苏氏圆腹肌肉化学成分分析与评价
刘修英,刘叶子,朱崇梅,赵德福
(1.河南水利与环境职业学院,河南郑州 450008;2.西南大学,重庆 400715;3.河南水产科学研究院,河南郑州 450044)

刘修英1,刘叶子2,朱崇梅1,赵德福3
(1.河南水利与环境职业学院,河南郑州 450008;2.西南大学,重庆 400715;3.河南水产科学研究院,河南郑州 450044)



1 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器

Foss 2300全自动凯氏定氮仪 瑞典Foss Tecator公司;新嘉SZF-06A半自动索氏抽提仪 上海新嘉电子有限公司;马弗炉 北京中兴伟业仪器有限公司;日立835-30型氨基酸分析仪 日本Hitachi公司;Agilent 7890B-5977A气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国Agilent科技公司。
1.2 样品鱼处理
样品鱼去皮,取侧线以上背部肌肉,混匀,分两份,一份用于常规成分测定,一份用于脂肪酸测定,用塑料袋密封,储存在-20 ℃冰箱中保存。
1.3 检测方法
鱼肉样品在常规成分分析前用高压灭菌锅120 ℃蒸煮30 min,75 ℃烘干,用高速粉碎机粉碎、过40目筛。按AOAC方法[5]分析样品中水分、粗蛋白、粗脂肪、氨基酸含量,色氨酸用6 mol/L的氢氧化钠溶液水解后测定。
采用气相色谱-质谱联用仪测定样品中脂肪酸。参照Bligh-Dyer的方法[6]用氯仿-甲醇提取脂肪,经14%三氟化硼-甲醇溶液甲酯化后,加入正己烷进行萃取,静置分层后,取上层有机相用针头滤器(0.22 μm)过滤后进样分析,按峰面积归一化法计算脂肪酸相对百分含量。气相色谱条件:毛细管柱为HP-INNOWax(30 m×0.25 mm i.d.×0.50 μm),柱初始温度为120 ℃,保持2 min,以3 ℃/min升温至230 ℃,保持20 min;气化室温度250 ℃;载气:氦气;柱流速:1 mL/min;分流比:1∶1;进样量:1 μL。质谱条件:离子化方式:电子轰击(EI);离子化能量:70 eV;离子源温度:230 ℃;传输线温度:250 ℃;四极杆温度:150 ℃;溶剂延迟:3 min;扫描方式:全离子扫描(SCAN);扫描范围:50~450 amu。
1.4 评价方法
鱼肉蛋白质营养价值评定根据FAO/WHO1973年建议的每克氮氨基酸评分标准模式和鸡蛋蛋白质评分标准模式进行,分别按照以下公式计算必需氨基酸评分(AAS)、必需氨基酸化学分数(CS)、必需氨基酸指数(EAAI)[7]。
AAS=被测蛋白质中氨基酸含量(mg/gN)÷FAO/WHO评分标准中同种氨基酸含量(mg/gN)
式(1)
式(2)
式(3)
公式(3)中a:被测蛋白必需氨基酸含量(mg/g N);A:参考蛋白(鸡蛋)必需氨基酸含量(mg/g N);n:比较的必需氨基酸个数。
鱼肉脂肪酸的评价按照致动脉粥样硬化指数AI值进行,计算公式[6]如下
式(4)
式(4)中,∑MFA为单不饱和脂肪酸含量总和;∑PUFA为多不饱和脂肪酸含量总和。C12∶0为月桂酸含量;C14∶0为豆蔻酸含量;C16∶0为棕榈酸含量。
1.5 数据处理
实验结果为3个平行样测试的平均值,以平均值±标准差(mean±SD)表示,数据处理用SPSS 16.0。
2 结果与分析

表1 苏氏圆腹与其它经济鱼类肌肉营养成分含量比较(n=3,%鲜重)Table 1 Comparison of nutritional components in muscle of P. hypophthalmu with other economic fish species(n=3,% wet basis)
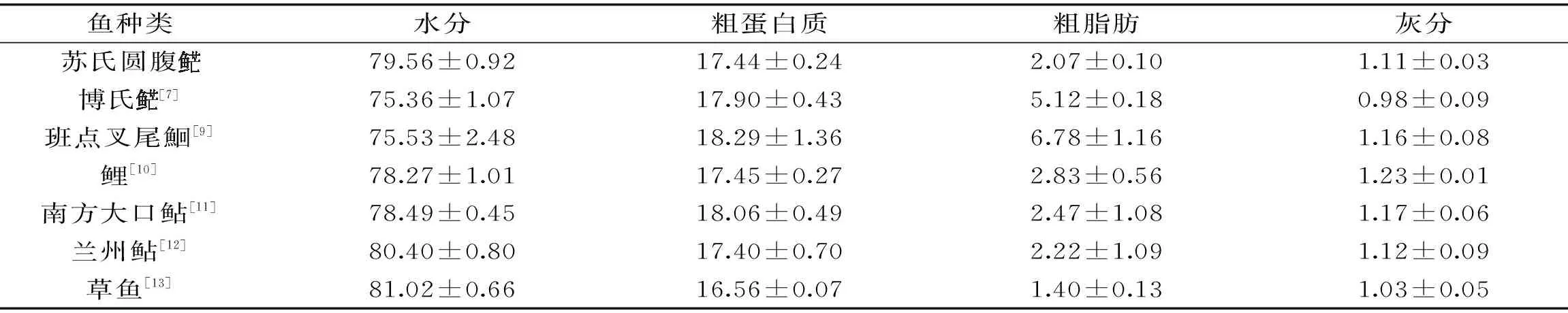
表1 苏氏圆腹与其它经济鱼类肌肉营养成分含量比较(n=3,%鲜重)Table 1 Comparison of nutritional components in muscle of P. hypophthalmu with other economic fish species(n=3,% wet basis)
鱼种类水分粗蛋白质粗脂肪灰分苏氏圆腹79.56±0.9217.44±0.242.07±0.101.11±0.03博氏[7]75.36±1.0717.90±0.435.12±0.180.98±0.09班点叉尾鮰[9]75.53±2.4818.29±1.366.78±1.161.16±0.08鲤[10]78.27±1.0117.45±0.272.83±0.561.23±0.01南方大口鲇[11]78.49±0.4518.06±0.492.47±1.081.17±0.06兰州鲇[12]80.40±0.8017.40±0.702.22±1.091.12±0.09草鱼[13]81.02±0.6616.56±0.071.40±0.131.03±0.05
表2 苏氏圆腹肌肉氨基酸组成和含量(n=3,%干基)Table 2 Amino acids composition and contents of muscle of P. hypophthalmus(n=3,% dry basis)

表2 苏氏圆腹肌肉氨基酸组成和含量(n=3,%干基)Table 2 Amino acids composition and contents of muscle of P. hypophthalmus(n=3,% dry basis)
氨基酸种类含量氨基酸种类含量苏氨酸*3.72±0.05天冬氨酸#8.28±0.07缬氨酸*3.87±0.09甘氨酸#3.83±0.05蛋氨酸*2.30±0.02谷氨酸#13.78±0.17异亮氨酸*3.68±0.10丙氨酸#4.91±0.09亮氨酸*6.81±0.07脯氨酸2.64±0.05苯丙氨酸*3.53±0.05氨基酸总和79.90±0.97赖氨酸*7.70±0.03必需氨基酸(EAA)32.32±0.42色氨酸*0.71±0.03非必需氨基酸(NEAA)47.58±0.71组氨酸2.06±0.02呈味氨基酸30.80±0.33精氨酸5.30±0.10EAA/TAA40.45%胱氨酸0.82±0.07EAA/NEAA67.93%酪氨酸2.67±0.10DAA/TAA38.55%丝氨酸3.29±0.12



表3 苏氏圆腹肌肉必需氨基酸组成(mg/g N,以氮为基础)评价Table 3 Evaluation of essential amino acid composition(mg/g N,based on nitrogen)in muscle of P. hypophthalmus
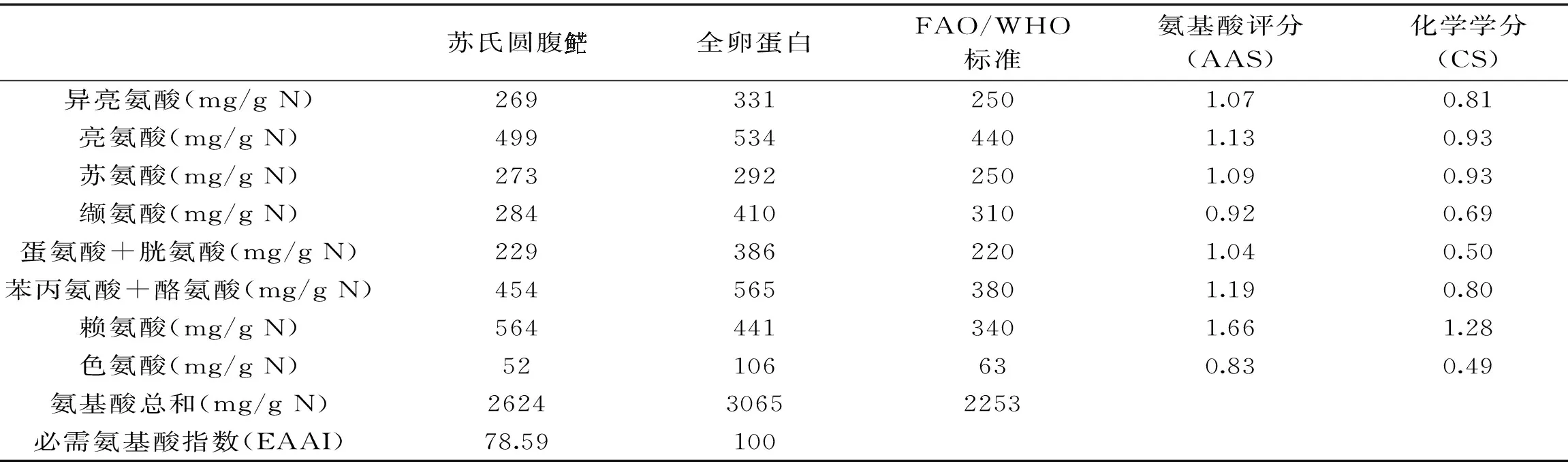
表3 苏氏圆腹肌肉必需氨基酸组成(mg/g N,以氮为基础)评价Table 3 Evaluation of essential amino acid composition(mg/g N,based on nitrogen)in muscle of P. hypophthalmus
苏氏圆腹全卵蛋白FAO/WHO标准氨基酸评分(AAS)化学学分(CS)异亮氨酸(mg/gN)2693312501.070.81亮氨酸(mg/gN)4995344401.130.93苏氨酸(mg/gN)2732922501.090.93缬氨酸(mg/gN)2844103100.920.69蛋氨酸+胱氨酸(mg/gN)2293862201.040.50苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸(mg/gN)4545653801.190.80赖氨酸(mg/gN)5644413401.661.28色氨酸(mg/gN)52106630.830.49氨基酸总和(mg/gN)262430652253必需氨基酸指数(EAAI)78.59100
表4 苏氏圆腹与其它经济鱼类肌肉必需氨基酸和呈味氨基酸含量的比较Table 4 Comparison essential amino acids and delicious amino acids in muscle of P. hypophthalmus with other economic fish species
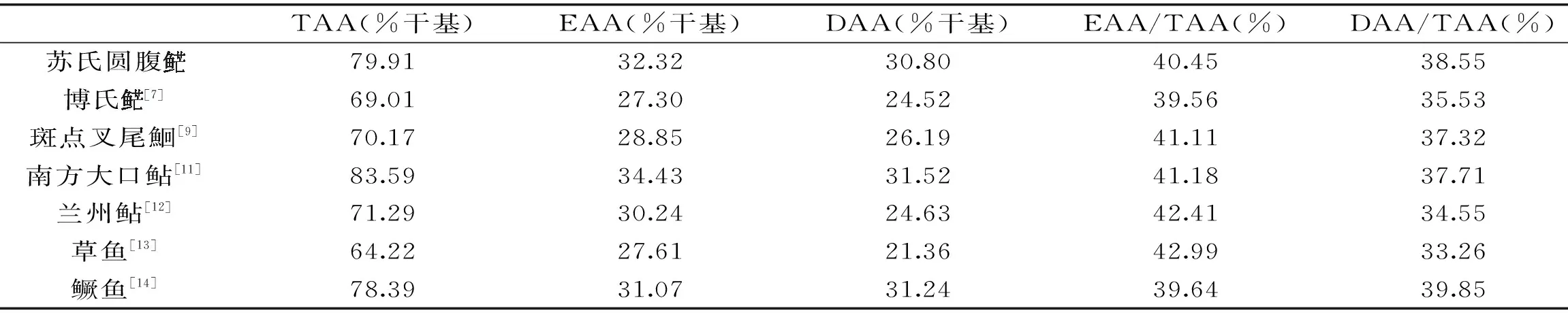
表4 苏氏圆腹与其它经济鱼类肌肉必需氨基酸和呈味氨基酸含量的比较Table 4 Comparison essential amino acids and delicious amino acids in muscle of P. hypophthalmus with other economic fish species
TAA(%干基)EAA(%干基)DAA(%干基)EAA/TAA(%)DAA/TAA(%)苏氏圆腹79.9132.3230.8040.4538.55博氏[7]69.0127.3024.5239.5635.53斑点叉尾鮰[9]70.1728.8526.1941.1137.32南方大口鲇[11]83.5934.4331.5241.1837.71兰州鲇[12]71.2930.2424.6342.4134.55草鱼[13]64.2227.6121.3642.9933.26鳜鱼[14]78.3931.0731.2439.6439.85

表5 苏氏圆腹肌肉脂肪酸组成(n=3,%总脂肪酸)Table 5 Fatty acid profiles of muscle ofP. hypophthalmus(n=3,% total fatty acids)
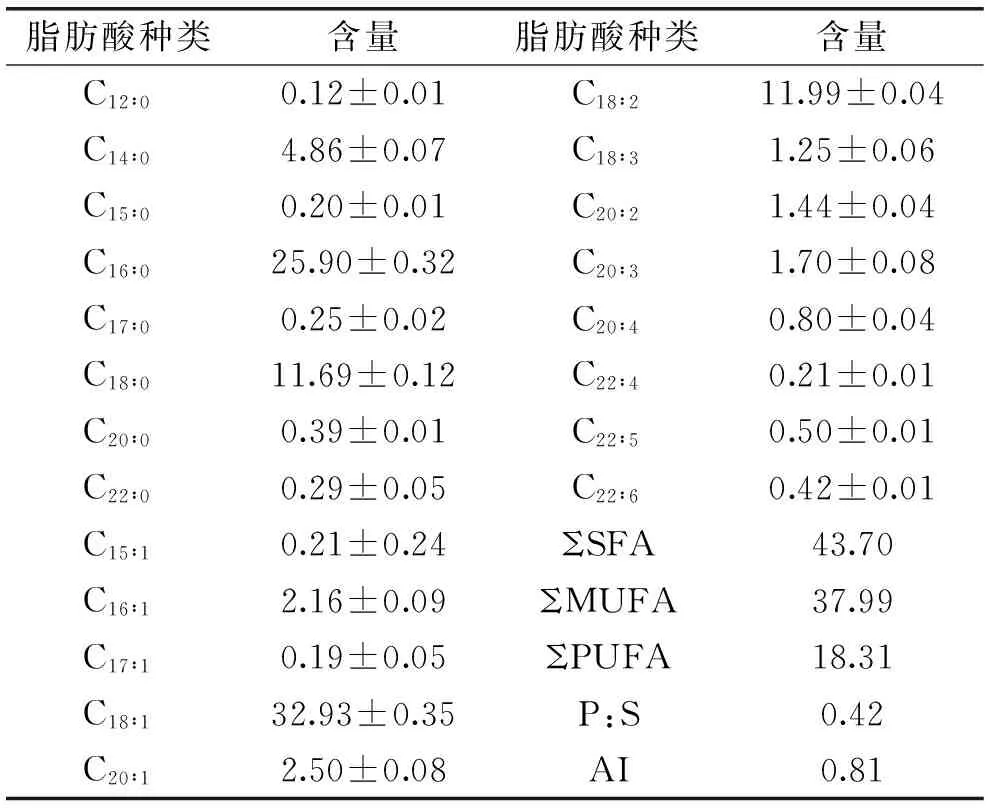
表5 苏氏圆腹肌肉脂肪酸组成(n=3,%总脂肪酸)Table 5 Fatty acid profiles of muscle ofP. hypophthalmus(n=3,% total fatty acids)
脂肪酸种类含量脂肪酸种类含量C12∶00.12±0.01C18∶211.99±0.04C14∶04.86±0.07C18∶31.25±0.06C15∶00.20±0.01C20∶21.44±0.04C16∶025.90±0.32C20∶31.70±0.08C17∶00.25±0.02C20∶40.80±0.04C18∶011.69±0.12C22∶40.21±0.01C20∶00.39±0.01C22∶50.50±0.01C22∶00.29±0.05C22∶60.42±0.01C15∶10.21±0.24ΣSFA43.70C16∶12.16±0.09ΣMUFA37.99C17∶10.19±0.05ΣPUFA18.31C18∶132.93±0.35P:S0.42C20∶12.50±0.08AI0.81
3 结论
[1]Orban E,Nevigato T,Lena G Di,et al. New trends in the seafood market. Sutchi catfish(Pangasiushypophthalmus)fillets from Vietnam:Nutritional quality and safety aspects[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,110(2):383-389.
[2]Ho BT,Paul DR. Fatty acid profile of Tra Catfish(Pangasiushypophthalmus)compared to Atlantic Salmon (Salmo solar)and Asian Seabass(Lates calcarifer)[J]. International Food Research Journal,2009,16(4):501-506.
[3]Domiszewski Z,Bienkiewicz G,Plust D. Effects of different heat at treatments on lipid quality of striped catfish(Pangasiushypophthalmus)[J]. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum. Technologia Alimentaria,2011,10(3):359-373.
[4]Men LT,Thanh VC,Hirata Y,et al. Evaluation of the genetic diversities and the nutritional values of the Tra(Pangasiushypophthalmus)and the Basa(Pangasiusbocourti)Catfish cultivated in the Mekong river delta of Vietnam[J]. Asian Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences,2005,18(5):671-676.
[5]Cunniff P. Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International[M]. 16th edn. Arlington USA:AOAC international,1995:1-28.
[6]李玉琪,朱永祥,陶宁萍. 气相色谱法测定不同水域刀鲚肉中脂肪酸含量[J].食品工业科技,2014,35(20):57-65.

[8]Hung LT,Suhenda N,Slembrouck J,et al. Comparison of dietary protein and energy utilization in three Asian catfishes(Pangasiusbocourti,P.hypophthalmusandP.djambal)[J]. Aquaculture Nutrition,2004,10(5):317-326.
[9]甄润英,陶秉春,马俪珍,等. 3种鲶鱼肌肉主要营养成分的对比分析[J].食品与机械,2008,24(4):109-142.
[10]闫学春,梁利群,曹顶臣,等. 转基因鲤与普通鲤的肌肉营养成分比较[J]. 农业生物技术学报,2005,13(4):528-532.
[11]张凤枰,宋军,张瑞,等. 养殖南方大口鲶肌肉营养成分分析和品质评价[J].食品科学,2012,33(17):274-278.
[12]杨元昊,李维平,龚月生,等. 兰州鲇肌肉生化成分分析及营养学评价[J].水生生物学报,2009,33(1):54-60.
[13]程汉良,蒋飞,彭永兴,等. 野生与养殖草鱼肌肉营养成分比较分析[J].食品科学,2013,34(13):266-270.
[14]梁银铨,崔希群,刘友亮. 鳜肌肉生化成分分析和营养品质评价[J].水生生物学报,1998,22(4):386-388.
[15]缪凌鸿,戈贤平,刘波,等. 三角鲂和长春鳊肌肉营养成分分析与品质评价[J].动物学杂志,2013,48(1):87-94.
[16]王伟,陈志成,魏壹纯,等. 彩色谷物营养组分与复配技术研究[J]. 粮食与饲料工业,2016,12(2):5-9.
[17]高瑞昌,苏丽,黄星奕,等. 水产品风味物质的研究进展[J].水产科学,2013,32(1):59-62.
[18]缪凌鸿,刘波,何杰,等. 吉富罗非鱼肌肉营养成分分析与品质评价[J]. 上海海洋大学学报,2010,19(5):635-641.
[19]张飞,柏云爱,鲁海龙. 饱和脂肪酸与健康研究进展[J].中国油脂,2012,37(4):29-33.
[20]王心昕,杨茜,李媛,等. 膳食脂肪酸摄入及构成与心脑血管疾病相关性的研究进展[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2012,33(6):154-158.
Analysis and evaluation of chemical components of muscles ofPangasiushypophthalmus
LIU Xiu-ying1,LIU Ye-zi2,ZHU Chong-mei1,ZHAO De-fu3
(1.Henan Vocational College of Water Conservancy and Environment,Zhengzhou 450008,China;2.Southwest University,Chongqing 400715,China;3.Henan Academy of Fishery Science,Zhengzhou 450044,China)
Chemical components of muscle ofPangasiushypophthalmuscultivated in ponds were analyzed and evaluated in this study. The results showed that contents of moisture,crude protein,crude fat and ash in fresh muscle ofP.hypophthalmuswere 79.56%,17.44%,2.07%,1.11%,respectively. Eighteen kinds of amino acids were detected in its muscle,in which the contents of total amino acids(TAA),essential amino acids(EAA)and non-essential amino acids(NEAA)were 79.90%,32.32% and 47.58%(dry basis)respectively. The ratios of EAA/TAA and EAA/NEAA in its muscle were 40.45% and 67.93%,respectively. These data suggest that the EAA profile of the muscle ofP.hypophthalmuscan meet completely the FAO/WHO standard. According to amino acids score(AAS)and chemical score(CS),lysine was the most abundant while tryptophan was the main limiting amino acid in the muscle. Besides,the essential amino acids index(78.59)or the content of delicious amino acids(30.80% of dry basis)of muscle ofP.hypophthalmuswas both higher than those of some economic fish species. Total lipids were characterized by high percentages of saturated fatty acids(43.70% of total fatty acid),low percentages of polyunsaturated fatty acids(18.31% of total fatty acids)and very low percentages of docosapentenoic acid(0.50% of total fatty acids)and docosahexaenoic acid(0.42% of total fatty acids)in its muscle. The P:S ratio was 0.42. These results indicate thatP.hypophthalmuscan be an excellent source of protein and lysine,a potential source of polyunsaturated fatty acids and low-fat food for human.
Pangasiushypophthalmus;muscle;chemical component;evaluation of nutritive quality
2016-07-25
刘修英(1963-),女,博士,副教授,主要从事鱼类营养和饲料方面的研究,E-mail:lxy7310@163.com。
河南省教育厅科学技术研究重点项目([2013]-14B610015);河南省教育科学“十二五规划”重点项目([2013]-JKGHB-0104)。
TS254.2
A
1002-0306(2017)02-0349-05
10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.02.059

