不同尺寸六边形一水草酸钙晶体的合成、表征、性质及其细胞毒性
郭 达 徐 猛 孙新园 欧阳健明
(暨南大学化学系,生物矿化与结石病防治研究所,广州 510632)
0 Introduction
The smaller the size of themineral crystal,which result in more cell damage[1-3],the larger its specific surface area,the higher the surface activity,and the greater the ability to produce reactive oxygen species.For instance,the inhibiting ability of hydroxyapatite(HAP)on cell proliferation of U2OS cell decreases as its size from 20 to 40 and 80 nm[4].In contrast,ordinary rob HAP(with length of 300~500 nm and diameter of 30~80 nm)can nothinder the U2OS cell proliferation.The SiO2of20 nm (specific surface area ≥600m2·g-1)produce greater toxicity effect to the mouse macrophages (RAW264.7)than that with a size of 60 nm(specific surface area ≥400 m2·g-1)[5],and both the nano-SiO2paticles produce stronger toxicity than micron SiO2with a size of 0.5~10 μm.
It was showed that calcium oxalate monohydrate(COM)and calcium oxalate dihydrate (COD)crystals existing in urine had different sizes[6-10].The crystals with different sizes may have different toxicity on renal tubular epithelial cell(REC)[11-13].Therefore,the study on the relationship between the physical properties of calcium oxalate crystals and their cytotoxicity can help to provide theoretical references for inhibiting stone formation.Based on this,four kinds of COM crystalswith size of(1.5±0.4),(3.5±0.5),(5.5±0.5)and(9.5±1)μm(COM-1,COM-3,COM-5,COM-9,respectively)were synthesized and their physiochemical propertieswere comparely investigated.
1 M aterials and methods
1.1 Reagents and apparatus
1.1.1 Reagents
Sodium citrate (Na3Cit)and the conventional reagents used were analytically pure. The experimental water is distilled water.Human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells (HK-2) were purchased from Shanghai Cell bank of Chinese Academy of Sciences;DMEM culture medium was purchased from Hyclone Biochemical Products Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).Fetal bovine serum was purchased from Hyclone Biochemical Products Co.,Ltd.(Beijing,China).Cell proliferation assay kit(Cell Counting Kit-8,CCK-8)was purchased from Dojindo Laboratory(Kumamoto,Japan).
1.1.2 Apparatus
The apparatus included X-L type environmental scanning electron microscope (SEM,Philips,Eindhoven,Netherlands),Nano-ZS nano particle sizer(Malvem,UK),D/max 2400-X ray powder diffractometer(Rigaku,Japan),fourier transform infrared spectrometer (Nicolet,American),tristar 3000 surface area and porosity analyzer(Micromeritics,American).
1.2 Preparation of COM crystalsw ith various sizes
1.2.1 COM-1
Approximately 250 mL of Na2Ox(10 mmol·L-1)solution(with 130mLethanol)and 0.588 2 g ofNa3Cit(8mmol·L-1)were added in 500 mL beaker,evenly stirred,and heated to 65℃.Afterward,250 mL of CaCl2(5mmol·L-1)solution preheated to 65 ℃ was added in the reaction mixture,and the reaction was maintained at 65℃under continuous stirring at 600 r·min-1for 5 min.The final solution was incubated overnight at room temperature and subsequently washed three times with distilled water and anhydrous ethanol under ultrasonication.Crystals were collected via suction filtration and dried in a drying oven at 55℃.Finally,COM-1 were obtained.
1.2.2 COM-3
Approximately 250 mL of Na2Ox(10 mmol·L-1)solution (with 110 mL ethanol)in 500 mL beaker,evenly stirred,and heated to 65℃under continuous stirring at 300 r·min-1.The other experimental condition was the same processing as the synthesis of COM-1.
1.2.3 COM-5
A total of 500 mL of Na2Ox (10 mmol·L-1)solution and 1.176 g of Na3Cit (8 mmol·L-1)were added in 2 000mL beaker,evenly stirred,and heated to 65 ℃.Afterward,500 mL of CaCl2(5 mmol·L-1)solution preheated to 65℃was added in the reaction mixture,and the reaction was maintained at 65℃under continuous stirring at 200 r·min-1for 4 min.The final solution was incubated overnight at room temperature.The prepared crystalswere collected with the same processing as the synthesis of COM-1.
1.2.4 COM-9
A total of 500 mL of Na2Ox (10 mmol·L-1)and 1.176 g Na3Citweremixed in 2 000mL beaker,evenly stirred,and heated to 75℃.Subsequently,500 mL of CaCl2(5mmol·L-1)solution preheated to 75 ℃ was added in the reaction mixture,and the reaction was maintained at 75℃for 30 min in a static condition.The final solution was incubated overnight at room temperature.The prepared crystalswere collected with the same processing as the synthesis of COM-1.
1.3 Characterization of COM crystals
Themorphology and structure of COM of various sizes were observed with an X-L type environmental scanning electron microscope (SEM)operated at 30 kV.The X-ray powder diffraction(XRD)patterns of the products were recorded with Cu Kα (λ=0.154 06 nm)radiation at a scanning rate of 8°·min-1in the 2θ range from 5°to 55°at 40 kV and 30 mA.Fouriertransform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR)analysis was conducted with KBr discs in the region of 4 000~400 cm-1.
1.4 Specific surface areameasurement of COM crystals
The COM crystals of various sizes were degassed at 80℃.Subsequently,adsorbance experiments were conducted at-196℃by using N2adsorbent.The specific surface area (SBET)of crystals was calculated using the Brunauer-Emmet-Teller(BET)equation.Pore-size distribution curves,pore volume,and average pore diameter were determined using the Barrett-Joyner-Halendamethod.
1.5 ζpotential detection of COM crystals
Appropriate amounts of COM crystals of various sizes were dispersed in deionized water until the final crystal concentration was 0.2 mg·mL-1.After 5min of ultrasonication,theζpotential was detected by a Zetasizer Nano ZS90 apparatus at25℃.
1.6 Cell culture
HK-2 cells were cultured in DMEM culture medium containing 10%fetal bovine serum in a 5%(V/V)CO2humidied atmosphere at 37℃.The culture medium was replaced once in a day.Trypsin digestion method was adopted for cell propagation.Upon reaching 80%~90%confluence,the cells were rinsed twice with PBS.A certain amount of 0.25%trypsin digestion solution was then added and maintained for 3~5 min at 37 ℃.Afterward,DMEM culturemedium containing 10%fetal bovine serum was added to terminate the digestion.The cells were then blown well to form single cell suspensions.
One hundred microliters of cell suspension with a cell concentration of 1×105cells·mL-1was inoculated per well in 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h.Afterward,the medium was changed to serum-free culturemedia and then incubated for another 12 h to achieve synchronization.The experimentalmodel was divided into two groups:(A)control group,in which only serum-free culture medium was added;(B)treatment group with COM crystals,in which cells were exposed to four sizes of COM crystals at a concentration of 200 μg·mL-1prepared with serumfree culture medium,respectively.Each experiment was repeated in three parallel wells.After incubation for 6 h,10μL CCK-8 was added to each well and incubated for 1.5 h.Absorbance(A)wasmeasured by using the enzyme mark instrument at 450nm.Cell viability was determined using the equation below.

2 Results and discussion
2.1 Preparation of varying sizesof COM crystals COM crystals with different sizes were synthes-
ized by changing reaction temperature,solvent,additive and stirring speed[14-17].The detailed synthetic conditions are shown in Table 1 and the SEM images of the prepared crystals are shown in Fig.1.The results showed that crystals with the sizes of(1.5±0.4),(3.5±0.5),(5.5±0.5)and(9.5±1)μm,were named as COM-1,COM-3,COM-5 and COM-9,respectively for convenient description. When the crystal size increased,the crystal surface changed to smooth and itsmorphology became oval thin sheet.
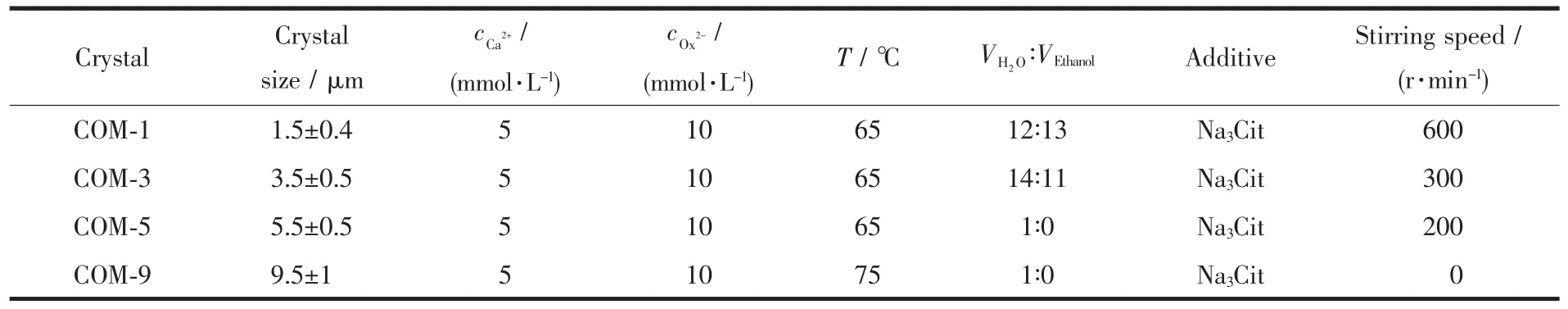
Table 1 Synthesis conditions of COM crystalsw ith different sizes
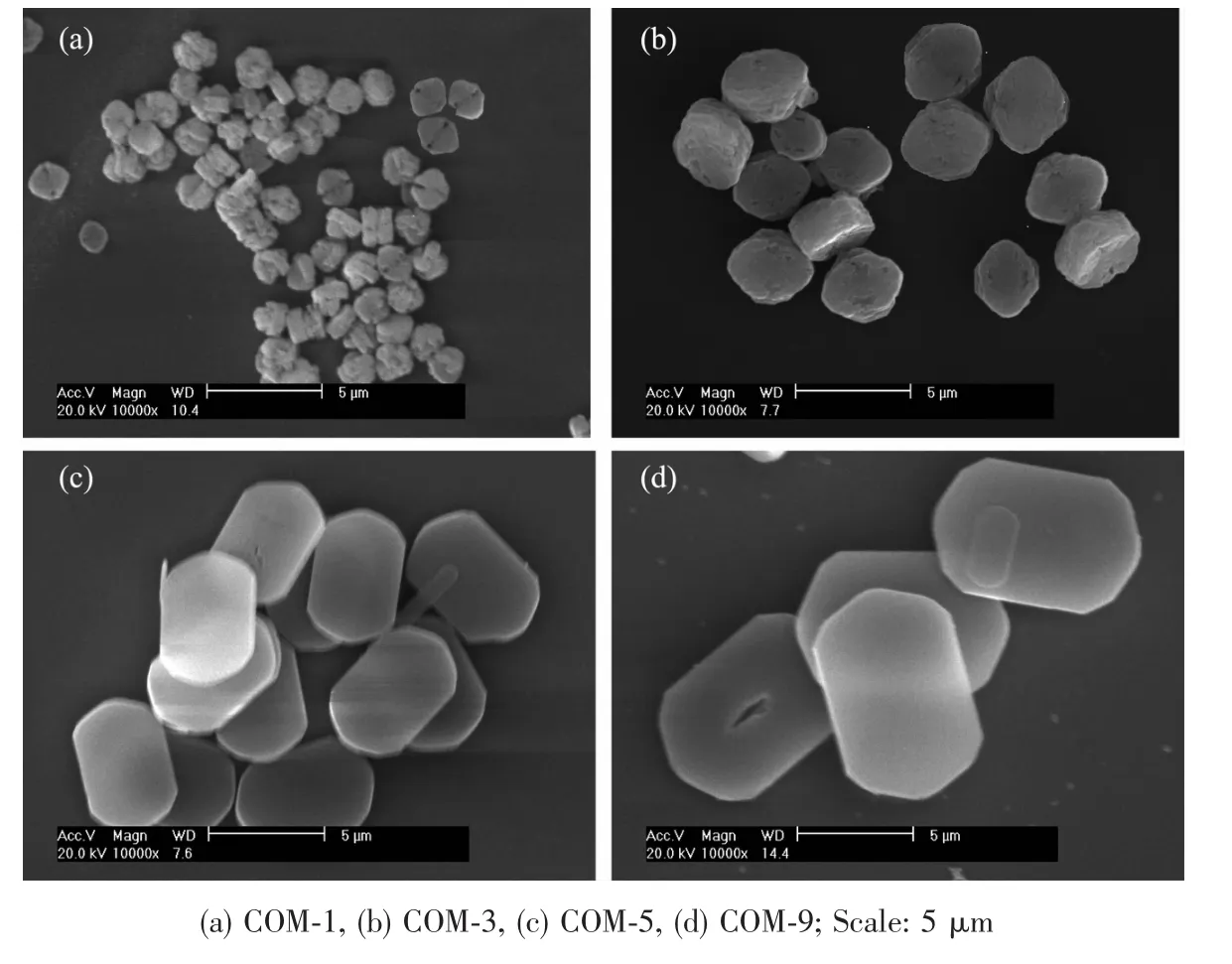

Fig.1 SEM images of different sizes of blunt COM crystals
Effect of Na3Cit additive on COM sizes.The combination of Na3Citwith (101)face of COM crystal inhibited the crystal growth along the [001]direction,which reduced the length of COM in the[001]direction (Fig.2)and therefore it showed rectangular oval.In addition,the edges and corners became blunt as the dissociation-complexing balance between cit3-and Ca2+during the synthesis process.
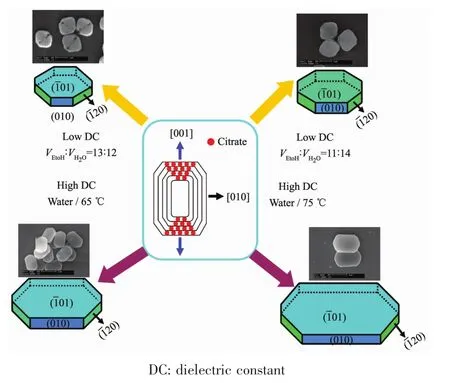
Fig.2 diagram of the growth of COM crystals with different sizes
Effect of stirring speed on COM sizes.During the synthesis process,the crystal size become smaller with the increasing stirring speed.As shown in Table 1,when the stirring speed were 600,300,200 and 0 r·min-1,the COM crystals were synthesized with the sizes of 1,3,5 and 9μm,respectively.The above results indicated that the increasing degree of nucleation rate is greater than growth rates with increasing stirring speed,therefore,the number of formed nuclei ismore and crystal size is smaller.
Effect of reaction temperature on COM sizes.The growth rates increased while nucleation rates of COM decreased with increasing temperature[18],therefore,the crystal size increased.
Effect of solvent on COM sizes.The smaller dielectric constant resulted in the formation of COM crystals with smaller sizes.At 20℃,the dielectric constantof 25.7 F·m-1(ethanol)was far less than 80.1 F·m-1(pure water).The dielectric constant in system decreased when the ethanol was added to water,and dielectric constant was smaller with larger volume fraction of ethanol,which reduces the stable COM precipitate size inmixed solvent[19].
In addition,stable cyclic trimer associated structure was formed due to the stronger hydrogen bond between ethanol and water,which reduces the free water molecule and limited diffusion motion of Ca2+and Ox2-in solution.Moreover,themutual effect between precipitated particle as well as particle and solvent are attenuated,which also make all crystal face growth rate be same[20].Thus,COM crystals with smaller size tend to be round(Fig.1a).
2.2 XRD analysis of varying sizes of COM crystals
The XRD patterns of COM crystals with various sizes are shown in Fig.3A.The diffraction peaks appeared at the spacing d101=0.593,d020=0.365,d202=0.296,d130=0.235 and d303=0.197 nm of COM crystals,respectively(PDF No.20-231)[21].XRD analysis results reveal that the synthetic crystals are pure COM phase.
The intensity ratios of(101)and(010)planes of COM with different sizes are shown in Table 2.The intensity ratio of I101/I010plane increased gradually with the increasing crystal size.The above result suggests that with the increasing of crystal size,the crystals gradually change to thin,the (010)face of COM crystals reduces,and (01)face increases(Fig.4).It can also be found from Fig.1 that the crystal thickness of COM-1 and COM-3 were larger and their area ratio of (01)face was relatively smaller,which was opposite with COM-5 and COM-9.Thus,the intensity ratio of I101/I010is gradually increased with increasing crystal size.
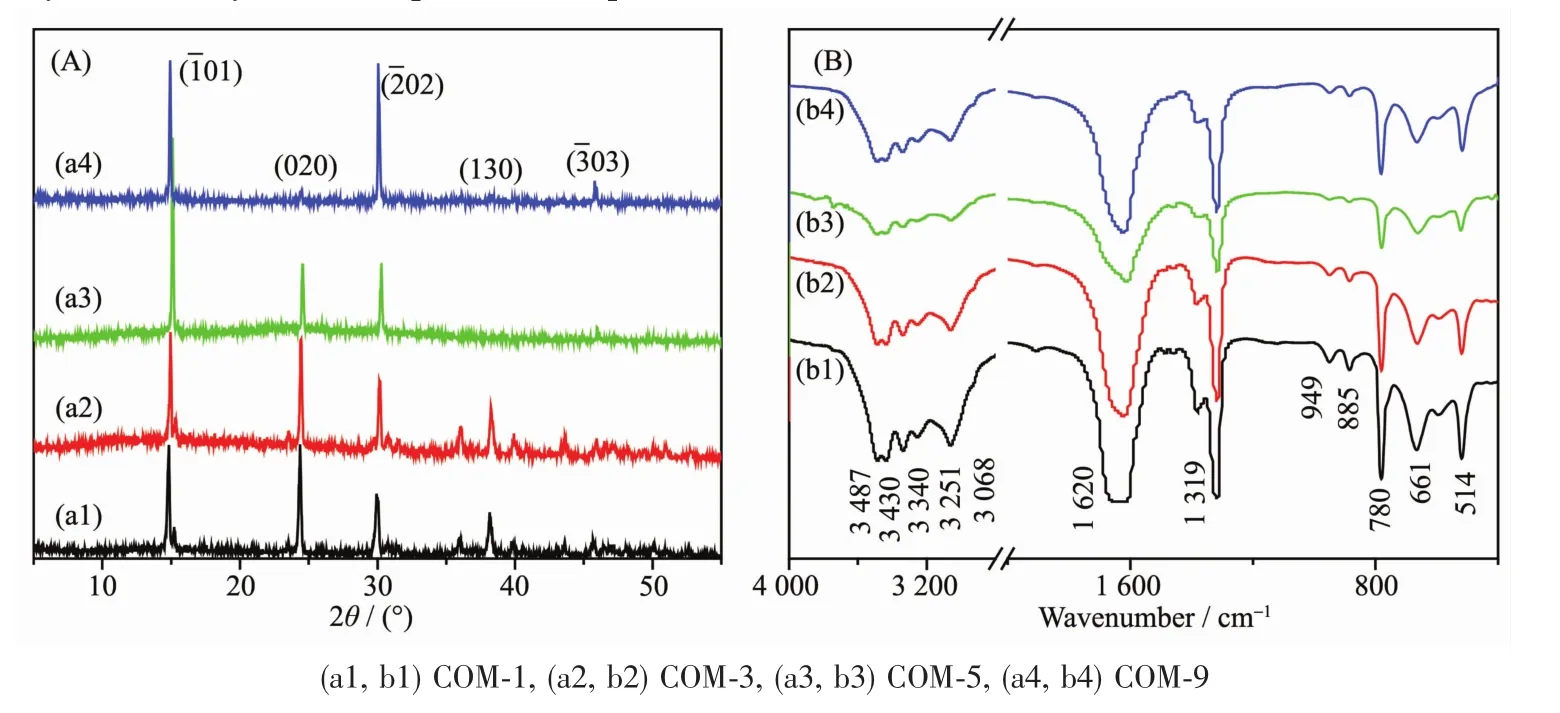
Fig.3 XRD patterns(A)and FT-IR spectra(B)of four different sizes of COM crystals
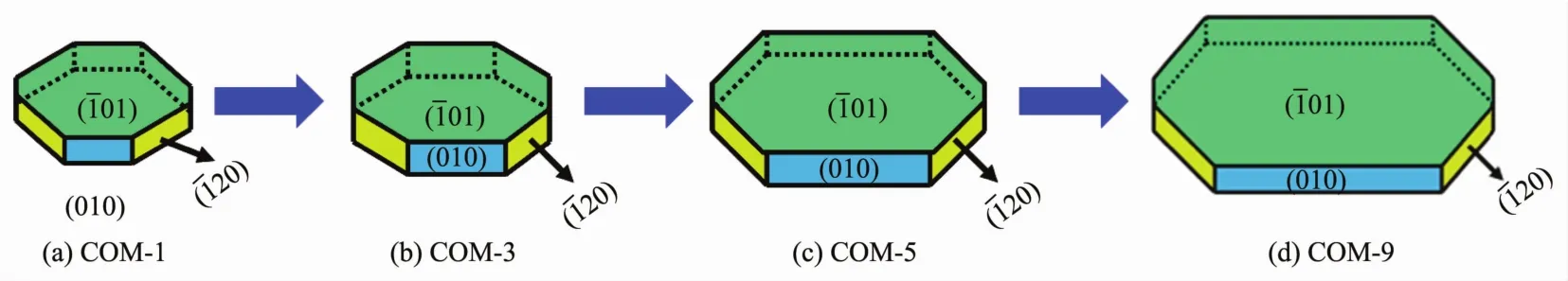
Fig.4 diagram of the surface change of COM crystalswith different sizes

Table 2 Intensity ratios of I101/I010 for COM crystalsw ith different sizes
2.3 FT-IR spectra analysis of varying sizes of COM crystals
The FT-IR spectra of COM crystals with various sizes were shown in Fig.3B.The shift at 3 487~3 068 cm-1belonged to the symmetric and asymmetric stretching vibration peaks of O-H bond of crystalwater.It could be splited into 5 absorption peaks at 3 487,3 430,3 340,3 251 and 3 068 cm-1,respectively,which are characteristic peaks of COM[22].The asymmetric stretching(νas)and symmetric stretching vibration(νs)of carboxylgroup(COO-)in COM crystalsappeared atapproximately 1 620 and 1 319 cm-1,respectively[23].In the fingerprint region,the absorption peaks of COM crystals occurred at about 949,885,780,661 and 514 cm-1,repectively.
2.4 Specific surface area and pore structure analysis of varying sizes of COM crystals
As shown in Table 3,the crystals with smaller crystal size had a larger specific surface area.The dramatical increase of the specific surface area is due to rough crystal surface and holes of the two smallsized COM crystals.Nevertheless,the two large-sized crystals with smooth surface and small holes result in significant decrease of their specific surface area.
The N2adsorption-desorption curves of the COM crystals with various sizes are shown in Fig.5.In the high-pressure part(P/P0>0.85),the nitrogen adsorption quantity increased dramatically,especially for the two small-sized COM-1 and COM-3 crystals.The results indicate that a certain pore structure exists in its surface and is consistentwith themeasurement results of pore volume and pore diameter(Table 3).

Table 3 Specific surface area,pore volume,pore size,ζpotential and electrical conductivity of COM

Fig.5 N2 adsorption-desorption and pore size distribution of COM crystalswith various sizes
2.5 ζpotential and conductivity of varying sizes of COM crystals in pure water
All theζpotentials of COM with various sizes dispersed in pure water were negative (Fig.6a).With increasing crystal size,the absolute value ofζ potential was constantly increased.The above results are attributed to the small-sized crystals with a higher specific surface area,which can be easy to aggregate in pure water.All of these factors and decreasing of apparent charge lower the absolute value ofζ potential.It can also be found from Fig.1 and 4 that the01)face of small-sized crystals(such as COM-1)which with higher charge density was smaller,while the large-sized crystal (such as COM-9)had more complete01)face.Therefore,COM-9 occ-upied a larger charge than COM-1 on their face.The higher absolute value ofζpotential of crystal in solution suggested larger repulsive force among crystals,greater dispersion of crystal and worse crystal aggregation.All of these results showed that the absolute value ofζpotential on crystal surface was positively related with stability of crystal suspension.
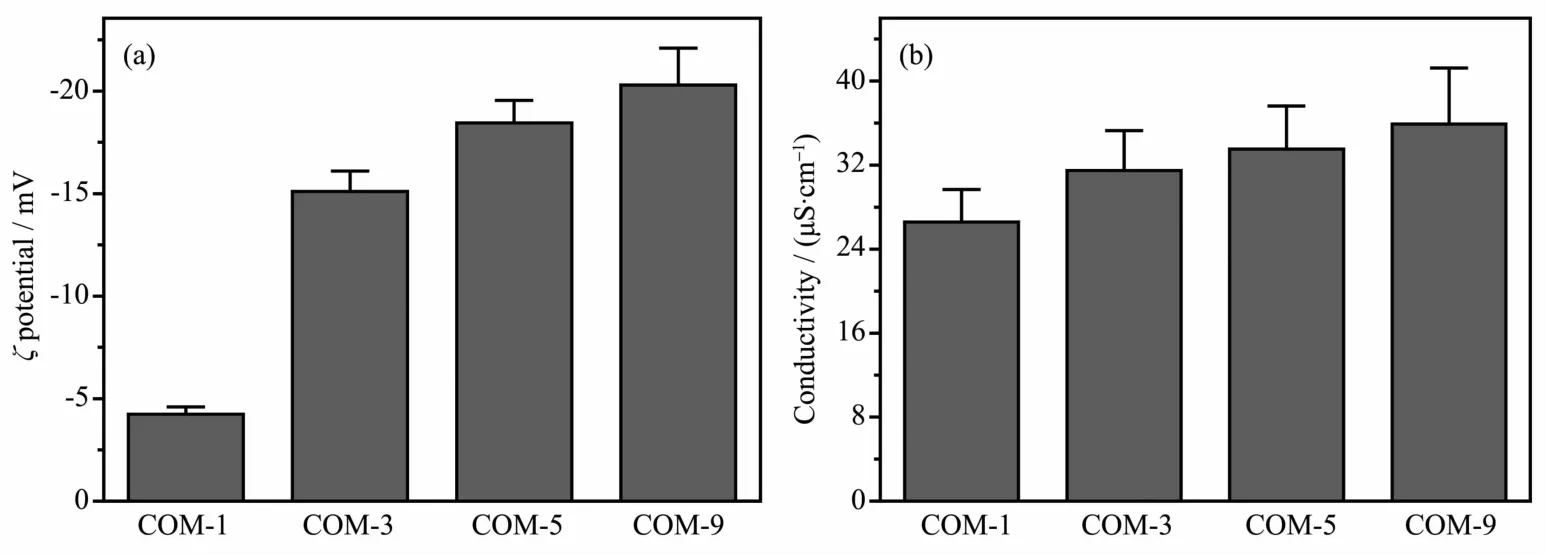
Fig.6 ζpotentials(a)and electrical conductivities(b)of COM crystalswith different sizes in purewater
The conductivity of the crystals with larger size was higher(Fig.6b).It is possibly due to the serious aggregation and worse dispersion of small-sized COM-1 and COM-3 in solution,which leads to lower conductivity.By comparison,large-sized COM crystal disperses better and it is not easy to aggregate.Therefore,the conductivity of COM-9 is highest.
2.6 Cell viability assay by CCK-8
The CCK-8 method was performed to detect the injury of normal HK-2 cells after exposure to different-sized COM crystals(Fig.7).The survival rate of HK-2 cells treated with COM crystals was closely related to crystal size.COM-1 crystals caused the most evident injury to HK-2 cells and induced 35.3%cell death compared with the control group.The injury to HK-2 cells caused by different-sized COM crystals was found in the following order:COM-1>COM-3>COM-5>COM-9.
Crystals with larger specific surface area generally have larger contact area between crystal and cell surface,thus easily causing serious damage to cells.COM-1 possessed the largest specific surface area(Table 3),thereby showing the highest toxicity on HK-2 cells.

Fig.7 Changes in cell viability of HK-2 cells after exposure to COM crystalswith different sizes for 6 h
Owing to the high surface area of small COM crystals,more active sites are created to capture oxygen molecules,which leads to the production of superoxide radical(·O2-)and other ROS through dismutation or Fenton reaction[24].Excessive formation of cellular ROS could inducemitochondrialmembrane permeability,ultrastructural mitochondrial damage,and disruption of the respiratory chain to trigger apoptosis[25].Therefore,cell apoptosis induced by small COM crystals ismore serious than that of large-sized crystals.
Theζpotential values of the four sizes of crystals in DMEM medium were all negative,and all the values ranged from-4.24 to-20.3 mV.Furthermore,the surface ofmost cell types was negatively charged.Generally,negatively charged particles adsorb much less on the negatively charged cell-membrane surface compared with the positively charged particles[26].The crystals with more negative charges will be more difficult to adhere to cell surface,and causing weaker damage to cells.Thus,the COM-1 with the lowest absolute value ofζpotential causes the most serious damage to HK-2 cells.
In summary,the cytotoxicity of COM crystals with different sizes is not determined via a single factor.Cytotoxicity is affected synthetically by(01)face area,specific surface area,andζpotential.
3 Conclusions
The COM crystals with the sizes of(1.5±0.4),(3.5±0.5),(5.5±0.5)and(9.5±1)μm respectively,were synthesized by changing reaction temperature,solvent,additive and stirring speed.Itwas beneficial to obtain crystal with small size by adding additive Na3Cit,increasing stirring speed,reducing reaction temperature or decreasing dielectric constant of the solvent.With the increasing of crystal sizes,the (01)crystal face with high charge density was larger,charge density of crystal surface was increased,absolute value ofζpotential on crystal surface was greater,and stability of crystal suspension was higher.The injury to HK-2 cells caused by different-sized COM crystals was found in the following order:COM-1>COM-3>COM-5>COM-9.Since multitud-inous varying sizes of urine crystallines are present in human urine,this study could contribute to elucidate the relationship between the physical properties of crystals and cytotoxicity and provided theoretical references for inhibiting stone formation.

