Cytological evaluation by Caco-2 and KU812 of non-allergenic peptides from simulated digestion of infant formula in vitro
Zihao Xu, Hao Bai, Xin Ma, Yong Wu, Zhihua Wu, Anshu Yang,Weixiang Mao*, Xin Li,d,*, Hongbing Chen
a State Key Laboratory Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330047, China
b School of food science and Technology, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330047, China
c Sino-German Joint Research Institute, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330047, China
d Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Food Allergy, Nanchang University, Nanchang 330047, China
e Jiangxi Institute of Quality and Standardization, Nanchang 330046, China
Keywords:Milk allergy Epitopes Peptides Hy poallergenic Im mune tolerance
A B S T R A C T Milk allergy is a common allergic reaction found in infants and young children, most of them appear tolerance after growing up. In this study, infant formula was digested by simulated in vitro digestion method. The potential non-allergenic peptides were further screened from undigested products by exclusion of the known epitopes from β-lactoglobulin (BLG) and α-lactalbumin (ALA). These potential non-allergenic peptides were synthesized and their transferability were determined by Caco-2 cell monolayer model. Finally, the potential allergenicity were evaluated by KU812 cell degranulation model. The results showed that 7 peptides were screened as non-allergenic sequences, among which were 3 from ALA and 4 from BLG. The Caco-2 cell model showed that all the synthetic peptides were ab sorbed and transported well. However, only peptide BLG107-118 showed potential allegencity by KU812 model. In conclusion, 6 peptides, including ALA29-51,ALA80-90, ALA94-103, BLG1-20, BLG24-50, and BLG123-139 were evaluated as hypoallergenic peptides, which could be used for ca ndidates of peptides inducing immune tolerance for persons with milk allergy.* Corresponding authors.
1. Introduction
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is recognized as the most common food allergies in the world [1], especially for infants and children. Studies have demonstrated that the prevalence of conf irmed CMPA was 0.5%-3.0% of infant about 12 months [2], and 2.69% of infants under 12 months in China [3]. The common way of avoiding intake allergens t o relieve allergies seriously affects the growth and development of allergic infants. For allergic infants, there are currently low-allergenic infant milk products, including partially hydrolyzed [4], extensively hydrolyzed [5], and amino acid formula milk powder [6,7]. These foods play an important role in avoiding the problem of food allergies in infants and yo ung children, but they cannot fundamentally solve the problem since some children were allergic to milk or other food when they grew up [8].
Recently, “avoiding allergic foods” is questioned to “cure” food allergies. More and more research found that immune tolerance has been an effective method for allergic persons. Immune tolerance was reported as early in 1909 [9], which is the “immune non-response” state of the body’s immune system to specific antigens [10]. There were some food allergies such as milk [11],eggs [12], wheat and soybeans [13] existed naturally tolerance [14].For example, about 50% of children allergic to cow’s milk could tolerate cow’s milk before 5 years old, and preschool children could reach 75% [11]. Immune tolerance can also be acquired by intake of allergen under doctor’s supervision [15]. Differed from the naturally tolerance, acquired tolerance mainly effected by the physicochemical properties of the antigen, the dose, route of entry,and individual physiological differences. According to reports,peptides containing linear epitopes were more likely to induce tolerance [16]. Oral immunotherapy was more likely to cause systemic tolerance than sublingual and epidermal immunotherapy [17,18],younger individuals were more likely to be successfully induced tolerance than older ones [19]. The latest research also found that some food allergens changed more tolerable after thermal processing and enzymatic hydrolysis. Some researchers have found that some peptides in milk protein might play a regulatory role in the immune response and alleviate allergic reactions [20-22].
In our study, the potential non-allergenic peptides were firstly obtained from byin vitrosimulated infant gastrointestinal digestion of infant formula. Then, the non-allergenic peptides were screened based on reported and predicted epitopes. After that, the candidate peptides were synthesized and their potential allergencity were evaluated using Caco-2 and the KU812 model.
2. Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Caco-2 cells were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis,MO, USA). KU812 cells were purchased from Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell (Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai,China). CCK-8 kit was purchased from Beyotime Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Humanβ-hexosaminidase (β-HEX),histamine enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits were purchased from Shanghai Fusheng Industrial Co., Ltd.(Shanghai, China). Human interleukin-4 (IL-4), interleukin-6 (IL-6),tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) ELISA kits were purchased from Xinbosheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). Other chemical reagents were of analytical grade and were commercially available common reagents.
2.2 Screening of potential hypoallergenic peptides after digestion
Infant formula was digestedin vitroby referring DuPont’s method [23]. The amino acid sequences smaller than 10 kDa were analyzed by PTM Biolab, Inc. (Hangzhou, China), and the information of the remaining peptides after digestion was shown in Table S1. The distribution characteristics of the remaining peptides were analyzed, and the concentrated area of peptides was obtained.Based on the data in Table 1, the sequences of the remaining peptides were analyzed and arranged using bioinformatics methods. The amino acid sequence of certain allergenic peptides in the remaining peptides was eliminated, so as to obtain the screened possible non-allergenic peptide sequence in bovine whey protein. The screened non-sensitized peptides were synthesized by Shanghai Qiangyao Biotechnology Co.,Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and the purity of the synthesized peptides were higher than 95%.

Table 1 Major allergen epitopes in whey protein.
2.3 Assessment of peptide transport and absorption capacity by Caco-2 model
2.3.1 Establish of a single-layer small intestinal epithelial model
Caco-2 cells were cultured in DMEM medium with 10% fatal bovine serum (FBS), 1% nonessential amino acids, 1%L-glutamine,penicillin (10 000 U/mL) and streptomycin (10 000 U/mL). And the cells were cultured at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2and 95%air. The proliferation ability of Caco-2 cells and toxicity of peptides was detected using the CCK-8 kit. Caco-2 cells passaged to 30-40 generations can be used to build a monolayer intestinal epithelial cell model. Cells (2 × 105cells/well) in logarithmic phase were inoculated into the upper chamber of the transwell inserts for 21 days. The medium was changed every other day for the first 10 day and every day of the rest time. At the same time, the trans-epithelial resistance(TEER) values were measured on days 11, 13, 15, 17, 19 and 21 (until the TEER reached 500 Ω·cm2). The TEER formula is as follows:

Where the effective membrane area of the 12-well Transwell Plate cell used in our work is 1.12 cm2.
In order to determine whether the established Caco-2 monolayer cell model was successfully established, permeability of the monolayer membrane should be comprehensively detected. The original medium in the transwell insert was replaced with the same amount of Hank’s solution to rinse the well at 37 °C and 5% CO2for 30 min. After removing the Hank’s solution, 0.5 mL sodium fluorescein solution with a concentration of 100 µg/mL was added to the upper chamber of the transwell inserts, another 1.5 mL of Hank’s solution was added to the lower chamber. After incubated for 2 h,the concentration of sodium fluorescein in the lower chamber of the transwell insert was detected.
2.3.2 The resistance of Caco-2-cell monolayer to synthetic peptides
The wells were rinsed with Hank’s solution, then 450 µL of 1%FBS medium and 50 µL peptides with different concentrations were added to the upper chamber. Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) as a negative control. After that, 1.5 mL of 1% FBS medium was added to the lower chamber. The initial resistance value of each well were detected and record it asT0. Then, the Transwell Plate was incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2for 6 h. After the incubation, the resistance value of each well was measured again and recorded asT6. The ratio ofT6toT0indicated the resistance of Caco-2-cell monolayer to synthetic peptides.
2.3.3 Determination of the transport rate of synthetic peptides
The transport ability of synthetic peptides was detected by intact Caco-2 cell monolayers. The wells were rinsed with Hank’s solution for 30 min. After that, the Hank’s solution was replaced with peptide solutions at their optimal concentrations in the upper chamber, and 1.5 mL Hank’s solution was added to the lower chamber.Respectively, the 100 µL samples from the lower chamber at 30, 60,90, and 120 min were taken out to measure the peptides concentration,the content of peptides in upper and below of Transwell Plate by Pierce™ Quantitative Colorimetric Peptide kit, and the transport rate of sample and apparent permeability coefficient (Papp) were calculated as the following formulas.

Where dQ/dt, sample permeability (µg/s);A, area of cell membrane monolayer;C0, total sample added in upper chamber (µg).
2.4 Allergenicity evaluation by KU812 cell experiment
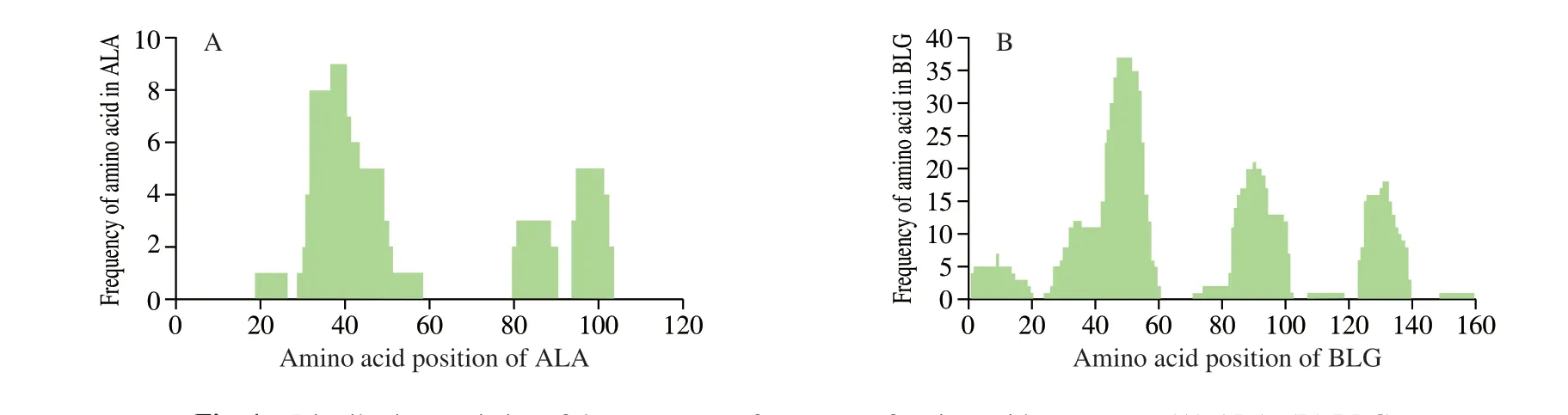
Fig. 1 Distribution statistics of the occurrence frequency of amino acid sequences. (A) ALA; (B) BLG.
The sera pool is prepared by mixing the equal volume of serum of 10 patients who were diagnosed as milk allergy. The information of patients was listed in Table 2. All the experiment with human sera were performed in compliance with the NCH guidelines from China(NHC Publication No. 11, Rev. 2016) and approved by the Medical Research Ethics Committee from the Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University (Nanchang, China).
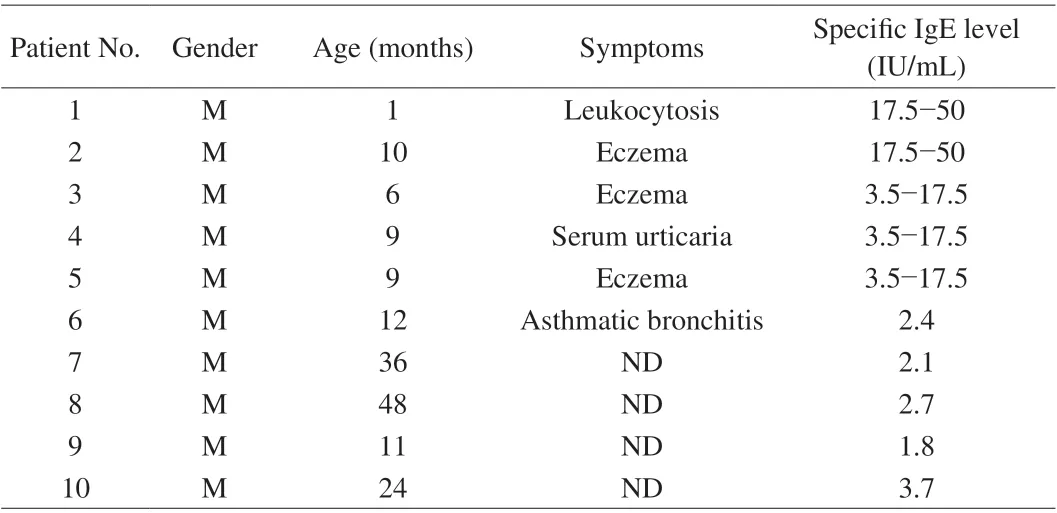
Table 2 Information of cow’s milk allergy patients.
KU812 cells were maintained in RPMI1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% nonessential amino acids, 1%L-glutamine,penicillin (10 000 U/mL) and streptomycin (10 000 U/mL),and were cultured at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere with 5%CO2. The cells (106-108cells/mL in 500 µL of the medium) were incubated in 12-well plate and cultured for 24 h. Then, 100 µL of serum was added to each well and cultured at 37 °C for 24 h in a 5%CO2incubator. Next day, 10 µL of synthetic peptides were added to incubate for 4 h. After allergen challenge, the indicators includingβ-HEX, histamine, IL-4, IL-6 and TNF-α, were measured using a commercial ELISA kit.
2.5 Statistical analysis of data
Statistical analysis was assessed using SPSS 11.0.1 and Origin 8.0 software. Results were evaluated by a one-way analysis of variance,P< 0.05 was regarded as the significant difference.
3. Results
3.1 Amino acid sequence of gastrointestinal digestion products
There were more than 731 peptides below 10 kDa were obtained from digested products by sequence analysis. The sequence of 731 peptides were aligned with bovine major allergens (bovine ALA,BLG and casein) as shown in Fig. 1. From Fig. 1A, the peptides derived from ALA were mainly distributed in the region of AA 19-26, AA 29-58, AA 80-90, and AA 94-103 in which there were no peptides located in N and C terminal. Moreover, we found that AA 29-58 appeared frequently most in undigested peptides, which might contribute to allergic reaction much. While in Fig. 1B, there were 6 peptides derived from BLG, which was located in AA 1-20, AA 24-60, AA 71-102, AA 107-118, AA 123-139 and AA 149-159. The most appeared peptides was AA 24-60.
3.2 Prediction of the hypoallergenic peptides
The reported epitopes on bovine allergens were summarized in Table 1, which were aligned with the undigested peptides. IgE, IgG and T-cell epitopes were excluded from the undigested peptides from ALA and BLG, the residual 7 peptides were considered as potential non-allergenic peptide sequences as shown in Table 3. These 7 peptides were then synthesized and named as P1-P7.

Table 3 The information of the synthetic hypoallergenic peptides.
3.3 Cytology results
3.3.1 Effect of synthetic peptides on the proliferation of Caco-2 cells
The cytotoxicity of synthetic peptides on Caco-2 cells was indicated by cell survival rate. Cell survival rates greater than 95%were considered to be non-toxic. When the cell survival rate exceeds 70%, it can be used for subsequent cell transport experiments [24].The effect of P1-P7on the proliferation of Caco-2 cells was shown in Fig. 2. When the concentration was less than 500 µg/mL (including 500, 200 and 50 µg/mL), none of the peptides were toxic to the cells.While the concentration reached 1 000 µg/mL, only P6showed no toxicity to the cells. Therefore, the concentration of 500 µg/mL was selected for the subsequent Caco-2 cell experiments.

Fig. 2 Cytotoxicity of the synthetic peptides against Caco-2 cells. The reason why the cell viability exceeds 100% is that the peptides has no toxic effect on the cells, and the cells continue to proliferate.
3.3.2 Cell monolayer membrane integrity test
The resistance value and fluorescein sodium transfer rate were used to test the intact of the Caco-2 cell monolayer. On days 11, 13, 15, 17, 19 and 21, the resistance values of the Transwell monolayer cell membrane were measured. It can be found from Fig. 3 that the resistance value of the monolayer cell membrane generally increased with the culture time,and the resistance value exceeded 500 Ω·cm2on day 13 and reached the peak on day 15 with 576.4 Ω·cm2. After that the data decreased slightly, but it remained above 500 Ω·cm2(about 525 Ω·cm2), which indicated that cell monolayer membrane kept integrity [24].
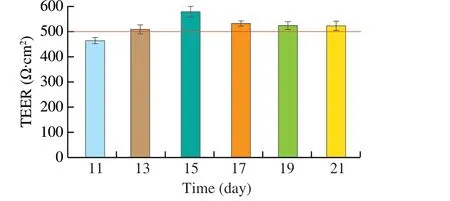
Fig. 3 TEER of Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane over time. The red line in the figure represents a resistance value of 500 Ω·cm2.
Sodium fluorescein is a substance that is hypotonic and difficult to absorb, the permeability of constructed Caco-2 monolayer cell membrane to sodium fluorescein cannot exceed 4.8 µg/(h·cm2). The well with the smallest resistance was chosen for detection of the sodium fluorescein transport experiment. The final concentration of sodium fluorescein in the lower chamber was 6.19 µg/mL. The calculated sodium fluorescein permeability was 4.15 µg/(h·cm2),and it showed that the permeability and integrity of the Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane model was successfully established.
3.3.3 Effect of synthetic peptides on the permeability of monolayer cells
The permeability of Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane was evaluated by measuring the effect of synthetic peptides on the resistance value of Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane. The results were shown in Fig. 4.Among the 7 synthetic peptides, the resistance of Caco-2 cell to P1-P5decreased obviously compared toT0and their reduction rate were 22.64%, 17.91%, 11.02%, 13.33%, and 9.21%, respectively. The data suggested that the 5 peptides could damage the Caco-2 monolayer cell membrane in different extents. However, their damage rate did not exceed 30%, which suggested that the 5 peptides were not lethal to Caco-2 cells. But for P6and P7, the resistance of Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane increased 1.40% and 15.96%, respectively, which indicated that the two peptides even promote the cell growth.
Fig. 4 Effect of synthetic peptides on monolayer permeability.
3.3.4 Transport rate of peptides through the Caco-2 cell monolayer membrane
The peptide concentrations in the lower chamber were measured at 30, 60, 90 and 120 min, respectively (Fig. 5). The transfer rate of P6was the highest with the value of 34.68%, while P5was 12.07%,lowest among tested peptides. The transfer rate of the other 5 peptides were mainly ranged 18% to 22%, without significant difference.And it can be found that the transfer rates of all the 7 synthetic peptides increased over time. The Papp of the 7 peptides were 2.69 × 10-5, 2.56 × 10-5, 2.56 × 10-5, 2.03 × 10-5, 1.50 × 10-5,4.30 × 10-5and 2.27 × 10-5cm/s, respectively. According to the classification of drugs, the substances with Papp > 1 × 10-5cm/s were regarded as well-absorbed, while the Papp of substances’ between 1 × 10-5-1 × 10-6cm/s belonged to the general absorption substances [25].Based on the above classification, the most and least absorbed peptides were P6and P5, respectively. There were no significant differences for the absorption effects of the other 5 peptides.

Fig. 5 Transfer rate of synthetic peptides at different transit times.
3.3.5 Effect of synthetic peptides on proliferation of KU812 cells
The proliferation toxicity test of synthetic peptides on KU812 cells was indicated by cell survival rate, and the results were shown in Fig. 6. When the cell survival rate was greater than 95%, it was considered non-toxic to the cells. The cell survival rate of P1, P4, P6,P7were higher than 95% at the 4 concentrations of 2.5, 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL, which meant the 4 peptides showed no toxicity to KU812 cells. Interestingly, with the increase of peptide concentration, P7promoted cell proliferation. The cell survival rate of P2, P3, P5were less than 95% at 20 µg/mL, indicating that at this time, the P2, P3, P5were toxic to the cells. The cell survival rate was higher than 95%when the concentration of all peptides was 10 µg/mL. Therefore,the concentration of 10 µg/mL was uniformly selected as the final concentration for the further experiment.
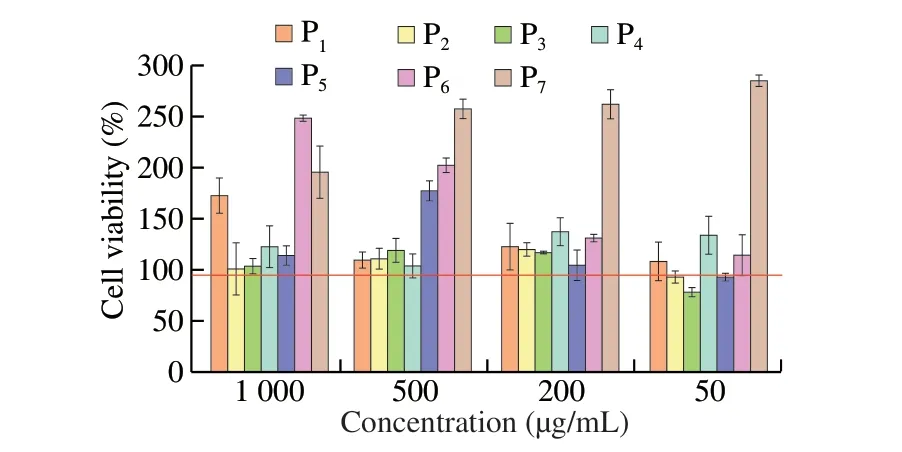
Fig. 6 Effect of synthetic peptides on proliferation of KU812 cells.
3.3.6 Effect of synthetic peptides on the degranulation of KU812 cells
In this study, human histamine EILSA kit was used to detect the release of histamine from KU812 cells induced by seven synthetic peptides as shown in Fig. 7A. P3and P7induced more histamine production than those in positive control group and P1, P2, P5, P6stimulated KU812 cells to produce the similar amount of histamine content as the positive control group. The least histamine contents were induced by P4. All the 7 peptides did not show significantly different from those in the control group (P> 0.05).
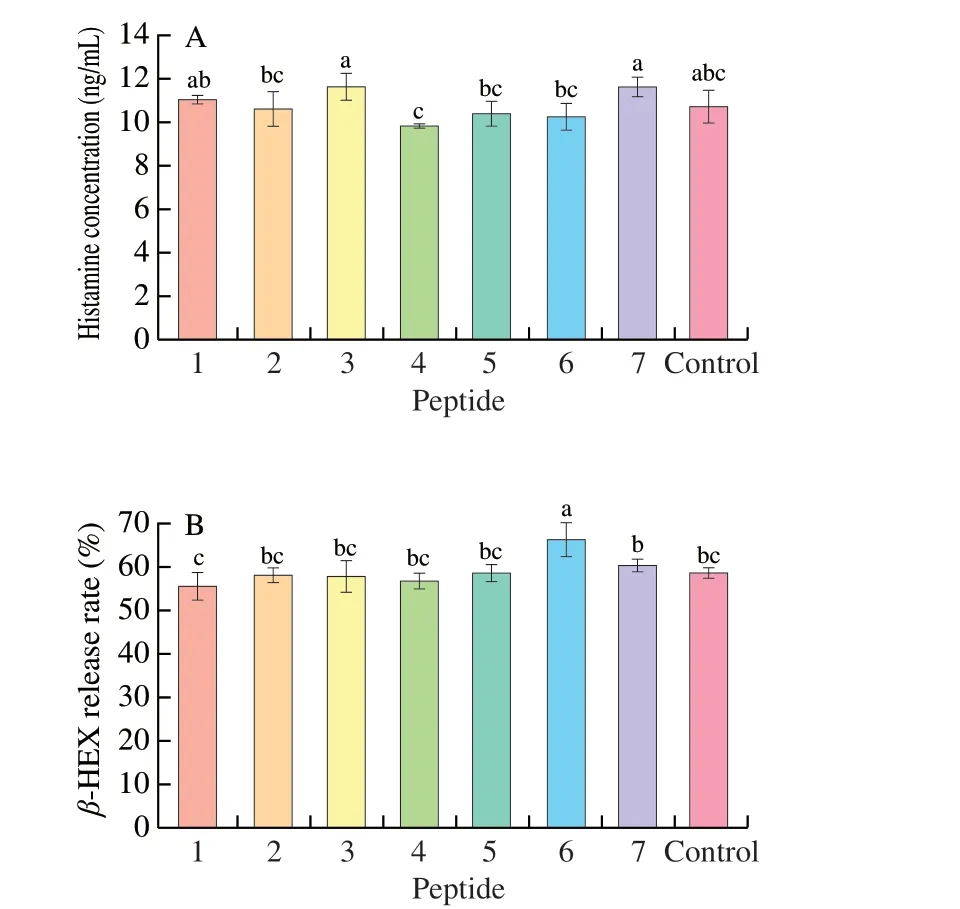
Fig. 7 The release of intracellular markers from mast cells in the presence of synthetic peptides. (A) Histamine release; (B) β-HEX release rate. 1-7,Synthetic peptides 1-7; control, positive control group. Different letters represent significant differences (P < 0.05).
As a hallmark particle of basophils,β-HEX changes in the plasma content only when the body has an allergic reaction. Therefore,β-HEX is usually used as a marker for basophils degranulation. In this study,humanβ-HEX ELISA kit was used to detect the release rates ofβ-HEX from KU812 cells induced by seven synthetic peptides. As shown in Fig. 7B, theβ-HEX release rates of P1-P5and P7were not apparently different from those of the positive control group (P> 0.05), and they were in a non-sensitized state, whereas theβ-HEX release rate of P6was significantly higher than that of the positive control group (P< 0.05). Which suggested the P6induced stronger basophil degranulation.
3.3.7 Effect of synthetic peptides on inflammatory factors released by KU812 cells
Human IL-4 ELISA kit was used to detect the IL-4 released by KU812 cells in Fig. 8A. The figure showed that the abilities of P1-P7to stimulate KU812 to produce IL-4 were different. P1, P3, P5, P7promoted less content of IL-4 production by KU812 cells. While P2,P4, P6stimulated the cells to produce more IL-4, Among them, only P6showed a significant difference (P< 0.05).
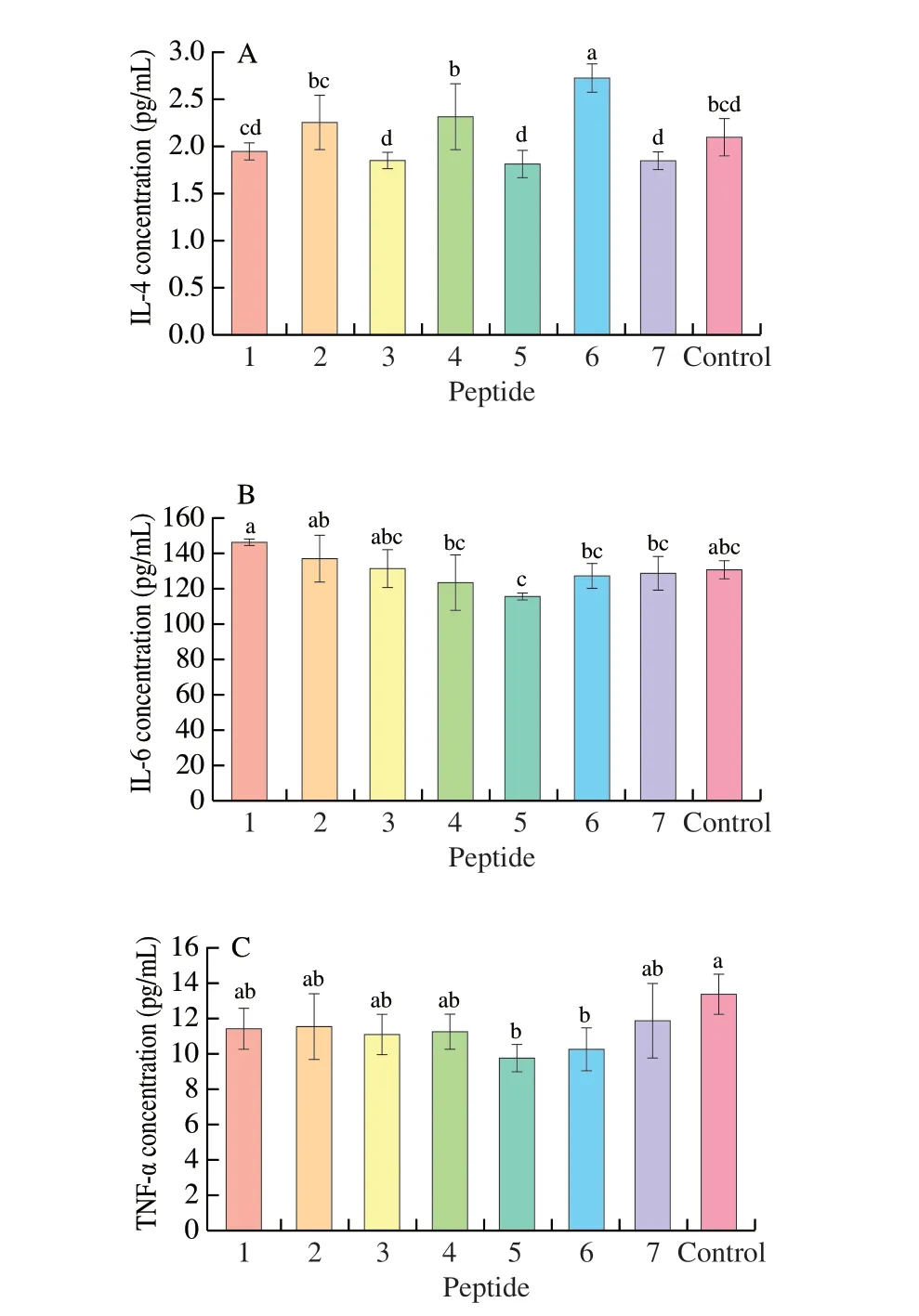
Fig. 8 Inflammatory factors release in the presence of synthetic peptides.(A) IL-4, (B) IL-6, (C) TNF-α. 1-7, Synthetic peptides 1-7; control, positive control group. Different letters represent significant differences (P < 0.05).
IL-6 is the earliest elevated marker when inflammation occurs in the body. As a Th2-type cytokine, IL-6 can affect both cellular and humoral immunity. At the same time, IL-6 can regulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells, induce B cells to produce antibodies, and secrete more IgE, which triggers a serious degranulation reaction and pro-inflammatory effects. In this study,the human IL-6 ELISA kit was used to detect the IL-6 released by KU812 cells. The results were shown in Fig. 8B. We found that P3, P6,P7have the same ability to stimulate IL-6 secretion by KU812 cells as the positive control group, while P4, P5showed a least ability to secrete IL-6, but there was no significant difference (P> 0.05). At the same time, P1, P2stimulated cells to higher IL-6 production than that of control group, and there was no significant difference (P> 0.05).Therefore, all seven peptide groups are in a non-sensitized state by induction of IL-6.
Similar to IL-6, TNF-α is a typical pro-inflammatory cytokine involved in immune regulation. As shown in Fig. 8C, TNF-α produced by KU812 cells stimulated by P1-P7got decreased, and the effects of P1-P4and P7were not significantly different from that of the positive control group (P> 0.05). The ability of P5, P6to induce TNF-α production was significantly lower (P< 0.05). All in all, the ability of the 7 peptides to stimulate KU812 cells to produce TNF-α did not exceed the positive control group, which proved that all the peptide did not induce the sensitization of the cell by stimulation of TNF-α.
4. Discussion
4.1 Application of Caco-2 cell monolayer model
Caco-2 cells are derived from human colon cancer cell lines and have many physical and chemical properties similar to small intestinal epithelial cells, such as morphology, osmotic characteristics,and functional expression of marker enzymes [26]. The results of Rubas et al. [27] showed that the absorption rate of certain drug in the Caco-2 cell monolayer model, which is highly consistent with the result of the human small intestine. In the field of medicine, the Caco-2 cells were often constructed as cell monolayer models to simulatein vitrodrug transport and cytotoxicity in intestinal epithelial cells [28,29].With respect to food material, the Caco-2 cell model was used to evaluate the bioavailability and transmembrane transport of protein and peptides, glucose [30], fatty acid [31], flavonoids [32] and so on. For peptides, it was found that oligopeptides with more than three amino acids were transport through the Caco-2 cell monolayers via the tight junctions (TJs) mediated by paracellular pathway [33].While transcytosis was considered as a dominant way for the peptides containing more than 10 amino acids, such as YWDHNNPQIR [34]and bradykinin RPPGFSPFR [35]. Shimizu et al. [36] has proved that transepithelial transport of collagen peptides by paracellular pathway and their permeability depend on their molecular weight. In addition,Sun et al. [37] also constructed a Caco-2 cell monolayer model to evaluate the bioavailability of vitamin K. In this study, transport and absorption capacity of 7 synthetic peptides were evaluated by constructing Caco-2 cell model. The results demonstrated that when the sample concentration was 500 µg/mL, the sample has no proliferative toxicity to Caco-2 cells. Therefore, different transfer rate for peptides in our work was derived from differences of molecular size, hydrophobicity, amino acid composition and so on [36,38-40],which should be proved in further. However, all the peptides were transported and absorbed well with Caco-2 cell model.
4.2 Effects of 7 peptides on proliferation toxicity and degranulation of KU812 cells
When the allergen enters the body, it will cause an immune response in the body, and the permeability of the basophils in the body will change accordingly. Histamine is usually used as a related receptor molecule to achieve mediation. As the “gold standard” in clinical diagnosis, changes in histamine release have been used as indicators for monitoring acute allergies. Basophils are the important cells involved in allergic reactions [41]. After basophils are exposed to allergens for the second time, they induce cell activation and degranulation to release a large number of inflammatory mediators,causing a series of allergic symptoms [42,43].
Human peripheral blood basophils KU812 were selected to evaluate the effects of 7 synthetic peptides on IgE-mediated degranulation of KU812 cells. Firstly, cytotoxicity experiments were performed to determine the optimal peptides concentration.For the cytotoxicity experiments, a commercial CCK-8 kit was selected. The results showed there was no cell proliferation toxicity to KU812 cells at concentration of 10 µg/mL for the synthetic peptide, and subsequent experiments can use this concentration for experiments for further study.
Histamine andβ-HEX are both pre-synthesized in the granules of basophils. When basophils are in the activated phase of sensitization,histamine andβ-HEX are firstly released by the cell and exerting their physiological effects, and then some pro-inflammatory factors such as interleukins (IL-4, IL-6, etc.) and interferons are also synthesized during the degranulation reaction. Therefore, the content of the cytokines in these intracellular particles can be used to determine whether the allergic reaction occurs and the degree of the reaction. In our study, the results showed the content ofβ-HEX and IL-4 released by KU812 cells stimulated by P6were significantly higher than the positive control group, while the other 3 indicators were no significant difference from the positive control group; and the P1-P5and P7have no significant difference from the positive control group on the 5 indicators.
5. Conclusion
In this study, 7 hypoallergenic peptides were obtained through prediction, all of the selected 7 peptides were transported and absorbed well in the Caco-2 cell monolayer model. The KU812 cell degranulation mode demonstrated that 6 peptides of whey major allergen proteins ALA29-51, ALA80-90, ALA94-103, BLG1-20, BLG24-50,and BLG123-139were low-allergenic, these peptides can be used as candidates of tolerance peptides. This study provides a theoretical basis for the future production of low-allergenic dairy products that might induce immune tolerance. However, we need further prove its role of immune tolerance by sensitization with cell biologyin vitroand animal model.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China(2018YFC1604205), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31760431), and State Key Laboratory of Food Science and Technology, Nanchang University (SKLF-ZZA-201912).
Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at http://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2022.09.020.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- The role of probiotics in prevention and treatment of food allergy
- Roles of fermented plant-, dairy- and meat-based foods in the modulation of allergic responses
- The role of gut microbiota and its metabolites short-chain fatty acids in food allergy
- Association of nutrients intake during pregnancy with the risk of allergic disease in offspring: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
- Purif ication and immunoglobulin E epitopes identif ication of low molecular weight glutenin: an allergen in Chinese wheat
- Determination of egg and milk allergen in food products by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on signature peptides and isotope-labeled internal standard

