基于云端锻炼控制系统的可穿戴设备计步器对稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者生活质量的影响
陈铃 江瑞来

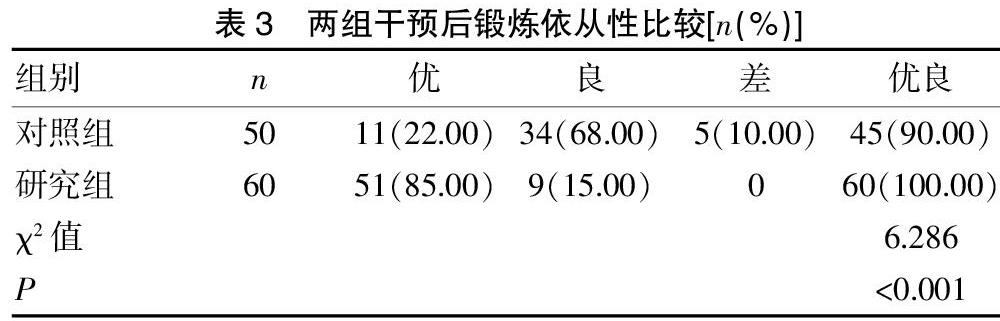
[摘要] 目的 探討基于云端锻炼控制系统(EXBC)的可穿戴设备计步器对稳定期慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)患者生活质量的影响。 方法 选取2019年1~12月在丽水市第二人民医院呼吸科就诊的110例稳定期COPD患者,随机分成对照组(50例)与研究组(60例),对照组予以常规肺功能康复训练,研究组在常规肺功能康复治疗的基础上增加计步器监督步行,干预9个月后观察两组患者肺功能指标、6 min步行距离(6MWT)、生活质量变化,并记录两组锻炼依从性、急性发作的次数。 结果 干预后两组FVC、FEV1占预计值、MMEF、PEF均较干预前增高(P<0.05),且干预后研究组上述指标均明显高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组6MWT均增高,CAT评分均降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),且研究组6MWT、CAT评分改变幅度大于对照组(P<0.05),研究组观察期间急性发作次数较对照组明显减少(P<0.05);干预期间研究组锻炼依从性为100.00%,明显高于对照组(90.00%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 基于EXBC的计步器可显著改善稳定期COPD患者的肺功能和生活质量,提高其体力活动能力和锻炼依从性,值得临床推广应用。
[关键词] 计步器;肺康复训练;慢性阻塞性肺疾病;肺功能;生活质量
[中图分类号] R563.9 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)36-0023-05
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of a wearable pedometer based on the cloud exercise control system(EXBC) on the quality of life of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD) in stable phase. Methods A total of 110 patients with stable COPD who were treated in the Respiratory Department of The Second People's Hospital of Lishui from January to December 2019 were randomly divided into the control group(50 cases) and the study group(60 cases). The control group received routine pulmonary function rehabilitation training, and the study group received a pedometer for supervising walking based on the routine pulmonary function rehabilitation. After nine months of intervention, the pulmonary function indexes, 6-min walking distance(6MWT) and quality of life changes were observed in the two groups. The exercise compliance and the number of acute attacks were recorded in the two groups. Results After the intervention, the predicted values of FVC, FEV1, MMEF and PEF in the two groups were higher than before the intervention(P<0.05), and the above indicators in the study group were significantly higher than those in the control group after the intervention, the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The 6MWT scores of the two groups both increased, the CAT scores decreased, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The study group's 6MWT and CAT scores changed more than the control group(P<0.05). The number of acute attacks of the study group was significantly lower than that of the control group during the observation period(P<0.05). The exercise compliance of the study group during the intervention period was 100.00%, which was significantly higher than in the control group(90.00%), and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion The EXBC-based pedometer can significantly improve and stabilize the lung function and quality of life of COPD patients, improve their physical activity ability, and exercise compliance, which is worthy of clinical application.

