A New Fusion Method for Conflicting Evidence
PENG Ying(彭颖),SHEN Huai-rong(沈怀荣),MA Yong-yi(马永一)
(1.Company of Postgraduate Management,the Academy of Equipment Command& Technology,Beijing 101416,China;2.Department of Space Equipment,the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology,Beijing 101416,China)
Introduction
Dempster-Shafer(D-S)theory[1-2]developed in 1970s is one of the evidence-based uncertainty reasoning tools,which can directly represent“uncertain”and“unknown”,and efficiently cope with an uncertainty problem resulted from imprecise and stochastic information without prior information.In the recent years,it has been gradually used in many fields,such as fault prediction[3],and air targets identification[4],etc.However,Dempster’s rule is deficient in fusing the highly conflicting evidences[5]which are caused by outside disturbance or unreliable sensors.The deficiency limits its application to a certain extent.
For the deficiency of Dempster’s rule in coupling the highly conflicting evidences,many alternative combination rules[6]have been proposed,which can be mainly classified into two categories:1)a new combination rule,such as Yager’s rule[7],Dubois and Prade’s rule[8],reassigns the conflicts to avoid wrong fusion result.However,the reassignment of conflicts is usually controlled by some subjective factors,and some alternative rules lose the associativity.On the whole,the alternate rules in this category are considered unsatisfactory;2)modified fusion rule is based on the data model,such as Dempster’s discounting rule[1],Murphy’s rule[9],etc.Haenni[10]indicated from the point of view of engineering,philosophy and mathematics that Dempster’s rule needs not have any alternative rules but rather its model should be modified,i.e.evidence source.From the comparison of several alternative rules[11]it is concluded that the alternative rules of modifying the data model is more effective in dealing with conflict evidences.
Discounting is a widely-used approach in alternative rules of modifying the data model.In the rules of this category,because the evidences are considered unreliable,the influence of these unreliable evidences on fusion result can be effectively decreased by discount the evidences.Two typical evidence discounting methods were presented in Ref.[12 - 13].However,these two methods reduce the supporting degree of most evidences for true hypothesis so that it makes the fusion results focus onto the true hypothesis weakly.To resolve this problem,a new fusion method for conflict evidences is proposed in this paper.The new method is to use a discounting way to keep the evidences supporting the true hypothesis to a great extent,and make the fusion result focus onto the true hypothesis more strongly.Hence,the new method presents good convergence.Finally,the examples of fault diagnosis for some missile show the superiority of the new method.
1 D-S Theory and Discounting Analysis
1.1 Some Definitions
Definition 1The frame of discernment is a finite set of mutually exclusive elements,denoted asΘ={a1,a2,…an}.
In real application,Θcorresponds to the range of discrete values for object under study.All subsets ofΘfrom the power set are as 2Θ.Evidence is the essential information carrier in D-S Theory and is represented by basic probability assignment(BPA).

Definition 3Letm1andm2be two BPAs defined on frameΘwhich are derived from two reliable and distinct sources.Dempster’s rule combining two BPAs is given bym=m1⊕m2:
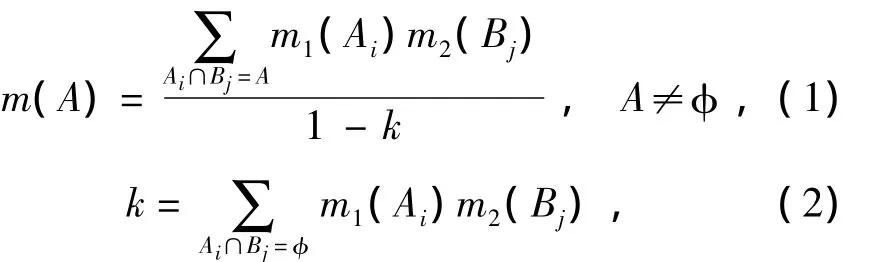
whereA,Ai,Bj∈2Θ,kis produced by conjunctive operation,so it is called a conjunctive conflict for short in this paper.kis often used to measure the degree of conflict.k∈[0,1].When the value ofkis relatively high,the conflict among the evidences is relatively severe.k=1 means that two evidences are totally conflicting.
However,the conjunctive conflict between two identical evidences may be very high[14],sokcannot be used to distinguish two identical evidences.Jousselme,et al.proposed a conflict measure,called evidence distance[15],which can distinguish two identical evidences.
Definition 4Letm1andm2be two BPAs defined on frameΘ,the distance betweenm1andm2is given by

wheredBPAis used to measure the dissimilarity between two evidences.WhendBPAis taken as a high value,the two evidences have little similarity.Especially,fordBPA=0,the two evidences are identical.
A counterintuitive result can be obtained by using Dempster’s rule to fuse the highly conflicting evidences.For example,supposeΘ={a,b,c},two pairs of BPAs are:m1({a})=0.99,m1({b})=0.01,m1({c})=0;m2({a})=0,m2({b})=0.01,m2({c})=0.99.The result obtained by using Dempster’s rule ism({a})=m({c})=0,m({b})=1.It is obvious that the two evidences assign very low belief tob,but the fusion result reassigns the whole belief tob.Hence,the fusion result is not right.Dempster’s rule cannot be used to cope with highly conflicting evidences.
1.2 Discounting Analysis
Supposemis the BPA of evidencee,and its discounting factor isα,the discounted evidence is:

The evidencee*supported by other evidences to the highest was first recognized in Ref.[12 -13].The discounting factor ofe*is 1,and other evidences obtain the corresponding discounting factors according to the conflict between them ande*.After discounted by Eq.(5),they are fused using Dempster’s rule.In the following,the evidence sets are classified simply to an-alyze the influence of evidence discounting on fusion results.SupposeΘ={a,b,c},the BPA of evidencee*ism*({a})=0.9,m*({b})=0.1.
1.2.1 Reliable Evidence
Reliable evidence is defined as an evidence that gets higher degree of support from other evidences in an evidence set.The dissimilarity between the reliable evidences is small.
e*belongs to reliable evidence.Suppose the BPA of another reliable evidencee1to satisfym1({a})=0.8,m1({b})=0.1,m1({c})=0.1.The evidence distance betweene*ande1isdBPA(m*,m1)=0.1,which indicates small dissimilarity.If Dempster’s rule is used to fuse them,we obtain:m1({a})=0.986 3,andm1({b})=0.013 7.It is clear that the fusion result is focused onto the true hypothesisa.Fig.1 shows the changing trend of mass of right hypothesisawhen the discounting factor ofe1changes in range[0,1].

Fig.1 Influence of reliable evidence discount on mass of right hypothesis a
It can be seen from Fig.1 that,when the discounting factor ofe1is 1,the fusion result assigns the highest supporting degree to the true hypothesisa.When the discounting factor is decreased,the fusion result assigns lower supporting degree toa.Therefore,the reliable evidences are discounted to decrease their supporting degree for true hypothesis.Accordingly,it is necessary to set all the discounting factor of reliable evidences to 1 to ensure that the fusion result is focused onto the true hypothesis to the greatest extent.
1.2.2 Non-conflicting Evidence
Non-conflicting evidence is defined as an evidence which has large dissimialrity and small conjunctive conflict with the reliable evidences in evidence set.Reliable evidence and non-conflicting evidence support each other.
Suppose BPA of a non-conflicting evidencee2to satisfym2({a,c})=0.9 andm2({b})=0.1.The evidence distance and conjunctive conflict betweene*ande2aredBPA(m*,m2)=0.64,andk(m*,m2)=0.18,respectively.If Dempster’s rule is used to fuse them,we obtain:m2({a})=0.987 8,andm2({b})=0.012 2.It is clear that the fusion result is focused onto the true hypothesisa.So the non-conflicting evidence and the reliable evidence support each other.The uncertainty of focal element can be effectively decreased to focus the fusion result onto the true hypothesis by using Dempster’s rule.Fig.2 shows the changing trend of mass of right hypothesisawhen the discounting factor ofe2changes in range[0,1].
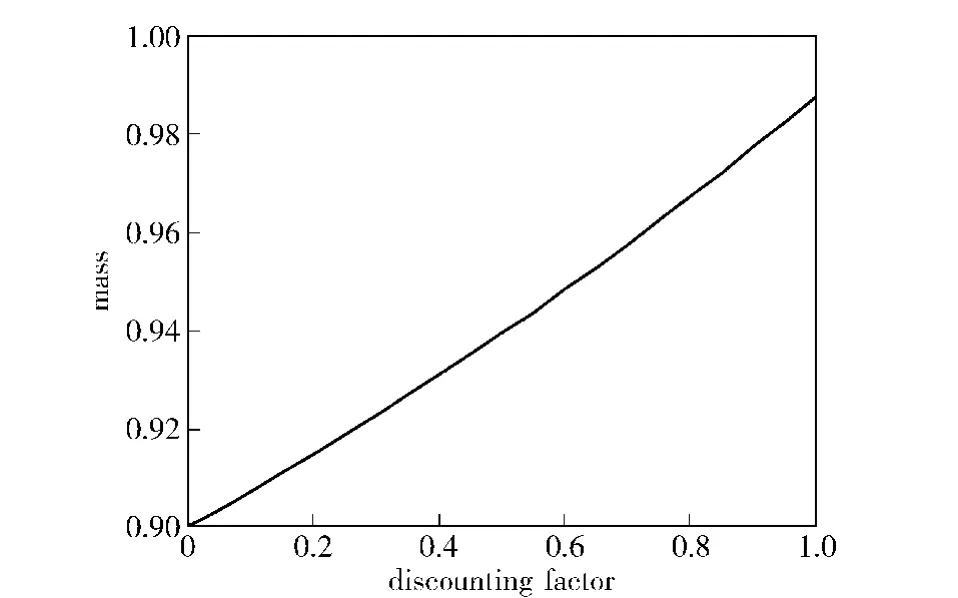
Fig.2 Influence of non-conflicting evidence discount on mass of right hypothesis a
It can be seen from Fig.2 that the fusion result assigns the highest supporting degree to the true hypothesisawhen the discounting factor ofe2is 1.The fusion result assigns lower supporting degree toawhen the discounting factor is decreased.Therefore,the reliable evidences are discounted to decrease their supporting degree for true hypothesis.It is necessary to set all the discounting factor of non-conflicting evidences to 1 to ensure that the fusion result is focused onto the true hypothesis to the greatest extent.
1.2.3 Conflicting Evidence
Conflicting evidence is defined as an evidence which has large dissimialrity and large conjunctive conflict with the reliable evidences in evidence set.
Suppose BPA of a conflicting evidencee3to satisfym3({a})=0.05,andm3({b})=0.9,m3({c})=0.05.The evidence distance and conjunctive conflict betweene*ande3aredBPA(m*,m3)=0.826,andk(m*,m3)=0.865 ,respectively.If Dempster’s rule is used to fuse them,we obtain:m3({a})=0.333 3,andm3({b})=0.666 7.It can be seen from the fusion result that the belief assigned to the true hypothesisais smaller than that assigned to the incorrect hypothesisb.It is obvious that the fusion result can be deviated from the true hypothesis by fusing the conflicting evidence and the reliable evidence using Dempster’s rule.Therefore,the conflicting evidence cannot be directly fused using Dempster’s rule.Fig.3 shows the changing trend of mass of right hypothesisawhen the discounting factor ofe3changes in range[0,1].

Fig.3 Influence of conflicting evidence discount on mass of right hypothesis a
From Fig.3,we can see that the fusion result assigns the highest supporting degree to the true hypothesisawhen the discounting factor of conflicting evidence is 0.When the discounting factor is increased,the fusion result assigns lower supporting degree toa.Therefore,the conflicting evidence can be discounted to decrease its effect on the fusion result.
Consequently,when the discounting method is used to fuse the evidences,the reliable evidences and non-conflicting evidences should be recognized as more as possible.The discounting factor of the two categories of evidences should be set to 1 to keep their largest supporting degree to the true hypothesis.For the conflicting evidences,to set their discounting factor to 0 is like to completely abandon them.It is reasonable to assign a discounting factor to the conflicting evidence according its conflicting degree,thereby retaining the partial information of evidence is retained,and decreasing the influence of conflicting evidence on the fusion result.
In Ref.[12 -13],the evidence distance and the Pignistic probability distance are used to measure the evidence conflicts,respectively.There is a certain behavior similarity in the Pignistic probability distance and the evidence distance[14,16]. Theirdiscouting methods have two major drawbacks:
1)Only the discounting factor ofe*is set to 1,and the others are set to the values that are smaller than 1.The supporting degree of the evidences to the true hypothesis is decreased.
2)The non-conflicting evidences get very small discounting factor because of their large dissimilarity with reliable evidence,thus decreasing the supporting degree of the evidences to the true hypothesis.A new fusion method for conflicting evidence is proposed in order to resolve these problems.
2 New Fusion Method for Conflicting Evidence
2.1 Evidence Recognition
The average evidence distance and the average conjunctive conflict of evidence and evidence set are defined firstly.Suppose an evidence set isE={ei,i=1…n},the corresponding BPAs areM={mi,i=1…n}.
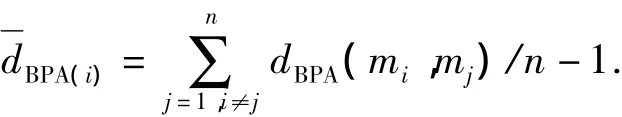
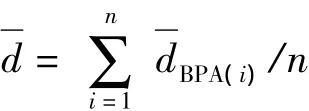

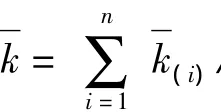
Practically,the conflicting evidences are in the minority in the evidence set related to the same object,and the most of evidences are reliable.The dissimilarity between the reliable evidences is small.And the evidence distance is used to measure the dissimilarity.The shorter the evidence distance is,the smaller the dissimilarity between the evidences is.Therefore,the new method proposed in this paper recognizes the reliable evidences by using evidence distance.Firstly,the evidences with short average evidence distance are recognized as the reliable evidences in an evidence set.Secondly,the evidences which has a small conjunctive conflict with the reliable evidences are recognized.These evidences are taken as non-conflicting evidences.And at last,the evidences which are not recognized in evidence set are not totally reliable evidences which contain the conflicting evidences,the possible minority of reliable evidences,and the nonconflicting evidences.
Suppose the evidence set to beE0={e1,e2,…,en},and the corresponding BPAs areM0={m1,m2,…,mn}.The evidence recognition steps are as follows:
1)Recognition of reliable evidence
Theaverage evidence distance (denoted asBPA(i))ofeiand the average evidence distance(denoted as)of the evidence setE0are computed.The minimal average evidence distance is denoted asdmin=min().
2)Recognition of non-conflicting evidences and uncomplete reliable evidences

An example will be given to explain how the evidences are recognized and the validity of recognition is verified.
Suppose the evidence set to beE0={e1,e2,…,e5}.The five evidences are distinct and based on a recognition frame,i.e.Θ={a,b}.The corresponding BPAs are:
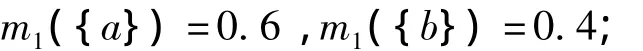
m2({a})=0.65,m2({b})=0.3,m2(Θ)=0.05;


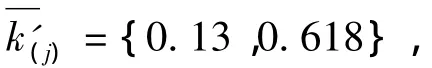
In fact,three evidences in set explicitly supportaas true hypothesis,only one evidence set supportsbas true hypothesis.According to the idea of that the minority is subordinate to the majority,the true hypothesis should bea.Hence,the evidencese1,e2ande3which supportaas true hypothesis are reliable.The evidencee4may support eitheraorbas true hypothesis.Combininge4with the reliable evidence,we obtain a result that focuses onto the true hypothesisa.So the evidencee4is a non-conflicting evidence.The evidencee5strongly supportsbas true hypothesis,which conflict with most of evidences in setE0.e5is a conflicting evidence.The recognition result agrees with the analysis result,which shows the validity of recognition.
2.2 Discounting and Fusion
1)Discounting factor

2)Fusion
According to Eq.(5),the evidences are discounted and combined using Dempster’s rule.
The new method proposed in this paper is fit for over two evidences.For two evidences,Murphy’s rule is recommended.Actually,if only two evidences support the different hypotheses,we cannot draw a right conclusion just from them.In this case,more evidences are required to get more information on truth to help us with judgement.
3 Application
The validity of the new method is validated by taking the fault diagnosis of some missile during testing for example.
A missile is at fault during testing.Four featurelevel fusion approaches are utilized to fuse and diagnose several sets of fault signals,respectively,and four primary results about the true fault are obtained.The primary results refer to three possible faults which are denoted asa,bandc,respectively.Modeling with DS theory,we denote the recognition frame asΘ={a,b,c},and four primary results are described by the evidencese1,e2,e3ande4.The two tests are carried out on normal and disturbing conditions,respectively.
1)Normal condition
The BPAs of four evidences are:
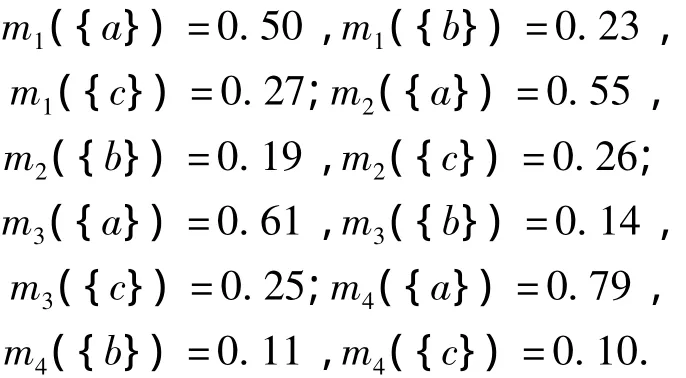
On normal condition,non-conflicting evidence exists in the evidence set.The fusion results of the four evidences obtained by Dempster’s rule,Yager’s rule,Murphy’s rule,the rules in Ref.[12 -13],and the method proposed in this paper are listed in Tab.1.

Tab.1 Comparison offusion results
It can be seen from Tab.1 that,except for Yager's,all the rules are useful on normal testing condition,and the fusion result is the faulta.Yager’s rule assigns all the conjunctive conflicts to the recognition frame,which leads to an increasing mass of the recognition frame.The result is bad for decision-making.Among the useful rules,Dempster’s rule and the new method proposed in this paper show better convergence.When the new method is used,e1,e2ande3are reliable evidences,e4is non-conflicting evidence,and the discounting factors of all these four evidences are 1.In Ref.[12 -13],only the discounting factor ofe2is assigned to 1,and other discounting factors are less than 1.The dealing decreases the supporting degree of the evidences for true hypothesis.
2)On disturbing condition
The fault signals are disturbed during testing so that the BPAs of the second evidence is changed to:m2({a})=0,m2({b})=0.85,m2({c})=0.15.In this case,the experts gave out a new diagnostic result according to the sound,light and electric information from the testbed.The new result is taken as the fifth evidence,and its BPA ism5({a,c})=0.8,andm5({b})=0.2.The fusion results of the four evidences obtained by Dempster’s rule,Yager’s rule,Murphy’s rule,the rules in Ref.[12 -13],and the method proposed in this paper are listed in Tab.2.
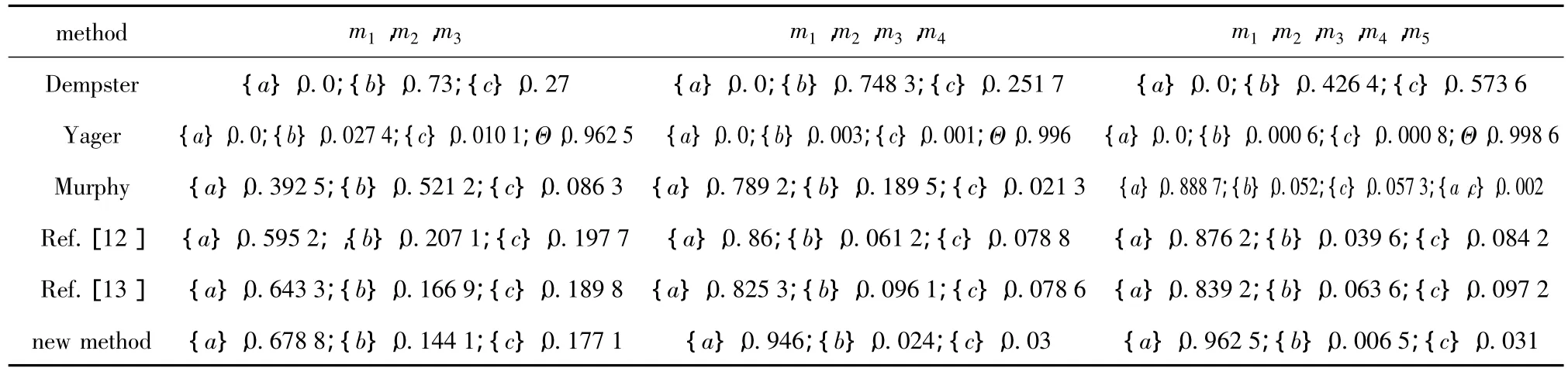
Tab.2 Comparison of fusion results
It can be seen from Tab.2 that the new method is used to assign the highest mass to the faultacompared to other methods.
Dempster’s rule and Yager’s rule are‘one-votedown’,i.e.,if one evidence in the evidence set assigns mass of 0 to propositionA,the mass of propositionAin final fusion result is always 0,regardless of whether other evidences in the evidence set highly support propositionA.Murphy’s rule decreases the influence of conflicting evidences by adding all evidences.The rule ignores the reliability of evidence,and needs much more reliable evidences to counteract the influence of conflicting evidences.
In Ref.[12],only the discounting factor ofe1is 1.In Ref.[13],only the discounting factor ofe3is 1.The discounting factors of other evidences are less than 1.
In our new method,when three evidences are collected,e1ande3are recognized as the reliable evidences.Hence,their discounting factors are set to 1.Compared with other methods,the new method increases the supporting degree of the evidences for the true hypothesis,and obtains the best fusion result.When four evidences are collected,e1,e3ande4are recognized as the reliable evidences,and their discounting factors are 1.After fusion,the mass ofareaches 0.946,which is increased by 10%and 14.6%compared with the rules in Ref.[12 - 13].respectively.When five evidences are collected,e1,e3ande4are recognized as the reliable evidences,ande5is recognized as non-conflict evidence.The discounting factor of all the four evidences are set to 1.After fusion,the mass ofareaches 0.962 5,which is increased 9.8%and 14.7%compared with the rules in Ref.[12 -13],respectively.
It can be found from comparison that the new method can deal with the highly conflicting evidences and obtain right fusion result.The method indicates better convergence.It improves the accuracy of missile fault diagnosis on disturbing condition.
4 Conclusions
D-S theory indicates its superiority in expressing and fusing the uncertain information.It can be used for fault diagnosis,and object recognition,etc.However,Dempster’s rule cannot deal with highly conflicting evidences caused by outside disturbance or unreliable sensors.The discounting is a common method,while it’s difficulty is how to obtain the discounting factor.
In this article,the evidences are classified into three categories:reliable evidence,non-conflicting evidence,and conflicting evidence.The influences of these three categories of evidences on fusion result are analyzed,it is concluded that:when the discounting factor of reliable evidence and non-conflicting evidence are set to 1,the evidences keep their most supporting degree for true hypothesis.On this base,a new fusion method is put forward.The new method recognizes most of reliable evidences and non-conflicting evidences.The discounting factor of these evidences are set to 1.The fault diagnosis example of some missile shows that the new method can effectively cope with the conflicting evidences and the non-conflicting evidences.The new method shows its superiority in convergence and reliability.
[1]Dempster A P.Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multi-valued mapping[J].Annals of Mathematical Statistics,1967,38:325 -339.
[2]Shafer G.A mathematical theory of evidence[M].Princeton:Princeton University Press,1976.
[3]SI Xiao-sheng,HU Chang-hua,ZHOU Zhi-jie.Fault prediction model based on evidential reasoning approach[J].Science China(Information Sciences),2010,40(7):954-967.(in Chinese)
[4]JIANG Wen,ZHANG An,DENG Yong.Dynamic determination of sesor credibility in data fusion and its application[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2010,42(7):1137-1140.(in Chinese)
[5]Zadeh L A.Simple view of the Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence and its implication for the rule of combination[J].AI Magazine,1986,7(1):85-90.
[6]LI Wen-li,GUO Kai-hong.Combination rules of D-S evidence theory and conflict problem[J].System Engineering-Theory& Practice,2010,30(8):1422-1432.(in Chinese)
[7]Yager R R.On the Dempster-Shafer framework and new combination rules[J].Information Sciences,1987,41(2):93-137.
[8]Dubois D,Prade H.Representation and combination of uncertainty with belief functions and possibility measures[J].Comput Intell,1988,(4):244-264.
[9]Murphy C.Combining of belief functions when evidence conflicts[J].Decision Support Systems,2000,29(1):1-9.
[10]Haenni R.Are alternatives to Dempster’s rule of combination real alternatives?comments on“about the belief combination and the conflict management problem”[J].Infomation Fusion,2002,3(3):237-239.
[11]CHEN Tian-lu,QUE Pei-wen.Research on invalidation of D-S evidential theory in data fusion[J].Journal of Transducer Technology,2004,23(12):25-27.(in Chinese)
[12]LU Wen-xing,LIAN Chang-yong,DING Yong.A method determining the objective weights of experts based on evidence distance[J].Chinese Journal of Management Science,2008,16(6):95-98.(in Chinese)
[13]HU Chang-hua,SI Xiao-sheng,ZHOU Zhi-jie,et al.An improved D-S algorithm under new measure criteria of evidence conflict[J].Acta Electronica Sinica,2009,37(7):1578-1583.(in Chinese)
[14]LIU Wei-ru.Analyzing the degree of conflict among belief functions[J].Artifical Intelligence,2006,170(11):909-924.
[15]Jousselme A L,Dominic G,Bosse E.A new distance between two bodies of evidence[J].Information Fusion,2001,2(2):91-111.
[16]Smets P,Kennes R.The transferable belief model[J].Artifical Intelligence,1994,66(3):191-234.
- Defence Technology的其它文章
- Study on Effects of Diesel Engine Cooling System Parameters on Water Temperature
- Numerical Simulation and Performance Analysis on Windmill Starting Process of Small Turbojet Engine
- New Wideband Beam-forming Method Used in Underwater Communication System
- Research on Estimation of Time Delay Difference in Passive Locating for Impulse Signal
- Reliability Sensitivity Analysis for Location Scale Family
- Waveguide Invariant and Passive Ranging Using Double Element

