Study of partial discharge characteristics in HFO-1234ze(E)/N2 mixtures
Key Laboratory of Engineering Dielectrics and its Application of Ministry of Education,Harbin University of Science and Technology,Harbin 150080,People’s Republic of China
Abstract
Keywords:SF6 alternative gas,greenhouse effect,partial discharge inception voltage,uneven electric field,relative insulation performance
1.Introduction
Compared with solid and liquid media,gas insulation media has outstanding characteristics such as long service life,high safety level,flexible configuration,simple maintenance and little influence from external factors.Sulfur hexafluoride(SF6)has the advantages of non-toxic,non-flammable,high insulation strength and arc extinguishing ability far exceeding the general dielectric[1].It is widely used in medium voltage circuit breakers,gas insulated current transformers,cabinet type gas insulated switchgear and other media and low voltage electrical equipment.But SF6is a greenhouse gas that has been restricted.It is expected to exist in the atmospheric environment for 3200 years[2],and its global warming potential(GWP)is about 23 900 times that of carbon dioxide(CO2).The global chemical industry produces more than 10 000 tons of SF6gas annually,of which more than 80% is used in the electrical industry[3].These SF6gases may leak into the air at various stages in the life cycle of electrical equipment.The annual emissions of SF6gas in the global electrical industry is equivalent to 125 million tons of CO2,and it continues to grow at a rate of 10% per year[4,5].The power industry urgently needs to find an environmentally friendly insulating gas that can break through the SF6short board,replace the application of SF6in electrical equipment,and completely solve the impact of SF6on the greenhouse effect[6,7].
In recent years,with the deepening of research work,a new type of environmentally friendly insulating gas HFO-1234ze(E)has gradually entered the vision of researchers.HFO-1234ze(E)has an ozone depletion potential(ODP)of 0 and a GWP of 6,and its use has almost no impact on the environment[8-11].
The amount of gas medium used in high-voltage electrical equipment is extremely large,so the preparation method and economic cost are also important factors that limit the application of new environmentally friendly insulating gases[12].People have studied HFO-1234ze(E)for more than 20 years.Industrial preparation methods are mature,mainly including 1,1,1,3,3-pentafluoropropane(HFC-245fa)dehydrofluorination preparation method[13,14]and 1,1,1,3,3-pentachloropropane(HCC-240fa)by the preparation method of fluorine-chlorine exchange reaction[15].The synthesis route for preparing HFO-1234ze(E)with HFC-245fa as raw material is simple and the product conversion efficiency is high.The raw material HFC-245fa has achieved industrial scale production in China.Adequate raw material guarantee and mature preparation process greatly reduce the economic cost of HFO-1234ze(E),and increase the feasibility of the application of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures in electrical equipment.
At present,scholars from various countries have made some achievements in the research of HFO-1234ze(E)insulation performance.Lesaint et al tested the breakdown characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)under direct current high voltage and impulse voltage[16].Franck et al studied the breakdown characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)under the action of alternating current(AC)voltage and lightning impulse voltage through simulation calculations and experiments[17].Chachereau et al tested the electron group parameters,electron drift rate,and effective ionization coefficient of HFO-1234ze(E),HFO-1234ze(E)/CO2,and HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures[18,19].Preve et al studied the application of HFO-1234ze(E)as an insulating medium instead of SF6in medium voltage switchgear[20].
Many research results show that HFO-1234ze(E)and its mixtures have good insulation properties,but there are few studies on the characteristics of PD.PD is not only the initial performance of insulation breakdown and flashover,but also an important basis for finding partial defects and hidden dangers,judging insulation reliability and life evaluation.Highvoltage tip defects in gas insulated equipment refer to scratches or burrs that appear on the high-voltage conductor of equipment.Most of these are caused by non-standard processing or non-standard operation of personnel during transportation,installation and maintenance.When the device is operated under high voltage,PD may be caused around the tip due to excessive partial field strength[21].The gas insulating medium will decompose under the influence of PD,thereby changing the composition of the gas medium and affecting the insulation performance[22].Generally speaking,the tiny tip will disappear after several burns.However,if the device is subjected to lightning or operating overvoltage during operation,the tip will break down under the instantaneous high electric field strength and cause insulation failure.Therefore,it is of great significance to study the PD insulation characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures under common defects,and further provide more sufficient evidence for its use as an insulation substitute for SF6in gas insulation equipment.
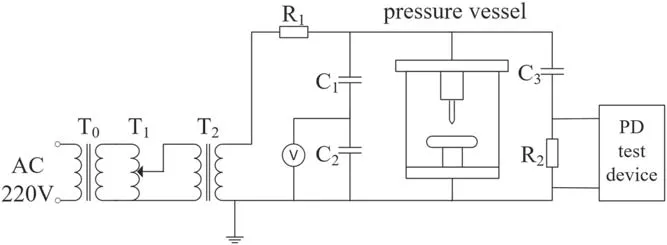
Figure 1.Test circuit diagram.
2.Experiment method
2.1.Test platform
In this paper,the pulse current method is used to test the PD characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures.The test circuit diagram is shown in figure 1.The power frequency voltage of 220 V is output as AC high voltage through the isolation filter transformer T0(10 kVA),the non-partial discharge voltage regulator T1(10 kVA/220 V)and the nonpartial discharge inflatable test transformer T2(10 kVA/100 kV).The protection resistor R1(10 kΩ)is connected in series in the line to limit the breakdown current of the air gap.C1and C2form a capacitive voltage divider,used to measure the AC high voltage applied on the pattern.When PD occurs in gas insulation,a pulse current flows through the closed loop composed of the pressure vessel,the coupling capacitor C3(0.8 μF)and the detection impedance R2(50 Ω),which can be detected by the pulse voltage proportional to the pulse current on R2,and pass the pulse signal to the PD tester.At the same time,the pulse signal is transmitted to the PD test device through the loop and displays the discharge signal.The rated power supply voltage of the PD test device is 220 V and the power is 300 W.In order to reduce the interference of environmental noise,all the work in this study was completed in the shielding room.
The electrode material selected for the experiment is brass with good electrical conductivity.The electrode model is shown in figure 2.The electrode spacing d is set to 5 and 20 mm.Due to the small curvature radius of the tip of the needle electrode,the electric field lines will be induced to concentrate on the surface of the needle electrode,especially the needle tip,resulting in uneven distribution of the electric field and the formation of an extremely uneven electric field.In order to compare the difference between the effects of short and long spacings on PD characteristics of the mixture,the electric field non-uniformity coefficient f(the ratio of maximum electric field strength to average electric field strength)is used to characterize the unevenness of the electric field between two electrode spacings.The larger the electric field non-uniformity coefficient,the more uneven the electric field distribution between the electrodes.Using COMSOL software to simulate the electric field distribution under two spacings,the simulation results show that when d=5 mm,the electric field non-uniformity coefficient of the needle plate electrode is 4.2; when d=20 mm,the electric field nonuniformity coefficient is as high as 7.9.voltage of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2is higher,which is consistent with the conclusion in[18]that HFO-1234ze(E)/N2has higher electrical strength than HFO-1234ze(E)/CO2.Therefore,N2was selected as the buffer gas in this study.The purity of HFO-1234ze(E)used in the experiment was 99.8%,and the purity of N2and SF6was 99.999%.

Figure 2.Schematic diagram of needle plate electrode.
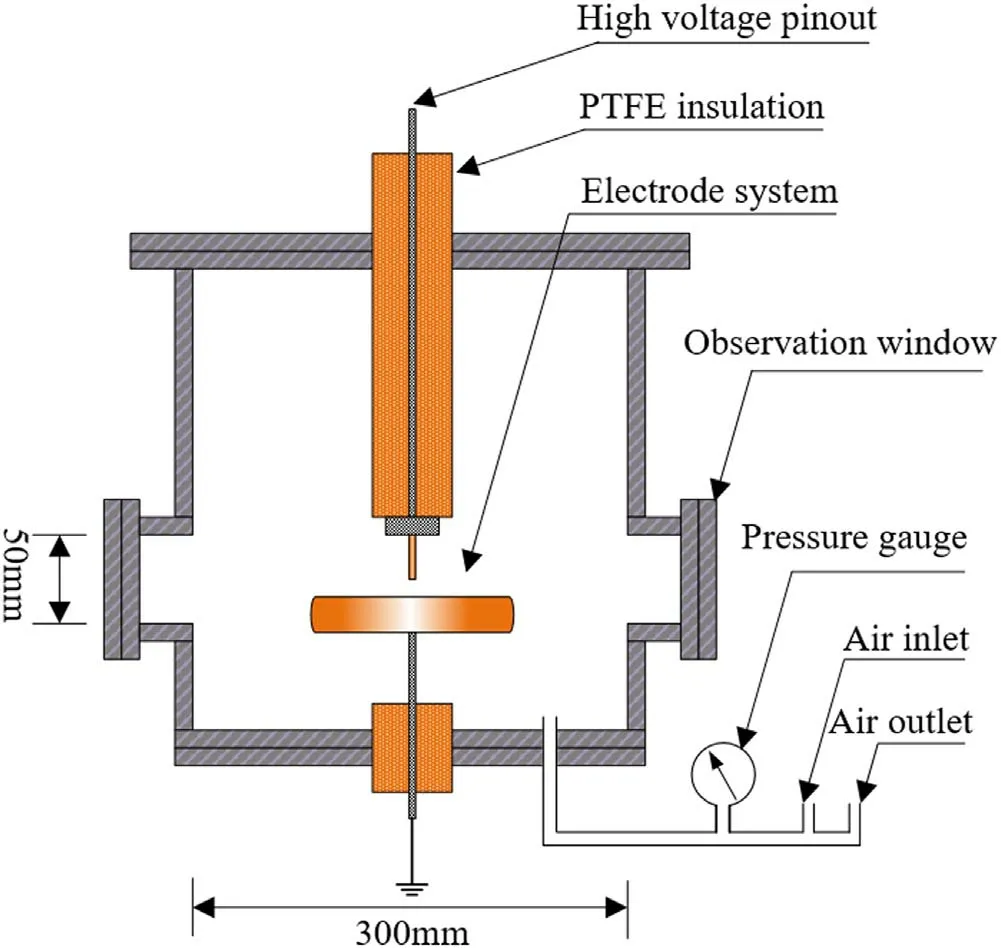
Figure 3.Schematic diagram of pressure vessel.
Prior to experiment,the inner wall of the pressure vessel and electrode surface were wiped with absolute ethanol.When the ethanol is completely volatilized,electrodes need to be installed inside the pressure vessel.After the vessel is assembled,fill the tank with 0.3 MPa N2from the inlet and let stand for 30 min.If the pressure in the vessel does not change,it means that the device has good air tightness,and the gas in the device can be extracted for gas scrubbing.The device is filled with 0.1 MPa of N2,and then evacuated to vacuum.After the entire scrubbing process is repeated 2-3 times,the inside of the device is evacuated to a vacuum state using a vacuum pump.Then,the mixture to be tested with a specific mixing ratio is filled into the vessel.The mixing ratio is changed by controlling the partial pressure of different gases.Taking 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixture with a pressure of 0.3 MPa as an example to explain the inflation process.At this time,the partial pressure of HFO-1234ze(E)is 0.12 MPa,and the partial pressure of N2is 0.18 MPa.First,close the air outlet and fill the inside of the vacuum vessel with HFO-1234ze(E)at a pressure of 0.12 MPa through the air inlet,followed by N2with a pressure of 0.18 MPa.Finally,the mixture is allowed to stand for 30 min to achieve a uniform mixing state through the diffusion of gas molecules.
The measurement process of each data point to be measured is divided into two parts.For the first time,the voltage is increased at a rate of 1 kV min−1until the PD signal appears,and the voltage at this time is recorded as the coarse measurement voltage.In order to make the subsequent measurement results more accurate,during the second step,after increasing the voltage at 1 kV min−1to 80% of the coarse measurement voltage,we then increase the voltage at a rate of 0.5 kV min−1until the appearance of the partial discharge signal which will be recorded at that time.Then,we repeat the second step 5 times,the time interval for each measurement is 10 min,and take the average value as the test result at that point for recording.The PD signal displayed by the PD test device is shown in figure 4.
The pressure vessel is a stainless steel vessel with an inner diameter of 300 mm and a height of 470 mm,which can withstand a maximum pressure of 0.7 MPa.The upper part of the vessel can be removed when the electrode is replaced.There are two observation windows with a diameter of 50 mm on both sides of the vessel to observe the internal test phenomenon.The observation window consists of tempered glass and stainless steel flanges.The schematic diagram of the pressure vessel is shown in figure 3.
Before the formal experiment,we tested the partial discharge initial voltages of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2and HFO-1234ze(E)/CO2under the same conditions.The results show that the initial
2.2.Determination of mixing ratio
Liquefaction temperature is a key factor affecting the application of new environmentally friendly insulating gas engineering.Many gas media with insulating properties better than SF6cannot be used in high-voltage electrical equipment due to the high liquefaction temperature.Under normal circumstances,the liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)is−18.98 °C,so it cannot be directly used in electrical equipment.The liquefaction temperature of the buffer gas N2selected in this paper is−196°C,far lower than that of HFO-1234ze(E).If the mixture is regarded as an ideal gas,the liquefaction temperature of the mixture is the liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)under the corresponding partial pressure[23].The saturated vapor pressure equation of HFO-1234ze(E)is as follows[24]
综上所述,对样品热电偶动态特性和炉体加热系统动态响应均进行了补偿,理论上已经满足动态测试需求,反应过程中样品和炉体之间不再存在散热或散热很小可忽略,所以本文不对样品反应过程中的散热进行补偿。

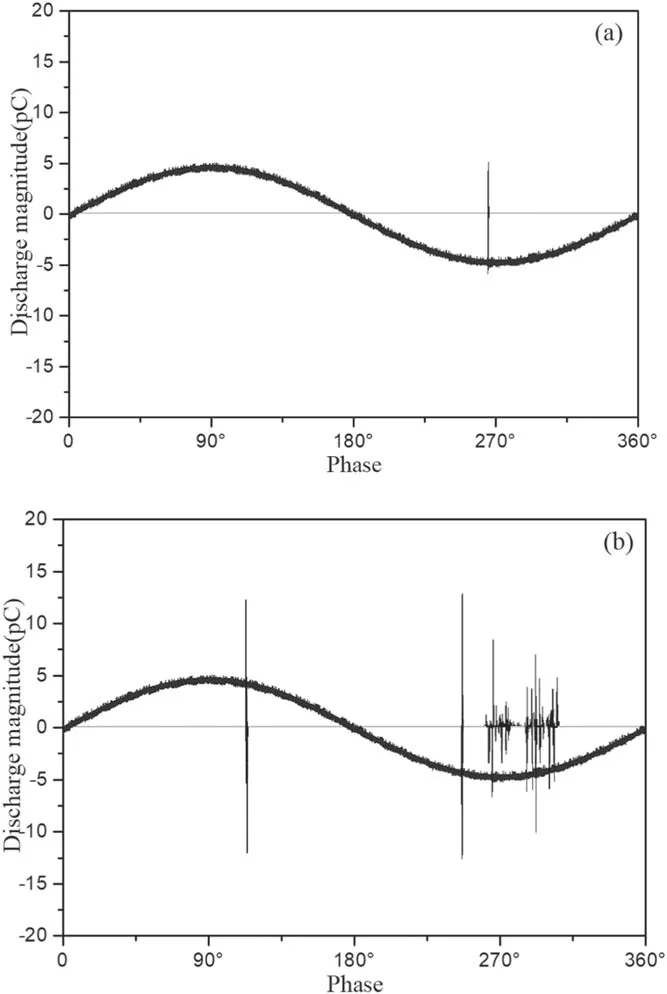
Figure 4.PD signal diagram.(a)Power frequency negative halfcycle discharge signal diagram.(b)Power frequency positive halfcycle discharge signal diagram.
In the formula:P is the corresponding partial pressure of HFO-1234ze(E)in the mixture; T is the liquefaction temperature of the mixture; Tcand Pcdenote the critical temperature and critical pressure respectively,Tc=382.51 K,Pc=3.362 MPa;the reduced temperature difference τ means 1−T/Tc; the values of coefficients A1to A4are−7.5046,1.5524,−2.2353,and−4.1018.
The liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures with different mixing ratios under the pressure of 0.3 and 0.5 MPa was calculated according to formula(1).The results are shown in table 1.
It can be seen from the results in table 1 that the liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures with a mixing ratio of 40%at 0.3 MPa is−13.14°C,which can meet the working requirements in most environments except extreme conditions.In addition,the liquefaction temperature of the 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixtures at 0.2 MPa is−22.52 °C according to formula(1).

Table 1.Liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2 mixture at different mixing ratios.
For high-voltage equipment with an internal pressure range of 0.3-0.5 MPa,the liquefaction temperature has a relatively large effect on the gas medium.In the case of this high filling pressure,the percentage of HFO-1234ze(E)in the mixture will be very limited due to the limitation of the liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E).For medium and low voltage equipment with an internal pressure of less than 0.3 MPa,the liquefaction temperature has a relatively small effect on the gas medium.The insulation performance of the gas medium can be improved by increasing the mixing ratio.In order to ensure that the mixtures have good insulation performance,and at the same time avoid the key problem of excessively high liquefaction temperature,this work selects the HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures with mixing ratios of 5%,10%,20%,40% and pure HFO-1234ze(E)as the research object.
3.Results and analysis
3.1.PDIV- characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2 mixtures
In the uneven electric field,the PD characteristics of the gas have obvious polar effects.When the voltage applied to the needle electrode occurs during the negative half cycle of the AC voltage,the needle electrode exhibits negative polarity and emits electrons to the plate electrode.At the same time,the positive ions generated by ionization in the air gap will move toward the tip of the needle,and a large amount of positively charged space charge will accumulate near the needle electrode.The presence of space charge strengthens the nearby electric field strength and makes PD more likely to occur.When the voltage applied to the needle electrode occurs during the positive half cycle of the AC voltage,the needle electrode shows positive polarity,and the positively charged space charge near the needle tip weakens the electric field and suppresses the occurrence of PD.Therefore,the occurrence of PD starts at the negative half of the power frequency,and the applied voltage at this time is recorded as the negative partial discharge inception voltage(PDIV−).With the increase in voltage,PD also began to occur in the positive half cycle,and the applied voltage at this time was recorded as the positive partial discharge inception voltage(PDIV+).
Under the effect of AC voltage,PDIV−is the initial manifestation of PD.Figures 5 and 6 are the test results of PDIV−at different mixing ratios of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2at pressures in the range of 0.05-0.3 MPa at 5 mm and 20 mm electrode spacing respectively.Figures 7 and 8 show the experimental results of relative insulation performance at 5 and 20 mm electrode spacing.The relative insulation performance is the ratio of PDIV−measured under the same conditions for HFO-1234ze(E)/N2and SF6/N2mixtures.
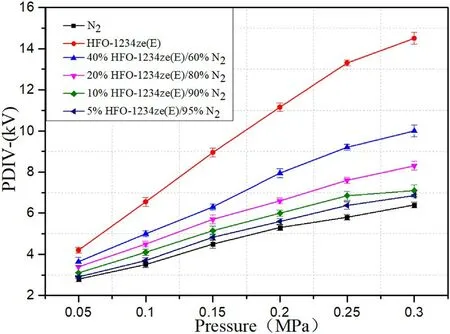
Figure 5.PDIV−of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing 5 mm.
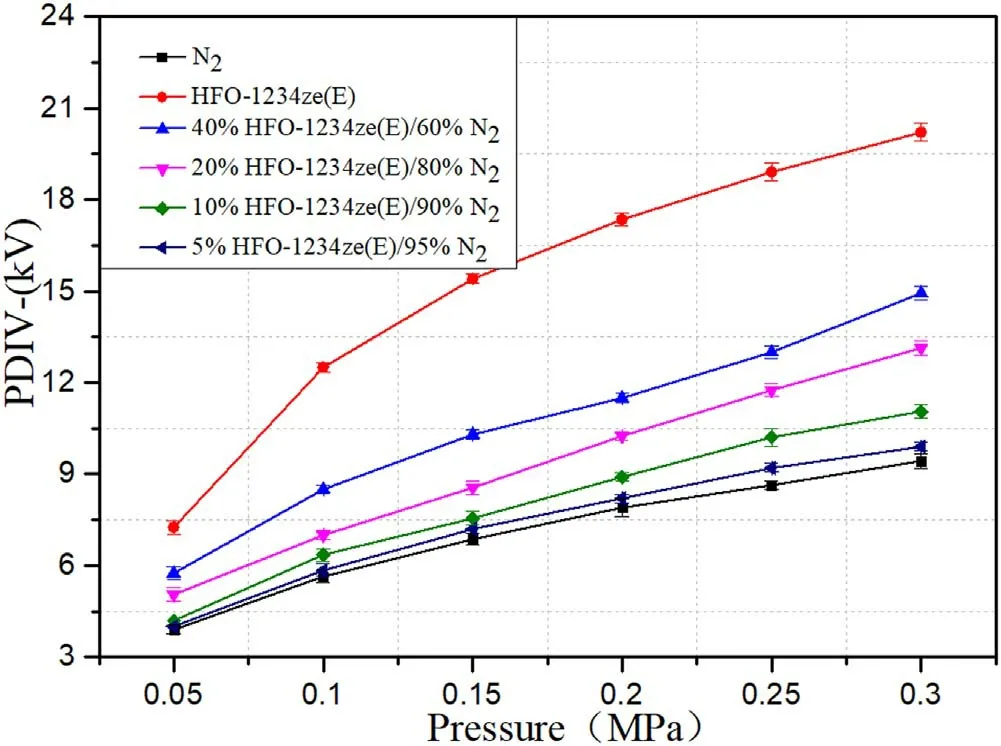
Figure 6.PDIV−of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing 20 mm.

Figure 7.Relative PDIV−of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing of 5 mm.
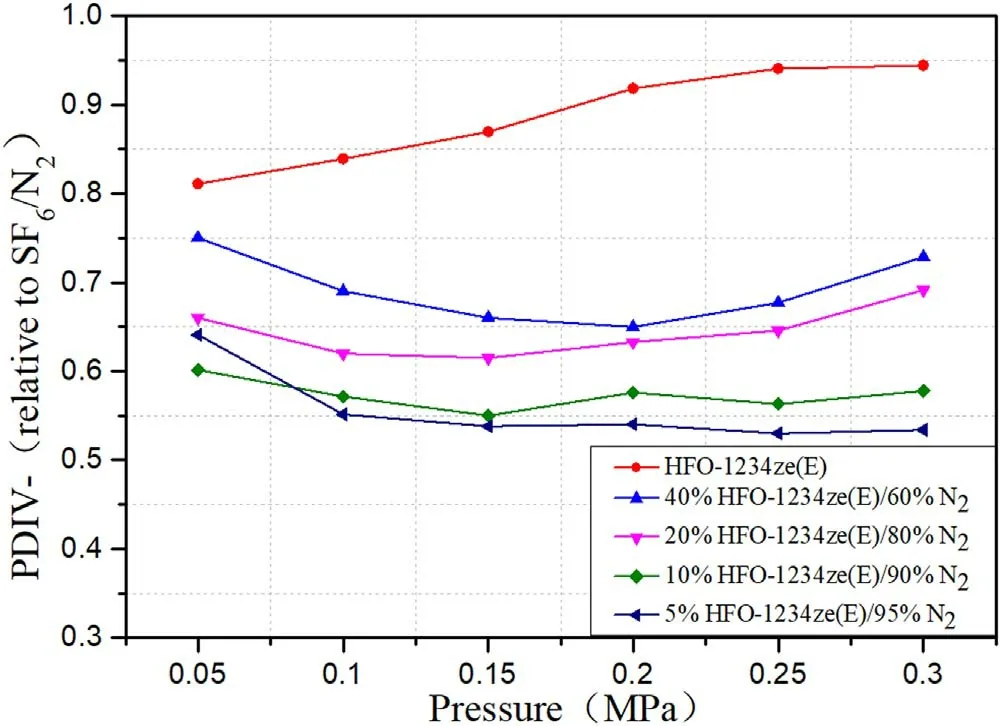
Figure 8.Relative PDIV−of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing of 20 mm.
Comparing figures 5 and 6,it can be seen that the PDIV−of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2with different mixing ratios shows a similar trend with the long and short electrode spacing.With the increase of pressure,PDIV−has an obvious upward trend,and the increase of the mixing ratio also effectively improves the insulation performance of the mixture.This is because at higher pressures,the density of the mixtures is greater,which will reduce the average free travel of free electrons,making the accumulated kinetic energy of the electrons insufficient to stimulate collision ionization.Increasing the mixing ratio will increase the molecular density.Due to the strong electronegativity of HFO-1234ze(E)molecules,it is easy to capture free electrons in space,reduce the generation of electron collision ionization,and thus improve the insulation performance of the gas medium.It is shown that in engineering applications,on the premise of ensuring that the mixture does not liquefy,the method of appropriately increasing the gas pressure and mixing ratio according to the operating environment of the equipment can improve the insulation performance of the gas medium.
According to figure 7,the PDIV−of pure HFO-1234ze(E)is slightly higher than that of pure SF6under the conditions of short electrode spacing and high pressure.It can reach 1.04 times of pure SF6at 5 mm spacing at 0.25 MPa pressure.It can be seen from the analysis of figures 7 and 8 that the relative PDIV−of the mixtures has a similar ‘U’ -shaped change trend that decreases first and then rises with the increase of gas pressure under the long and short spacing.At pressures in the range of 0.05-0.1 MPa,the molecular distance in the mixture is much larger than that at high pressure,and the average free path of free electrons is also larger,which makes collision ionization more likely to occur.The insulation performance of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2and SF6/N2under this pressure is very poor.As the pressure increased,the advantage of SF6molecules with greater electronegativity is shown.At the same time,the synergistic effect of SF6/N2also strengthens the insulating performance of the mixture.These two factors made the growth rate of PDIV−in SF6/N2exceed that of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2,so relative PDIV−showed a downward trend at pressures in the range of 0.05-0.2 MPa.When the pressure rises to 0.2-0.3 MPa,the growth trend of SF6/N2PDIV−tends to be flat.However,the insulation performance of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2is more sensitive to the increase in pressure,and the growth rate of PDIV−also exceeds that of SF6/N2,so relative PDIV−shows an upward trend.If the pressure continues to increase,relative PDIV−may continue to increase,and the insulation performance of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2will also be closer to SF6/N2.This suggests that the insulation performance of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2will be better at higher pressures.The relative PDIV−of pure HFO-1234ze(E)gas showed an upward trend at two spacings.Under the short spacing,the peak value is reached at 0.25 MPa.Under the long spacing,it tends to be flat after 0.2 MPa.The PDIV−of 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixtures can reach 0.85-0.95 times of 40%SF6/60%N2mixtures under the same conditions under different pressures,and 0.87-1.07 times of 20%SF6/80%N2mixtures under the same conditions with different pressures.
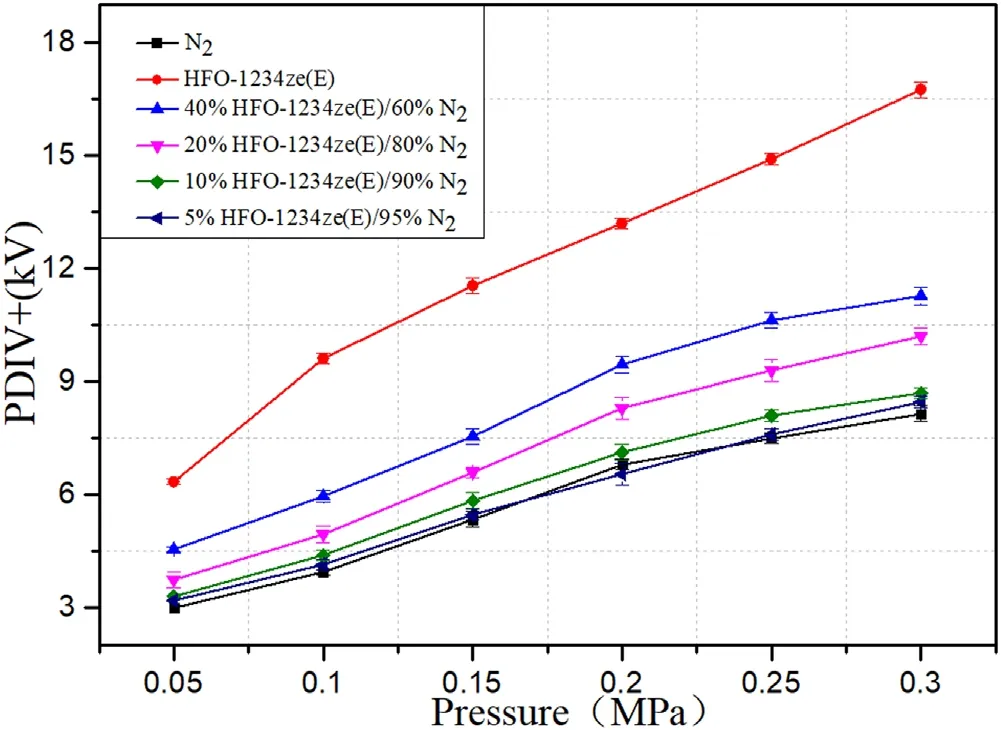
Figure 9.PDIV+of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing 5 mm.

Figure 10.PDIV+of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing 20 mm.
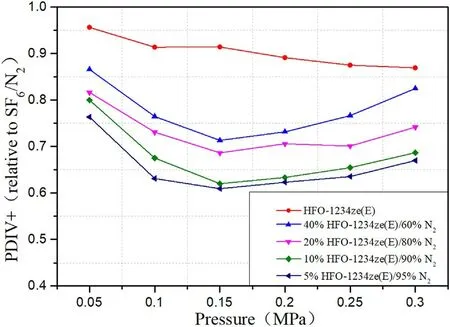
Figure 11.Relative PDIV+of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing of 5 mm.
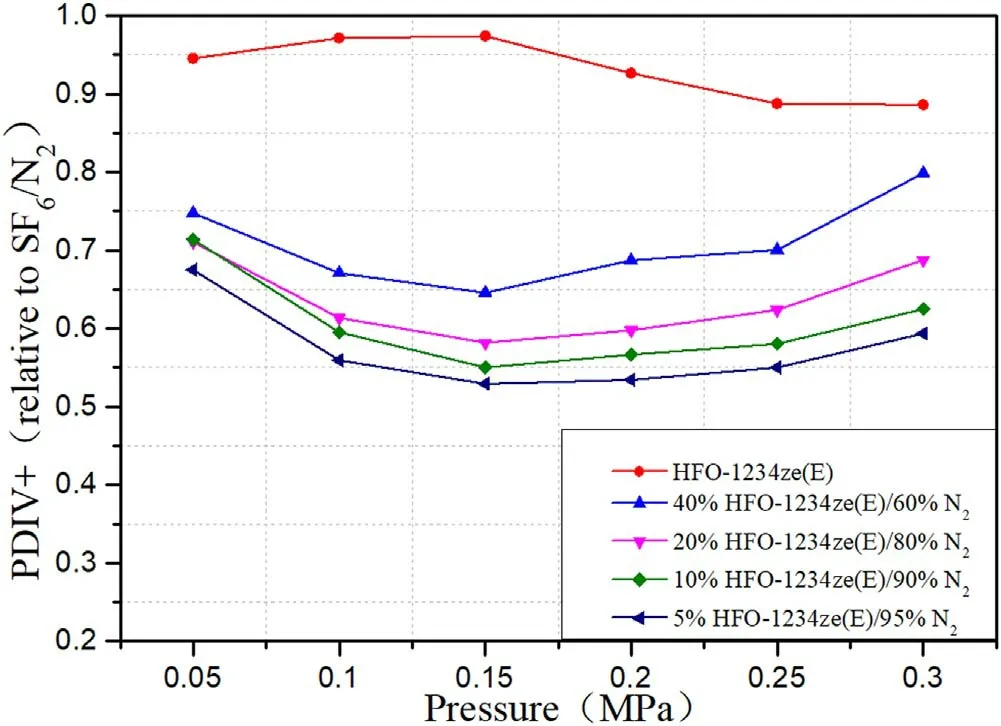
Figure 12.Relative PDIV+of mixtures with different mixing ratios at spacing of 20 mm.
3.2.PDIV+characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2 mixtures
PDIV+is close to the breakdown voltage of the medium.At this time,the gas insulation is in a severely vulnerable state.The test and analysis of PDIV+help to increase the understanding of the insulation performance of HFO-1234ze(E)and its mixtures.Figures 9 and 10 are the test results of PDIV+at pressures in the range of 0.05-0.3 MPa for HFO-1234ze(E)/N2with different mixing ratios at 5 and 20 mm electrode spacing.Figures 11 and 12 show the experimental results of relative insulation performance at 5 and 20 mm spacing.The relative insulation performance at this time is the ratio of PDIV+measured by HFO-1234ze(E)/N2and SF6/N2under the same conditions.
It can be seen from figures 9 and 10 that PDIV+under long and short spacing shows a similar change trend as PDIV−.When the electrode spacing is 5 mm,as the pressure increases,the growth trend of the mixtures PDIV+slows down,gradually saturating at pressures in the range of 0.2-0.3 MPa,but it has not reached the maximum value.The difference between PDIV+of 5%HFO-1234ze(E)/95%N2mixtures and PDIV+of pure N2is extremely small,only 0.3 kV higher than N2at 0.3 MPa.It is shown that under such conditions,HFO-1234ze(E)and N2have poor synergy.The addition of a small amount of HFO-1234ze(E)gas does not significantly improve the insulation performance of the mixtures.With the increase of the mixing ratio,the growth rate of PDIV+at a spacing of 20 mm is significantly greater than that at a spacing of 5 mm.The difference with the 5 mm spacing is that when the mixing rate is 20% or 40%,the PDIV+increases greatly when the pressure increases from 0.25 to 0.3 MPa.
It can be seen from the analysis of figures 11 and 12 that the relative PDIV+of the mixtures shows a similar ‘U’trend that decreases first and then increases,similar to the relative PDIV−.The difference from the relative PDIV−is that the relative PDIV+of pure HFO-1234ze(E)gas shows a downward trend with increasing pressure,especially at short spacing.In addition,all relative PIDV+are smaller than relative PIDV−under the same conditions,and during the test,it was found that in the process of gradually increasing the voltage,after the discharge signal appeared in the negative half cycle of the power frequency,the PD signal in HFO-1234ze/N2mixture appears faster than in SF6/N2in the positive half cycle of the AC voltage.This is because the electronegativity of HFO-1234ze(E)is not as strong as SF6,and the ability to attract surrounding electrons is relatively weak,so there are more free electrons in the electrode spacing.These free electrons move to the positive needle electrode under the action of the electric field,which strengthens the electric field near the needle electrode and makes PD more likely to occur.
The liquefaction temperature of 20%HFO-1234ze(E)/80%N2mixtures at 0.3 MPa is−28.73 °C.Under the above conditions,the PDIV+of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures is 0.68-0.88 times that of SF6/N2.The liquefaction temperature of 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixtures at 0.2 MPa is−22.52°C.Under the above conditions,the PDIV+of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures is 0.65-0.85 times that of SF6/N2.The liquefaction temperature of 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixtures at 0.3 MPa is−13.14°C.Under the above conditions,the PDIV+of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures is 0.67-0.89 times that of SF6/N2.The above two mixtures have the advantages of insulation performance and liquefaction temperature,which can ensure the stable operation of electrical equipment in most working environments except very cold areas.Among them,HFO-1234ze(E)/N2with a mixing ratio of 40%at 0.3 MPa has the potential to be applied to medium and low voltage electrical equipment.
4.Conclusions
In this paper,the PD characteristics of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures under extremely uneven electric field are studied through experiments.At the same time,SF6/N2was used as a control group to compare and analyze the effects of electrode spacing,mixing ratio and pressure on PDIV−and PDIV+.According to the experimental results,potential application of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures in electrical equipment was evaluated.This work has made a good foundation for the research of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures as an insulation substitute,and the following conclusions were drawn specifically:
(1)The variation trends of PDIV−and PDIV+of HFO-1234ze(E)/N2mixtures with a mixing ratio in the range of 5%-40% are similar at long and short electrode spacings.Both increase with the increase of mixing ratio and pressure.
(2)Since the electronegativity of HFO-1234ze(E)is not as strong as SF6,the relative PDIV−and relative PDIV+have a ‘U’ shaped change trend that decrease first and then increase with the pressure increases.
(3)Under the condition that the pressure is less than or equal to 0.3 MPa,increasing the mixing ratio can significantly improve the insulation performance of the mixtures.The 40%HFO-1234ze(E)/60%N2mixtures at 0.3 MPa has great application prospects in medium and low voltage equipment.In high-voltage electrical equipment,the liquefaction temperature of HFO-1234ze(E)will increase due to the high internal filling gas pressure.This results in a very limited percentage of HFO-1234ze(E)in the mixture at high pressure.
 Plasma Science and Technology2020年11期
Plasma Science and Technology2020年11期
- Plasma Science and Technology的其它文章
- The effect of resonant magnetic perturbation with different poloidal mode numbers on peeling-ballooning modes
- Soft landing of runaway currents by ohmic field in J-TEXT tokamak
- Numerical simulations of the wavefront distortion of inter-spacecraft laser beams caused by solar wind and magnetospheric plasmas
- Effect of insulating oil covering electrodes on the characteristics of a dielectric barrier discharge
- Numerical study on the modulation of THz wave propagation by collisional microplasma photonic crystal
- Power absorption,plasma parameters and wave structure in inductive RF plasma source with low value external magnetic field
