个性化护理干预在肾功能失代偿期IgA肾病患者护理中的应用效果分析
袁娜

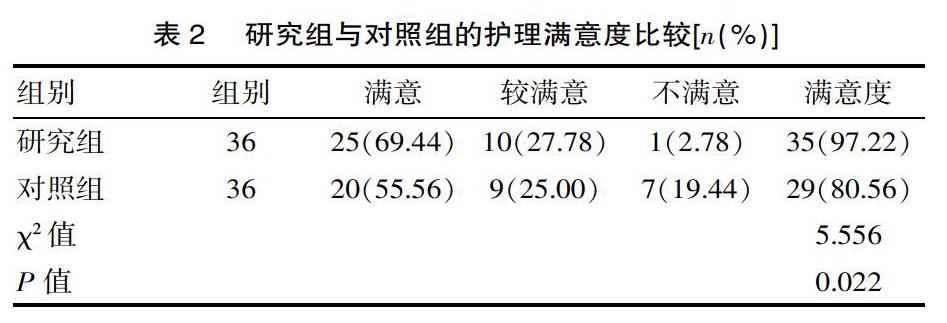

[摘要] 目的 观察并探讨个性化护理干预在肾功能失代偿期IgA肾病患者护理中的应用效果。 方法 方便选取2018年1—12月期间的72例肾功能失代偿期IgA肾病患者当作研究对象。按照护理方案的不同,将72例患者分为2组,各36例。对照组采取常规护理干预,研究组采取个性化护理干预。观察并比较2组的护理效果。结果 研究组的总有效率94.44%明显高于对照组的72.22%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=5.625,P=0.021);研究组的护理满意度97.22%明显高于对照组的80.56%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=5.556,P=0.022);护理后,研究组的CD4+(42.36±3.58)个/mm3、CD4+/CD8+(1.12±0.23)、尿蛋白(253.16±55.32)mg/d明显低于对照组的CD4+(51.63±4.12)个/mm3、CD4+/CD8+(1.31±0.28)、尿蛋白(325.24±71.36)mg/d,差異有统计学意义(t=6.152、5.221、8.416,P=0.015、0.028、0.002),研究组的CD8+(39.25±3.46)个/mm3与对照组的CD8+(39.37±3.64)个/mm3比较,差异无统计学意义(t=1.513,P=0.072)。结论 个性化护理干预在肾功能失代偿期IgA肾病患者护理中的应用效果显著,值得推广。
[关键词] 个性化护理干预;肾功能失代偿期IgA肾病;护理
[中图分类号] R473 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2019)07(c)-0133-03
Analysis of the Application Effect of Personalized Nursing Intervention in the Nursing of Patients with Decompensated Renal Function IgA Nephropathy
YUAN Na
Department of Nephrology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, Baotou, Inner Mongolia, 014010 China
[Abstract] Objective To observe and explore the application effect of personalized nursing intervention in the nursing of patients with decompensated renal function IgA nephropathy. Methods Convenient select seventy-two patients with renal decompensated IgA nephropathy from January to December 2018 were enrolled. According to the different care plans, 72 patients were divided into 2 groups, 36 cases each. The control group received routine nursing intervention and the study group took personalized nursing intervention. Observe and compare the care effects of the 2 groups. Results The total effective rate of the study group was 94.44%, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (72.22%). The difference was statistically significant (χ2=5.625, P=0.021). The nursing satisfaction of the study group was 97.22%, which was significantly higher than that of the control group (80.56%). The difference was statistically significant (χ2=5.556, P=0.022); after treatment, the study group had significantly lower CD4+(42.36±3.58)/mm3, CD4+/CD8+(1.12±0.23), and urinary protein (253.16±55.32) mg/d. In the control group, CD4+(51.63±4.12)/mm3, CD4+/CD8+(1.31±0.28), and urinary protein (325.24±71.36) mg/d, the difference was statistically significant (t=6.152, 5.221, 8.416, P=0.015, 0.028, 0.002), the study group's CD8+ (39.25±3.46)/mm3 compared with the control group of CD8+(39.37±3.64)/mm3, the difference was not statistically significant (t=1.513, P=0.072). Conclusion The application of personalized nursing intervention in the nursing of patients with decompensated renal function IgA nephropathy is significant and worthy of promotion.

