颈脊髓损伤重症患者护理中循证护理的应用对护理人员主观能动性的影响
姚丹
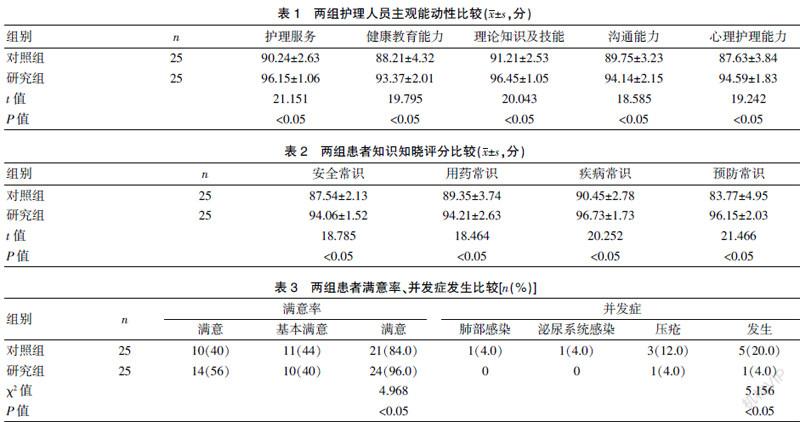
[摘要] 目的 探讨颈脊髓损伤重症患者护理中循证护理的应用对护理人员主觀能动性的影响。 方法 选取2019年1月至2020年1月我院收治的50例颈脊髓损伤重症患者,随机数字表法分为两组,对照组应用常规护理,研究组应用循证护理,比较两组应用不同方法护理后对护理人员的主观能动性、患者知识的知晓评分、并发症发生及满意率的影响。 结果 研究组护理服务(96.15±1.06)分、健康教育能力(93.37±2.01)分、理论知识及技能(96.45±1.05)分、沟通能力(94.14±2.15)分及心理护理能力(94.59±1.83)分,高于对照组护理服务(90.24±2.63)分、健康教育能力(88.21±4.32)分、理论知识及技能(91.21±2.53)分、沟通能力(89.75±3.23)分及心理护理能力(87.63±3.84)分(P<0.05);研究组安全常识(94.06±1.52)分、用药常识(94.21±2.63)分、疾病常识(96.73±1.73)分、预防常识(96.15±2.03)分,高于对照组安全常识(87.54±2.13)分、用药常识(89.35±3.74)分、疾病常识(90.45±2.78)分、预防常识(83.77±4.95)分(P<0.05);肺部感染、泌尿系统感染及压疮并发症的发生率4.0%低于对照组20.0%,满意率96.0%高于对照组的84.0%(P<0.05)。 结论 颈脊髓损伤重症患者护理中,实施循证护理取得了满意的效果,能够提高护理人员的主观能动性,利于临床护理的实施,值得临床进一步推广应用。
[关键词] 循证护理;颈脊髓损伤重症;主观能动性;护理人员
[中图分类号] R473.6 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0165-04
Effect of evidence-based nursing on nurses′ subjective initiative in nursing care for severe patients with cervical spinal cord injury
YAO Dan
Intensive Care Unit, Zhejiang Provincial People′s Hospital, People′s Hospital of Hangzhou Medical College, Hangzhou 310012, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the effect of evidence-based nursing on nurses′ subjective initiative in nursing care for severe patients with cervical spinal cord injury (CSCI). Methods A total of 50 severe patients with CSCI treated in our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were randomly divided into the control group (n=25) and the study group(n=25). Routine nursing was used in the control group and evidence-based nursing was used in the study group. The effects of different nursing methods on the subjective initiative of nurses, the score of patient knowledge, the occurrence of complications and satisfaction rate were compared between the two groups. Results The scores of nursing service, health education ability, theoretical knowledge and skills, communication ability and psychological nursing ability in the study group were (96.15±1.06), (93.37±2.01), (96.45±1.05), (94.14±2.15) and (94.59±1.83), respectively, which were higher than those in the control group [(90.24±2.63), (88.21±4.32), (91.21±2.53), (89.75±3.23) and (87.63±3.84), respectively] (P<0.05).The scores of safety knowledge, medication knowledge, disease knowledge and prevention knowledge of the study group were (94.06±1.52), (94.21±2.63), (96.73±1.73) and (96.15±2.03), respectively, which were higher than those of the control group [(87.54±2.13), (89.35±3.74), (90.45±2.78) and (83.77±4.95), respectively] (P<0.05). The incidence of pulmonary infection, urinary system infection and pressure sore complications in the control group was 4.0%, lower than that in the control group (20.0%), and the satisfaction rate was 96.0%, higher than that in the control group 84.0%(P<0.05). Conclusion In the nursing care of severe patients with CSCI, evidence-based nursing has achieved satisfactory results, which can improve the subjective initiative of nurses and be helpful for the implementation of clinical nursing. Therefore, it is worthy of further clinical application.

