真菌提取物抗肿瘤研究进展
曾炫皓 章强强
(复旦大学附属华山医院皮肤科,上海 200040)
·综述·
真菌提取物抗肿瘤研究进展
曾炫皓 章强强
(复旦大学附属华山医院皮肤科,上海 200040)
本文总结了近几年真菌提取物的抗癌作用相关的研究成果。一方面包括了最近几年关于真菌提取物诱导癌细胞凋亡、抑制癌细胞增生、减少癌细胞血管生成的各种机制研究,另一方面归纳了多种真菌提取物对癌细胞抑制作用的研究结果。近几年的研究结果显示,真菌提取物能够抑制多种肿瘤细胞的增殖,并诱导其凋亡,其机制与Wnt、NK-κB、MAPK、线粒体凋亡等多种信号通路相关,靶点包括了p38、bcl-2、c-jun、IκB、β-catenin、Akt等多种与细胞生物活动密切相关的蛋白。
真菌;肿瘤;机制;进展
[Chin J Mycol,2017,12(3):184-192]
随着世界人口老龄化,各种类型肿瘤的发病率不断升高,严重威胁着人类的健康。真菌是大自然赋予人类的一座宝库,从中我们提取出了大量的活性物质用于治疗各种不同类型的肿瘤。随着对各种真菌研究的深入,一方面大量新的真菌活性物质被发现,另一方面真菌活性物质抗肿瘤的作用机制不断被发现和完善。本文就近5 a发表的与抗癌真菌提取物相关的研究进行总结和归纳。
1 真菌抗肿瘤活性物质研究新进展
1.1 真菌多糖
真菌多糖是一类10个以上的单糖以糖苷键连接而成的天然高分子多聚物,具有螺旋状的立体构型。近年来有多篇与真菌多糖研究进展相关文章发表。其中Li等[1]报道了传统中药槐耳 (Huaier)的一种多糖类提取物TP-1对HCC SMMC-7721肝癌细胞的作用,其研究发现0.5、1和2 mg/kg剂量的TP-1能够显著抑制HCC SMMC-7721细胞的生长和转移,并且对普通的细胞毒作用较弱。由于在试验中发现TP-1能增加E-cadherin蛋白的表达,抑制N-cadherin蛋白的表达,他们认为TP-1的抗肿瘤作用与其对AUF-1信号通路的调节作用相关。此外,TP-1还被发现可以通过抑制HIF-1α、VEGF、AUF-1以及AEG-1的表达,阻止肿瘤的血管生长。Zhang等[2]报道了一种从草茎点霉 (Phomaherbarum)YS4108的菌丝中提取出的真菌多糖YCP,YCP在实验中能够YCP能够通过TLR2与TLR4相关机制来调节细胞内p38、ERK、JNK、NF-κβ的表达,从而刺激B细胞产生更多的IgG抗体,并能在小鼠移植瘤模型上抑制Heps (肝癌细胞)、S180 (小鼠肉瘤细胞)、Lewis (肺癌细胞)肿瘤细胞的增殖。Li等[3]的研究发现姬松茸多糖 (A.blazeipolysaccharides)能够影响HL-60 (人早幼粒白血病细胞)细胞线粒体膜电位,使线粒体释放cytochrome c (细胞色素C),从而诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡。
1.2 凝集素类
凝集素是普遍存在于自然界动植物和微生物中的一类非免疫来源的蛋白质或糖蛋白,一般由2或4个相同亚基组成。Nagre等[4]从丝核菌 (Rhizoctoniabataticola)中分离出一种命名为RBL的凝集素,它的N端终点有独特的氨基酸序列KKKAYSSRII,这与其他凝集素不同。RBL对人类卵巢癌细胞具有很强的细胞毒性作用,并且能与卵巢癌细胞标记蛋白CA125结合,其具体的作用机制尚不明确。Barkeer等[5]报道了分离自齐整小核菌 (Sclerotiumrolfsii)的一种凝集素Sclerotiumrolfsiilectin (SRL)能够通过调节c-JUN与SOCS,抑制MAPK信号通路与JAK/STAT信号系统,最终诱导HT-29细胞 (人结肠癌癌细胞)凋亡。此外,其作用还被发现与miRNA密切相关。
1.3 萜类
萜类是真菌中广泛存在的一种化合物,具有多种生物活性。Cheng等[6]的研究发现茯苓酸 (Pachymic acid)的抗癌作用的机制与热休克蛋白激活以及蛋白质折叠相关基因的表达引起的内质网应激有关,并且在应用内质网应激阻滞剂后,其抗癌作用显著减弱。Yang等[7]最新的研究发现,从Chondrostereumsp.提取出的Hirsutanol A的作用机制与ROS和线粒体膜电位改变造成的线粒体损伤,并释放细胞色素C,而导致的细胞凋亡相关。Deng等[8]从地花菌 (Albatrellusconfluens)分离出一种名为neoalbaconol (NA)的小分子萜类物质。NA能够通过PI3-K/HK2信号通路发挥抗癌活性,能有效抑制多种癌细胞的增生。Gill等[9]的研究阐述了灵芝 (Ganodermalucidum)中的萜类化合物灵芝酸 (Ganoderic Acid)通过Wnt信号通路杀伤肿瘤细胞的机制。
1.4 真菌次级代谢产物
Zhao等[10]分离出一种命名为alternariol (AOH)的化合物,并在研究中发现它能够抑制NIH3T3 (小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞)细胞DNA pol-β的过度表达,通过p38激活MAPK信号通路,增加ATF2的表达量,进而杀伤NIH3T3细胞。Koul等[11]报道了来自嗜松青霉 (Penicilliumpinophilum)的dicatenarin和skyrin诱导人类胰腺癌细胞凋亡的机制,其作用机制可能与线粒体膜渗透性改变引起的caspase-3蛋白的表达增加相关。Tao等[12]的研究描述了来自镰刀菌No.DZ27 (Fusariumsp.No.DZ27)的beauvericin对KB (口腔癌细胞)和KBv200 (耐长春新碱的口腔癌细胞)细胞的增殖的抑制作用,与线粒体凋亡通路的联系。Chen等[13]的研究发现来自Neosartoryapseufofischeri的gliotoxin (GTX)对肿瘤细胞的杀伤机制与Wnt和Caspase信号通路相关蛋白的激活密切相关。Kim等[14]从海洋藻类共生微生物中分离出名为Toluhydroquinone的化合物。Toluhydroquinone在实验中能够通过抑制β-catenin的激活,激活Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路相关蛋白质,进而诱导癌细胞凋亡。
1.5 近几年新发现的真菌活性物质
Ramos等[15]分别从N.laciniosaKUFC 7896以及soilfungusN.fischeriKUFC 6344提取出的乙酸乙酯混合物E2和E3对多种肿瘤细胞有细胞毒性作用。Kim等[16]从Cordyceps提取出的Cordyceps pruinosa butanol fraction (CPBF)能通过多个细胞信号通路诱导Hela细胞 (实验用增殖表皮癌细胞)的凋亡。Harms等[17]分离出化学式为C15H16N2O5S的化合物,这种化合物能够抑制K562细胞的增殖,并且这种作用与TNF相关的NF-κB信号通路密切相关。Ai等[18]从裙带菜内生真菌KcF8 (Guignardiasp.KcF8)提取的几种化合物显示出了对多种肿瘤细胞增殖的抑制作用。
2 真菌抗癌相关作用机制研究进展
近几年真菌提取物抗癌机制研究的进展总结见表1。
如表1所示,真菌提取物抗癌机制常常与多个信号通路相关,下文就真菌提取物对肿瘤细胞作用的几个主要途径进行叙述。
2.1 调节Wnt信号通路
如图1所示,Wnt/β-catenin信号由Wnt蛋白、跨膜受体胞质蛋白、核内转录因子、下游靶基因等组成,包括:①经典Wnt/β-catenin信号通路。②Wnt/Ca2+信号通路。③c-Jun N端激酶介导的细胞集性信号通路。Wnt信号通路在细胞增殖、转化、黏附、存活、和凋亡等都有重要作用。目前,较为明确的是经典Wnt信号通路。通常情况下β-catenin与轴蛋白、APC、GSK-3β组成多蛋白复合体结合后被磷酸,进而被泛素化降解,保持β-catenin处于较低水平。但当Wnt信号激活的时候,会抑制下游蛋白复合体磷酸化,促进β-catenin释放。在肿瘤细胞中,Wnt异常持续激活导致大量β-catenin进入细胞核,从而导致肿瘤细胞增殖异常[42]。近几年的研究中发现Cordycepin可以通过增强GSK-3β介导的β-catenin磷酸化,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖[23];真菌化合物Ganoderic acid、gliotoxin (GTX)、Toluhydroquinone、Antrodia camphorata (AC)能够通过调节参与Wnt信号通路的蛋白质,抑制β-catenin的激活,从而抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖[9,13-14,37]。

表1 真菌提取物抗癌作用相关作用机制和信号通路
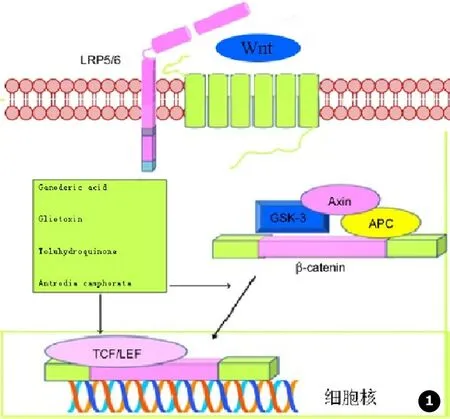
图1 Wnt信号通路示意以及真菌提取物作用位点
Fig.1 Wnt signal pathway and the targets of anti-cancer fungal extracts
2.2 调节NF-κB信号通路
NF-κB的激活机制主要依赖于IκB蛋白磷酸化所导致的泛素化蛋白的水解作用。通常,细胞质中的NF-κB与其抑制蛋白IκB相结合而处于失活状态,IκB激酶 (IκK)在接受到有效的刺激后激活,诱使IκB发生磷酸化,进而IκB被泛素连接酶所识别而发生泛素化。IκB在泛素化后水解,解除了其对NF-κB的抑制作用,其NLS的重新暴露使其迅速与细胞核κB位点发生特异结合,实现对相关基因表达的调控作用。该通路的异常活化与肿瘤细胞的增生、侵袭和转移都有密切的联系[42]。近年发现的多种真菌提取物均能通过干扰该通路,达到抗癌效果。如表1所示,ascochlorin (ASC)能够与NF-κB结合,而阻止其对DNA的调控作用[21];Allantopyrone A通过调节TNF-α的表达对TNF-R1-TRADD-RIP通路进行调节,最终通过RIP抑制NF-κB的激活[24];6-acetylmonodethiogliotoxin除了调节TNF-α,还可以通过直接阻止NF-κB p65进入DNA[17];isosclerone可以通过降低Iκk活性,减少IκB磷酸化,从而抑制NF-κB的激活[31];isotetrahydro-auroglaucin与flavoglaucin能够直接抑制IκB-α磷酸化,也可以抑制NF-κB p65与DNA的连接[30];Trichothecin (TCN)能够通过抑制IκK-β的磷酸化,阻止NF-κB的激活[34]。
2.3 调节caspase家族蛋白
含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶 (Caspase)家族与哺乳动物的细胞凋亡密切相关。其中caspase-8 (MACH)参与细胞凋亡的起始,它既可以自我活化也可以在颗粒酶B的剪切下活化。活化后的caspase-8可以剪切PARP,还参与caspase3或caspase8的活化过程。在Fas、DR4、DR5等介导的外源性细胞凋亡中,caspase-8能够引发caspase蛋白酶的级联反应。同时caspase也可以裂解促细胞凋亡因子蛋白 (BH3 interacting domain death agonist protein,Bid),其裂解产生的羧基端片段tBid能够诱导线粒体释放细胞色素c。caspase-3是细胞凋亡主要的终末剪切酶,是细胞凋亡的执行者,其激活是细胞凋亡进入不可逆阶段的标志。Caspase最主要的作用机制包括:①降解调节死亡蛋白bcl-2。②催化RARP的裂解。③活化核酸内切酶DFF、CAD[43]。如表1所示,在实验中多种真菌提取物作用于癌细胞后都可以引起caspase3以及caspase8表达的增加,以及bcl-2和RARP的减少。
2.4 调节线粒体凋亡通路
线粒体凋亡通路包括内源性线粒体凋亡通路以及外源性死亡受体通路。内源性的线粒体死亡受体通路:各种刺激导致的线粒体损伤,引起线粒体细胞色素C释放,从而激活caspase蛋白,诱导细胞凋亡。外源性死亡受体通路包括:①由系列级联反应导致的caspase-3激活,如Fas/FasL介导的死亡结构域蛋白激活。②由于Bid、bcl-2等活性变化导致的线粒体外膜通透性改变所引起的caspase-3激活[44]。
近几年的研究发现多种真菌提取物能够通过上述两种途径介导细胞凋亡。如表1所示,dicatenarin、skyrin物质等能够改变线粒体膜,导致细胞色素C释放,激活caspase3而引起细胞凋亡[11];A.blazeipolysaccharides (ABP)能够通过影响线粒体膜电位改变引起细胞色素C,而导致细胞凋亡[3]。Verrucarin A (VA)能够通过影响ROS的浓度导致线粒体损伤[35]。Cordycepspruinosabutanol fraction (CPBF)通过调节bcl-2蛋白,引起线粒体膜通透性改变而导致caspase-3激活[16]。
2.5 调节MAPK信号通路
丝裂原活化蛋白激酶 (MAPK)信号通路是在真核细胞中广泛存在的一类丝/苏氨酸蛋白激酶,MAPKs家族包括了p38 MAPK、ERK、BML/ERK5、ERK27、NLK、ERK8,具体分为3种类型:①ERK通路。②p38 MAPK通路。③JNK/SAPK通路。其中ERK的激活与细胞增殖相关,JNK与细胞应激与凋亡相关,p38与炎症密切相关。在多种肿瘤的发生发展中均可以检测到MAPK信号通路的异常激活[45]。此外,MAPK信号通路还与肿瘤新生血管的生成有密切联系[46]。Lee等的研究发现ascochlorin能够调节ERK1/2与p38的磷酸化水平,进而抑制MAPK信号通路的激活。如表1所示,Zhao等[10]在实验中发现Alternariol能够通过促进p38 MAPK磷酸化,抑制肿瘤细胞中DNA-pol β的过度表达。Barkeer等[5]在实验中发现Sclerotiumrolfsiilectin (SRL)能够显著降低c-JUN在细胞中的浓度,并且引起多种MAPK通路相关蛋白浓度的变化。Kim等[14]的研究发现Toluhydroquinone能够抑制MEK1/2和ERK1/2的磷酸化,并且可以抑制Rac1的表达。Xia等[38]在实验中发现Mycoepoxydiene可以抑制ERK、c-jun、JNK、p38等MAPK相关蛋白的磷酸化。此外,部分真菌提取物可以通过MAPK信号通路影响肿瘤的血管生成,如Ascochlorin、TP-1、Compound (3)[1,21,40]。
2.6 其他机制
Song等[27]的研究发现diaporine A能够通过上调mTOR的靶向性作用因子miR-99a,影响肿瘤细胞的增殖。Cheng等[6]的研究发现Pachymic acid能够通过增加XBP-1s、ATF4、Hsp70、CHOP和phospho-eIF2α的表达,引起内质网应激,进而抑制肿瘤细胞增殖。Deng等[8]的研究发现neoalbaconol (NA)通过调节磷脂酰肌醇-3-羟激酶 (phosphatidylinositol 3-hydroxy kinase,PI3K)与蛋白激酶B (protein kinase B,AKT)的磷酸化,引起己糖激酶2 (hexokinase 2,HK2)的活性的降低,抑制肿瘤细胞的增殖。
3 真菌提取物抗癌作用实验汇总
2012~2016年40篇文章报道的真菌提取物对各种不同癌细胞的抑制作用总结见表2。从表2可以看出,不同的真菌提取物对不同类型的肿瘤细胞有抑制作用,并且部分真菌提取物在抑制肿瘤细胞的同时,对正常细胞的毒性较小。除外少数几种真菌提取物只在相对较高的剂量时才能显著抑制肿瘤细胞生长,大部分真菌提取物都能在较低浓度下显著抑制肿瘤细胞生长,表现出显著的抗癌作用。
4 小 结
真菌是大自然赋予人类的一座宝库,从真菌中筛选抗癌天然物质的潜力巨大。一方面,真菌提取物的种类繁多,既能找到针对癌症发生的共同机制和信号通路发挥作用的物质,也能找到针对特殊类型的癌症机制发挥作用的物质。另一方面,从生物体中筛选天然药物相比通过化学合成药物更为方便和快捷,并且不会存在化学合成药物的诸多限制[50]。随着研究技术的不断提高,越来越多的真菌提取物的作用机制被揭示。近几年研究的真菌提取物的抗癌作用机制主要为通过调节MAPK、Wnt、NK-κB等信号通路抑制肿瘤细胞增殖,以及通过线粒体直接或间接激活caspase家族蛋白诱导癌细胞凋亡。真菌提取物抗癌的有效性与可靠性已经在大量的细胞实验中被证实,但是大量真菌提取物在活体中的作用还有待进一步的研究。真菌提取物用作抗癌药物有巨大前景,对其进一步研究有助我们发现新的抗肿瘤药物。
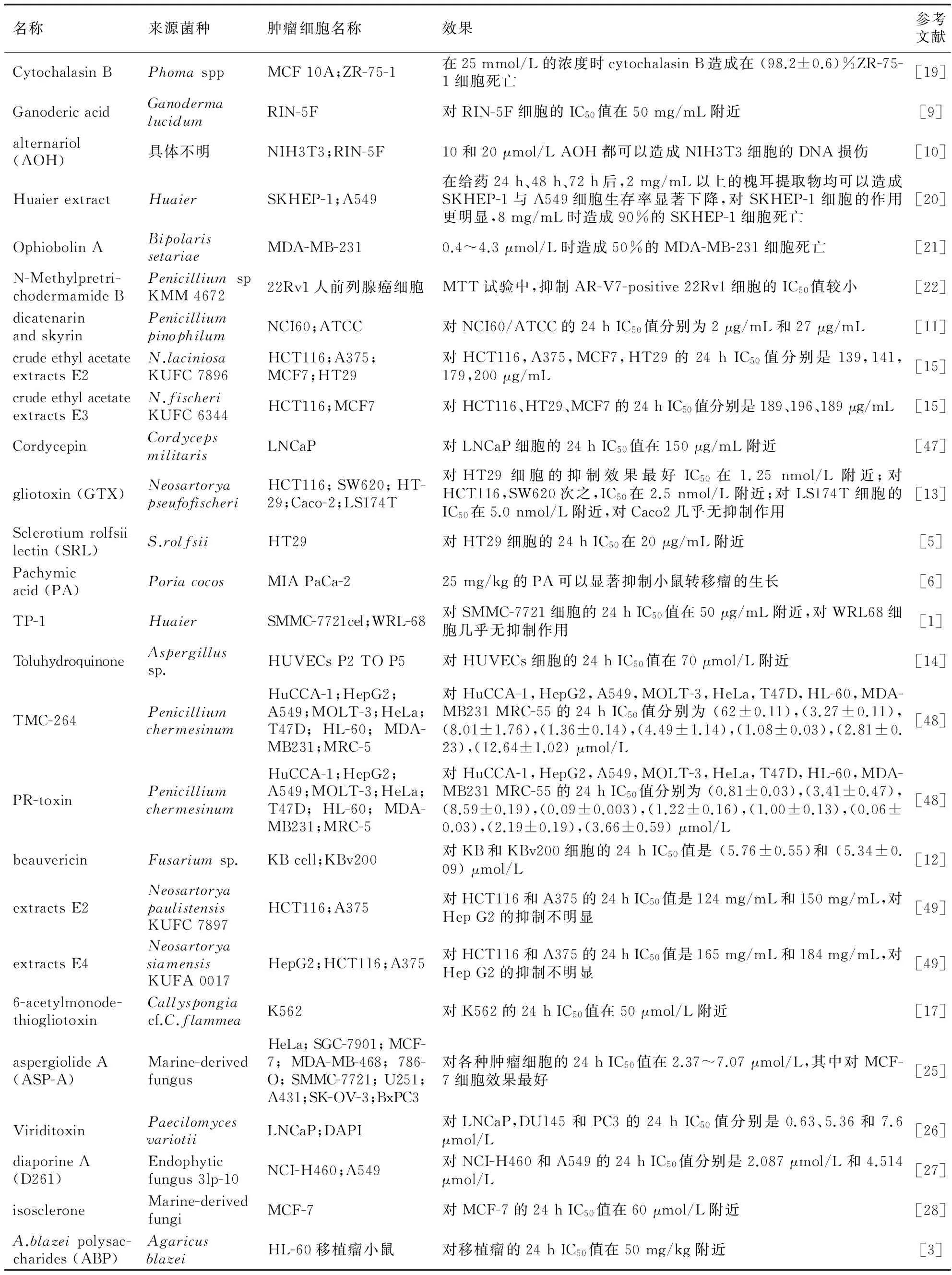
表2 真菌提取物对各类肿瘤细胞的抑制作用
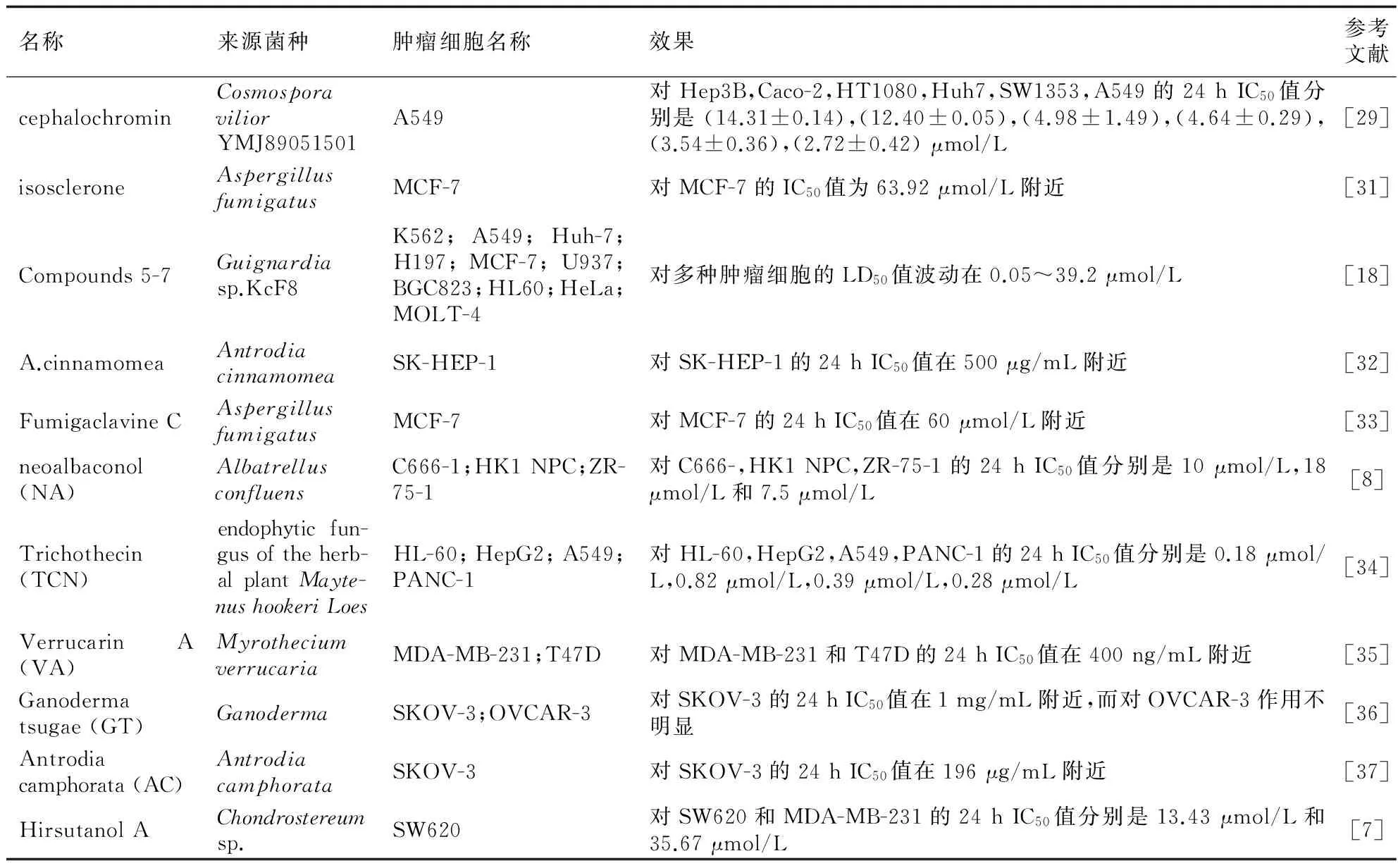
名称来源菌种肿瘤细胞名称效果参考文献cephalochrominCosmosporaviliorYMJ89051501A549对Hep3B,Caco-2,HT1080,Huh7,SW1353,A549的24hIC50值分别是(14.31±0.14),(12.40±0.05),(4.98±1.49),(4.64±0.29),(3.54±0.36),(2.72±0.42)μmol/L[29]isoscleroneAspergillusfumigatusMCF-7对MCF-7的IC50值为63.92μmol/L附近[31]Compounds5-7Guignardiasp.KcF8K562;A549;Huh-7;H197;MCF-7;U937;BGC823;HL60;HeLa;MOLT-4对多种肿瘤细胞的LD50值波动在0.05~39.2μmol/L[18]A.cinnamomeaAntrodiacinnamomeaSK-HEP-1对SK-HEP-1的24hIC50值在500μg/mL附近[32]FumigaclavineCAspergillusfumigatusMCF-7对MCF-7的24hIC50值在60μmol/L附近[33]neoalbaconol(NA)AlbatrellusconfluensC666-1;HK1NPC;ZR-75-1对C666-,HK1NPC,ZR-75-1的24hIC50值分别是10μmol/L,18μmol/L和7.5μmol/L[8]Trichothecin(TCN)endophyticfun-gusoftheherb-alplantMayte-nushookeriLoesHL-60;HepG2;A549;PANC-1对HL-60,HepG2,A549,PANC-1的24hIC50值分别是0.18μmol/L,0.82μmol/L,0.39μmol/L,0.28μmol/L[34]VerrucarinA(VA)MyrotheciumverrucariaMDA-MB-231;T47D对MDA-MB-231和T47D的24hIC50值在400ng/mL附近[35]Ganodermatsugae(GT)GanodermaSKOV-3;OVCAR-3对SKOV-3的24hIC50值在1mg/mL附近,而对OVCAR-3作用不明显[36]Antrodiacamphorata(AC)AntrodiacamphorataSKOV-3对SKOV-3的24hIC50值在196μg/mL附近[37]HirsutanolAChondrostereumsp.SW620对SW620和MDA-MB-231的24hIC50值分别是13.43μmol/L和35.67μmol/L[7]
[1] Li C,Wu X,Zhang H,et al.A Huaier polysaccharide reduced metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via modulating AUF-1 signaling pathway[J].Tumour Biol,2015,36(8):6285-6293.
[2] Zhang X,Ding R,Zhou Y,et al.Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4-dependent activation of B cells by a polysaccharide from marine fungusPhomaherbarumYS4108[J].PLoS ONE,2013,8(3):e60781.
[3] Li X,Zhao X,Wang H,et al.A polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells[J].Tumour Biol,2014,35(9):8963-8968.
[4] Nagre NN,Chachadi VB,Sundaram PM,et al.A potent mitogenic lectin from the mycelia of a phytopathogenic fungus,Rhizoctoniabataticola,with complex sugar specificity and cytotoxic effect on human ovarian cancer cells[J].Glycoconj J,2010,27(3):375-386.
[5] Barkeer S,Guha N,Hothpet V,et al.Molecular mechanism of anticancer effect ofSclerotiumrolfsiilectin in HT29 cells involves differential expression of genes associated with multiple signaling pathways:A microarray analysis[J].Glycobiology,2015,25(12):1375-1391.
[6] Cheng S,Swanson K,Eliaz I,et al.Pachymic acid inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancerinvitroandinvivoby targeting ER stress[J].PLoS One,2015,10(4):e122270.
[7] Yang F,Chen WD,Deng R,et al.Hirsutanol A,a novel sesquiterpene compound from fungusChondrostereumsp.,induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth through mitochondrial-independent ROS production:hirsutanol A inhibits tumor growth through ROS production[J].J Transl Med,2013,11:32.
[8] Deng Q,Yu X,Xiao L,et al.Neoalbaconol induces energy depletion and multiple cell death in cancer cells by targeting PDK1-PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway[J].Cell Death Dis,2013,4:e804.
[9] Gill BS,Kumar S,Navgeet.Ganoderic acid A targeting beta-catenin in Wnt signaling pathway:in silico andinvitrostudy[J].Interdiscip Sci,2016.
[10] Zhao J,Ma J,Lu J,et al.Involvement of p38MAPK-ATF2 signaling pathway in alternariol induced DNA polymerase beta expression[J].Oncol Lett,2016,12(1):675-679.
[11] Koul M,Meena S,Kumar A,et al.Secondary metabolites from endophytic fungusPenicilliumpinophiluminduce ROS-mediated apoptosis through mitochondrial pathway in Pancreatic Cancer Cells[J].Planta Med,2016,82(4):344-355.
[12] Tao YW,Lin YC,She ZG,et al.Anticancer activity and mechanism investigation of beauvericin isolated from secondary metabolites of the mangrove endophytic fungi[J].Anticancer Agents Med Chem,2015,15(2):258-266.
[13] Chen J,Wang C,Lan W,et al.Gliotoxin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells[J].Mar Drugs,2015,13(10):6259-6273.
[14] Kim NH,Jung HI,Choi WS,et al.Toluhydroquinone,the secondary metabolite of marine algae symbiotic microorganism,inhibits angiogenesis in HUVECs[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2015,70:129-139.
[15] Ramos AA,Castro-Carvalho B,Prata-Sena M,et al.Crude extracts of marine-derived and soil fungi of the genus neosartorya exhibit selective anticancer activity by inducing cell death in colon,breast and skin cancer cell lines[J].Pharmacognosy Res,2016,8(1):8-15.
[16] Kim HG,Song H,Yoon DH,et al.Cordycepspruinosaextracts induce apoptosis of HeLa cells by a caspase dependent pathway[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2010,128(2):342-351.
[17] Harms H,Orlikova B,Ji S,et al.Epipolythiodiketopiperazines from the marine derived fungusDichotomomycescejpiiwith NF-kappa B inhibitory potential[J].Mar Drugs,2015,13(8):4949-4966.
[18] Ai W,Wei XY,Lin XP,et al.Guignardins A-F,spirodioxynaphthalenes from the endophytic fungusGuignardiasp KcF8 as a new class of PTP1B and SIRT1 inhibitors[J].TETRAHEDRON,2014,70(35):5806-5814.
[19] Chang HT,Chou CT,Chen IS,et al.Mechanisms underlying effect of the mycotoxin cytochalasin B on induction of cytotoxicity,modulation of cell cycle,Ca2+homeostasis and ROS production in human breast cells[J].Toxicology,2016,370:1-19.
[20] Hu Z,Yang A,Fan H,et al.Huaier aqueous extract sensitizes cells to rapamycin and cisplatin through activating mTOR signaling[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2016,186:143-150.
[21] Lee SH,Kwak CH,Lee SK,et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of ascochlorin in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells is accompanied with the down-regulation of iNOS,COX-2 and proinflammatory cytokines through NF-kappaB,ERK1/2,and p38 signaling pathway[J].J Cell Biochem,2016,117(4):978-987.
[22] Bhatia DR,Dhar P,Mutalik V,et al.Anticancer activity of Ophiobolin A,isolated from the endophytic fungus bipolaris setariae[J].Nat Prod Res,2016,30(12):1455-1458.
[23] Tian X,Li Y,Shen Y,et al.Apoptosis and inhibition of proliferation of cancer cells induced by cordycepin[J].Oncol Lett,2015,10(2):595-599.
[24] Yokoigawa J,Morimoto K,Shiono Y,et al.Allantopyrone A,an alpha-pyrone metabolite from an endophytic fungus,inhibits the tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway[J].J Antibiot(Tokyo),2015,68(2):71-75.
[25] Wang Y,Qi X,Li D,et al.Anticancer efficacy and absorption,distribution,metabolism,and toxicity studies of aspergiolide A in early drug development[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2014,8:1965-1977.
[26] Kundu S,Kim TH,Yoon JH,et al.Viriditoxin regulates apoptosis and autophagy via mitotic catastrophe and microtubule formation in human prostate cancer cells[J].Int J Oncol,2014,45(6):2331-2340.
[27] Song Y,Dou H,Wang P,et al.A novel small-molecule compound diaporine A inhibits non-small cell lung cancer growth by regulating miR-99a/mTOR signaling[J].Cancer Biol Ther,2014,15(10):1423-1430.
[28] Li YX,Kang KH,Kim HJ,et al.Invitroinduction of apoptosis by isosclerone from marine-derived fungusAspergillusfumigatus[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2014,24(16):3923-3927.
[29] Hsiao CJ,Hsiao G,Chen WL,et al.Cephalochromin induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in A549 human non-small-cell lung cancer cells by inflicting mitochondrial disruption[J].J Nat Prod,2014,77(4):758-765.
[30] Kim KS,Cui X,Lee DS,et al.Inhibitory effects of benzaldehyde derivatives from the marine fungusEurotiumsp SF-5989 on inflammatory mediators via the induction of heme oxygenase-1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages[J].Int J Mol Sci,2014,15(12):23749-23765.
[31] Li YX,Himaya S,Dewapriya P,et al.Anti-proliferative effects of isosclerone isolated from marine fungusAspergillusfumigatusin MCF-7 human breast cancer cells[J].Process Biochemistry,2014,49(12):2292-2298.
[32] Chen YJ,Thang MW,Chan YT,et al.Global assessment ofAntrodiacinnamomea-induced microRNA alterations in hepatocarcinoma cells[J].PLoS One,2013,8(12):e82751.
[33] Li YX,Himaya SW,Dewapriya P,et al.Fumigaclavine C from a marine-derived fungusAspergillusfumigatusinduces apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J].Mar Drugs,2013,11(12):5063-5086.
[34] Su J,Zhao P,Kong L,et al.Trichothecin induces cell death in NF-kappaB constitutively activated human cancer cells via inhibition of IKKbeta phosphorylation[J].PLoS One,2013,8(8):e71333.
[35] Palanivel K,Kanimozhi V,Kadalmani B,et al.Verrucarin A,a protein synthesis inhibitor,induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and T47D[J].Biotechnol Lett,2013,35(9):1395-1403.
[36] Kuo HP,Hsu SC,Ou CC,et al.Ganoderma tsugae extract inhibits growth of HER2-Overexpressing cancer cells via Modulation of HER2/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway[J].Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2013,2013:219472.
[37] Yang HL,Lin KY,Juan YC,et al.The anti-cancer activity ofAntrodiacamphorata against human ovarian carcinoma (SKOV-3) cells via modulation of HER-2/neu signaling pathway[J].J Ethnopharmacol,2013,148(1):254-265.
[38] Xia XC,Chen Q,Liu K,et al.Mycoepoxydiene inhibits antigen-stimulated activation of mast cells and suppresses IgE-mediated anaphylaxis in mice[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2013,17(2):336-341.
[39] Chen Q,Chen T,Li W,et al.Mycoepoxydiene inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses through the suppression of TRAF6 polyubiquitination[corrected][J].PLoS One,2012,7(9):e44890.
[40] Cao S,Cryan L,Habeshian KA,et al.Phenolic compounds as antiangiogenic CMG2 inhibitors fromCostaricanendophytic fungi[J].Bioorg Med Chem Lett,2012,22(18):5885-5888.
[41] Jeong JH,Jeong YJ,Cho HJ,et al.Ascochlorin inhibits growth factor-induced HIF-1alpha activation and tumor-angiogenesis through the suppression of EGFR/ERK/p70S6K signaling pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells[J].J Cell Biochem,2012,113(4):1302-1313.
[42] Ma B,Hottiger MO.Crosstalk between Wnt/beta-Catenin and NF-kappaB signaling pathway during inflammation[J].Front Immunol,2016,7:378.
[43] Chen H,Yang X,Feng Z,et al.Prognostic value of Caspase-3 expression in cancers of digestive tract:a meta-analysis and systematic review[J].Int J Clin Exp Med,2015,8(7):10225-10234.
[44] Chen Y,Zhang H,Zhou HJ,et al.Mitochondrial redox signaling and tumor progression[J].Cancers (Basel),2016,8(4).
[45] Rauch N,Rukhlenko OS,Kolch W,et al.MAPK kinase signalling dynamics regulate cell fate decisions and drug resistance[J].Curr Opin Struct Biol,2016,41:151-158.
[46] Varinska L,Gal P,Mojzisova G,et al.Soy and breast cancer:focus on angiogenesis[J].Int J Mol Sci,2015,16(5):11728-11749.
[47] Lee HH,Kim SO,Kim GY,et al.Involvement of autophagy in cordycepin-induced apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma LNCaP cells[J].Environ Toxicol Pharmacol,2014,38(1):239-250.
[48] Darsih C,Prachyawarakorn V,Wiyakrutta S,et al.Cytotoxic metabolites from the endophytic fungusPenicilliumchermesinum:discovery of a cysteine-targeted Michael acceptor as a pharmacophore for fragment-based drug discovery,bioconjugation and click reactions[J].Rsc Advances,2015,5(86):70595-70603.
[49] Ramos AA,Prata-Sena M,Castro-Carvalho B,et al.Potential of four marine-derived fungi extracts as anti-proliferative and cell death-inducing agents in seven human cancer cell lines[J].Asian Pac J Trop Med,2015,8(10):782-790.
[50] Gill BS,Kumar S,Navgeet.Triterpenes in cancer:significance and their influence[J].Mol Biol Rep,2016,43(9):881-896.
[本文编辑] 王 飞
·消息·
The recent progresses of anti-cancer fungal extracts
ZENG Xuan-hao,ZHANG Qiang-qiang
(DepartmentofDermatology,HuaShanHospital,FudanUniversity,Shanghai200040,China)
This review summaries theadvance in anti-cancer fungal extracts in recent years.On the one hand,related multiple mechanisms might include the anti-cancer fungal extracts inducing apoptosis,inhibiting proliferation and angiogenesis.On the other hand,the anti-cancer effects of various anti-cancer fungal extracts in cancer cells are also reviewed.These study show that anti-cancer fungal extracts can inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells and induce apoptosis in cancer cells.The mechanisms of those functions involved various signal pathways,including Wnt,NK-κB,MAPK and Mitochondria related apoptosis signal pathways,and related to various proteins related to biological activity such as p38,bcl-2,c-jun,IκB,β-catenin,Akt.
fungus;cancer;mechanisms;progresses
国家自然科学基金 (81573056)
曾炫皓,男 (汉族),硕士研究生在读.E-mail:969358560@qq.com
章强强,E-mail:zhangqq8@163.com
R 979.1
A
1673-3827(2017)12-0184-09
2016-10-24

