Prediction method of highway pavement rutting based on the grey theory
Zhou LanNi FujianZhao Yanjing
(1School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China)
(2School of Civil Engineering,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China)
Prediction method of highway pavement rutting based on the grey theory
Zhou Lan1Ni Fujian1Zhao Yanjing2
(1School of Transportation,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China)
(2School of Civil Engineering,Southeast University,Nanjing 210096,China)
In order to make a scientific pavementmaintenance decision,a grey-theory-based prediction methodological framework is proposed to predict pavement performance.Based on the field pavement rutting data,analysis of variance(ANOVA)was first used to study the influence of different factors on pavement rutting.Cluster analysis was then employed to investigate the rutting development trend.Based on the clustering results,the grey theory was applied to build pavement rutting models for each cluster,which can effectively reduce the complexity of the predictivemodel.The results show that axial load and asphalt binder type play important roles in rutting development.The prediction model is capable of capturing the uncertainty in the pavement performance prediction process and canmeet the requirements of highway pavementmaintenance,and,therefore,hasaw ide application prospects.
prediction method;grey theory;cluster analysis;analysis of variance;pavement rutting
Pavement performance prediction models are important tools for management systems at both network and project levels because they are essential for designing and planning maintenance and rehabilitation activities,as well as for the estimation of the necessary budget.
Most deterministic models are based on establishing regression relationships between relevant performance dependent indicators and independent variables,such as experienced traffic loadings,material characteristics,and environmental conditions[13].In particular,pavement performance quantifications involve complex mechanisms,some of which are unclear to users.It is,therefore,difficult to use regression_ techniques to determ ine these relationships quantitatively[46].
The grey model is suitable for the scenario of lim ited data and ismore competitive in short-term span[7].Pavement performance prediction can be deemed as a grey system wheremany parameters do not have analytical solutions and suffer from various lim itationswhen using traditional statistical analysis[8].To overcome the shortcomings of the existing models,this paper intends to develop a methodological framework based on the grey theory to predict pavement performance at the project level for highways.
1 M ethodology
The existing pavement performance data on Chinese highways typically has the lim ited data and is unreliable.The small sample size makes the traditional statistical analysis approach designed for the large sample size unfeasible,and,meanwhile,the unreliability cripples the accuracy of the determ inistic prediction models[5].Therefore,this paper develops a new method for establishing a pavement performance prediction model,combining the grey theory and cluster analysis.Fig.1 shows the proposed methodological framework of pavement performancemodels.Themethodology consists of threemajormodules:data analysis,model development and results analysis.
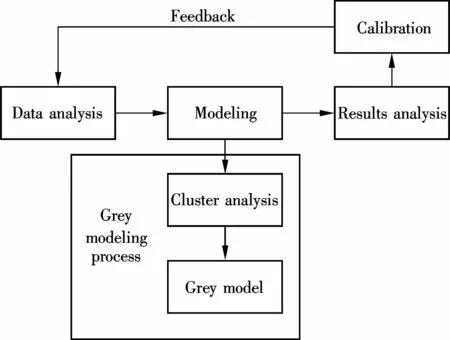
Fig.1 Methodological framework
2 Case Study
Due to the traffic and environment,distresses of various types and severity levels,such as rutting,occur on asphalt pavements.Rutting may affect pavement riding quality and safety,especially on rainy days.Thus the study collected pavement rutting as the data sample to establish a grey model of pavement performance for JiangsuProvince’s highways at a project level.
In Jiangsu province,a vehicle mounted laser profiler has been used to measure pavement rutting every year since 2003.The data of pavement rutting depth(RD)was collected every 10 m to evaluate pavement rutting conditions[9].The data used to establish the grey model consists of the follow ing variables:
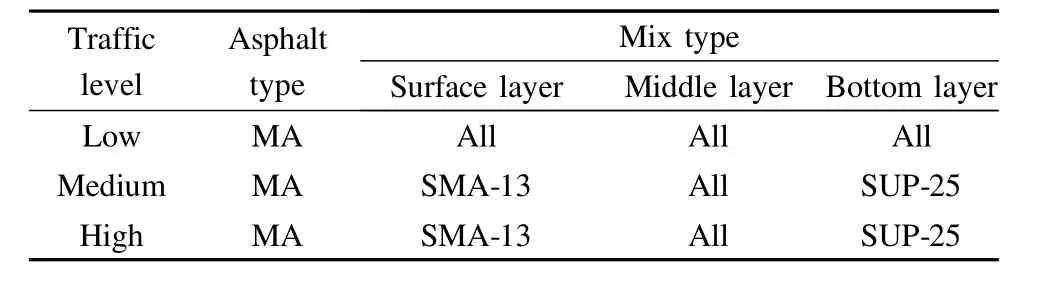
Traffic level:low(<1 000 AADTT(average annual daily truck traffic)),medium(≥1 000 and≤4 000 AADTT),high(>4 000 AADTT).
Asphalt type:modified asphalt(MA)and base asphalt(OA).
M ix type:stonemastic asphalt concrete SMA-13;dense graded asphalt concrete AK-13,AC-20 and AC-25;Superpave 20(SUP-20)and Superpave 25(SUP-25)
The data collected from four highways are analyzed in this paper.The descriptive information about four highways is summarized in Tab.1.
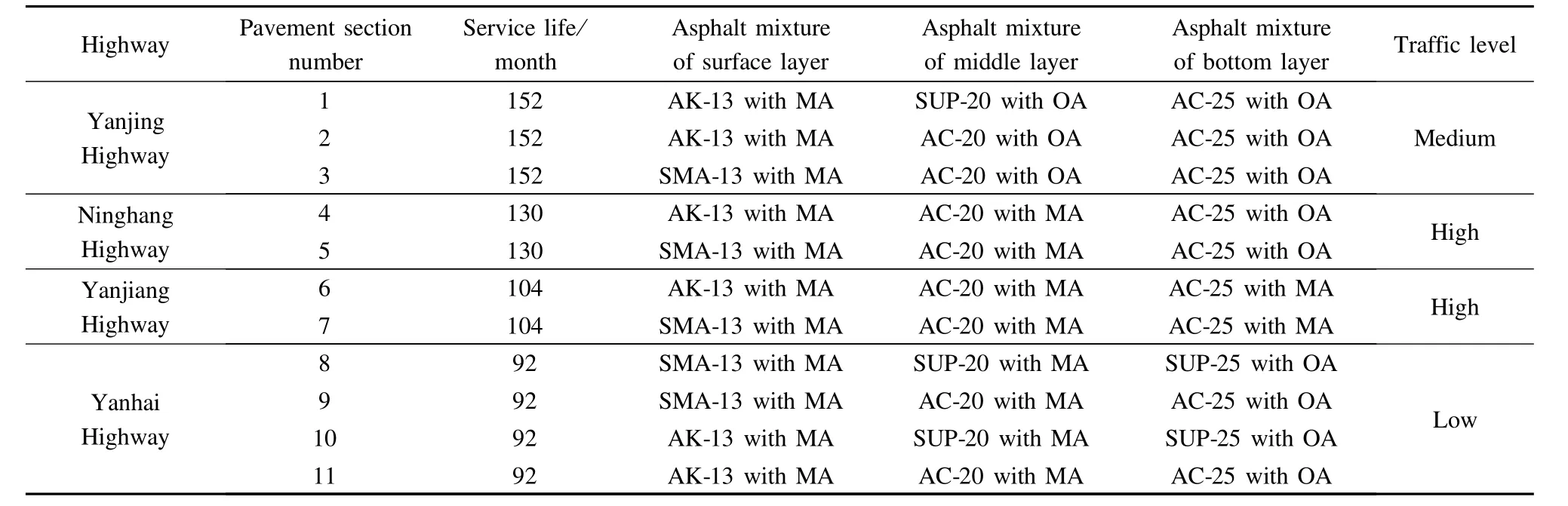
Tab.1 Descriptive information about four highways
2.1 Data analysis
Statistical analysis is performed to reveal the relationship between pavement rutting and influence factors.The influence factors considered in this paper include traffic,asphalt type,and the aggregate grade type for different surface layers.
Analysis of variance(ANOVA)is used to inspect the correlations between rutting and the influence factors for each highway and traffic level group.Also,it is used to determ ine whether the asphalt binder type and m ix type have any impact on the RD values[2].The null hypothesis of the ANOVA statistical test is that all themean values of the two asphalt types and differentmix types of three layers are the same(i.e.,μMA=μOA,μSMA-13=μAK-13,μAC-20=μSUP-20,μAC-25=μSUP-25);otherw ise,the alternative hypothesis is that at least one differs from the others[10].
The ANOVA results of eleven cases obtained from the combination of highway and traffic levels are shown in Tab.2.Four tests are performed for each combination[2,56],which are the aggregate grade type of the surface layer,the aggregate grade type of them iddle layer,the aggregate grade type of the bottom layer and all themodified asphalt pavement vs.all the ordinary asphaltpavement values.
Tab.2 ANOVA results
Based on the ANOVA results,the follow ing conclusions are obtained:
1)There is significant difference between modified asphalt and ordinary asphalt,especially for pavements at low traffic level.However,the difference reduces gradually w ith increasing service time and an equivalent cumulative axle.
2)Significant differences are observed between different aggregate grade types of the surface layer except for the highways at low traffic volume,but the impact ofm ix type on pavement rutting varies for different pavement sections.The pavementsw ith SMA-13 have better rutting resistance than those w ith AK-13.No significant differences are observed between different aggregate grade types of themiddle layer.
3)For the bottom layer,there is no significant difference between aggregate grade types at the low traffic level,which is contrary for scenarios of medium and high traffic levels.Also,the pavements w ith SUP-25 have better rutting resistance than those w ith AC-25.
2.2 Cluster analysis
It is difficult to take all the influence factors into consideration when establishing the prediction model.The K-means clustering algorithm,a classical clustering algorithm based on centroid,is used to group the pavement sections and identify clusters w ith sim ilar rutting deterioration process in order to avoid om itting redundant factors in this paper.
Rutting data from 2003 to 2011 was collected from theYanjing highway as the analysis sample.The sample included 5 399 data points in north bound direction and 4 118 data points in south bound direction.Rutting data is grouped using the cluster analysis for both directions by the SPSS statistical analysis software[10].The cluster results are summarized in Tab.3.
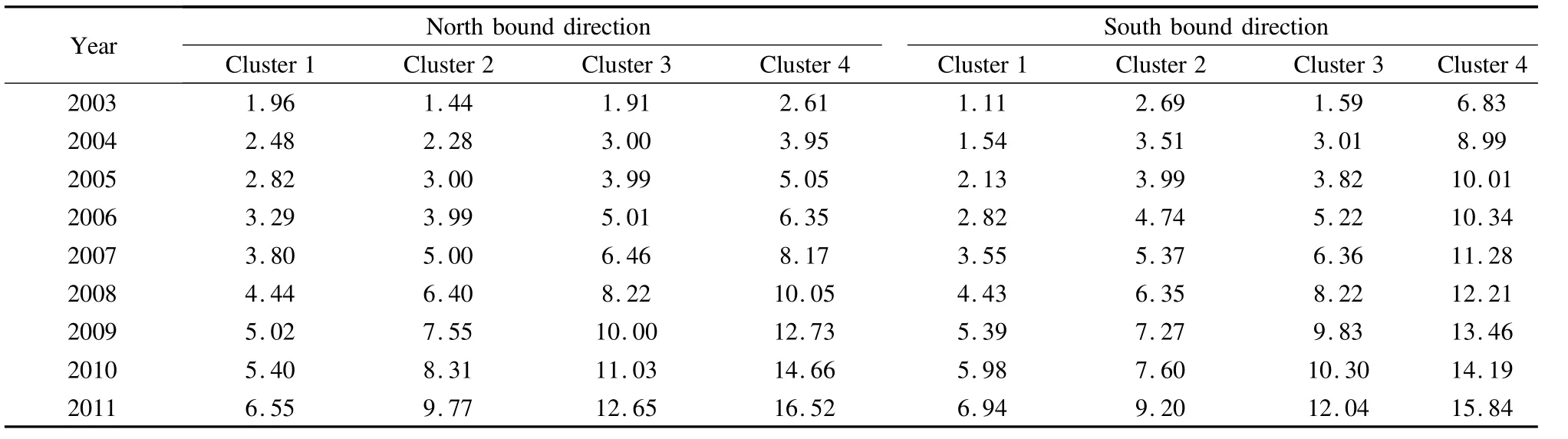
Tab.3 Cluster results
It can be seen from Tab.3 that the rutting data in the north and south directions obtained from the Yanjing highway are divided into four clusters.Cluster 1 suggests that the deterioration rate of pavement rutting over time is very slow,while Cluster 4 suggests that the deterioration process of pavement rutting over time is very rapid.From the cluster results,the rutting deterioration rates for the four clusters are ranked as:Cluster 4>Cluster 3>Cluster 2>Cluster 1.A ll four clusters are used to establish the pavement rutting prediction model which represents different pavement rutting severities and deterioration rates.
2.3 Grey model development
The GM(1,1)model is commonly used as a prediction model in the grey system,meaning that there is only one variable in the GM model[7-8].The data series should be a time series w ith comprehensive effect.Therefore,the GM(1,1)model for time series forecasting is used in this paper for the pavement rutting model development w ith five steps[8]:
1)Define original datamatrix X(0).
2)Perform AGO operations on the original data series,defined as X(1).
3)Develop the grey coefficient,where the coefficient vector can be expressed as^a={α,μ}T.
4)Insert grey coefficients into a differential equation.The grey model of AGO data series^X(1)(t+1)is developed as

5)Obtain the estimations of the original data series.The basic computational formula of the GM(1,1)prediction model is

Follow ing the five steps described above,the pavement rutting prediction models using the cluster results for the north bound direction of the Yanjing highway can be obtained,as shown in Tab.4.

Tab.4 Grey model for each rutting cluster
2.4 Results analysis
The developed pavement ruttingmodels should be validated to determ ine whether themodel is applicable to the rutting data and to explain the data reasonably.Three test methods[7,10],which are commonly used to evaluate the performance of a grey model,are used in this paper.They are the residual test,the grey relational degree test and the posteriorierror test.The residual test and posteriori error test are chosen to test themodel because the grey relational degree test is very complex.The assessment criteria of posteriori error test for the GM model are summarized in Tab.5.

Tab.5 Assessment criteria of posteriori error test
C and P are two important indicators of the posteriori error test.The smaller the C,the larger the P,the better the grey model.The results of residual test and posteriori error test are calculated,as listed in Tab.6.
As shown in Tab.6,themeans of relative residual error¯e of the grey models developed in this paper are all less than 10%and the posterior error ratios C are all much smaller than 0.35,indicating that the establishedgrey models have a high level of accuracy and can meet the requirements of highway pavement maintenance.Therefore,the GM(1,1)model is reasonable and suitable for predicting the pavement rutting at the project level.Themodel can describe the rutting deterioration law for most pavement sections.
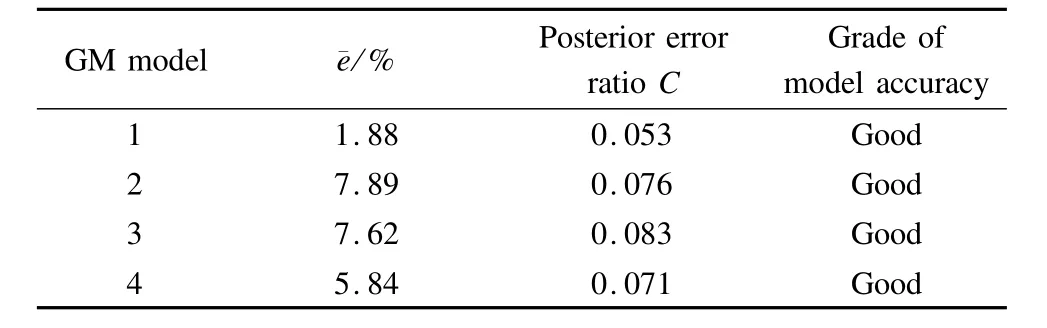
Tab.6 Results ofmodel accuracy test
3 M odel Verification
The data sets of north bound direction were used for model development,and the clusters of south bound direction were used for validation of the GM models.Two criteria[6,8],percentage error and relative root-mean square error(RMSE),are employed in this paper to compare the RD predictions from GM modelsw ith the actual RD data.The analysis results between the actual data and GM predictions are presented in Tab.7.
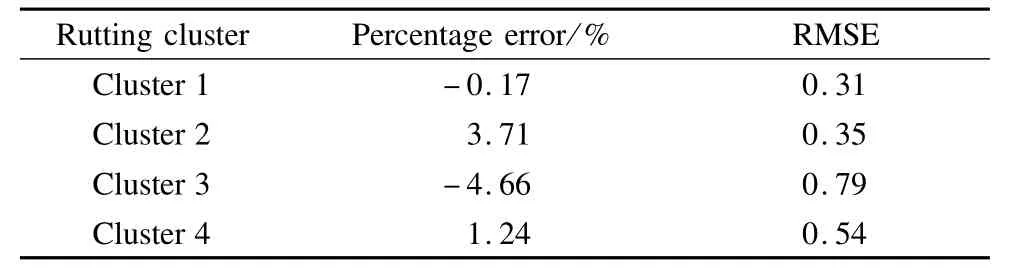
Tab.7 Comparison between the actual RD data and GM model predictions
The best predictions are observed in Cluster1 and Cluster 4,in which the deterioration rates of pavement rutting are either very slow or very fast.Meanwhile,the percentage error and RMSE values of each model are small,indicating that the GM models show satisfactory results and provide acceptable project-level pavement performance predictions.
4 Conclusion
This paper presents an experimental study based on the grey theory methodology to develop pavement rutting prediction models.Themethodology is proved to be feasible by the case study.
Based on the ANOVA results,the pavement structure does have impact on pavement rutting.Although the influence of the pavement structure on pavement rutting is not significant at early pavement service time,it becomes significant w ith the grow th of pavement service time and cumulative traffic load.
The results of themodel tests show that the grey model established in this study has high accuracy and can meet the requirements of highway pavementmaintenance.The model can describe the rutting deterioration trend for almost all pavement sections.
The proposed framework,as demonstrated by the case study,can be applied to a w ide range of conditions for various highways.It provides a relatively easy methodology for establishing pavement deterioration models and enhances the decision-making process in highway agenciesw ith limited pavement data,especially at the project level.
[1]Somayeh N,Mohammad H S,Alireza B.Development of roughness prediction models using Alberta transportation’s pavementmanagement system[J].International Journal of Pavement Research and Technology,2013,6(6):714-720.
[2]Arambula E,George R,Xiong W X,etal.Development and validation of pavement performance models for the state of Maryland[J].Transportation Research Record,2011,2225:25- 31.
[3]Wu Z,Chen X W,Yang X M,et al.Finite element model for rutting prediction of flexible pavement w ith cementitiously stabilized base-subbase[J].Transportation Research Record,2011,2226:104- 110.
[4]Porras-A lvarado JD,Zhang ZM,Salazar L G L.Probabilistic approach to modeling pavement performance using IRIdata[C]//Transportation Research Board 93rd Annual Meeting.Washington DC,USA,2014:145437-1-145437-15.
[5]Prozzi J,Madanat S.Development of pavement performancemodels by combining experimentaland field data[J].Journal of Infrastructure Systems,2004,10(1):9- 22.
[6]Ma JX,Xu F Y,Huang R.A linear and nonlinear autoregressivemodel and its application in modeling and forecasting[J].Journal of Southeast University:Natural Science Edition,2013,43(3):509- 514.(in Chinese)
[7]Wang K C P,Li Q,Hall K D,et al.Experimentation w ith grey theory for pavement smoothness prediction[J].Transportation Research Record,2007,1990:3- 13.
[8]Yi J,Shuo L.Grey system model for estimating the pavement international roughness index[J].Journal of Performance of Constructed Facilities,2005,19(1):62-68.
[9]M inistry of Communications of the People’s Republic of China.JTG H20—2007 Highway performance assessment standards[S].Beijing:People Transportation Publishing House,2008.(in Chinese)
[10]Lu W D.Statistical package for the social sciences(SPSS)tutorial:statistical analysis[M].Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry,2012:64- 145.(in Chinese)
基于灰色理论的高速公路路面车辙预测方法
周 岚1倪富健1赵岩荆2
(1东南大学交通学院,南京210096)
(2东南大学土木工程学院,南京210096)
为了制定科学的路面养护决策,提出了一种基于灰色理论的路面性能预测方法.基于路面车辙检测数据,采用方差分析方法研究不同因素对车辙的影响;利用聚类分析方法研究路面车辙发展规律;基于聚类结果,采用灰色理论分类建立了路面车辙灰色预测模型,有效降低了模型的复杂程度.研究结果表明,轴载和沥青类型对车辙的发展影响最大.所提预测模型精度较高,具有一定的实用价值,能满足高速公路路面养护工程要求,并能较好地解决路面性能预测中的不确定性.
预测方法;灰色理论;聚类分析;方差分析;路面车辙
U416.217
10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2015.03.017
2015-01-27.
Biographies:Zhou Lan(1984—),female,graduate;Ni Fujian(corresponding author),male,doctor,professor,nifujian@gmail.com.
The Major Scientific and Technological Special Project of Jiangsu Provincial Communications Department(No.2011Y/02-G1).
:Zhou Lan,Ni Fujian,Zhao Yanjing.Prediction method of highway pavement rutting based on the grey theory[J].Journal of Southeast University(English Edition),2015,31(3):396- 400.
10.3969/j.issn.1003-7985.2015.03.017
 Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)2015年3期
Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)2015年3期
- Journal of Southeast University(English Edition)的其它文章
- CoMP-transm ission-based energy-efficient scheme selection algorithm for LTE-A system s
- Detection optim ization for resonance region radar w ith densemulti-carrier waveform
- Dimensional emotion recognition in whispered speech signal based on cognitive performance evaluation
- Cascaded projection of Gaussian m ixturemodel for emotion recognition in speech and ECG signals
- Action recognition using a hierarchy of feature groups
- Ergodic capacity analysis for device-to-device communication underlaying cellular networks
