Effects of electroacupuncture with different frequencies on hippocampal neuronal apoptosis and JNK signaling pathway in rats with vascular dementia
CHEN Shiyu (陈世雨), ZHANG Chuang (张闯), GAO Fei (高飞), ZHANG Xiaoqi (张晓琪), YU Wentao (于文涛),WU Zehui (武泽惠), GUO Fei (郭菲), DONG Qianbo (董倩波), ZHANG Huizhen (张会珍)
1 Hebei University of Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, China
2 The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
Abstract
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Electroacupuncture; Frequency; Dementia, Vascular; Reperfusion Injury; Rats
Vascular dementia (VD) is a chronic progressive disease based on cerebrovascular diseases and clinically characterized by cognitive decline as the primary manifestation[1]. VD not only endangers patients’physical and mental health, but also aggravates the burden on the family and society. The incidence of VD increases with age. Epidemiological surveys have shown that the incidence rate of people over 65 years old is 3.13 per 1 000 persons per year[2]. VD has become a research hotspot in recent years[3-4]. However, so far,the pathogenesis of VD remains unclear[5]. Studies have shown that the hippocampal neuronal apoptosis induced by repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion is an important pathological basis of VD[6]. Moreover, the Caspase family is a key protease in the induction of apoptosis, among which Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 are important initiators and executors in the Caspase cascade, respectively[7]. C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) is a serine/threonine protein kinase involved in a series of physiopathological activities such as cell proliferation,differentiation, and apoptosis[8-9]. Repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion is one of the stress stimuli that can activate JNK signaling pathway. The activated JNK can regulate downstream apoptosis-related proteins,ultimately leading to neuronal cell apoptosis[10].
Electroacupuncture (EA) therapy has been widely used in the clinic because of its simple operation and no toxic or side effects. Studies have confirmed the good effect of EA on VD[11], but the mechanism of EA in the treatment of VD remains unknown. Frequency is an important parameter of EA stimulation, and the effects of different frequencies in EA treatment are different.However, the selection of frequency in clinical applications has not been unified[12-13]. Based on our previous research[14-17], three frequencies, 2 Hz, 100 Hz,and 2 Hz/100 Hz, were selected as the frequency stimulation parameters to observe the effects of EA on the behaviors and pathological morphological changes of VD rat. In order to further explore the mechanism and appropriate frequency of EA in the treatment of VD,we also detected the neuronal apoptosis in the CA1 region of the hippocampus and the protein expression levels of JNK, phosphorylated JNK (p-JNK), Caspase-8,and Caspase-3. We hope to provide an experimental basis for the clinical treatment of VD with EA.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 Experimental animals and grouping
A total of 50 adult male Sprague-Dawley rats of specific-pathogen-free grade were purchased from Beijing Weitong Lihua Experimental Animal Technology Co., Ltd., China [License No. SCXK (Beijing) 2018-0006],weighing (200±20) g. The rats were fed at room temperature (22±2) ℃ and the humidity was kept at(55±15)%. All rats were free to food and drink. The rats were randomly divided into a sham operation group, a model group, a 100 Hz EA group, a 2 Hz EA group, and a 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group, with 10 rats in each group. The experimental process strictly followed theGuiding Opinions on Treatment of Experimental Animalsissued by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China in 2006.
1.2 Main instruments and reagents
Sterile acupuncture needles (0.30 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length, Suzhou Medical Appliance Co.,Ltd., China); Morris water maze (Beijing Zhongshidichuang Science and Technology Development Co., Ltd., China); HANS-200E type EA instrument (Nanjing Jisheng Medical Technology Co.,Ltd., China); Neofuge 13R high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Shanghai Likang Biomedical Technology Holding Co., Ltd., China); Xts20 continuous zoom stereomicroscope (Beijing Hainaxingye Technology Co.,Ltd., China); V300 scanner (Epson Co., Ltd., Japan);Nikon eclipse E100 ortho optical microscope (Shanghai Nikon Instrument Co., Ltd., China); electrophoresis instrument and electric rotation instrument (Beijing Liuyi Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China). JNK antibody(Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China);Caspase-8 antibody, β-actin antibody, ECL kit, BCA kit(Wuhan Seville Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China); p-JNK antibody, Caspase-3 antibody (CST China Branch, USA);terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) test kit (CHE, Roche,Switzerland).
1.3 Model preparation method
The VD model was established according to the related literature[14]. The rats were anesthetized with 10% chloral hydrate by intraperitoneal injection at 350 mg/(kg·bw). Afterward, the rats were fixed on their back and disinfected routinely. The median cervical incision was performed. Bilateral common carotid arteries (CCAs) were bluntly separated and blocked by No. 4 silk thread buckle. Meanwhile, sodium nitroprusside (NPS) was intraperitoneally injected at 2.5 mg/(kg·bw). After 10 min of blocking, the fixed suture was released, and reperfusion was carried on for 10 min. Meanwhile, the iris color turned pale within a few seconds after ischemia and returned normal after reperfusion[18]. The repeated ischemia-reperfusion was performed three times. Then, the wound was sutured,and the rats were put back into the cage to keep warm.In the sham operation group, bilateral CCAs were separated, but the blood flow was not blocked, and the NPS was not injected. Penicillin was injected intramuscularly 2 000 U/d for three consecutive days.
1.4 Intervention methods
The intervention started on the 3rd day after modeling.
1.4.1 EA groups
Acupoints: Baihui (GV20), Dazhui (GV14), Geshu(BL17), and Zusanli (ST36)[19].
Baihui (GV20) is located at the middle depression between the parietal bones; Dazhui (GV14) on the midline of the back, between the 7th cervical and the 1st thoracic vertebrae; Zusanli (ST36) at the posterolateral aspect of the knee joint of the rat hindlimb, approximately 2 mm below the small head of the fibula; Geshu (BL17) at the intercostal spaces on both sides under the 7th thoracic vertebra and 3 mm away from the posterior midline.
Method: The rat was captured and fixed with a piece of self-made rat clothing, and the acupoints were routinely disinfected. Acupuncture needles of 0.30 mm in diameter and 25 mm in length were selected and punctured at the four acupoints mentioned above. The needles were connected to the EA apparatus. One pair of electrodes were used for Baihui (GV20) and Dazhui(GV14), and the other pair for the ipsilateral Geshu(BL17) and Zusanli (ST36). The EA groups were stimulated with high frequency (100 Hz), low frequency(2 Hz), or variable frequency (2 Hz/100 Hz), respectively,and the stimulation intensity was determined by the reaction of the rat's limbs (gently vibrating without struggling to hiss, about 2 mA), 10 min once a day for 14 d.
1.4.2 Sham operation group and model group
Capturing and fixing methods of rats in the sham operation group and model group were the same as those in the EA groups, but without EA intervention.
1.5 Specimen collection
After the behavioral test, the rats were sacrificed with their heads put on ice and the brain tissues removed quickly. The left cerebral tissue was fixed in 4 % paraformaldehyde solution for the observation of tissue morphology and TUNEL detection. The hippocampus in the right brain tissue was quickly removed and placed in a cryopreservation tube. It was frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored in a refrigerator at-80 ℃ for Western blot (WB) detection.
1.6 Observation indicators and detection methods
1.6.1 Learning and memory performance test
Morris water maze test was carried out on the next day after the intervention ended. Morris water maze was divided into four quadrants, and a water entry point was marked at the midpoint of the edge of the pool in each quadrant. A circular platform was placed in the third quadrant, 2 cm lower than the water surface,and ink was poured in until the platform was invisible.The rats were put into the water clockwise from the four marked entry points, and the escape latency (the time to find and climb the platform) was recorded. If it exceeded 120 s, the rats were guided to the platform and stayed for 10 s. The escape latency was recorded as 120 s, once a day, for a total of 5 d. After the 5-day positioning navigation experiments, the platform was removed and the space exploration experiment was carried out. A marked water entry point was fixed and the rats were put into the water. The times of rats crossing the original platform position in 120 s were recorded.
1.6.2 Histological analysis
Cerebral tissue samples were dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, and cut into sections at 5 μm. The paraffin section was dewaxed and dehydrated. The nucleus was stained with hematoxylin. The sections were stained with Harris hematoxylin for 3-8 min, washed with tap water, differentiated with 1% hydrochloric acid alcohol for several seconds, rinsed with tap water, and then rinsed with 0.6% ammonia water. The cytoplasm was stained with eosin, and the sections were stained with eosin for 1-3 min. After that, the sections were dehydrated step by step and sealed with neutral gum.The morphology of the hippocampal CA1 region was observed under the microscope. One slice was randomly selected from each rat and three nonoverlapping fields were randomly selected under the high-power microscope for observation and counting.
1.6.3 TUNEL assay
The paraffin sections were dewaxed and rehydrated.After absorbing the liquid on the section, protease K working solution was added. Then, the sections were incubated at 37 ℃ and decolorized three times. After the incubation, decolorization was achieved. A proper amount of TDT and dUTP was selected from TUNEL kit,dropped on the slices and incubated in water bath at 37 ℃ for 2 h. The slices were incubated in H2O2at room temperature and decolorized. Then they were added with an appropriate amount of converter-POD,incubated in 37 ℃ incubator for 30 min, and rinsed for 15 min. DAB chromogenic solution was dripped, and the chromogenic time was controlled under the microscope. Then the samples were redyed with hematoxylin for 3 min, rinsed, differentiated, reversed blue and sealed. One slice was randomly selected from each rat, and three non-overlapping fields were randomly selected for observation and counting under the high-power microscope. Image Pro Plus 6.0 software was used to analyze and calculate the apoptotic index (AI). AI = Total number of apoptotic cells ÷ Total number of cells × 100%.
1.6.4 WB analysis
The right brain tissue was washed with ice-cold PBS three times to remove the blood stain. Then it was cut into small pieces and placed in the EP tube. The tissue was vibrated every 6 min to ensure the complete lysis of the tissue. Afterward, the protein samples were centrifuged (rotating speed 12 000 r/min) for 15 min.Next, the supernatant was collected into another EP tube, denatured in boiling water bath for 15 min, and stored in the refrigerator at -20 ℃. After electrophoresis and transfer, the PVDF membrane was blocked with 5% non-fat powdered milk in 0.5% TBST for 1 h and incubated at 4 ℃ overnight with primary antibodies against JNK (1:1 000), p-JNK (1:1 000), Caspase-8(1:500), and Caspase-3 (1:500). After being washed with TBST three times, membranes were incubated with the secondary antibodies (1:3 000) for 2 h at room temperature. The bands were detected with ECL reagent kit and imaged with Fusion FX5 Spectra. The imaged and the internal control β-actin was assessed by WB analysis.
1.7 Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed with SPSS version 22.0 statistical software. Average values were presented as mean ± standard deviation (±s). One-way analysis of variance was used to compare the normally distributed data and determine the statistical significance among groups. The least significant difference (LSD)t-test was used for multiple comparisons when the variance was homogeneous, and Dunnett’s T3 test was used when the variance was uneven.P<0.05 indicated statistical significance.
2 Results
2.1 Effects of EA with different frequencies on learning and memory ability in VD rats
2.1.1 Comparison of the escape latency
Compared with the sham operation group, the escape latency of rats in the model group was significantly longer (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the escape latencies of rats in the three EA groups were significantly shorter (P<0.01). Besides,compared with the 100 Hz EA group, the escape latencies of rats in the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group were significantly shorter(P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in the escape latency of rats between the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P>0.05). The results are shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
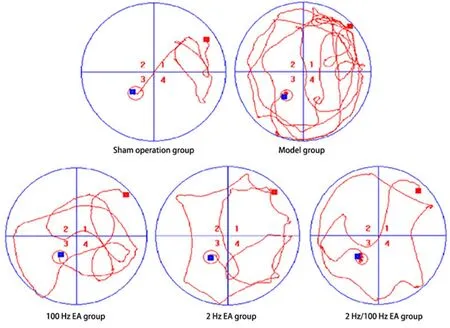
Figure 1. Morris water maze trajectory of rats in each group
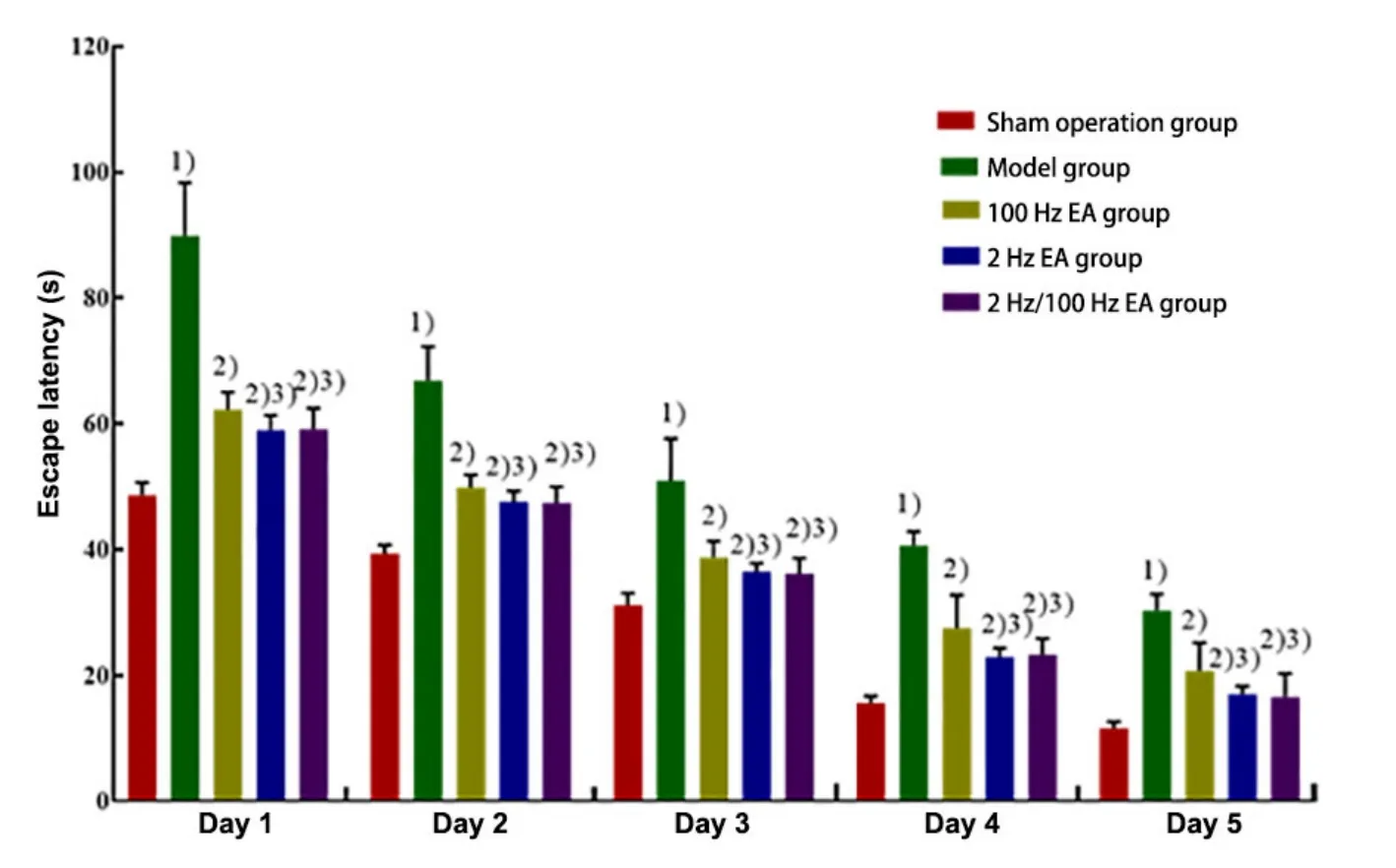
Figure 2. Comparison of the escape latency of rats in each group
2.1.2 Comparison of the number of rats crossing the original platform in each group
Compared with the sham operation group, the number of rats crossing the original platform in the model group was significantly decreased (P<0.01).Compared with the model group, the numbers in the three EA groups were significantly increased (P<0.01).Additionally, the numbers in the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group were more than that in the 100 Hz EA group (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in the number between the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P>0.05). The results are shown in Figure 3.
2.2 Effects of EA with different frequencies on hippocampal CA1 pathomorphology in VD rats
HE staining showed that the cells in CA1 region of the hippocampus were closely and regularly arranged in the sham operation group. There was no obvious cell loss.In the model group, the arrangement of neurons was disordered. The neuronal structure was loose (marked by the black dotted line) and the nucleus shrunk(marked by the black arrow). The cell shape was incomplete and the numbers of cells decreased greatly.The neuronal arrangement in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each EA group was more regular, and the neuronal structure was relatively complete. The results are shown in Figure 4.
The number of surviving neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region of the model group was significantly decreased compared with the sham operation group(P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the number of surviving neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region was significantly increased in the three EA groups (P<0.01).The neuron survival was increased in 2 Hz EA group and 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group compared with the 100 Hz EA group (P<0.05). There was no difference in the number of surviving neurons in the 2 Hz EA group compared with the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P>0.05). The results are shown in Figure 5.
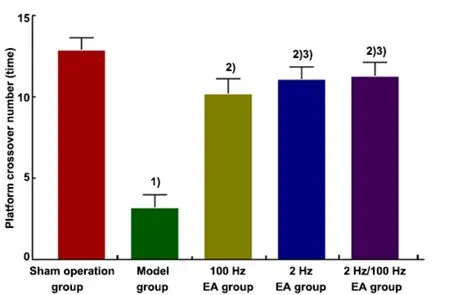
Figure 3. Comparison of the number of rats crossing the original platform in each group
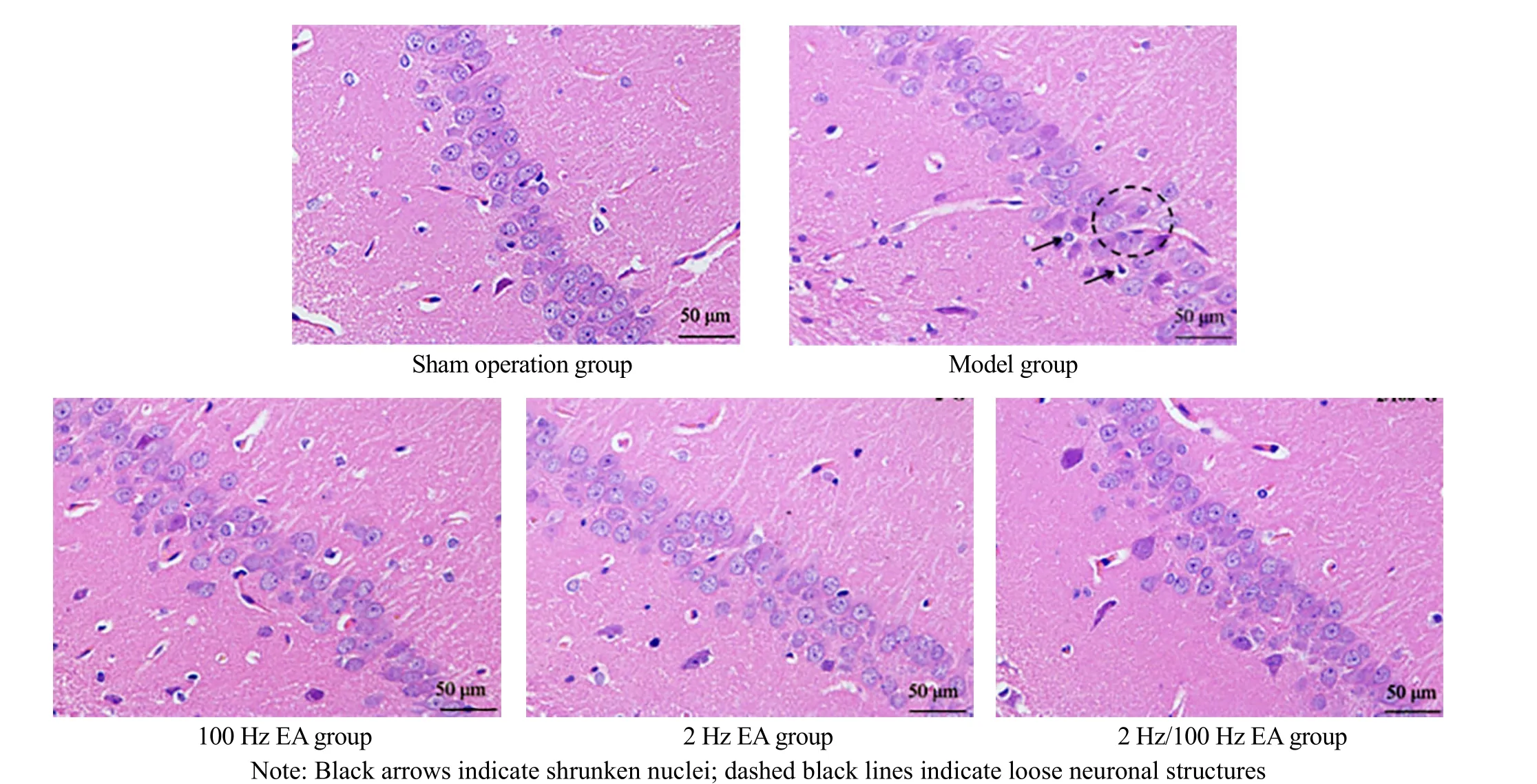
Figure 4. Pathomorphology of the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each group (HE, ×400)

Figure 5. The number of surviving neurons in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each group
2.3 Effects of EA with different frequencies on the hippocampal CA1 cell apoptosis in VD rats
TUNEL staining showed few positive cells (apoptotic nuclei were brownish yellow or tan, and normal neuronal nuclei were pale blue) in the hippocampal CA1 region in the sham operation group, and the AI value was low. Compared with the sham operation group, the model group had more positive cells and a higher AI value (P<0.01), (marked by the black arrows). Compared with the model group, the number of positive cells and AI value were decreased significantly in the three EA groups (P<0.01). Compared with the 100 Hz EA group,the AI value decreased in the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P<0.05). However, there was no significant difference in the AI value between the 2 Hz EA group and the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P>0.05). The results are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
2.4 Effects of EA with different frequencies on the JNK,p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 expression levels in the hippocampus of VD rats
To explore the role of JNK signaling effects of different frequencies, WB was performed to test the expression levels of JNK, p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3. Compared with the sham operation group,the expression levels of JNK, p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 proteins in the hippocampus of the model group were significantly increased (P<0.01). Compared with the model group, the expression levels of JNK,p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 proteins in each EA group were significantly decreased (P<0.01). Compared with the 100 Hz EA group, the expression levels of JNK,p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 proteins in the 2 Hz EA group were significantly lower (P<0.01). The expression levels of JNK and Caspase-3 proteins decreased in the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group (P<0.01), while the expression levels of p-JNK and Caspase-8 proteins were not statistically significant (P>0.05). Compared with the 2 Hz/100 Hz EA group, the expressions of p-JNK and Caspase-8 proteins in the 2 Hz EA group decreased(P<0.01), while the expression levels of JNK and Caspase-3 proteins showed no significant difference(P>0.05). The results are shown in Figure 8 and Figure 9.
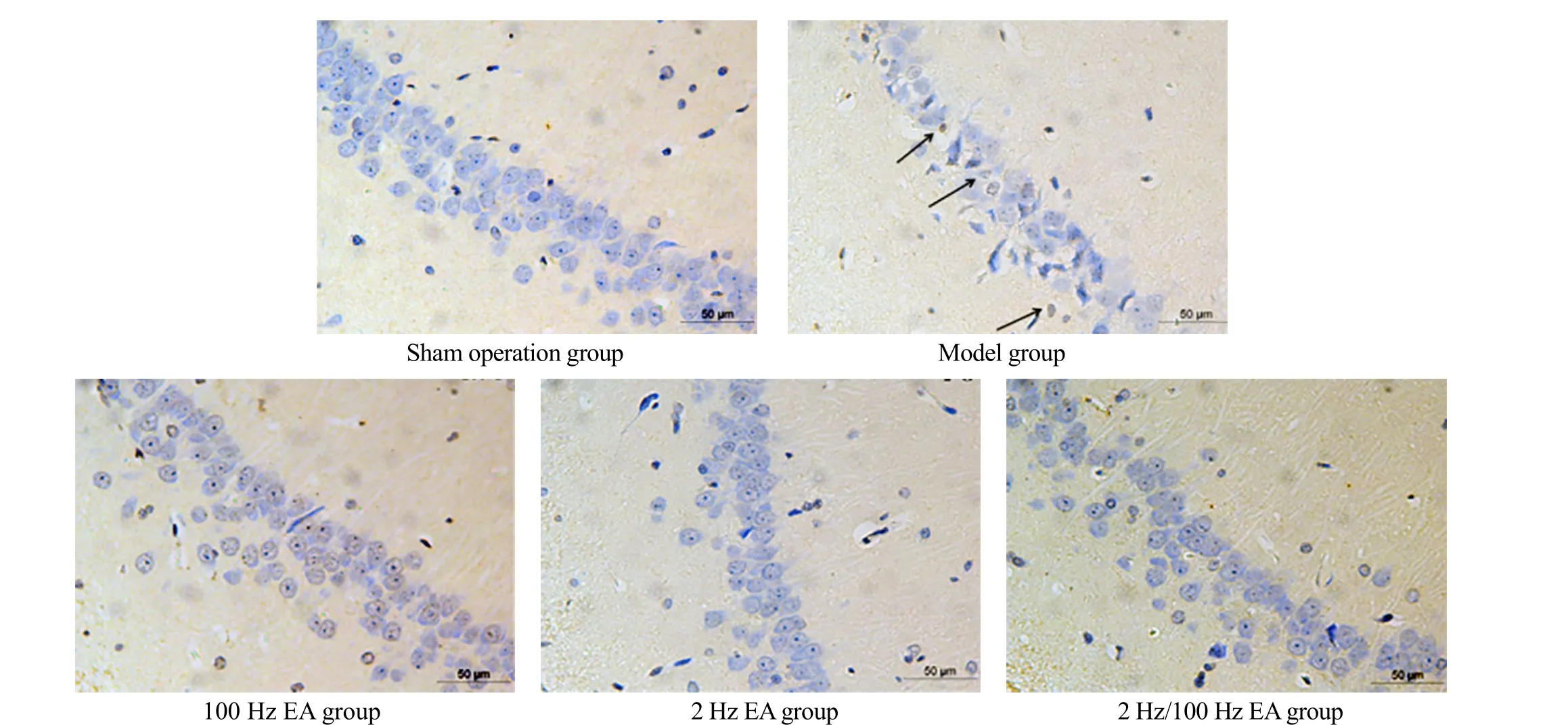
Figure 6. Apoptosis in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each group (TUNEL, ×400)
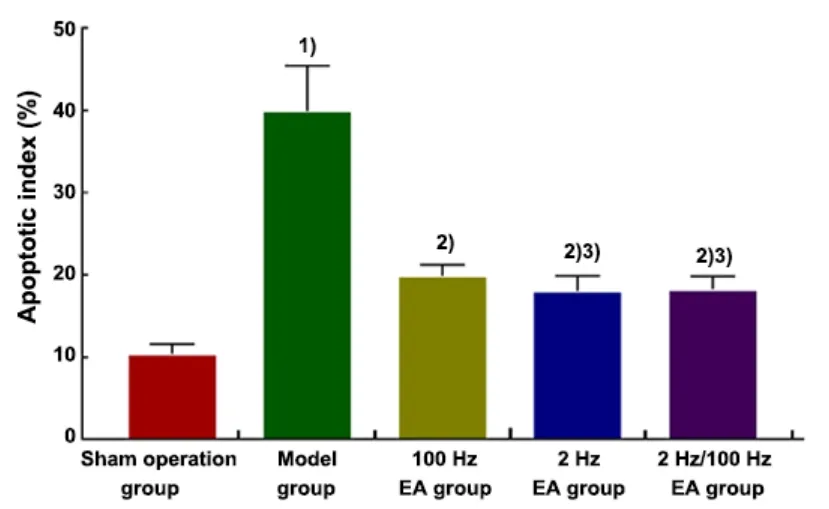
Figure 7. Apoptotic index in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats in each group
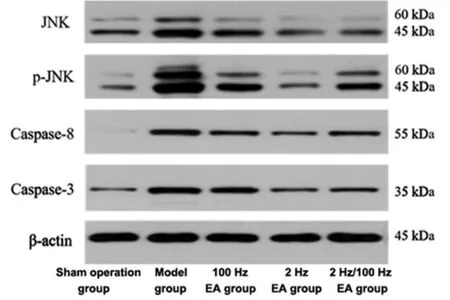
Figure 8. Expression levels of JNK, p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 in the hippocampus of rats in each group
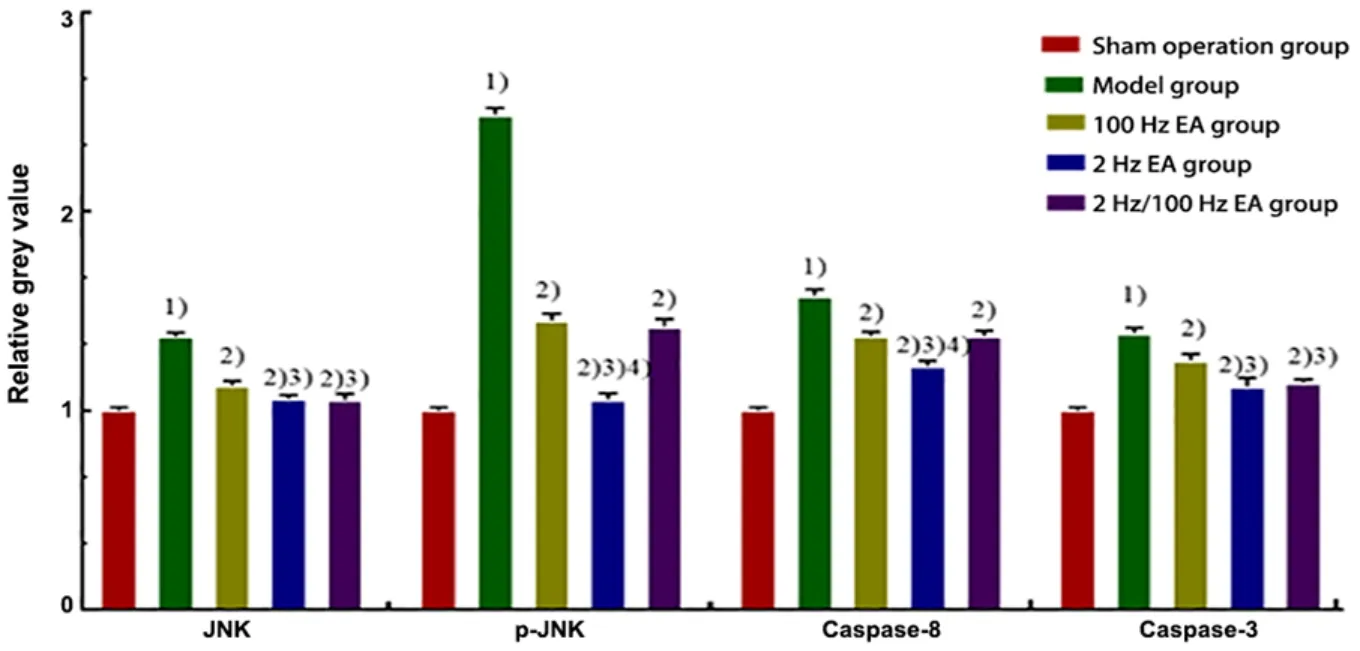
Figure 9. Comparison of the protein expression levels of JNK, p-JNK, Caspase-8, and Caspase-3 in the hippocampus of rats
3 Discussion
VD belongs to the category of “dementia”,“sluggishness” and “forgetfulness” in traditional Chinese medicine. Acupuncture therapy is one of the effective treatments for VD[20]. Acupuncture combined with electric current can enhance its stimulation to the acupoints. Baihui (GV20) is located at the top of the head and is the crossing point of five meridians,including three Yang meridians. Dazhui (GV14) is the crossing point of three Yang meridians of hand, three Yang meridians of foot, and the Governor Vessel. Thus,acupuncture at these two acupoints can regulate the Governor Vessel and the whole body’s Yang Qi. It can also boost the Yang Qi and invigorate the brain to improve intelligence. Geshu (BL17) belongs to the Bladder Meridian of Foot Taiyang.Nan Jing (Classic of Difficult Issues)documents that blood converges at Geshu (BL17). Acupuncture at Geshu (BL17) can activate the circulation of blood and remove blood stasis. It can also clean the cerebral collaterals. Zusanli(ST36) is an acupoint of the Stomach Meridian of Foot Yangming. Acupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) can invigorate the spleen and stomach. It can also generate and transform Qi and blood. The four points are matched to play the role of reinforcing Qi, activating blood circulation, refreshing the brain, and improving intelligence.
EA has its advantages in the treatment of VD.However, as one of the significant parameters of EA, the frequency has not been unified in clinical application[21-23]. Frequency-conversion EA can stimulate rhythmic contraction of muscles and promote local circulation and metabolism. High-frequency EA can reduce neural stress. Low-frequency EA can cause muscle contraction, change muscle tone, regulate vasoconstriction, and change blood circulation[18]. In this experiment, high-frequency at 100 Hz, lowfrequency at 2 Hz and frequency conversion at 2 Hz/100 Hz were respectively chosen to intervene VD rats to explore the EA therapeutic effect on VD and the mechanisms of EA with different frequencies. This research may provide an objective basis for rational clinical application.
The hippocampus plays a crucial part in advanced neural activities, such as learning and memorizing[24].The CA1 region of the hippocampus plays an important role in learning and memory and is sensitive to the damage caused by repeated cerebral ischemiareperfusion[25]. The processing and transmission of information in the hippocampus are closely related to the state and number of neurons in the CA1 region.Studies have confirmed that repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion leading to the degeneration of neurons and necrosis in the hippocampal CA1 region is an important cause of the pathogenesis of VD[6]. The Morris water maze test was designed to observe the learning and memory abilities of rats[26]. Our results showed that the model rats’ learning and memory ability decreased, and there were severe neuronal damages in the hippocampal CA1 region. These results suggest that cerebral ischemia- reperfusion may cause hippocampal neuronal damage and decrease the abilities of learning and memorizing in VD rats. After the treatment of EA with three frequencies, the neuronal damages in the hippocampal CA1 region of VD rats were significantly alleviated compared with the model group, and the learning and memory abilities of the rats were significantly improved, indicating that EA with three different frequencies can significantly improve the cognitive function of VD rats. The results also suggest that the intervention effects of EA with 2 Hz or 2 Hz/100 Hz are better than EA with 100 Hz.
JNK signaling pathway is an important pathway mediating cell apoptosis and closely related to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Researchers found that activating JNK signaling pathway plays a positive effect on the impairment of learning and memory in VD rats[27]. After neuronal damage is caused by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion, the transcription factor JNK in the cytosol can be activated by phosphorylation at its basic terminal residues, which may lead to too much p-JNK clustering at the damage site. Then, p-JNK can activate the death receptor pathway, regulate downstream apoptotic proteins’ expression, and induce neuronal apoptosis. Our results showed that the JNK and p-JNK protein expression levels were elevated in the hippocampus of VD rats, indicating that JNK signaling pathway is activated. After the treatment of EA with three frequencies, the protein expression levels of JNK and p-JNK in the hippocampus of VD rats were significantly decreased, suggesting that EA with three frequencies can inhibit the activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Besides, EA with 2 Hz and 2 Hz/100 Hz showed a more obvious inhibiting effect on the activation of JNK signaling pathway.
Studies have shown that neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampal CA1 region is a major factor contributing to learning and memory impairments[28]. The induction and execution of apoptosis require the common function of numerous protein molecular signals, and the Caspase family is the core functional protein in the process of apoptosis. Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 are key proteases in the Caspase family. Caspase-8, critical for initiating apoptosis, usually is present in the cells in the form of zymogen. Under stress stimulation, it induces pro-Caspase-8 self-activation, and the activated Caspase-8 in turn activates the Caspase cascade[29],leading to the apoptotic signal transferring downstream and activating Caspase-3. Caspase-3, one of the most important executors of apoptosis, plays an important role in the early initiation and execution of neuronal apoptosis[30]. Our results showed that more apoptotic cells were found in the hippocampal CA1 region of the model rats, and the protein expression levels of Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 were elevated in the hippocampal tissue, indicating that repeated cerebral ischemia-reperfusion induces neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampal region. After EA treatment with 100 Hz,2 Hz, and 2 Hz/100 Hz, only a few positive apoptotic cells were found in the hippocampal CA1 neurons of VD rats, and both Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 protein expression levels in the hippocampal tissue were significantly decreased, which suggests that all three frequencies of EA can inhibit hippocampal neuronal apoptosis by decreasing Caspase-8 and Caspase-3 protein expression levels. The treatment of EA with 2 Hz and 2 Hz/100 Hz showed more effective for VD.
In this study, EA intervention with three frequencies,100 Hz, 2 Hz, and 2 Hz/100 Hz, significantly attenuated the pathological damages in rat hippocampal neurons caused by ischemia-reperfusion and improved learning and memory abilities in VD model rats. Its mechanism may be associated with the inhibition of neuronal apoptosis and regulation of JNK signaling pathway in the hippocampus CA1 region of VD rats. At the same time, the intervention effects of EA with 2 Hz and 2 Hz/100 Hz are more significant.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Key Project of Science and Technology Research in Higher Education Institutions of Education Department of Hebei Province (河北省高等学校科学技术研究重点项目, No. ZD2018017);General Project of Hebei Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (河北省自然科学基金面上项目,No. H2013206245); Science and Technology Support Project of Hebei Provincial Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (河北省中医药管理局科技支撑项目,No. 2013002); Special Project of Basic Scientific Research of Provincial Colleges and Universities of Hebei University of Chinese Medicine (河北中医学院省属高校基本科研业务费专项项目, No. YXZ2019005).
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
The treatment of animals conformed to the ethical criteria in this experiment.
Received: 16 April 2021/Accepted: 28 July 2021
——张翼
 Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年1期
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science2022年1期
- Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on M1 polarization of alveolar macrophages in rats with acute lung injury
- Clinical observation on row needling at the Governor Vessel on the head for poststroke insomnia
- Effects of Tuina combined with graded motor imagery on the upper-limb motor function and quality of life of patients with hemiplegia after stroke
- Effects of acupuncture combined with Brunnstrom staging on upper-limb motor function, cerebral arterial blood flow velocity, and brain function remodeling after stroke
- Observation of the efficacy and safety of the Song-Relaxing and Zhen-Vibrating abdomen manipulation for patients with prediabetes
- Clinical study on Tuina plus Shen Ling Bai Zhu San in treating children with diarrhea due to spleen deficiency
