modified apically repositioned flap technique:a case series with a 6-month follow up[J]. J Periodontol,2007,78(9):1825-1830.
[15] Thoma DS,Benic GI,Zwahlen M,et al. A systematic review assessing soft tissue augmentation techniques[J]. Clin Oral Implants Res,2009,20(Suppl 4):146-165.
(收稿日期:2018-12-12)

