The impact of just-in-time teaching model on nursing students' learning in the background of"Internet+":a meta-analysis
Sha-Sha Jia,Chang Li,Xiang-Shu Cui*School of Nursing,Yanbian University,Yanji 33000,China.
Abstract Objective: To systematically evaluate the impact of just-in-time teaching methods on nursing students’ learning outcomes.Methods: Through the databases of CNKI, Wanfang,VIP, CBM, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase and Web of Science, the randomized controlled trials of just-in-time teaching in nursing field were collected from the establishment of the databases to the publication in November 2022.After literature screening, data extraction and quality evaluation, meta-analysis was performed using RevMan5.3 and Stata16.0 software.Results: Twenty articles were included, with a total of 1,865 nursing students.Meta-analysis results showed that compared with the traditional teaching method,the just-in-time teaching method had statistically significant differences in nursing students’ theoretical examination scores (standardized mean difference (SMD) =1.26,95%confidence interval(CI):1.03 to 1.48,P<0.001), operational skills scores(SMD= 1.56,95% CI: 1.21 to 1.90, P < 0.001), self-learning ability (SMD = 0.76, 95% CI: 0.61 to 0.91, P < 0.001) and just-in-time teaching method satisfaction (P < 0.05).Conclusion:The just-in-time teaching method combines the advantages of traditional teaching and networked teaching, improves nursing students’ theoretical performance, skill operation level and teaching satisfaction, and cultivates nursing students’ self-learning ability.
Keywords:JITT teaching; nursing students; learning effect; meta-analysis
Background
With the rapid development of information technology and the concept of “Internet+”, pedagogy has entered into a significant change based on information technology [1], multimedia, teaching resource libraries, network cloud platforms, online courses, and other informational carriers or means are increasingly enriched, and theoretical and practical research on web-based inquiry-based collaborative learning, flipped classroom, blended teaching, and theoretical and practical research on teaching modes such as web-based inquiry-based collaborative learning, flipped classroom,blended teaching, and pairwise classroom has been widely promoted[2].In this context, just-in-time teaching (JITT) strategies based on networked learning platforms have also entered people’s vision.
JITT method was proposed by Professor Nowak of the United States[3] and is a new teaching model based on the interaction of“‘web-based learning task’ and ‘learners’ active learning classroom”[4–6].The essence of JITT is a feedback loop consisting of students’out-of-class preparation and classroom activities, and that classroom activities are determined by out-of-class preparation.Its goal is mainly to use student feedback to guide instruction and motivate students.Specifically, it is as follows: before class, students carefully construct knowledge related to the new course topic based on tasks posted on the online platform.These tasks are often referred to as“warm-ups”or“preparatory activities”.Typically, teachers have students read the content and summarize the answers to the questions in advance.Students submit their answers electronically before class.The instructor reviews student feedback to see the level of self-study, the difficulty of the lesson, common problems, and the background of knowledge the students already have.The instructor selects questions from the student feedback, takes anonymous excerpts, and modifies the classroom activity “just in time” to make the most effective use of face-to-face instruction in class, based on the level of student knowledge.In the classroom, students learn and consolidate their knowledge primarily through teacher-organized discussions, debates,experiments, or hands-on activities.In these activities, the role played by the teacher is merely that of a guide and coordinator of the activities, while the students are the real masters of the classroom and must actively participate in the activities if they are to gain knowledge.Since students come prepared, they are more enthusiastic to participate in the activities and the learning effect is more obvious.In and out of the classroom, teachers encourage collaborative learning.For students, the course begins with their advance preparation;for teachers,the content is organised with the students in mind.
As we can see, in the teaching process using JITT, the “web-based learning task” is the basis for each lesson, and the quality of a lesson depends entirely on the students’pre-class warm-up, while the“active learning classroom” for learners.The “active learning classroom” is a test and improvement of the students’ warm-up exercises, through which their knowledge is consolidated and their ability to explore problems and collaborate is enhanced.The two complement each other.With the characteristics of strong feasibility, strong operability,and low cost, it has been vigorously promoted as the direction of education reform in the United States[7].Currently,JITT is still in the exploratory and experimental stage in nursing education.Therefore,through the meta-analysis method,this study systematically evaluated the impact of JITT teaching on nursing students’ learning effect to provide a reference for promoting the application of JITT teaching in nursing teaching.
Materials and methods
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria.The articles’ inclusion criteria were formulated according to the PICOS system evaluation principle.1.P: nursing students,age,gender and educational background were not limited.2.I: JITT teaching was used.3.C: traditional teaching model was used.(traditional teaching method: it refers to the teaching method in which the teacher can make students master a large amount of knowledge through systematic and detailed explanation, and the form is relatively single.Generally, the teacher stands on the podium and speaks, and the students passively accept it below.This teaching method has more freedom for the teacher,and the students only listen to the method desperately and hard.Between this point, the traditional teaching method is also often jokingly called duck-fill teaching.) 4.O: theoretical examination scores, operation skill scores,self-learning ability and JITT teaching method satisfaction.5.S:randomized controlled trial with unlimited language.
Exclusion criteria.1.Literatures for which the full text and data extraction cannot be obtained.2.Abstracts of nursing conferences.3.The statistical method is wrong and the intervention measures are unclear.4.Literature review and systematic review.
Literature search strategy
The computer searches CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases, and the time is set for the establishment of the database to November 2022.The keywords “护生 (nursing students) OR 护理专业学生 (nursing student) OR 护理教育 (nursing education) OR 护理教学 (nursing teaching)OR 护理(nursing),适时教学(just-in-time teaching)OR 及时教学(timely teaching) OR 即时教学(instant teaching) OR 准时教学法 (on-time teaching method),随机对照试验 (randomised controlled trials) OR 随机对照(randomized control) OR RCT OR 随机(Random) OR 随机对照实验(randomised controlled trial) OR 随机 对 照 研 究 (randomised controlled studies)” combined with synonyms were searched in Chinese.The search was conducted in English using the subject term “Students, Nursing OR Education,Nursing OR Nursing Teaching OR Nursing, Just-in-Time Teaching OR JITT OR JiTT OR Jitt OR jitt OR just-in-time teaching, Randomized Controlled Trial OR Clinical Trials, Randomized OR Randomized OR Trials, Randomized Clinical OR Controlled Clinical Trials,Randomized OR RCT”combined with free words.The search language was not restricted, while in the included literature, its references were tracked and expanded to avoid omissions in order to obtain relevant literature not found.
Literature screening and data extraction
According to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the two researchers independently screened the literature.After excluding the literature that was irrelevant to the theme and did not meet the inclusion criteria,the remaining literatures that might be included was read and screened in full and then crosschecked the literature.If there is disagreement, a third-party researcher will determine the final literature through discussion or arbitration.The two researchers used a pre-designed data extraction table to extract data independently from the included literature.The extracted contents include the first author’s name, publication year, teaching location, sample size,intervention measures,and outcome indicators.
Literature quality evaluation
The quality assessment of the included literature was conducted independently by two researchers, according to the Cochrane Handbook (5.1.0) quality evaluation criteria.“Low-risk bias”,“unclear”and“high-risk bias”were used to indicate the degree of bias risk.In case of uncertainty, a third researcher was invited to discuss it together.Quality grade A indicated that the included study’s bias was low risk and all met the above criteria; quality grade B indicated the possibility of bias in the included study and partially met the above criteria; quality grade C indicated a high risk of bias in the study which can be eliminated.
Statistical analysis
RevMan5.3 software was used for the data meta-analysis, and Stata16.0 software was used for publication bias detection and sensitivity analysis.The included studies were expressed as 95%confidence interval (CI), and inter-study heterogeneity was determined by chi-square test (α = 0.05).IfP≥0.1 and I2< 50%,there was no statistical heterogeneity, and the fix effect model was used for analysis.IfP< 0.1 and I2≥50%, there was clinical homogeneity,then the random effect model was used for analysis,and the subgroup analysis was conducted to find the source of possible heterogeneity.The stability of the results was assessed by sensitivity analysis through a study-by-study exclusion method.If there was no significant change in the combined results after excluding studies with a large effect on heterogeneity,it indicated that the results were stable despite the significant heterogeneity.When the source of heterogeneity could not be judged,only descriptive analysis was done.This study involved only measurement information, and standardized mean difference (SMD) was used for analysis.Funnel plots were used to analyze the potential publication bias,and Egger’s test[8]was used to analyze the results further.
Results
Literature retrieval results
A total of 365 articles were obtained after the search, 115 articles were excluded from duplicates, 156 articles were excluded from the readings and abstracts,of which 94 articles were potentially included,and the full text of the included studies was read again,and 20 articles were finally included.The specific literature screening process is detailed in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Flow diagram of study selection
General features of included trials
A total of 20 articles were included in this study, with a total of 1,865 study subjects, including 931 in the experimental group and 934 in the control group.The type of study was a randomized controlled trial, and the years of publication were from 2013 to 2022.The basic characteristics of the included literature are detailed in Table 1.

Table1 Basic features of the included literature
Quality evaluation of included studies
There were 20 articles included in our study, and all of them were rated B for the methodological quality of the literature.Three of the studies [19, 20, 26] described specific random sampling methods, 2 studies [17, 23] used the lottery method for grouping, 1 study [11]used the random number table method for grouping, 8 studies [10,14–16, 18, 21, 24, 25] mentioned random assignment but did not report a specific random assignment scheme, and 6 studies [9,12, 13,22, 27, 28] were unclear as to whether a random assignment scheme was used; only 1 of the 20 studies [21] did not compare nursing students’ baseline information, and the rest had inside comparable baseline information (P> 0.05).None of the included studies reported blinding, so there is the potential for measurement bias.Although the completeness of the outcomes in our included literature was good, most articles failed to adequately describe allocation concealment, blinding, and some other sources of risk and the methodological quality of the 20 articles was low overall, as shown in Table 2 for specific information and Figure 2 for a summary of the risk of bias.

Figure 2 Risk of bias summary
Meta-analysis results
Theory examination scores.Sixteen [9–15, 17–19, 22, 24–28]studies reported theoretical examination scores of nursing students.There was heterogeneity between studies(I2=74%,P< 0.001),so a random effects model was used for analysis.Meta-analysis results showed that the test group scored higher in theory scores than the control group (SMD = 1.26, 95% CI: 1.03 to 1.48, Z = 11.07,P<0.001, Figure 3), with statistically significant differences.Subgroup analysis of the 16 papers according to the teaching location showed that the theoretical scores of students in the test group were higher than those of the control group in both subgroups, in schools (I2=78%,P< 0.001) and hospitals (I2= 72%,P< 0.001), with a statistically significant difference(P< 0.05).
Operation skill scores.Thirteen [10, 11, 14–17, 19–23, 26, 27]papers reported on nursing students’performance in operational skills.There was heterogeneity among studies(I2=84%,P<0.001),which was analyzed using a random effects model.Meta-analysis results showed (SMD = 1.56, 95% CI: 1.21 to 1.90, Z = 8.84,P< 0.001,Figure 4) that the differences were statistically significant.The 13 papers were analyzed subgroups according to teaching location.The results showed that the theoretical scores of students in the test group were higher than those in the control group in both subgroups, in schools (I2= 92%,P< 0.001) and hospitals (I2= 76%,P< 0.001),with statistically significant differences (P< 0.05).
Self-learning ability.Nine [10, 15, 17, 19, 20, 24–27] studies reported the effect of JITT instruction on nursing students’self-directed learning ability.There was a large heterogeneity between studies (I2= 91%,P< 0.001) and the results were analyzed using a random effects model(SMD=1.18,95%CI:0.67 to 1.69,Z=4.55,P< 0.001).A sensitivity analysis revealed that the study by Chao Deng[26] was the primary source of heterogeneity.The exclusion of this study revealed the presence of no significant heterogeneity(I2=16%,P= 0.30),and further analysis using a fixed effects model showed no significant change in the results(SMD=0.76,95%CI:0.61 to 0.91,Z= 9.93,P< 0.001, Figure 5), with a difference of statistically significant.

Figure 3 Forest plot of the theory examination scores.SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance.
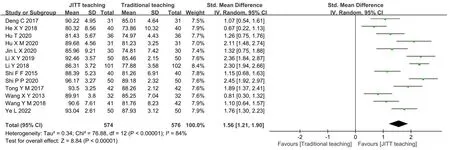
Figure 4 Forest plot of the operation skill scores.SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance.

Figure 5 Forest plot of the Self-learning ability.SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval; IV, inverse variance.
JITT teaching method satisfaction
Eleven [10–15, 18, 20, 21, 23, 24] studies reported on the evaluation of nursing students’ satisfaction with the JITT teaching method.Since the studies mainly evaluated nursing students’ satisfaction with teaching through self-administered questionnaires, the content and methods of evaluation differed significantly.Therefore,this part of the data was only analyzed descriptively.The study results showed that most students in the experimental group were very satisfied with the JITT mode based on the online teaching platform.The JITT teaching method could effectively broaden the knowledge and increase the effective interaction between teachers and students.The teaching content was enriched and reasonable, which could improve clinical thinking ability.
Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Sensitivity analysis was conducted using the study-by-exclusion method on the theoretical examination scores, operational skills scores, and sensitivity analysis of the nursing students included in the study.After excluding the included studies one by one, it was found that none of the results changed significantly, indicating that the Meta-analysis results were stable.Sensitivity analysis was also conducted using the same exclusion-by-study method on the independent learning ability.After excluding the included literature one by one, it was found that Chao Deng [26] was the primary source of heterogeneity.Since fewer than 10 papers were included for the outcome indicator self-directed learning ability, publication bias tests were done only for nursing students’ theoretical exam scores and operational skills scores.The funnel plots showed basic symmetry,which was further tested for bias using Egger’s test.The results showed that theory scores (t = 0.39, 95% CI: –3.33 to 4.81,P=0.703).And operational skills achievement(t=-0.53,95%CI:–14.69 to 9.01,P= 0.608), suggesting no significant publication bias and relatively stable study results,as detailed in Figures 6 and Figures 7.
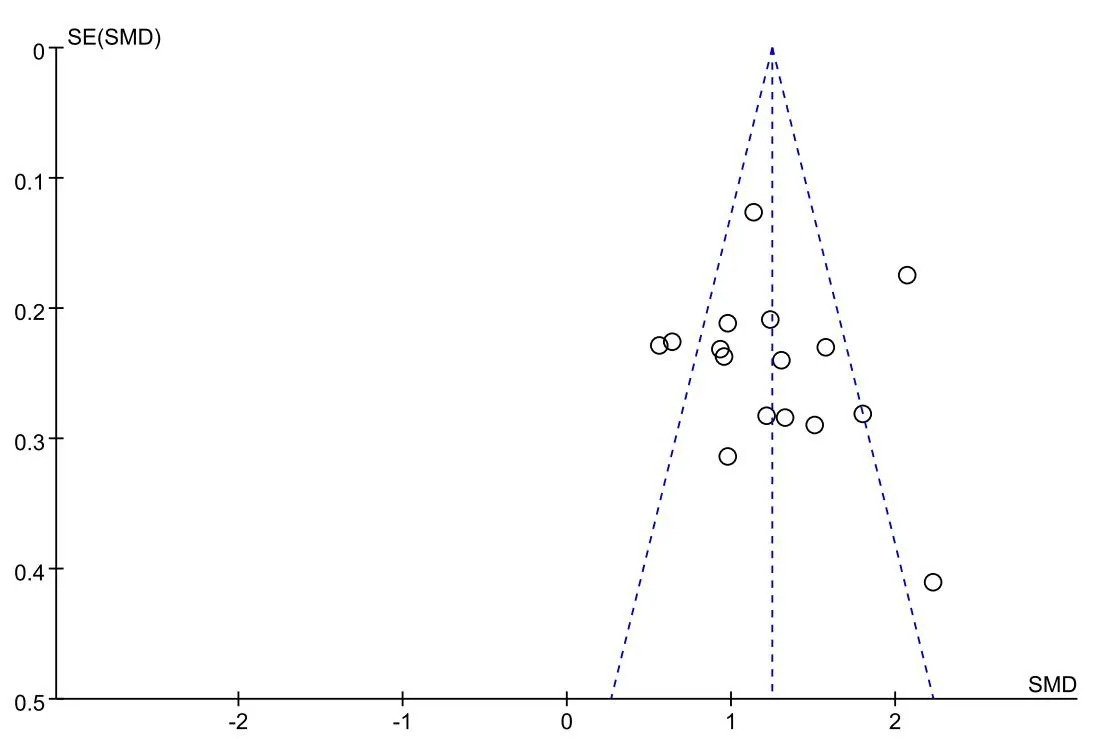
Figure 6 The funnel chart of nursing students’ theoretical test scores.SE, standard error; SMD, standardized mean difference.
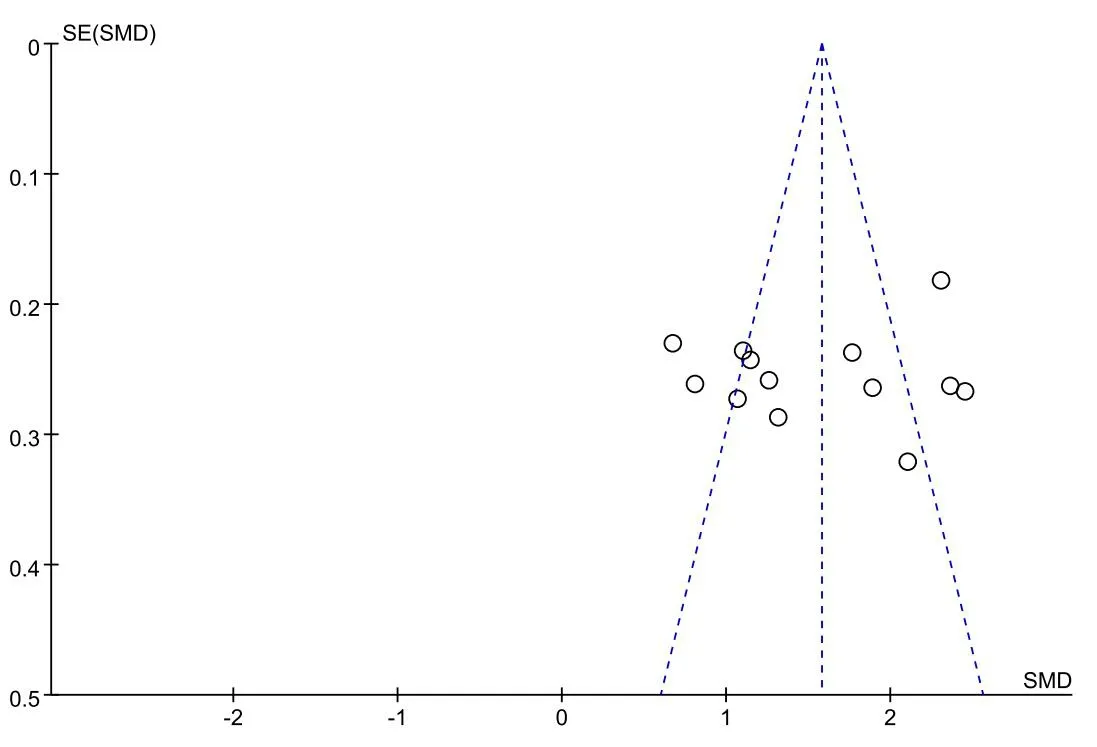
Figure 7 Funnel chart of nursing students’ operational skills achievement.SE,standard error;SMD,standardized mean difference.
Discussion
Summary of major findings
We found that JITT is beneficial to nursing students’ mastery of theoretical and operational knowledge and improves students’independent learning ability and classroom satisfaction.Therefore,the results of this study provide some theoretical support and examination for the application of just-in-time in nursing teaching.
The ultimate goal of nursing education is to promote the application of theoretical knowledge in clinical practice, and our findings indicate that JITT teaching helps nursing students to master theoretical knowledge and improve the operational skill level,which is consistent with the results of Qing study [4, 29–33].Teachers use JITT teaching method to teach, let students use extra-curricular time to learn through the network teaching platform,and actively guide students to participate in the whole teaching process,step by step to set questions,stimulate students’ desire to explore new knowledge, and guide students to quickly enter the best learning state, seriously participate in teaching activities,timely communication with the teacher learning problems encountered, and summarized, which can stimulate their interest in learning, improve the students’ network access to knowledge, but also improve their own theoretical knowledge and nursing skills.Although there were differences among the characteristics of the research subjects,the theoretical and operational results were divided into subgroups according to the different teaching locations, which showed that there was no significant heterogeneity between the studies.The inclusion study was found to have a good representation after the publication bias test, which would provide some evidence for promoting JITT teaching in nursing specialty.
Under the “Internet +” environment, it is of great significance to cultivate college students’ autonomous learning ability for the establishment of a learning society, especially for a major like medicine that needs for lifelong learning, which is also an important work content that conforms to the development of the times [34].Meta-analysis showed that JITT teaching could effectively improve nursing students’ independent learning ability.This is consistent with the results of previous studies [4, 35].The JiTT teaching method makes full use of Internet learning resources and platforms, assigns learning tasks to students online before class, and allows them to explore with questions in class and actively access relevant information through multiple channels.After acquiring the relevant information, the process of communicating with teachers online or in the classroom, analyzing, organizing, sorting, and finally solving problems is to cultivate students’ autonomy and self-reliance.Sensitivity analysis of nine literatures by exclusion-by-exclusion method, the results showed that Chao Deng [26] and others were the main sources of heterogeneity, which may be related to the difference of measurement tools.Other studies mostly used two instruments compiled by Xi-Yan Zhang [36] and Yi Lin [37] to measure the independent learning ability of nursing students, which mainly included the self-management ability, learning motivation,cooperation ability and information acquisition ability, and network for nursing students Learning is not much involved.In contrast, Chao Deng[26]used the Online Independent Learning Assessment Scale for nursing students developed by Dong-Yan Lu [38] to measure nursing students’ independent learning on the Internet, which is more compatible with the “web-based” just-in-time teaching method.After removing this literature, we found that the results did not change significantly, indicating that the results of the meta-analysis of independent learning ability are stable and have some reference value.
Through comprehensive evaluation and feedback on teaching effectiveness, we found that students’ satisfaction in terms of course learning, teaching progress, teaching teachers, and teaching effectiveness exceeded 90%, and most studies support this view.The core of just-in-time teaching is the “feedback chain”, which breaks teachers and students, and allows teachers to clarify learning goals through time and space constraints,increases communication between and tasks, grasp the difficulties students encounter in the learning process, overcome teaching difficulties, successfully complete teaching tasks, and improve nursing students’ satisfaction with teaching.In addition, the study found that there are certain shortcomings in the satisfaction evaluation of the JITT teaching method because the studies mainly evaluated the satisfaction of nursing students with teaching through self-administered questionnaires, and the evaluation content and methods are quite different.There is no quantitative and unified evaluation method about satisfaction; most of them are qualitative and subjective evaluation, and the evaluation mode is relatively single, which makes the quantitative analysis of the results impossible.It may be related to the lack of satisfaction evaluation tools with good reliability and validity at home and abroad.Future nursing educators can further explore constructing a teaching satisfaction evaluation system with good reliability and validity so that the evaluation results are comparable between studies and can provide a reference basis for subsequent studies.
Limitations of this study
Our study has some limitations, as the included literature is mainly in Chinese, and there is not much English literature on the JITT teaching model from English databases, and there are few randomized controlled trial studies; some of the included literature has a less rigorous study design, which may lead to some bias in the results.In addition, there is some heterogeneity among the studies, which may be related to the inconsistency of the intervention time among the included studies, the teaching of course content, the nature and difficulty of the courses taught.The level of faculty teaching nursing students, etc.Because of the inconsistency among studies regarding the above-mentioned confounding factors,subgroup analyses were not conducted for these factors, which may have some influence on the study results.
Conclusion
Our study found that JITT effectively compensates for the shortcomings in traditional nursing teaching, stimulates students’interest in learning,improves teaching satisfaction,and plays a crucial role in developing students’professional knowledge and abilities.This model provides a new direction and idea for the development of online teaching and online courses on the Internet, and is worthy of application and promotion in nursing teaching.Although the methodological quality of the literature included in our study for analysis was relatively low, the included literature data were still analyzed strictly according to the meta-analysis method, and the selected outcome indicators were more focused, which hopefully will provide some reference for the subsequent development of JITT teaching in nursing teaching.We expect more high-quality,large-sample studies to enhance the strength of the argument to obtain more rigorous results and provide a more reliable basis for applying JITT teaching in the field of nursing education.

