基于自抗扰-动态矩阵的油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制
张学军,李 茜,朱兴亮,马少腾
基于自抗扰-动态矩阵的油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制
张学军,李 茜,朱兴亮,马少腾
(新疆农业大学机电工程学院,乌鲁木齐 830052)
针对油葵联合收获机的脱粒滚筒控制方法的实时性、准确性和适应性问题,该文以油葵联合收获机行走速度为控制量,滚筒转速为目标建立油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒速度动力学模型,并将模型变换为适于自抗扰控制的仿射系统,设计了基于自抗扰和动态矩阵模型的控制系统,并对联合收获机的时变干扰进行在线估计,对脱粒滚筒的控制延迟进行基于动态矩阵模型预测控制,实现对其控制延迟的抵消和滚筒转速的实时控制。对所设计的脱粒滚筒控制器进行了仿真、台架试验和田间试验。结果表明,在自抗扰-动态矩阵控制器作用下,当喂入量较小时,随着收获机行走速度慢慢增加滚筒转速稳定在最优转速430 r/min;当喂入量加大时,滚筒转速降低;当喂入量有小幅度随机干扰时,滚筒实时控制转速与最优转速430 r/min的静态误差保持在5%之内,自抗扰-动态矩阵控制器能够使脱粒滚筒获得平稳的速度控制效果。研究结果可为油葵作物联合收获机控制提供参考。
农业机械;收获机;控制;滚筒转速;自抗扰控制器;动态矩阵;油葵
0 引 言
油葵是世界四大油料作物之一,中国东北、华北、西北等地约有300 万km2的地区种植油葵。油葵联合收获机是一种大型联合收获机,随着农业自动化技术的发展,对其自动控制的要求也越来越高,脱粒滚筒转速系统作为油葵联合收获机主要子系统之一呈现出强非线性、多干扰、控制时滞等特点[1-6]。
在实际生产中,联合收获机的控制模型参数往往存在不确定性,如复杂多变的地形和收割对象会给收获机的行走速度和脱粒装置的控制带来干扰,这对控制器的鲁棒性和自适应性提出了更高的要求[7]。目前,已有相关文献对其他作物的联合收割机脱粒滚筒的转速控制进行了研究,如,陈进等[8]针对联合收获机工作过程中的非线性、时变、大滞后特性,提出了采用灰色预测模糊控制方法,对联合收获机的前进速度进行自动控制;并以切纵流联合收获机为研究对象[9],设计了一种基于联合收获机前进速度的模糊自适应控制系统,建立了融合多个变量的自适应控制参考模型和模糊控制规则,但这2种方法针对不同地块及收割对象需要首先建立输入、输出量的偏差、偏差变化量的量化表和模糊规则查询表,工作量繁琐。宁小波等[10]在文献[9]基础上建立了控制性能和收获性能的优化目标函数来衡量联合收获机的作业性能,并利用多目标遗传算法对模糊控制系统的隶属度函数和输送槽、割台螺旋输送器和切流滚筒对前进速度的影响因子进行优化;宁小波等[11]以XG610 型联合收获机为应用对象,在对运动机构动力学分析和脱粒分离试验数据的基础上,分析了其他工作部件运动对脱粒滚筒转速变化的影响,建立了脱粒系统动力学模型,并与模糊逻辑控制器相结合构建了调速控制系统仿真模型;李鑫等[12]利用传感器采集滚筒信息,形成了滚筒转速的闭环反馈调节机制,并采用小波神经网络算法对转速精度进行调节;宿敬肖[13]等利用新型液压-机械控制方案,结合神经网络PID控制器,设计了一种新的小麦收割机械式行走装置。但这几种方法没有考虑控制时滞问题,即收割对象被收割后需要在传送槽内运送一定时间才能到达脱粒滚筒,使得脱粒滚筒不能达到实时控制。
对于油葵联合收获机而言,由于实际收割中油葵联合收获机的模型参数的不确定性和其他时变的随机干扰,其脱粒滚筒转速控制系统呈现出强非线性、多干扰、控制时滞等特点,大范围调速时非线性表现更加严重,且油葵盘传送带也引入控制的延迟,使得收获机行走速度改变不能很快调节脱粒滚筒的喂入量,难以达到真正的实时性、准确性和适应性,对滚筒控制器的鲁棒性提出了更高要求[14-18]。
近年来,自抗扰控制器(active disturbance rejection controller,ADRC)[19-21]得到了众多学者的重视,发展迅速,并在电机调速系统、传动装置的运动控制、精密控制领域以及机器人、兵器、航天等领域[22-26]获得了广泛应用。本文在分析油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制系统数学模型的基础上,引入自抗扰控制器并将其与动态矩阵模型预测控制方法相结合,设计一个基于自抗扰控制器的脱粒滚筒转速控制系统,实现了“大误差,小增益”、“小误差,大增益”的非线性控制[27],将系统的内扰、外扰以及速度张力之间的耦合影响等视为系统总扰动,由扩张状态观测器统一观测并加以补偿,并进一步利用动态矩阵预测控制方法(dynamic matrix predictive control,DMC)对控制延迟进行处理,以实现滚筒转速和收获机行走速度的解耦,并有效克服随机扰动对转速的影响。
1 脱粒滚筒转速控制模型
当收获机结构一定时,脱粒滚筒的转速主要依赖于滚筒的输入功率、收获机的行进速度、作物密度以及地表地貌等。本文采用文献[11-12]中基于滚筒角速度、作物密度、发动机功率和收获机行走速度的脱粒滚筒转速控制模型。
不同地块作物种植密度具有时变性和不确定性,是随机变量,不可控制,发生变化会导致喂入量的变化而使得脱粒滚筒工作状态发生改变,此时可以通过调节收获机行走速度实施对脱粒滚筒工作状态的控制。
2 滚筒转速ADRC控制策略
2.1 ADRC
ADRC是一种不依赖系统模型的新型控制技术,它能实时估计并补偿系统运行时受到的各种“外扰”和“内扰”的总和作用,并结合特殊的非线性反馈结构实现良好的控制品质,具有超调小、响应快、精度高、抗干扰能力强、算法简单等特点,可以非常有效地解决由式(1)描述的对象的控制问题[26-28]。
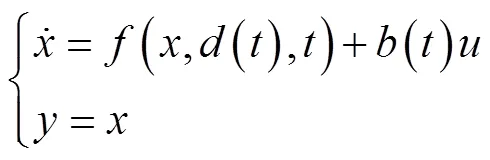
式中为状态变量,()为外部扰动,为控制量,()为控制量放大系数,为输出,(,(),)是对象“总扰动”。自抗扰控制器主要包括:非线性跟踪微分器(tracking differentiator,TD)、扩张状态观测器(extended state observer,ESO)和非线性组合(nonlinear state error feedback law,NLC)。对于该二阶对象,其ADRC控制器的标准结构参见文献[20-21]。
2.2 二阶滚筒转速ADRC控制策略
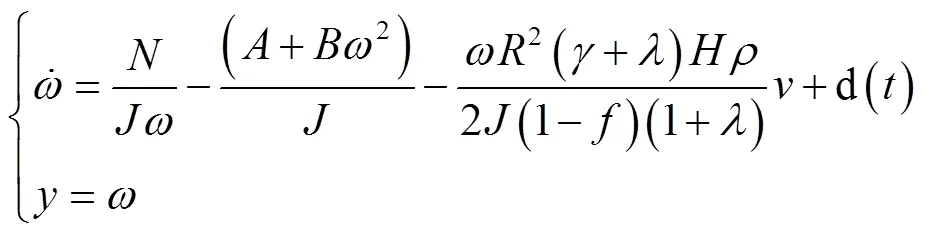
记
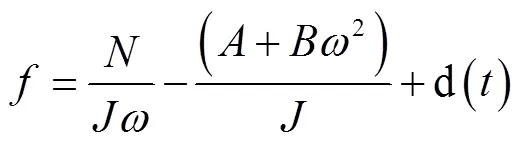
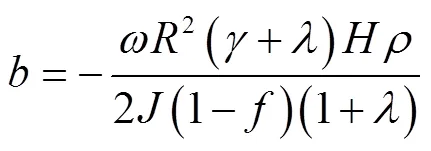
由此得到:
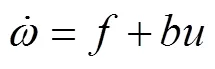
脱粒滚筒转速的干扰是时变的,根据ADRC设计思想,将式(5)中的视为系统的未知扰动,通过设计扩张状态观测器(ESO)将其估计出来,并通过控制量对其进行补偿,实现对滚筒转速系统内外干扰的克服,提高控制器的鲁棒性。
2.3 ADRC控制律设计
1)由跟踪微分器(TD)安排过渡过程
参考输入信号0(本文中参考输入信号为最优滚筒转速0),经TD后输出为1和2,1为参考输入0的跟踪信号,2为跟踪信号1的微分信号,1能很快跟踪参考输入0。
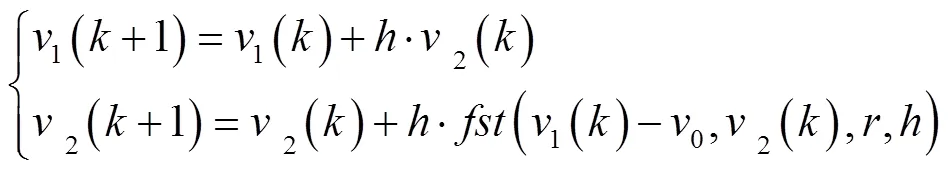
2)计算扩张状态观测器(ESO)的输出
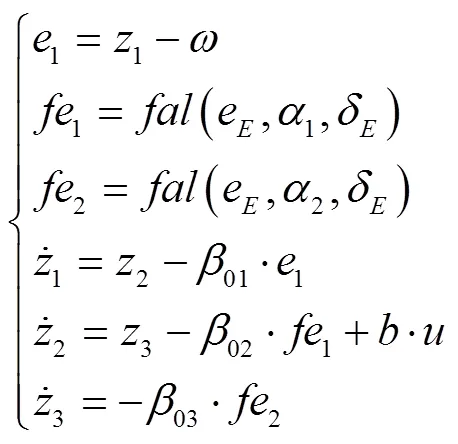
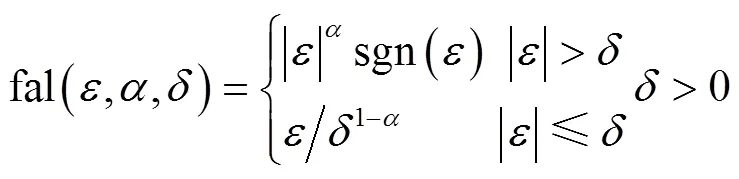

2.4 脱粒滚筒转速控制延迟的处理

文献[31-33]对动态矩阵模型预测控制(DMC, dynamic matrix predictive control)的基本原理已有叙述,本文根据油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒的特点和作业参数构建模型方程。
互联网时代打破了传统信息壁垒,形成了信息共享、结构重塑、透明开放、突破时空的互联互通格局。在这样的大环境下,客服人员招聘的弊端更易化解,人岗匹配度更为精准,总体而言互联网时代招聘客服人员有以下几个特点:
将其代入脱粒滚筒转速控制模型,得到对应的个滚筒转速:
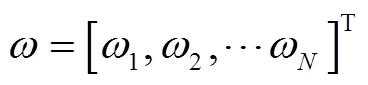

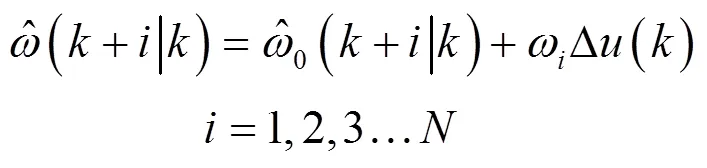
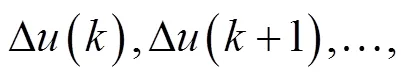
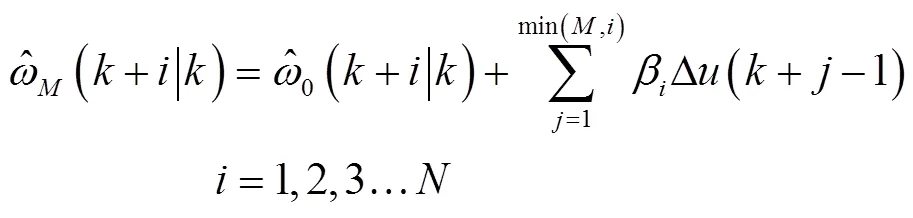
若优化性能指标为
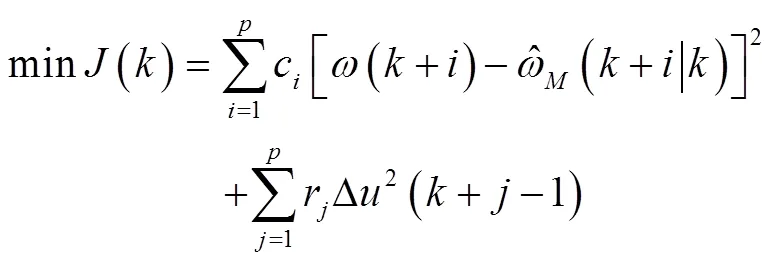
式中c和r是加权系数,c表示对滚筒给定转速的跟踪误差的抑制,r表示控制作用变化的抑制。
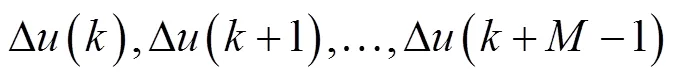
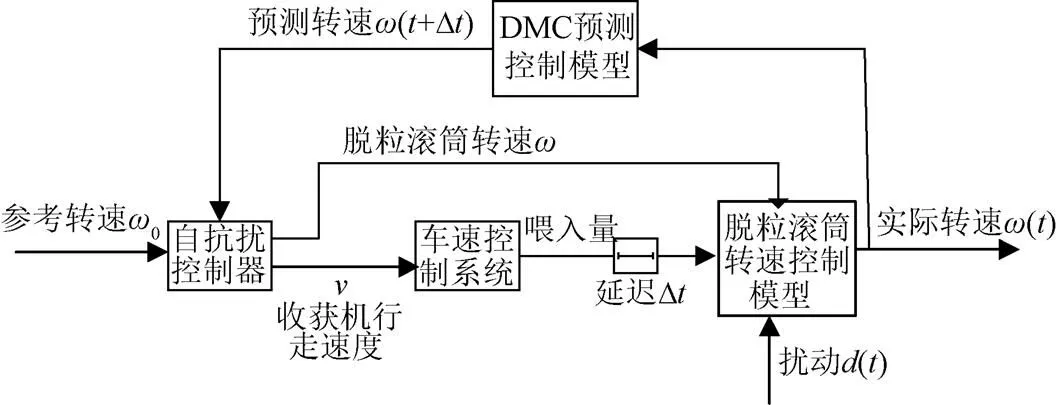
图1 油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速自抗扰控制流程
3 软硬件设计
基于上述控制算法设计了基于DSP的ADRC非线性控制器硬件系统,包括主系统模块、电源模块、基于A/D的转换模块和液晶显示模块,如图2所示。
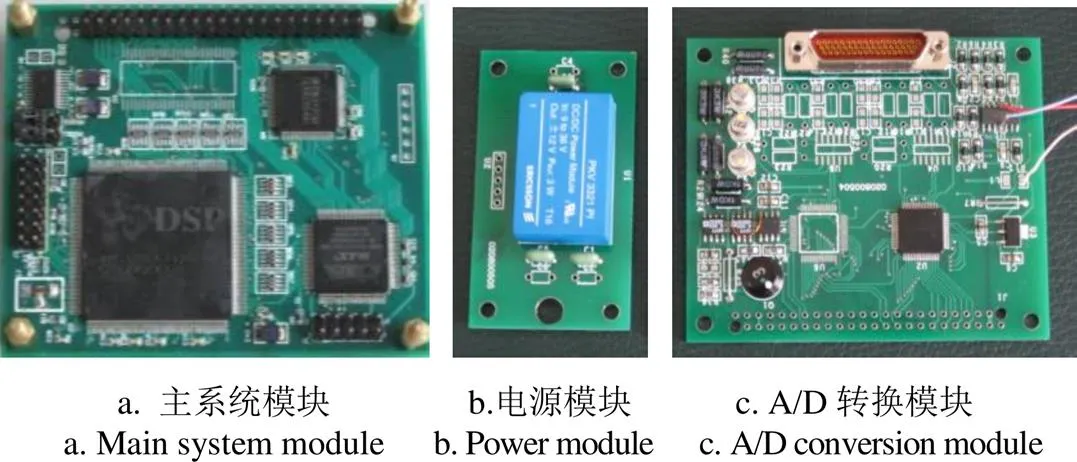
图2 基于DSP的控制器主系统
为使系统运行速度快,硬件系统选用TI公司的浮点DSP芯片TMS320C6713作滚筒转速控制算法处理器(将ADRC-DMC控制器程序通过编程下载到DSP中),TMS320C6713是32位高性能浮点数字信号处理器(DSP),贴片式封装,集成度高,体积小且DSP的主频很高,运算速度高达2 400 MFLOPS(每秒百万次浮点运算)、200 MIPS(每秒百万次指令)。算法解算系统模块电路由状态监控、系统恢复、微处理器I、微处理器II和DSP电路组成,微处理器I和微处理器II均选用C8051F120。TMS320C6713设置成微机工作模式,具有自主引导功能。控制程序固化在FLASH ROM中,该器件提供了256 K的内部存储器空间,整个运算全部是在器件内部进行,省去了DSP器件外扩RAM。各传感器的信号由运放调理后输入给ADS8364,经ADS8364采集后送给微处理器I,并进行简单的平滑滤波后送给微处理器II。微处理器II扩展了串口芯片TL16C554,外接数据存储模块存储原始数据和最终数据,并预留2个接口,以便初始时获取初始参数,并可将系统运行时的数据实时传送给笔记本电脑进行实时曲线显示。各传感器信息通过微处理器II将数据传输给滚筒转速控制处理器(DSP),经解算后将转速等信息送往显示单元。
为使控制器能正常工作且保证脱粒滚筒的最佳喂入量和最佳转速,设计了油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制系统软件,包括系统软件和功能软件,主要由自检模块、初始化模块、数据预处理模块、算法解算模块、中断服务程序模块和软件看门狗模块组成。在系统硬件配置的基础上,以DSP为算法运行环境,对系统软件进行检测、信息传输、数据处理和算法解算。
4 仿真试验
为验证本文所建立的油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制器的正确性,选取约翰迪尔W210油葵联合收割机的脱粒滚筒为对象进行仿真验证试验,仿真参数设置见表1[7,11-12]。在MATLAB环境下设计了ADRC-DMC控制器,为了验证其速度响应效果,根据前期试验结果,分别作如下仿真:1)假设喂入量为2.45 kg/s,最佳转速为430 r/min,采用阶跃输入信号对脱粒滚筒转速控制系统进行启动速度控制仿真;2)假设某时刻喂入量由2.45增加到3.01 kg/s,脱粒滚筒转速由430突变为390.2 r/min。速度响应曲线如图3所示。
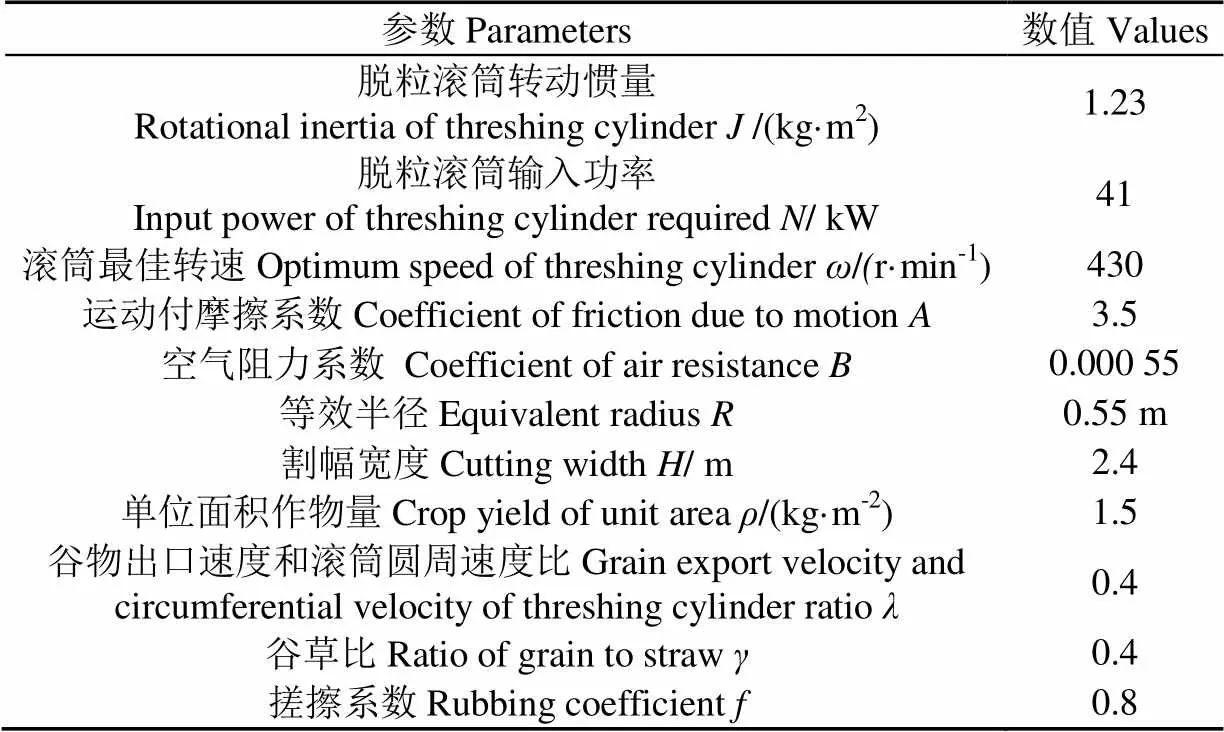
表1 仿真参数
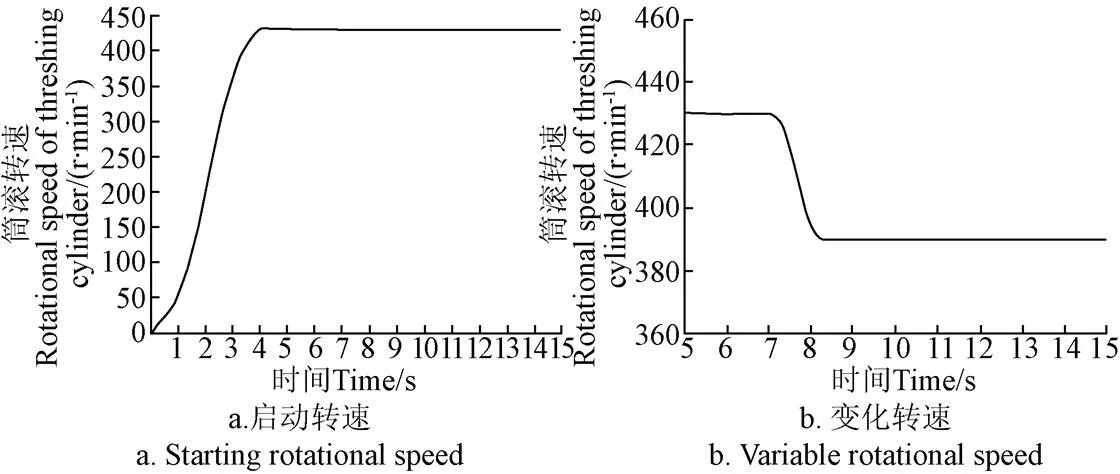
图3 基于ADRC的脱粒滚筒启动转速和变化转速仿真曲线
从图3a中可以看出,在没有随机干扰的情况下,系统的速度响应曲线比较光滑,且没有超调量,响应时间为4.078 s,响应速度比较快。从图3b可以看出,当喂入量突然加大时,系统进行自我调整,滚筒转速开始下降,经过约1.2 s稳定在390.2 r/min,速度响应曲线比较光滑,系统能及时对滚筒转速做出有效调节,避免出现堵塞现象。
5 台架试验与结果分析
为了在田间试验前验证所设计的软硬件的正确性,本文进行了台架试验,试验地点新疆农业大学机电工程学院机库,试验样机为油葵联合收获机脱粒装置,其结构图如图4a所示。试验物料为“油葵5号”,摘盘时油葵盘含水率为18%~23%。试验参照GB/T5982-2017《脱粒机试验方法》。在电动机和电源之间安装变频器,通过调整变频器频率改变电动机的转速,在脱粒滚筒输入轴一端安装扭矩传感器,测定滚筒转速、扭矩、功率,将所设计的硬件系统通过ATV38HD12N4型号变频器连接到YE2-112M-4型号三相异步电机,然后通过联轴器连接到LKN-205型号扭矩传感器,再将扭矩传感器连接到脱粒滚筒,喂入量为2.45 kg/s左右(为保证喂入量,事先计算并称量好放入多个容器,试验时平均每2秒快速倒入1次),在第15 s之后随机多投入0.15 kg左右的油葵盘改变喂入量,验证干扰信号下滚筒速度控制效果。台架试验现场如图4b所示。速度响应曲线如图5所示。
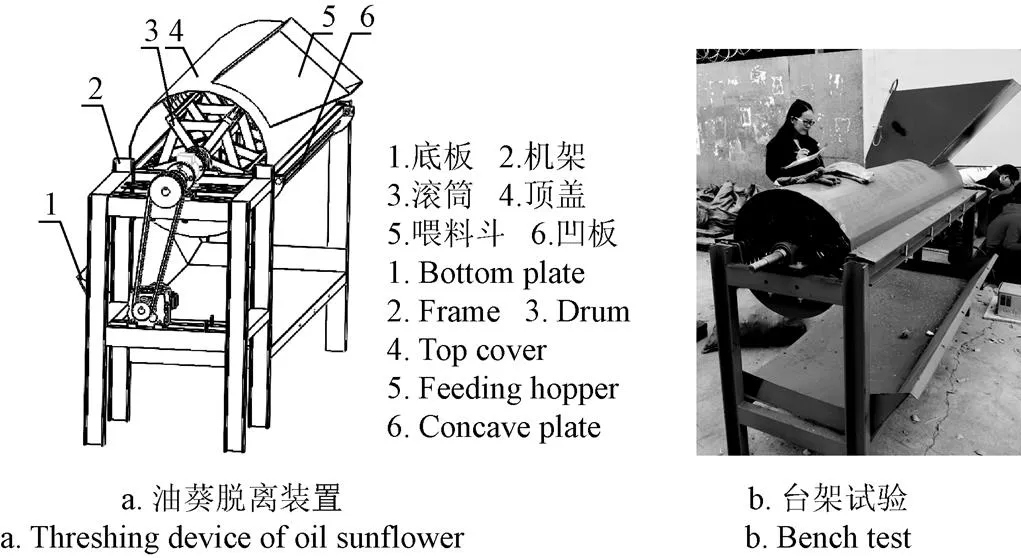
图4 脱粒装置及台架试验
从图5可以看出,基于ADRC的滚筒转速控制方法能使脱粒滚筒的转速稳定在最佳转速430 r/min附近,当有随机干扰(喂入量变化)时可小范围(0.5 r/min)调节脱粒滚筒的转速,对于农作物不确定性或随机干扰有较好抑制效果,能及时对滚筒转速做出有效调节。
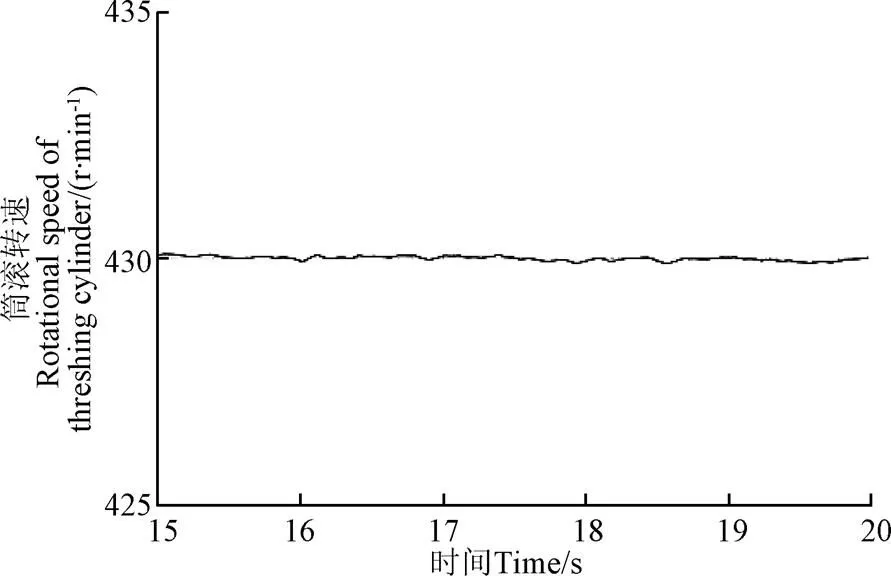
图5 有干扰信号的滚筒转速控制曲线
6 田间试验与结果分析
将所设计的硬件系统安装在约翰迪尔W210油葵联合收获机上于2018年9月进行田间试验,试验地点选在新疆生产建设兵团农六师103团油葵试验田,如图6所示。将霍尔传感器安装在约翰迪尔W210油葵联合收获机相应部件上获取滚筒转速和收获机行走速度,通过采用MP057NB213型步进电机连接减速器对操纵杆进行控制,收获机机手只需控制割台和收获机的行走方向,设置压力传感器采样周期0.25 s。

图6 田间试验
初始试验选择油葵种植密度较为均匀且地面较为干燥的地块,油葵品种为“油葵5号”,初始时收割宽度为6行(根据收获机行走速度和种植密度,对应喂入量为2.36~2.53 kg/s),行距37~40 cm,株距20~25 cm,株高约130 cm,盘高约112 cm,留茬高度约85 cm,籽粒含水率16.2%~17.8%,通过调整收获机行走速度调节喂入量,通过采用变割幅(收割宽度由6行增加到7行)的收割方法增加收获机相同行走速度下的喂入量,验证控制器的控制效果;选用种植情况相同的地块进行7次验证试验。其中1次的试验结果如图7所示。图7a为启动时滚筒转速跟踪曲线,图7b为喂入量为6行作业时滚筒转速和收获机行走速度控制曲线,图7c为喂入量由6行增加到7行时的滚筒转速和收获机行走速度控制曲线(稳定状态的喂入量在2.39~2.51 kg/s之间)。
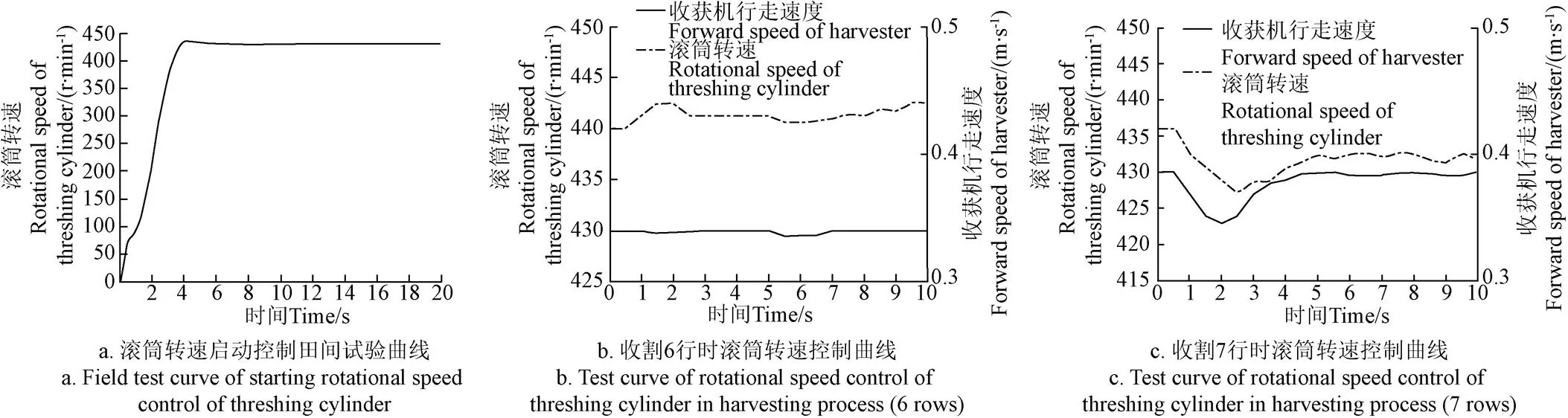
图7 田间试验的速度响应曲线
从图7a可以看出,在ADRC控制器作用下,由于随机干扰的存在,在油葵联合收获机启动时,滚筒转速有一定的超调,但超调量和超调时间很小,滚筒转速很快达到最优转速430 r/min左右,总体误差在5%(20 r/min)内,满足实际作业要求。
从图7b可以看出,收获机开始自动控制收割油葵后,由于喂入量较小,收获机行走速度慢慢加快而滚筒转速稳定在430 r/min;随着收获机行走速度继续加快,喂入量逐渐增加,达到设置的最优喂入量左右,控制器开始调节,滚筒转速降低同时调节收获机行走速度,经过小幅调节后,由于所选地块种植密度较均匀,滚筒转速和收获机行走速度均保持稳定,大约在5.1 s开始种植密度稍微增加,喂入量有小幅度的随机干扰,但经过调节后滚筒转速控制与最优转速430 r/min保持在5%的静态误差之内,运行稳定。
从图7c可以看出,当收割宽度增大到7行后,喂入量增加(约3.93 kg/s),已超出设置的最佳喂入量,如果收获机仍以当前速度行走,有可能使得脱粒滚筒堵塞,但经控制器调整后,收获机行走速度开始减小,滚筒转速也开始减小,控制器能实时的对收获机行走速度和滚筒转速进行调节,响应时间约为0.5 s,能很好处理控制延迟问题,实现滚筒转速的实时控制果。
7 结 论
本文针对油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒系统的强非线性和控制延迟的特性,设计了基于自抗扰和动态矩阵控制预测控制方法的脱粒滚筒转速ADRC-DMC控制器。对于控制延迟现象,本文在ADRC控制器的反馈回路中添加一个以喂入量为参数的动态矩阵控制预测控制器,以消除控制延迟的影响,并设计了相关软硬件。通过仿真、台架试验和田间试验验证了所设计控制器的有效性。试验结果表明,收获机开始自动控制收割油葵后,收获机自动调整行走速度改变喂入量并最终稳定在2.45 kg/s左右,滚筒转速稳定在430 r/min左右,当收割行数有6行突变为7行时,经过约0.5 s,控制器开始对收获机行走速度和滚筒转速进行调节,响应速度较快,说明本文所设计的控制器能很好的对油葵联合收获机的脱粒滚筒转速进行实时有效的控制。
[1] Chen J, Ning X, Li Y, et al. A fuzzy control strategy for the forward speed of a combine harvester based on KDD[J]. Applied Engineering in Agriculture, 2017, 33(1): 15-22.
[2] Sutisna S P, Setiawan R P A, Subrata I D M, et al. System identification and steering control characteristic of rice combine harvester Model[J]. IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 147(1): 1-7.
[3] 李茜,张学军,朱兴亮. 基于因素空间的油葵联合收获机故障诊断推理机制[J]. 农机化研究,2019(7):19-23.
Li Xi, Zhang Xuejun, Zhu Xingliang. Study on fault diagnosis reasoning mechanism of oil sunflower combine harvester based on factor space[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019(7): 19-23. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 刘正怀,戴素江,李明强,等. 半喂入联合收割机活动栅格凹板装置设计与试验[J]. 中国农机化学报,2018,39(5):13-18.
Liu Zhenghuai, Dai Sujiang, Li Mingqiang, et al. Design and test of the head-feeding harvester’s moving grate concave unit[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2018, 39(5): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Rahman M M, Ishii K. Heading estimation of robot combine harvesters during turning maneuveres[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(5): 1390-.
[6] 王刚,关卓怀,沐森林,等. 油菜联合收获机种子籽粒脱粒装置结构及运行参数优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(24):52-57.
Wang Gang, Guan Zhuohuai, Mu Senlin, et al. Optimization of operating parameter and structure for seed thresher device for rape combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering(Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(24): 52-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张军,赵德安,沈慧良. 一种联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速的鲁棒预测控制[J]. 控制工程,2011,18(4):568-571.
Zhang Jun, Zhao Dean, Shen Huiliang. robust predictive palstance control of combine cylinder threshing[J]. Control Engineering, 2011, 18(4): 568-571. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 陈进,郑世宇,李耀明,等. 联合收获机前进速度灰色预测模糊控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2011,42(10):110-115.
Chen Jin, Zheng Shiyu, Li Yaoming, et al. Grey predictive fuzzy control system of forward speed for combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2011, 42(10): 110-115. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 陈进,宁小波,李耀明,等. 联合收获机前进速度的模型参考模糊自适应控制系统[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(10):87-91.
Chen Jin, Ning Xiaobo, Li Yaoming, et al. Fuzzy adaptive control system of forward speed for combine harvester based on model reference[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(10): 87-91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 宁小波,陈进,李耀明,等. 联合收获机前进速度模糊控制系统多目标遗传优化[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(5):68-74.
Ning Xiaobo, Chen Jin, Li Yaoming, et al. Multi-objective genetic algorithm optimization of forward speed of fuzzy control system for combine harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(5): 68-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 宁小波,陈进,李耀明,等. 联合收获机脱粒系统动力学模型及调速控制仿真与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(21):25-34.
Ning Xiaobo, Chen Jin, Li Yaoming, et al. Kinetic model of combine harvester threshing system and simulation and experiment of speed control[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(21): 25-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 李鑫,孙祥云,李凌雁. 联合收获机脱粒滚筒角速度控制优化设计-基于小波神经网络[J]. 农机化研究,2016(11):64-68.
Li Xin, Sun Xianggun, Li Lingyan. Ptimization Design of angular velocity control of threshing cylinder in combine harvester based on wavelet neural network[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016(11): 64-68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 宿敬肖,张宾,林海霞,等. 基于神经网络PID的小麦收割机械式行走装置设计[J]. 农机化研究,2016,38(7):55-59.
Su Jingxiao, Zhang Bin, Lin Haixia, et al. Fuzzy control of constant load of combine threshing cylinder[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(7): 55-59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 尤惠媛,李武兴. 联合收获机脱粒滚筒的模糊恒负荷控制[J]. 中国农机化学报,2015,36(5):33-35.
You Huiyuan, Li Wuxing. Fuzzy control of constant load of combine threshing cylinder[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2015, 36(5): 33-35. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李菊,赵德安,秦云. 联合收割机脱粒滚筒的双闭环负荷控制[J]. 中国机械工程,2013,24(7):873-877.
Li Ju, Zhao De'an, Qin Yun. Double closed-loop load control of a combine cylinder[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2013, 24(7): 873-877. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 崔勇, 翟旭军, 陶德清. 联合收割机拨禾轮转速自动控制系统设计[J]. 农机化研究, 2018, 40(3):129-133.
Cui Yong, Zhai Xujun, Tao Deqing. Design of automatic speed control system of combine reel[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2018, 40(3):129-133. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] Kassen D, Kelkar A. Combine harvester header height control via robust feedback linearization[C]//Control Conference (ICC), 2017 Indian. IEEE, 2017: 1-6.
[18] Omid M, Lashgari M, Mobli H, et al. Design of fuzzy logic control system incorporating human expert knowledge for combine harvester[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2010, 37(10): 7080-7085.
[19] Tian C, Yan P, Zhang Z. Inter-sample output predictor based sampled-data ADRC supporting high precision control of VCM servo systems[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 85: 138-148.
[20] 丁力,马瑞,单文桃,等. 小型无人直升机航向线性自抗扰控制[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(5):22-27.
Ding Li, Ma Rui, San Wentao, et al. Linear active disturbance rejection control for yaw channel of a small-scale unmanned helicopter[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(5): 22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 刘敏,吉月辉,李俊芳,等. 四旋翼飞行器自抗扰姿态控制[J]. 计算机仿真,2016,33(3):71-75.
Liu Min, Ji Yuehui, Li Junfang, et al. Active disturbance rejection attitude control for quadrotor aircraft[J]. Computer Simulation, 2016, 33(3): 71-75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Xia Y, Pu F, Li S, et al. Lateral path tracking control of autonomous land vehicle based on ADRC and differential flatness[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(5): 3091-3099.
[23] Castañeda L A, Luviano-Juárez A, Ochoa-Ortega G, et al. Tracking control of uncertain time delay systems: An ADRC approach[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2018, 78: 97-104.
[24] Lotufo M A , Colangelo L , Perez-Montenegro C , et al. UAV quadrotor attitude control: An ADRC-EMC combined approach[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 84: 13-22.
[25] Luo S, Sun Q, Sun M, et al. On decoupling trajectory tracking control of unmanned powered parafoil using ADRC-based coupling analysis and dynamic feedforward compensation[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 92(4): 1619-1635.
[26] 杨立本,章卫国,黄得刚. 基于ADRC姿态解耦的四旋翼飞行器鲁棒轨迹跟踪[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报:自然版,2015,41(6):1026-1033.
Yang Liben, Zhang Weiguo, Huang Degang. Robust trajectory tracking for quadrotor aircraft based on ADRC attitude decoupling control[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2015, 41(6): 1026-1033. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 黄大山,张进秋,刘义乐,等. 车辆悬挂系统自抗扰控制器改进及其性能分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(2):61-72.
Huang Dashan, Zhang Jinqiu, Liu Yile, et al. Improved active disturbance rejection controller on suspension system and its performance analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(2): 61-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 张彬文,谭文,李健. 水轮机负荷频率控制系统的线性自抗扰整定[J]. 电机与控制学报,2019,23(1):117-124.
Zhang Binwen, Tan Wen, Li Jian. Tuning of linear active disturbance rejection control for load frequency control systems with hydro turbines[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2019, 23(1): 117-124. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 肖泽民,朱景伟,夏野,等. 基于自抗扰控制器的PMSM伺服控制系统研究[J]. 微电机,2018,51(3):57-61.
Xiao Zemin, Zhu Jingwei, Xia Ye, et al. Investigation of PMSM servo system based on active disturbance rejection controller[J]. Micromotors, 2018, 51(3): 57-61. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 姬江涛,王荣先,符丽君. 联合收获机喂入量灰色预测模糊PID控制[J]. 农业机械学报,2008,39(3):63-66.
Ji Jiangtao, Wang Rongxian, Fu Lijun. Grey prediction fuzzy PID control of the feeding quantity in combine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2008, 39(3): 63-66. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 高强,李航. 基于单变量与多变量系统的模型预测控制研究[J]. 计算机工程与设计,2013,34(9):3266-3272.
Gao Qiang, Li Hang. Research of model predictive control based on SISO and MIMO system[J]. Computer Engineering & Design, 2013, 34(9): 3266-3272. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 杜德伟,邹涛,李永民,等. 一种面向输入输出故障的变结构模型预测控制方法[J]. 信息与控制,2016,45(6):653-659.
Du Dewei, Zou Tao, Li Yongmin, et al. Model predictive control method with variable structure to input-output faults[J]. Information & Control, 2016, 45(6): 653-659. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[33] 邢小军,黄龙亮,范东生,等. 关于四旋翼无人机姿态优化控制仿真研究[J]. 计算机仿真,2017,34(4):110-114.
Xing Xiaojun, Huang Longliang, Fan Dongsheng, et al. The simulation research on optimizing attitude control for quadrotor[J]. Computer Simulation, 2017, 34(4): 110-114. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Rotational speed control of threshing cylinder of oil sunflower combine harvester based on active disturbance rejection controller-dynamic matrix predictive
Zhang Xuejun, Li Xi, Zhu Xingliang, Ma Shaoteng
(,,830052,)
Aiming at the real-time, accuracy and adaptability requirements of threshing cylinder control method of oil sunflower combine harvester, the mathematical model ofrotational speed control of threshing cylinder for oil sunflower harvesting is given in this paper. The walking speed of oil sunflower combine harvest was selected as the control variable and the rotational speed of threshing cylinder wasselected as controlled variable. The rotational speed dynamic model of the threshing cylinder was converted to a affine system which is suitable for ADRC (active disturbance rejection controller), and then the control system based on the ADRC. The internal disturbance, external disturbance and the coupling effect between velocity tension of the system are considered as the total disturbance of the system, the extended state observer is used to observe and compensate the control delay, and the dynamic matrix predictive (DMC) control method is further used to process the control delay. The DMC predictor continuously collects feeding quantity at the current time to predict the feeding quantity at the time according to the predictor. When the predicted value exceeded the setting range, the control system would adjust the walking speed of harvester and the rotational speed of threshing cylinder in time, i.e. to increase the walking speed of the harvester, to increase the feeding quantity, to improve the efficiency or to reduce the walking speed of the harvester, to reduce the feeding quantity and to avoid the blockage of the threshing cylinder, thus the feeding quantity is always kept within the setted optimum range, so that the speed of threshing cylinder can be controlled in advance. The hardware and software system of DSP based on ADRC-DMC nonlinear controller was designed, the simulations, laboratory test and field test were carried out for the designed threshing cylinder controller. Simulation results showed that in the absence of random disturbance, system response curve was smooth, and no overshoot, faster response and system could adjust itself when feeding quantity increased suddenly, the rotational speed of threshing cylinder began to decrease and stabilized at 390.2 r/min after about 1.2 s, and the system response curve was smooth. In the bench test,when the threshingcylinder ran at the optimum speed of 430 r/min, the optimum feeding quantity was 2.45 kg/s, after 15 s, randomly invested about 0.15 kg oil sunflower tray and stem to change the feeding quantity, the test results showed that the rotational speed control method based on ADRC-DMC could adjust the speed in a small range and had a good inhibitory effect on crop uncertainty or random interference, the rotation speed of the threshing cylinder could be adjusted in a small range (0.5 r/min). In order to further verify the effect of the controller, field tests were carried out. The feeding quantity was adjusted by adjusting the traveling speed of the harvester by changing the cutting width, i.e. the cutting width was increased from 6 rows to 7 rows. The results showed that the overall change trend of the record data curve of the rotational speed of threshing cylinder and walking speed of the combine harvester was in good agreement with the simulation results, and the speed response time was about 0.5 s, which can deal with the control delay problem well and realize the real-time control of the rotational speed of the threshing cylinder, ADRC-DMC controller could make the threshing cylinder achieve stable effect.
agricultural machinery; harvester; control; rotational speed of threshing cylinder; active disturbance rejection controller; dynamic matrix; oil sunflower
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.002
S225.31
A
1002-6819(2019)-15-0009-08
2019-02-16
2019-05-06
国家重点研发计划(2016YFD0702104-3)
张学军,博士,教授,主要研究方向为农业装备工程技术。Email:tuec@163.com
张学军,李 茜,朱兴亮,马少腾. 基于自抗扰-动态矩阵的油葵联合收获机脱粒滚筒转速控制[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(15):9-16. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Zhang Xuejun, Li Xi, Zhu Xingliang, Ma Shaoteng. Rotational speed control of threshing cylinder of oil sunflower combine harvester based on active disturbance rejection controller-dynamic matrix predictive[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(15): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.15.002 http://www.tcsae.org
———2020 款中农博远玉米收获机值得期待

