被动负刚度装置与线性滞回阻尼器组合对斜拉索多模态振动的阻尼效果
孙利民 孙浚杰 狄方殿 邹易清 王萌 陈林

摘 要:提出了结合负刚度装置提升线性滞回阻尼器对斜拉索多模態振动控制效果的方法.考虑被动负刚度装置与阻尼器在斜拉索上任意位置安装,采用斜拉索两点施控系统特征方程,讨论了安装位置、线性滞回阻尼器参数、负刚度系数等对斜拉索多模态阻尼的影响.结果表明,被动负刚度装置能有效提升线性滞回阻尼器对斜拉索的多阶模态阻尼比,其安装位置越靠近阻尼器,阻尼提升效果越明显.进一步,以苏通大桥某附有黏性剪切阻尼器的超长拉索为例进行了实际设计,讨论了被动负刚度的可行性,并与结合惯容器的阻尼器进行了对比,结果表明,被动负刚度装置对斜拉索-阻尼器系统多模态阻尼提升效果更好.
关键词:斜拉索振动;多模态阻尼;负刚度装置;线性滞回阻尼;惯容器
中图分类号:U441.3 文献标志码:A
Multimode Damping of a Stay Cable Attached with a Negative Stiffness Device and a Linaear Hysteretic Damper
SUN Limin1,2,SUN Junjie1,DI Fangdian2,ZOU Yiqing3,WANG Meng4,CHEN Lin1?
(1.Department of Bridge Engineering,Tongji University,Shanghai 200092,China;
2.State Key Laboratory of Disaster Reduction in Civil Engineering(Tongji University),Shanghai 200092,China;
3.Liuzhou OVM Machinery Co,Ltd,Liuzhou 545006,China;
4.Key Laboratory of Urban Security and Disaster Engineering of Ministry of Education(Beijing University of Technology),Beijing,100124,China)
Abstract:Multimode damping of a stay cable attached with a negative stiffness device(NSD)and a linear hys-teretic damper was studied.The frequency equation of a cable under transverse control forces at two locations is used for damping analyses by considering arbitrary NSD and damper locations.The effects of NSD and damper locations,damper parameters and negative stiffness values on multimode damping of stay cable are examined.It can be found that the multimode cable damping values can be significantly enhanced comparing with the single linear hysteretic
damper.The closer the installation locations,the higher the damping level.Furthermore,multimode damping effect of the combinations is verified by using a long stay cable installed with a viscous shear damper on the Sutong Bridge,together with an inertial damper.The feasibility of the NSD is carefully discussed.The results show that the NSD is more helpful to enhance the multimode damping comparing with the inertial damper.
Key words:stay cable vibration;multimode damping;negative stiffness;linear hysteretic damping;inertial damper
斜拉索是斜拉桥最为关键的受力构件之一,但 很容易出现异常振动[1].因此,斜拉索振动与控制问 题受到了广泛关注[2].例如,在运营期的风、雨和车 辆等作用下,其常出现明显甚至是大幅振动[3-4],严 重威胁着桥梁的适用性和安全性[5].
为有效控制斜拉索振动,工程中常在索端安装阻尼器增加索的模态阻尼[6].现有研究表明,阻尼器的固有刚度会减小斜拉索振动过程中阻尼器的相对变形,削弱对索的阻尼效果[5].相反,通过主动、半主动或被动控制方法实现的负刚度能够增加阻尼器位置处的斜拉索位移,从而提高阻尼效果.H?gsberg等[6]在结构振动控制中考虑了具有负刚度系数和可采用分数阶导数模型描述的阻尼器,表明该阻尼器可提供相位超前的阻尼力;还发现由于安装阻尼器而增加的质量同样能增大位移,从而增强阻尼效果.
近年来,基于惯性质量和负刚度机理的减振效果提升手段是结构减振抗震研究的热点.基于惯容器的结构振动控制研究可追溯到Ikago等[7]和Lazar等[8].后续研究考虑了不同惯容器、弹簧和阻尼器组 合的动力性 能[9-10]、振 控效果[11-12]和基 础 隔 震 性 能[13-14]等.Lazar等[15]、Sun等[16]、Lu等[17]较早在斜拉索-阻尼器系统中引入惯容器,引起了该领域学者的关注[18-22].进一步研究中关注了具有惯性质量效果的阻尼器的研发,如陈政清等[23]、孙洪鑫等[24]、李亚 敏等[25]采用电磁技术同时实现惯性力和阻尼力,并采用实索试验进行了验证[26].
结构振动控制中关于负刚度现象的研究可追溯到Iemura等[27-28].早期学者们从摩擦、半主动或主动控制装置的力-位移滞回曲线中观察到减振装置的负刚度行为,称其为表观负刚度或伪负刚度(PNS).随后,发展了基于PNS的半主动和主动控制算法,相关研究包括Iemura等[29]、Li等[30]、Ou等[31]、H?gs-berg[32]、Weber等[33].2013年,Sarlis等[34]、Pasala等[35]研发了基于预压缩弹簧的被动负刚度装置(NSD),并开展了试验验证.针对斜拉索减振,Chen等[36]将 NSD与黏滞阻尼器结合,突破了传统阻尼器对斜拉索附加阻尼的限制.Zhou等[37]进一步开展了附加NSD和黏滞阻尼器的斜拉索的模型试验,验证了NSD结合阻尼器可作为斜拉索半主动或主动拉索控 制的经济有效的替代方案[38-39].
斜拉索减振实践中常见的阻尼器,例如高阻尼橡胶阻尼器[40]和黏性剪切阻尼器[6],均可用线性滞回阻尼模型描述其力学行为.即将此类阻尼器建模为一个具有复刚度和损耗因子的弹簧.现有研究已量化了其对斜拉索的阻尼效果[41-42],亦分析了在斜拉索上同时安装多个线性滞回阻尼器以及与其他阻尼器组合时的优化设计[43-45].线性滞回阻尼器可为拉索各阶模态提供几乎相等的阻尼,但与黏滞阻尼器相比,其最优附加阻尼受到自身刚度效应的限制,导致阻尼效果偏低.因此,本文提出利用负刚度装置 提升线性滞回阻尼器对斜拉索的阻尼效果.NSD可与阻尼器在新桥建设时在同一位置安装,亦可以在斜拉索减振系统维护升级时安装.因此将考虑 NSD与阻尼器分别在索端部任意位置安装的情况,通过理论研究和实际设计案例,讨论NSD的效果和可行性.
1斜拉索阻尼器系统复频率方程
本节首先建立斜拉索阻尼器系统的动力方程,然后采用复数模态分析方法得到系统的复频率方程,进而建立系统复频率方程数值求解方法.
1.1系统动力方程
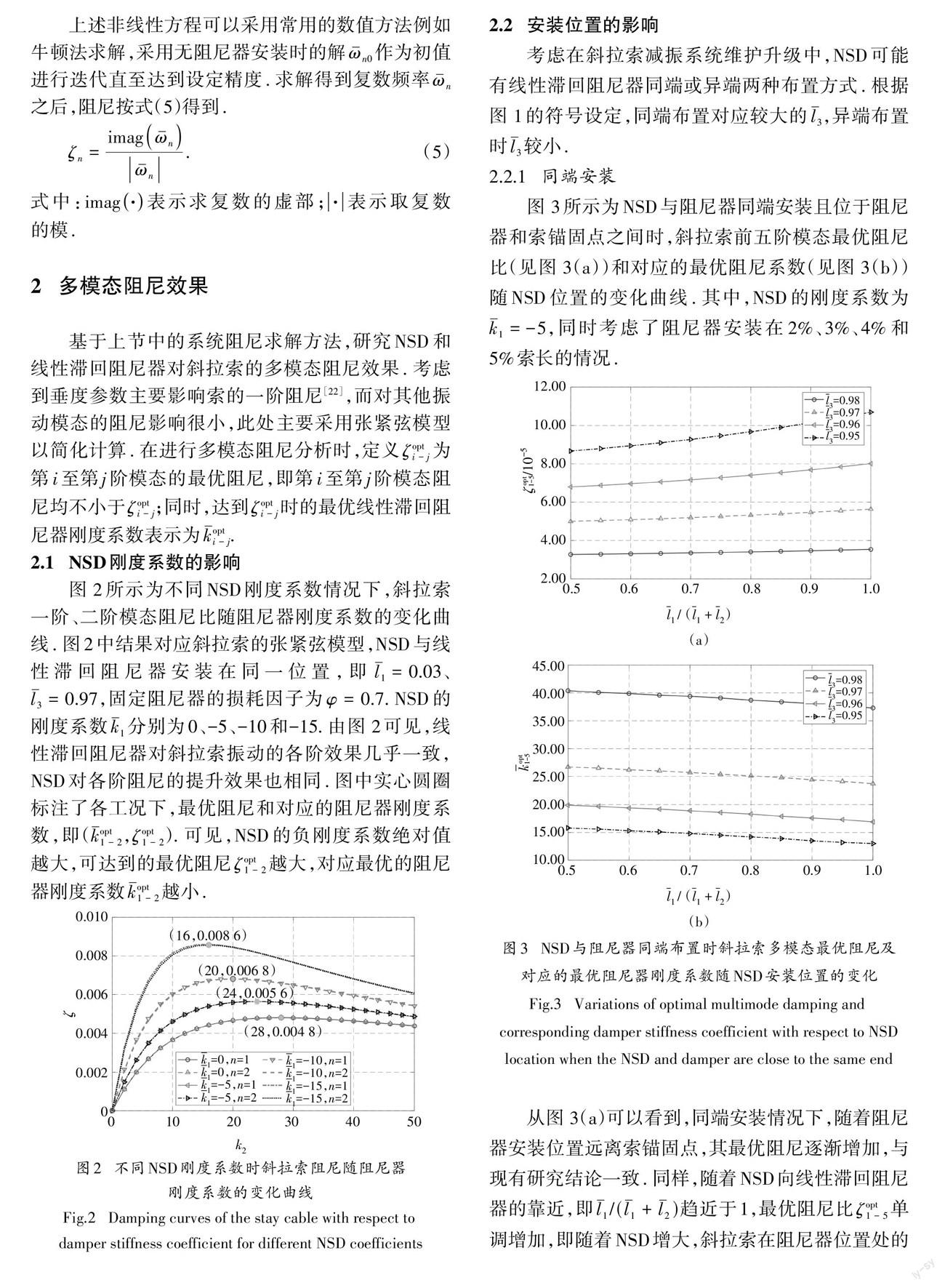
图1为一根斜拉索上安装 NSD和线性滞回阻尼器进行组合减振的示意图.斜拉索通过变换后水平 放置,以弦线为x 轴,其弦长为L,水平张力为T,拉索单位长度质量为m,轴向刚度为EA,对于长索,其抗 彎刚度和拉索自身阻尼可忽略不计[46].图1中,k1为NSD的刚度系数,k2为线性滞回阻尼器的刚度系数,φ为损耗因子.y(x)和v(x,t)分别表示斜拉索在重力下的变形和动位移.
对于斜拉索,其静止状态的形状可假定为抛物线函数:
2多模态阻尼效果
基于上节中的系统阻尼求解方法,研究 NSD 和线性滞回阻尼器对斜拉索的多模态阻尼效果. 考虑到垂度参数主要影响索的一阶阻尼[22],而对其他振动模态的阻尼影响很小,此处主要采用张紧弦模型以简化计算. 在进行多模态阻尼分析时,定义 ζoi p-t j为第i至第j阶模态的最优阻尼,即第i至第j阶模态阻尼均不小于ζoi p-t j;同时,达到ζopt i-j时的最优线性滞回阻尼器刚度系数表示为kˉoi p-t j.
2.1NSD刚度系数的影响
图2所示为不同NSD刚度系数情况下,斜拉索一阶、二阶模态阻尼比随阻尼器刚度系数的变化曲线. 图2中结果对应斜拉索的张紧弦模型,NSD与线性滞回阻尼器安装在同一位置,即lˉ1=0.03、l-3=0.97,固定阻尼器的损耗因子为φ= 0.7. NSD的刚度系数kˉ1分别为0、-5、-10和-15. 由图 2可见,线性滞回阻尼器对斜拉索振动的各阶效果几乎一致,NSD对各阶阻尼的提升效果也相同.图中实心圆圈标注了各工况下,最优阻尼和对应的阻尼器刚度系数,即(k-opt 1- 2,ζopt 1- 2).可见,NSD的负刚度系数绝对值越大,可达到的最优阻尼ζopt 1-2越大,对应最优的阻尼器刚度系数kˉopt 1-2越小.
2.2 安装位置的影响
考虑在斜拉索减振系统维护升级中,NSD可能有线性滞回阻尼器同端或异端两种布置方式.根据图1的符号设定,同端布置对应较大的3,异端布置时3较小.
2.2.1 同端安装
图3所示为NSD与阻尼器同端安装且位于阻尼器和索锚固点之间时,斜拉索前五阶模态最优阻尼比(见图3(a))和对应的最优阻尼系数(见图3(b))随NSD位置的变化曲线.其中,NSD的刚度系数为1=-5,同时考虑了阻尼器安装在2%、3%、4%和5%索长的情况.
从图3(a)可以看到,同端安装情况下,随着阻尼器安装位置远离索锚固点,其最优阻尼逐渐增加,与现有研究结论一致.同样,随着 NSD向线性滞回阻尼器的靠近,即1/(1 + 2)趋近于1,最优阻尼比ζpt-5 单 调增加,即随着 NSD增大,斜拉索在阻尼器位置处的相对位移的效果得到增强.由图3(b)可见,阻尼器距 跨中位置和NSD 越近,阻尼器的最优刚度系数越小.
2.2.2 异端安装
图4所示为NSD和阻尼器分别位于斜拉索两端时,前五阶模态阻尼比及对应的阻尼器最优刚度系数随NSD和阻尼器安装位置的变化曲线.其中,NSD的负刚度系数1=-5,考虑阻尼器安装在2%、3%、4%和5%索长的情况.可见,当NSD与阻尼器距离 很大时,其增强效应几乎为零,因为并没有增加阻尼器位置的振动位移.
2.3 损耗因子的影响
对于线性滞回阻尼器,损耗因子是一个重要的性能参数,图5 展示了损耗因子的影响.根据上一节结论,NSD 仅在同端安装的情况下有较好效果,因此 取 l3=0.97,一致地取1=-5.可见,其损耗因子越大,所能实现的最优阻尼越大,并且相应的最优刚度系数越小,不同影响因子情况下,NSD对其提升效果相近.
3 案例分析
进一步基于实际工程中的斜拉索,讨论NSD结合线性滞回阻尼器的可行性.以主跨1088 m的苏通 长江大桥安装有黏性剪切型阻尼器的SJ18U索为例,斜拉索位置见图6,参数列入表1.
為抑制该斜拉索振动,该索采用了常见的黏性剪切型阻尼器,相关研究[5]进行了阻尼器性能和实 桥阻尼效果试验.试验结果表明,黏性剪切型阻尼器对拉索多模态阻尼效果相近,可以考虑为线性滞回阻尼器.根据斜拉索-线性滞回阻尼器模型(本文模型在NSD系数为零的情况)和实测的多模态阻尼值进行拟合估计,得到该阻尼器采用线性滞回模型描述时的参数为k=385kN/m,φ=0.75,对应的拟合阻尼器的理论阻尼效果列入表2.
由表2可见,线性滞回模型的模拟结果良好,绝大部分模态误差均在5% 上下,最大误差为10%.以下基于上述拟合参数设计 NSD.如表3所示,考虑增加的NSD的量纲归一化刚度系数分别为-5和-10,NSD在阻尼器与锚固点间的中点和阻尼器位置安装,对应的NSD参数亦列入该表.
基于类似的机理,线性滞回阻尼器并联惯容器同样能提高其对斜拉索的阻尼效果[22].当阻尼器并 联一个惯性质量为bp的惯容器后,惯容器对斜拉索第n阶模态将产生-bp ω的等效负刚度.在此,基于表3中设计工况3,设计惯容器使其分别针对索第1阶、第4阶振动产生与工况3相同的等效负刚度.获得的惯容器的参数列入表4,记作工况4和5,其中,1为线性滞回阻尼器与并联惯容器位置,p= bp /(mL)为量纲归一化并联惯性质量.
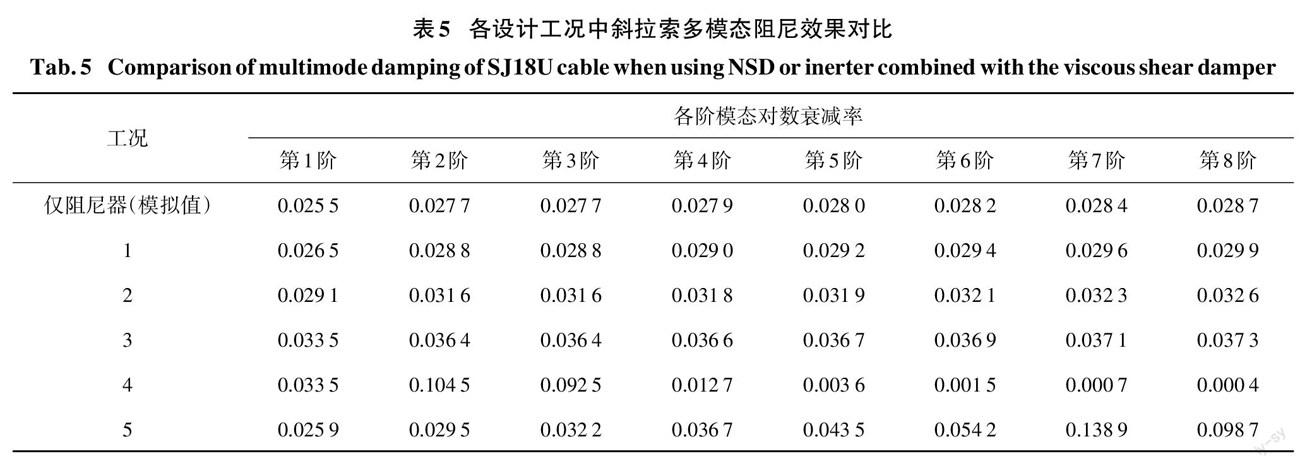
对比表5 工况1~3可见,提升后的阻尼效果对NSD安装位置和负刚度系数大小比较敏感.并且,NSD对各阶效果的提升程度一致.工况3中,采用刚度系数为-125.650kN/m的NSD,就可以实现各阶模态30%的阻尼比提升.根据现有NSD 试验研究[48],采用预压缩弹簧和杠杆放大即可实现-400kN/m的NSD,具有可行性.
对比表5 工况3和工况4、工况5,即分别采用NSD与惯容器对斜拉索阻尼器效果进行提升,可见,对于确定惯性质量系数时考虑的振动模态,安装 NSD和惯容器后,阻尼器对该阶模态的阻尼效果一致.对于其他模态,惯容器产生的等效负刚度效应在低阶时较小、高阶时较大.过大的负刚度与阻尼器结合反而会在索高阶振动时锁定阻尼器,降低高阶模态阻尼比.对比而言,NSD相比惯容器在与线性滞回阻尼器组合后对斜拉索的多模态宽频段减振中具有优势.
4结论
本文提出了结合负刚度装置与线性滞回阻尼器实现拉索多模态振动阻尼提升的方案,通过理论研究和实桥斜拉索案例分析得到如下结论:
1)NSD结合线性滞回阻尼器能实现斜拉索多阶模态阻尼比的同步提升.
2)NSD的负刚度系数一定时,其安装位置越靠 近阻尼器,可实现的多模态最优阻尼越高.
3)NSD相比于惯容器对斜拉索-阻尼器系统的多模态阻尼的均衡提升效果更好.
4)对于实际工程中的斜拉索,采用预压缩弹簧结合杠杆放大机制即可满足 NSD设计需求.
参考文献
[1]HIKAMI Y,SHIRAISHI N.Rain-wind induced vibrations of
cables stayed bridges[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Indus-trial Aerodynamics,1988,29(1/2/3):409-418.
[2]SPENCER B F J,NAGARAJAIAH S.State of the art of structural
control [J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2003,129(7) :845-856.
[3]FUJINO Y,KIMURA K,TANAKA H.Wind resistant design of
bridges in Japan :developments and practices [M].Tokyo: Springer,2012.
[4]KUMARASENA S,JONES N P,IRWIN P,et al.Wind-induced
vibration of stay cables:Technical Report FHWA-HRT-05-083[R].McLean,VA:Federal Highway Administration,2005.
[5]CHEN L,DI F D,XU Y Y,et al.Multimode cable vibration control
using a viscous-shear damper:case studies on the Sutong Bridge[J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2020,27(6) : e2536.
[6]H?GSBERG J R,KRENK S.Linear control strategies for damping
of flexible structures[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2006,293(1/2):59-77.
[7]IKAGO K,SAITO K,INOUE N.Seismic control of single-degree-
of-freedom structure using tuned viscous mass damper[J].Earth-quake Engineering & Structural Dynamics,2012,41(3) : 453-474.
[8]LAZAR I F,NEILD S A,WAGG D J.Using an inerter-based de-vice for structural vibration suppression[J].Earthquake Engineer-ing & Structural Dynamics,2014,43(8):1129-1147.
[9]周海俊,孙利民.斜拉索附加带刚度阻尼器的参数优化分析[J].力学季刊,2008,29(1):180-185.
ZHOU H J,SUN L M.Parameter optimization of damper with stiff-ness for stay cable[J].Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2008,29(1):180-185.(In Chinese)
[10]WEN Y K,CHEN Z Q,HUA X G.Design and evaluation of tuned
inerter-based dampers for the seismic control of MDOF structures[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2017,143(4):04016207.
[11]SARKAR S,FITZGERALD B.Vibration control of spar-type float-ing offshore wind turbine towers using a tuned mass-damper-inerter [J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2020,27(1):e2471.
[12]ZHANG Z L,LARSEN T G.Optimal calibration of the rotational
inertia double tuned mass damper(RIDTMD) for rotating wind turbine blades [J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2021,493:115827.
[13]DE DOMENICO D,RICCIARDI G.An enhanced base isolation
system equipped with optimal tuned mass damper inerter(TMDI)[J].Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics,2018,47(5):1169-1192.
[14]CAO L Y,LI C X.Tuned tandem mass dampers-inerters with
broadband high effectiveness for structures under white noise base excitations[J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2019,26(4):e2319.
[15]LAZAR I F,NEILD S A,WAGG D J.Vibration suppression of
cables using tuned inerter dampers [J].Engineering Structures,2016,122:62-71.
[16]SUN L M,HONG D X,CHEN L.Cables interconnected with tuned
inerter damper for vibration mitigation[J].Engineering Structures,2017,151:57-67.
[17]LU L,DUAN Y F,SPENCER B F J,et al.Inertial mass damper for
mitigating cable vibration[J].Structural Control and Health Moni-toring,2017,24(10):e1986.
[18]CU V H,HAN B,PHAM D H,et al.Free vibration and damping of
a taut cable with an attached viscous mass damper[J].KSCE Jour-nal of Civil Engineering,2018,22(5):1792-1802.
[19]SHI X,ZHU S Y.Dynamic characteristics of stay cables with in-
erter dampers [J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,2018,423: 287-305.
[20]李壽英,李振宇,陈政清.黏滞惯性质量阻尼器对斜拉索减振效果的数值分析[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(10):230-236. LI S Y,LI Z Y,CHEN Z Q.Numerical analysis on the effective-ness of viscous inertial mass dampers on stay cables of cable-stayed bridges[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2019,32(10):230-236.(In Chinese)
[21]WANG Z H,GAO H,FAN B Q,et al.Inertial mass damper for vi-bration control of cable with sag [J].Journal of Low Frequency Noise,Vibration and Active Control,2020,39(3):749-760.
[22]SUN L M,SUN J J,NAGARAJAIAH S,et al.Inerter dampers with
linear hysteretic damping for cable vibration control[J].Engineer-ing Structures,2021,247:113069.
[23]陳政清,华旭刚,牛华伟,等.永磁电涡流阻尼新技术及其在土木工程中的应用[J].中国公路学报,2020,33(11):83-100. CHEN Z Q,HUA X G,NIU H W,et al.Technological innovations in eddy current damping and its application in civil engineering[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2020,33(11):83-100.(In Chinese)
[24]孙洪鑫,邓军军,王修勇,等.电磁惯质阻尼器在结构中位置优化以及减 震分析[J].地 震 工 程与工 程 振动,2019,39(2):69-78.
SUN H X,DENG J J,WANG X Y,et al.Position optimization and damping analysis of electromagnetic inerter dampers in structures[J].Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,2019,39(2):69-78.(In Chinese)
[25]李亚敏,沈文爱,朱宏平.电磁惯质阻尼器对超长斜拉索的减振性能分析[J].土木工程与管理学报,2020,37(6):93-100. LI Y M,SHEN W A,ZHU H P.Vibration mitigation performance analysis of electromagnetic inertial mass damper for super-long stay cables [J].Journal of Civil Engineering and Management,2020,37(6):93-100.(In Chinese)
[26]LI Y M,SHEN W A,ZHU H P.Vibration mitigation of stay cables
using electromagnetic inertial mass dampers:full-scale experi-ment and analysis[J].Engineering Structures,2019,200:109693.
[27]IEMURA H,PRADONO M H.Application of pseudo-negative
stiffness control to the benchmark cable-stayed bridge[J].Journal of Structural Control,2003,10(3/4):187-203.
[28]IEMURA H,IGARASHI A,PRADONO M H,et al.Negative stiff-ness friction damping for seismically isolated structures[J].Struc-tural Control and Health Monitoring,2006,13(2/3):775-791.
[29]IEMURA H,PRADONO M H.Advances in the development of
pseudo-negative-stiffness dampers for seismic response control[J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2009,16(7/8): 784-799.
[30]LI H,LIU M,OU J P.Negative stiffness characteristics of active
and semi-active control systems for stay cables[J].Structural Con-trol and Health Monitoring,2008,15(2):120-142.
[31]OU J P,LI H.Analysis of capability for semi-active or passive
damping systems to achieve the performance of active control sys-tems[J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2010,17(7): 778-794.
[32]H?GSBERG J.The role of negative stiffness in semi-active con-trol of magneto-rheological dampers [J].Structural Control and Health Monitoring,2011,18(3):289-304.
[33]WEBER F,BOSTON C,MA?LANKA M.An adaptive tuned mass
damper based on the emulation of positive and negative stiffness with an MR damper[J].Smart Materials and Structures,2011,20(1):015012.
[34]SARLIS A A,PASALA D T R,CONSTANTINOU M C,et al.
Negative stiffness device for seismic protection of structures[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2013,139(7):1124-1133.
[35]PASALA D T R,SARLIS A A,NAGARAJAIAH S,et al.Adaptive
negative stiffness:new structural modification approach for seismic protection[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2013,139(7):1112-1123.
[36]CHEN L,SUN L M,NAGARAJAIAH S.Cable with discrete nega-tive stiffness device and viscous damper:passive realization and general characteristics[J].Smart Structures and Systems,2015,15(3):627-643.
[37]ZHOU P,LI H.Modeling and control performance of a negative
stiffness damper for suppressing stay cable vibrations [J].Struc-tural Control and Health Monitoring,2016,23(4):764-782.
[38]JOHNSON E A,CHRISTENSON R E,SPENCER JR B F.Semiac-tive damping of cables with sag[J].Computer-Aided Civil and In-frastructure Engineering,2003,18(2):132-146.
[39]JOHNSON E A,BAKER G A,SPENCER B F J,et al.Semiactive
damping of stay cables [J].Journal of Engineering Mechanics,2007,133(1):1-11.
[40]NAKAMURA A,KASUGA A,ARAI H.The effects of mechanical
dampers on stay cables with high-damping rubber[J].Construc-tion and Building Materials,1998,12(2/3):115-123.
[41]FUJINO Y,HOANG N.Design formulas for damping of a stay
cable with a damper[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2008,134(2):269-278.
[42]CU V H,HAN B.High-damping rubber damper for taut cable vi-bration reduction[J].Australian Journal of Structural Engineering,2015,16(4):283-291.
[43]CU V H,HAN B,WANG F.Damping of a taut cable with two at-tached high damping rubber dampers[J].Structural Engineering and Mechanics,2015,55(6):1261-1278.
[44]DI F D,SUN L M,CHEN L.Cable vibration control with internal
and external dampers:theoretical analysis and field test validation[J].Smart Structures and Systems,2020,26:575-589.
[45]DI F D,SUN L M,CHEN L.Suppression of vortex-induced high-mode vibrations of a cable-damper system by an additional damper[J].Engineering Structures,2021,242:112495.
[46]HOANG N,FUJINO Y.Analytical study on bending effects in a
stay cable with a damper[J].Journal f Engineering Mechanics,2007,133(11):1241-1246.
[47]孫利民,狄方殿,陈林,等.斜拉索-双阻尼器系统多模态减振理论与试验研究[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(7):975-985.
SUN L M,DI F D,CHEN L,et al.Theoretical and experimental studies on multimode vibration mitigation of cable with two damp-ers[J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2021,49(7):975-985.(In Chinese)
[48]WANG M,SUN F F,NAGARAJAIAH S,et al.Frequency-
dependency/independency analysis of damping magnification ef-fect provided by tuned inerter absorber and negative stiffness am-plifying damper considering soil-structure interaction [J].Me-chanical Systems and Signal Processing,2022,172:108965.

