Experimental study on the synergistic inhibition of malignant biological behavior of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by the combination of DMDD and sorafenib
NONG Ying-dan, PHAM THI Thai Hoa, HAN Xiao, HE Yong-fei, LIANG Tian-yi,LU Chun-miao, TANG Li-bo, YANG Zi-ye, HAN Chuang-ye,6, LUO Xiao-ling,5✉
1.Department of Experimental Research, Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China
2.Guangxi Key Laboratory of Early Cancer Prevention and Treatment, Ministry of Education, Nanning 530021, China
3.Zhuang Yao Pharmaceutical Research and Development Center, Guangxi International Zhuang Medical Hospital, Nanning 530201, China
4.Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China
5.School of Basic Medical Sciences, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, China
6.Guangxi Key Laboratory of Accelerated Rehabilitation for Gastrointestinal Tumors (ERAS), Nanning 530021, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the effects and possible mechanisms of the combination of DMDD(2-dodecyl-6-methoxycyclohexa-2-5-diene-1-4-dione), a traditional Chinese medicine monomer, and sorafenib on the malignant biological behavior of human hepatocellular carcinoma Huh7 cells.Methods: The experiment was divided into four groups: Huh7 cells control group, DMDD group, sorafenib group and DMDD and sorafenib combination group.The CCK-8 assay was used to measure the viability of Huh7 cells, and the Kim's formula was used to determine the synergistic effect.The plate cloning experiment was conducted to test colony formation ability of Huh7 cells.The scratch and Transwell experiments were performed to evaluate the migration ability and the invasion ability of Huh7 cells.The cell cycle of Huh7 cells was detected by flow cytometry.RT-qPCR and Western blot were used to measure the mRNA transcription level and protein expression level of PHGDH in the serine synthesis pathway.Results: The plate cloning experiment, scratch experiment, and Transwell migration experiment showed that the combined application of DMDD and Sorafenib significantly enhanced the inhibitory effect on the proliferation, migration, and invasion ability of Huh7 cells compared to the control group, DMDD group, and Sorafenib group (P<0.05).According to the Kim's formula, the combination of DMDD (final concentrations of 2, 4, 8 μmol/L)and Sorafenib (final concentrations of 1, 2, 4 μmol/L) had a synergistic inhibitory effect on the proliferation of Huh7 cells (Q>1.15).6, 10 μmol/L DMDD combined with 3, 5 μmol/L Sorafenib showed additive effect.The cell cycle of Huh7 cells was detected by flow cytometry,and the results showed that after 48 hours of drug intervention, the proportion of G2/M phase cells in the control group, DMDD group, Sorafenib group, and combination group were(10.63±0.32)%, (35.77±1.22)%, (30.03±2.22)%, and (38.97±0.60)%, respectively.Compared with the control group, the proportion of G2/M phase cells in the three groups significantly increased (P<0.000 1).Compared with the Sorafenib group, the proportion of G2/M phase cells in the combination group significantly increased (P<0.000 1).RT-qPCR and Western blot results showed that the combined application of DMDD and Sorafenib significantly inhibited the mRNA transcription level and protein expression level of PHGDH (P<0.05).Conclusion:The combined application of DMDD and Sorafenib has a synergistic effect that can enhance the inhibitory effect on the proliferation, invasion, and migration ability of Huh7 cells.The mechanism of this effect is related to the synergistic inhibition of the gene transcription and protein expression of PHGDH in the serine synthesis pathway.
1.Introduction
Primary liver canceris the fourth most common tumor in China,with a high mortality rate ranking second among all malignant tumors.75~85% of primary liver cancer cases are classified as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[1].Radical resection is the preferred treatment for long-term survival in patients with HCC.However, due to the lack of obvious symptoms in the early stages of HCC, 70% of patients are already in the advanced stages when they seek medical attention, making radical resection unattainable[2, 3].For patients with advanced liver cancer who have multiple tumors, vascular invasion, distant metastasis, or insufficient residual liver volume due to a large tumor size, molecular targeted therapy is the main treatment approach[4].Sorafenib is the first-line medication approved by the U.S.FDA for systemic treatment of HCC.It is the earliest small molecule multi-targeted drug used in systemic anti-tumor therapy for HCC and remains a first-line medication recommended in HCC treatment guidelines[1].Clinical studies have shown that sorafenib can effectively prolong overall survival in patients with advanced liver cancer and improve their quality of life[5].However,clinical observations have revealed that some patients are initially insensitive to sorafenib, a condition known as primary resistance.Additionally, some patients gradually develop reduced sensitivity to sorafenib during its use, known as acquired resistance[6].Drug resistance limits the effectiveness of sorafenib.Therefore, enhancing the sensitivity to sorafenib and reversing sorafenib resistance have been research focuses and hot topics in the field of HCC treatment.The integration of traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine has become one of the treatment modalities for HCC in China.Numerous studies have shown that traditional Chinese medicine can control tumor progression through various pathways.It can induce cell apoptosis, inhibit cell proliferation, and have antitumor angiogenesis effects.Traditional Chinese medicine also plays a positive role in improving the body’s immune function[7-9].The combined application of traditional Chinese medicine and sorafenib has a synergistic and enhanced effect on the treatment of HCC[10,11].In recent years, we conducted studies on the therapeutic effects of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine on HCC, as well as their ability to enhance sensitivity to sorafenib and reverse drug resistance.We have isolated a traditional Chinese medicine monomer, DMDD (2-dodecyl-6-methoxy-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione), from the roots of the star fruit plant.Preliminary experiments have demonstrated the efficacy of DMDD as an anti-hepatocellular carcinoma drug[12].Therefore, this study aims to further investigate the impact of the combined application of DMDD and sorafenib on the malignant biological behavior of hepatoma cells.The study aims to determine whether they have a synergistic and enhanced effect, providing reference for improving the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib in the treatment of liver cancer.
2.Materials and Methods
2.1 Materials
The Huh7 cell line was purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(Shanghai,China).Sorafenib(MCE,USA).The traditional Chinese medicine monomer DMDD was extracted by Dr.PHAM THI Thai Hoa from the Zhuang-Yao Medicine Research and Development Center, Guangxi International Zhuang Medicine Hospital.DMDD has been applied for a patent in 2021 with the title “Application of Star Fruit Root and its Extract in the Preparation of Medicines for the Treatment and/or Prevention of HCC.” The patent application number is 202011305629.9[12]; DMEM (Gibco,USA).CCK-8 cell proliferation-toxicity assay kit (Biosharp,China).Transwell cell culture plates and matrix gel (Corning,USA).Cell cycle detection assay kit (Biyun Tian Biotechnology Company, China).Rabbit-origin PHGDH antibody, anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody, mouseorigin microtubule protein tubulin, and anti-mouse IgG secondary antibody (Proteintech,China).PHGDH gene primers and tubulin gene primers(Tsingke Biotechnology,China).CO2 cell culture incubator(Thermo Scientific Varioskan,USA).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 CCK-8 assay to measure the viability of Huh7 cells
Huh7 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate at a density of 5×103cells per well.After cell adhesion, 100 μL of culture medium containing different drugs was replaced.The DMDD group was intervened with a concentration gradient of 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 μmol/L, the Sorafenib group was intervened with a concentration gradient of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 μmol/L, and the combination group was treated with combinations of the corresponding concentrations of DMDD and Sorafenib.An equal amount of culture medium without cells and drugs was used as the blank control group.After 48 hours of intervention, the absorbance at 450 nm (OD) was measured, and cell viability and cell proliferation inhibition were calculated.Cell viability = [(OD value of the experimental group - OD value of the blank control group) / (OD value of the control group - OD value of the blank control group)] × 100%.Cell proliferation inhibition= [(OD value of the control group - OD value of the experimental group) / (OD value of the control group - OD value of the blank control group)].The combination effect of the drugs was evaluated using the Chou-Talalay equation[13], where Q = Ea+b / (Ea + Eb -EaEb).Ea and Eb represent the inhibition rates of individual drugs,and Ea+b represents the inhibition rate of the combined drugs.Q< 0.85 indicates an antagonistic effect of the drug combination, Q values between 0.85 and 1.15 indicate an additive effect of the drug combination, and Q > 1.15 indicates a synergistic effect of the drug combination.
2.2.2 Plate cloning experiment to assess the colony-forming ability of Huh7 cells
Based on the CCK-8 results, the drug concentrations were determined.The experimental groups included the Huh7 cell blank control group, DMDD 5 μmol/L group, Sorafenib 2 μmol/L group,and the combination group (DMDD 5 μmol/L and Sorafenib 2 μmol/L).After 48 hours of drug intervention in each group, cells were collected and seeded in a 6-well plate at a density of 500 cells per well.The cells were cultured in an incubator, with medium change every 3-4 days.After 14 days, the culture plates were taken out,the culture medium was removed, and the cells were fixed with 4%paraformaldehyde for 15 min, followed by crystal violet staining for 30 min.After washing and drying, the cell colonies were counted under a microscope, considering cell clusters with 10 cells as individual colonies.
2.2.3 Scratch assay to assess the migration ability of Huh7 cells
Huh7 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate and allowed to reach a growth density of 90% to 100%.Using a 100 μL pipette tip, a straight line was scratched along the edge of a sterile ruler, followed by 2 washes with PBS.Various drug concentrations were prepared using 2% serum-containing medium for intervention, with the same grouping and dosages as described in section 1.2.2.The area near the scratch line was photographed and its location recorded under an inverted microscope.Images were taken at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h to locate the marked positions under the inverted microscope.The images were processed using Image J software to calculate the scratch closure rate.The scratch closure rate was calculated as follows: Scratch closure rate = (Area at 0 h - Area at 72 h) / Area at 0 hours 100%.
2.2.4 Transwell assay to assess the migration and invasion abilities of Huh7 cells
In the cell migration assay, the grouping and dosages of various drugs are the same as described in section 1.2.2.Huh7 cells treated with different drugs were seeded in the upper chamber at a density of 1×105cells per well, while complete culture medium was added to the lower chamber.After 24 h, the inserts were removed, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, and stained with crystal violet for 30 min.The excess crystal violet was washed off, and a cotton swab was used to carefully remove the cells on the upper side of the chamber.After the inserts were dried, three fields of view were selected under an inverted microscope and photographed to count the migration cells.
In the cell invasion assay, the grouping and dosages of various drugs are the same as described in section 1.2.2.The upper chamber is coated with 100 μL of Matrigel per well and incubated at 37 ℃for 1 hour to allow gel formation.Huh7 cells treated with different drugs are seeded in the upper chamber at a density of 1×105cells per well,while complete culture medium is added to the lower chamber.After 24 h, the inserts are removed, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,and stained with crystal violet for 30 min.The excess crystal violet is washed off, and a cotton swab is used to carefully remove the cells on the upper side of the chamber.After the inserts are dried,three fields of view are selected under an inverted microscope and photographed to count the invaded cells.
2.2.5 Flow cytometry was used to analyze the cell cycle
Huh7 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate and allowed to adhere overnight.The drugs were added according to the same grouping and dosage as described in 1.2.2.After 48 h of incubation, the cells were collected, washed twice with PBS, and fixed overnight with pre-chilled 70% ethanol.The following day, after centrifugation and washing, the cells were stained with a staining solution containing RNase A and propidium iodide (PI) and incubated at 37 ℃ in the dark for 30 min.The cell cycle distribution was analyzed using a flow cytometer, and the data were analyzed using FlowJo software.
2.2.6 RT-qPCR was performed to detect the mRNA expression levels of PHGDH in Huh7 cells.
Huh7 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate and allowed to adhere overnight.The drugs were added according to the same grouping and dosage as described in 1.2.2.After 48 hours of incubation,the cells were collected, and total RNA was extracted using the Omega RNA kit.The RNA was then reverse transcribed into cDNA using the TaKaRa reverse transcription kit.The primer sequences were as follows: upstream primer for PHGDH: 5’-ATGAACTTCTTCCGCTCCCATTT-3’, downstream primer: 3’-TCGGTGAAATGCTGTGGTTTAAA-5’.Upstream primer for tubulin: 5’-CTTGGGTCTGTAACAAAGCATTC-3’, downstream primer: 3’-AAGTTAAAACGTCACAAAGGTGCT-3’.The expression of the target gene in cells was detected using SYBR Green dye with tubulin as the reference gene.The relative expression level of the target gene was calculated using the relative quantification formula: 2^(-ΔΔCt).
2.2.7 Western blot was performed to detect the protein expression levels of PHGDH in Huh7 cells
Huh7 cells treated with different drugs were lysed on ice for 30 minutes using lysis buffer.The lysate was collected and centrifuged at 14,000 g for 15 min, and the supernatant was collected.Protein concentration was measured, and equal amounts of total protein were transferred from SDS-polyacrylamide gel to a PVDF membrane.The membrane was blocked with skim milk for 1 hour, incubated with primary antibody solution at 4 ℃ for 12-16 h, washed the membrane three times, and then incubated with secondary antibody at room temperature for 2 h.After soaking the membrane in ECL developing solution for 20 seconds, the membrane was scanned, and the images were processed and analyzed for grayscale values using ImageJ software.
2.2.8 Statistical analysis
We used GraphPad Prism 8 software for data analysis and graph plotting.The quantitative data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (±s).One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for multiple group comparisons, followed by Tukey’s test for post hoc multiple comparisons.A significance level ofP< 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 Effects of different drugs on the viability of Huh7 cells
CCK-8 assay results showed that compared to the control group, the cell viability of Huh7 cells decreased with increasing concentrations of DMDD, sorafenib, and the combination of DMDD and sorafenib.The combined application group exhibited significantly reduced cell viability in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig.1).According to the Kim’s formula method, the combinations of 2, 4, and 8 μmol/L DMDD with 1, 2, and 4 μmol/L sorafenib, respectively,demonstrated synergistic effects (Q>1.15), while the combinations of 6 and 10 μmol/L DMDD with 3 and 5 μmol/L sorafenib,respectively, showed additive effects (0.85<Q<1.15) (Tab.1).
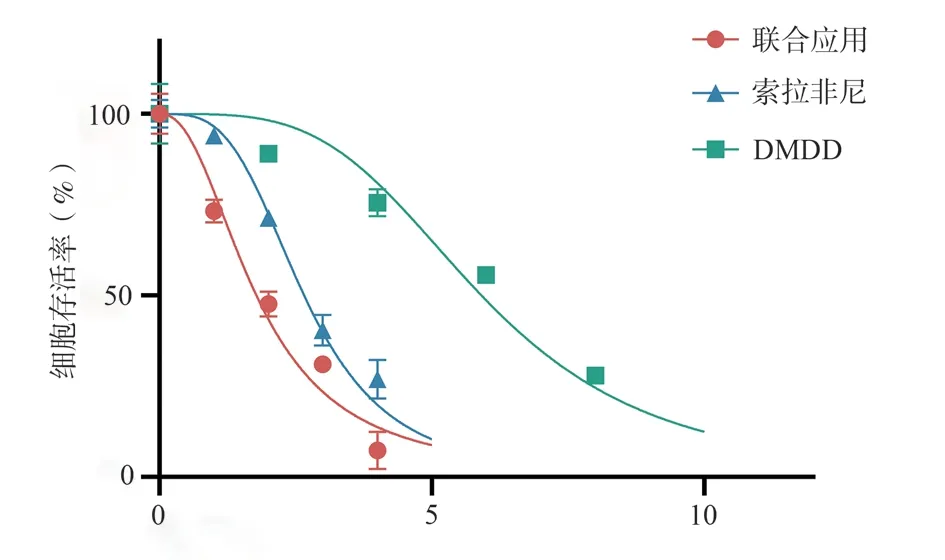
Fig 1 Effects of different drugs on the viability of Huh7 cells

Tab 1 Evaluation of the combined effect of different concentrations of DMDD and sorafenib by Q value of Kim’s formula
3.2 Effects of different drugs on the Colony formation of Huh7 cells
The results of the plate clone experiment showed that after 48 h of intervention, the number of cell colonies in the control group,DMDD group, sorafenib group, and combination treatment group were (99.00±6.56), (47.67±8.02), (71.33±5.51), and (28.33±6.03),respectively.Compared to the control group, the number of Huh7 cell colonies decreased in all three groups, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.000 1,P<0.01,P<0.000 1).When compared to the DMDD group and sorafenib group, the combination treatment group showed a significant decrease in the number of cell colonies (P<0.05,P<0.001) (Fig.2).
3.3 The effect of different drugs on the scratch healing capacity of Huh7 cells
The scratch assay results showed that after 48 hours of intervention,the healing rates in the control group, DMDD group, sorafenib group, and combination treatment group were (40.43±5.10)%,(31.38±1.56)%, (22.04±1.51)%, and (15.02±2.76)%, respectively.Compared to the control group, all three groups demonstrated a decrease in healing of Huh7 cells, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05,P<0.001,P<0.000 1).When compared to the DMDD group, the combination treatment group showed a significantly lower healing (P<0.001).There was no statistically significant difference in the healing rates between the combination treatment group and the sorafenib group (P>0.05)( Fig.3).
3.4 The effect of different drugs on the migration ability of Huh7 cells
The results of the Transwell migration assay showed that after 48 h of intervention, the number of migrated cells in the control group, DMDD group, sorafenib group, and combination group were (346.70±17.50), (247.70±14.57), (233.30±10.50), and(97.00±13.75), respectively.Compared to the control group, the number of migrated cells significantly decreased in all three groups,with statistical significance (P<0.001,P<0.000 1,P<0.000 1).When compared to the DMDD group and sorafenib group, the combination group showed a significant decrease in the number of migrated cells,with statistical significance (bothP<0.000 1)( Fig.4).
3.5 The effect of different drugs on the invasive capacity of Huh7 cells
The results of the Transwell invasion assay showed that after 48 h of intervention, the number of invaded cells in the control group,DMDD group, sorafenib group, and combination group of Huh7 cells were (443.00±17.06), (177.00±19.67), (186.00±16.70), and(54.67±7.371), respectively.When compared to the control group,all three groups exhibited a decrease in the number of invaded cells,and the differences were statistically significant (allP<0.000 1).Additionally, when compared to the DMDD group and sorafenib group, the combination group demonstrated a significant reduction in the number of invaded cells (allP<0.000 1)(Fig.5).
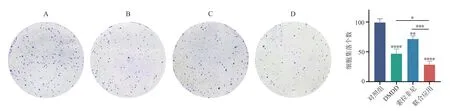
Fig 2 Effects of different drugs on clony formation of Huh7 cells
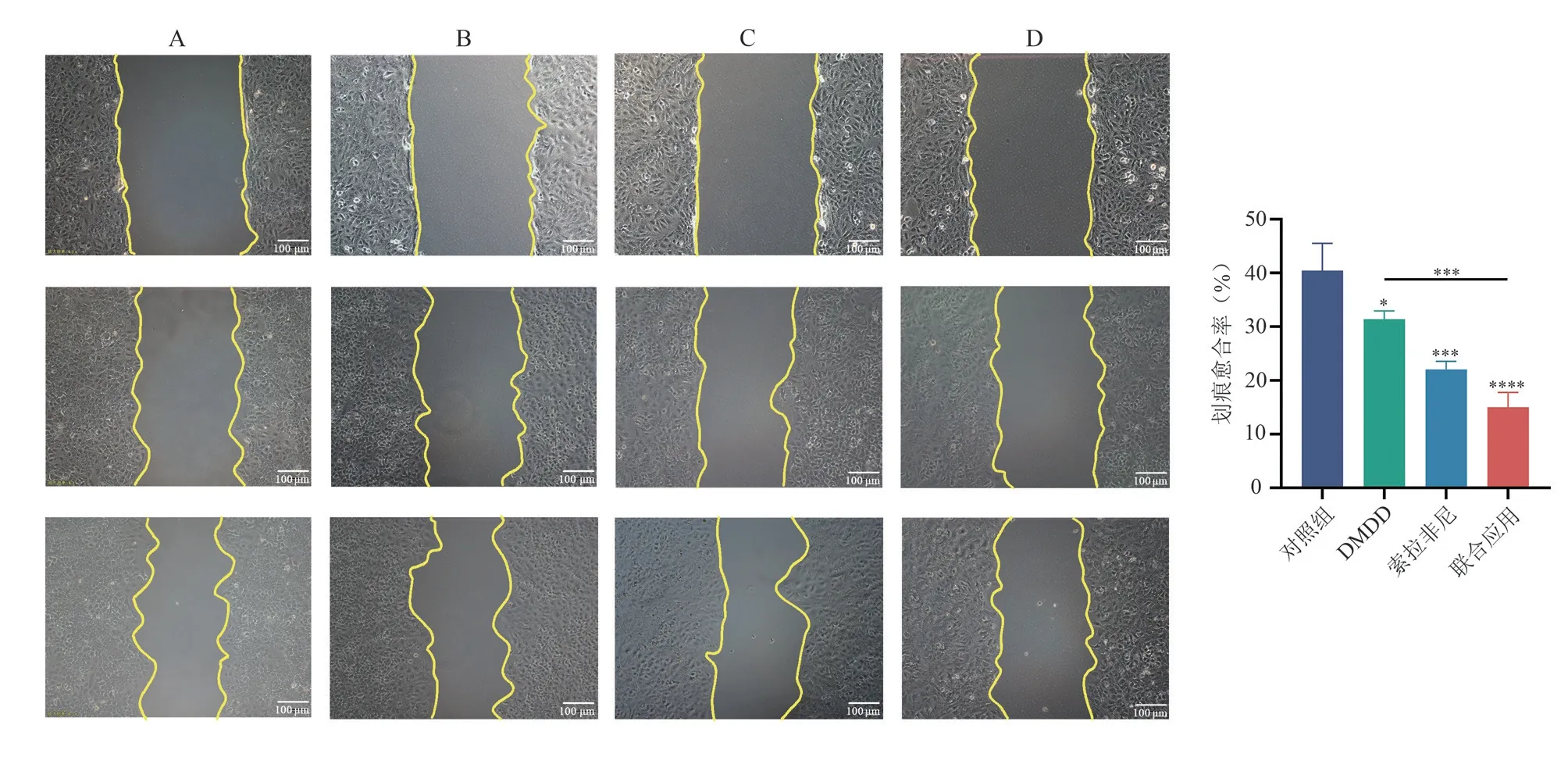
Fig 3 Effects of different drugs on the migration ability of Huh7 cells(×100)
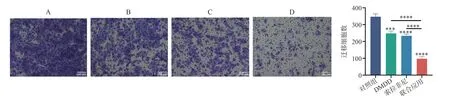
Fig 4 Effects of different drugs on the migration ability of Huh7 cells(×100)
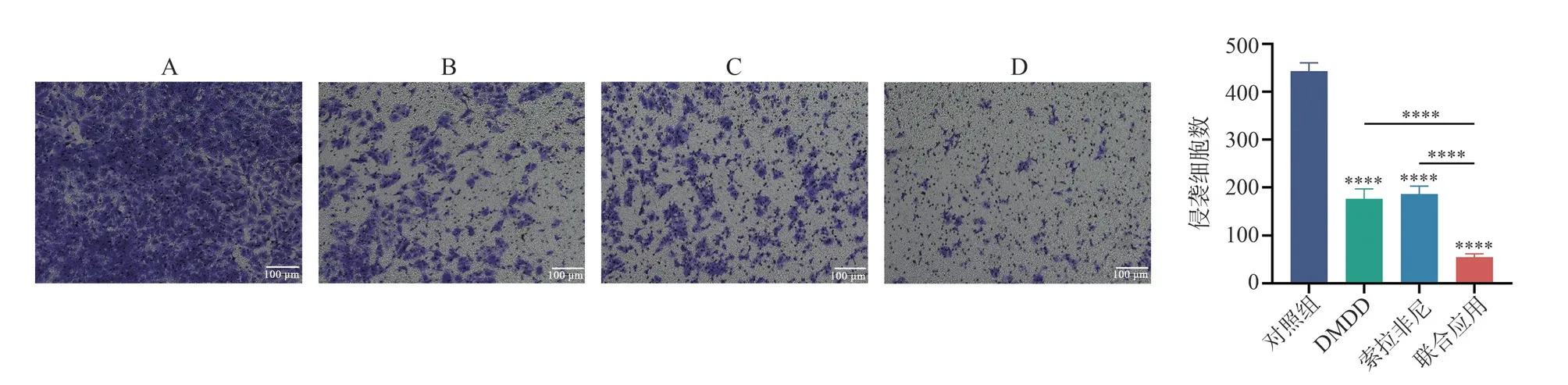
Fig 5 Effects of different drugs on the invasive ability of Huh7 cells(×100)
3.6 The effect of different drugs on the cell cycle of Huh7 cells
The results of the flow cytometry cell cycle experiment showed that after 48 h of drug intervention, the proportions of G2/M phase cells in the control group, DMDD group, sorafenib group,and combination group were (10.63±0.32)%, (35.77±1.22)%,(30.03±2.22)%, and (38.97±0.60)%, respectively.Compared to the control group, all three groups showed a significant increase in the proportion of G2/M phase cells, with statistically significant differences (allP<0.000 1).When compared to the sorafenib group,the combination group showed an increase in the proportion of G2/M phase cells (P<0.001).There was no statistically significant difference between the combination group and the DMDD group(P>0.05)( Fig.6).
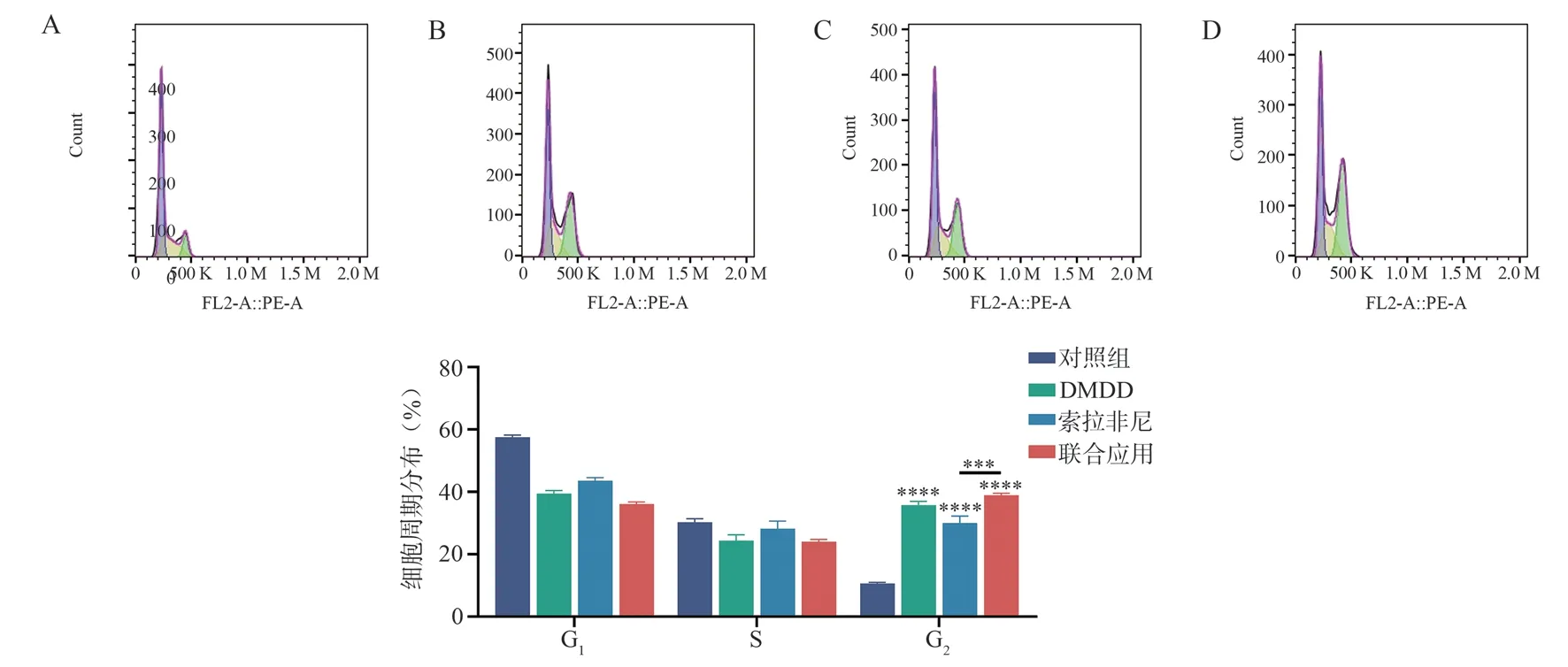
Fig 6 Effects of different drugs on Huh7 cell cycle
3.7 The effect of different drugs on the transcription level and protein expression level of PHGDH mRNA in Huh7 cells
The results of the RT-qPCR experiment showed that after 48 h of intervention, compared to the control group, the DMDD group,sorafenib group, and combination group exhibited a decrease in the transcription levels of PHGDH mRNA in Huh7 cells, and the differences were statistically significant (allP<0.000 1).When comparing the combination group with the DMDD group and sorafenib group, there was a significant decrease in the transcription levels of PHGDH mRNA in Huh7 cells in the combination group(P<0.05,P<0.01) (Fig.7A).The results of the Western blot experiment showed that compared to the control group, all three groups (DMDD group, sorafenib group, and combination group)exhibited a decrease in the protein expression levels of PHGDH in Huh7 cells, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.01,P<0.000 1,P<0.000 1).When comparing the combination group with the DMDD group and sorafenib group, there was a significant decrease in the protein expression levels of PHGDH in the combination group (P<0.000 1,P<0.001) (Fig.7B-C).
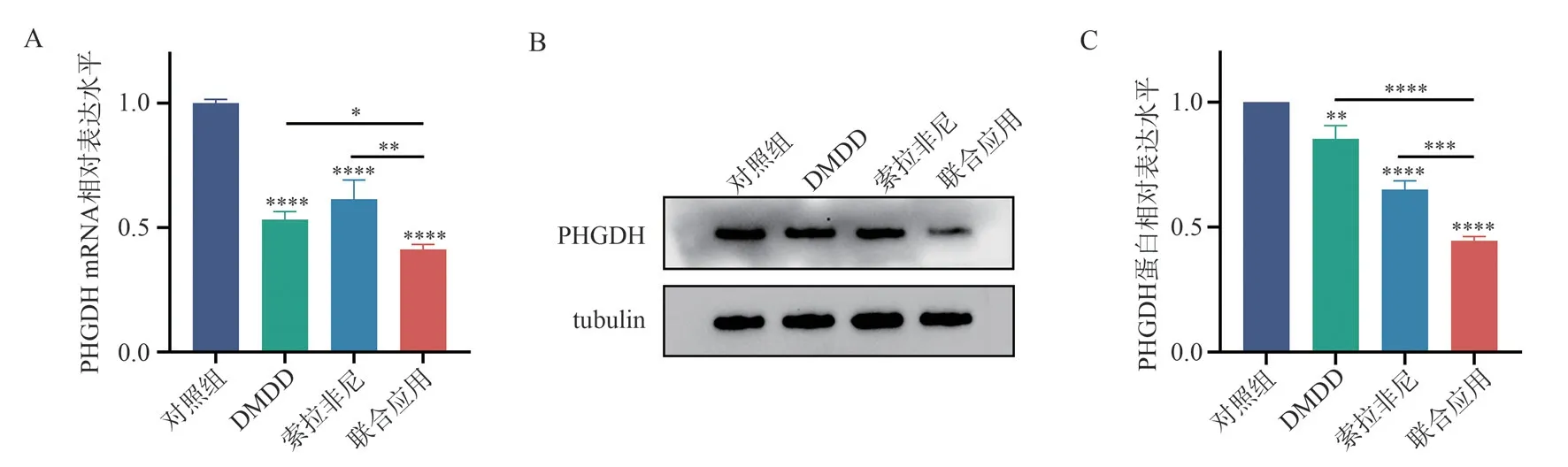
Fig 7 Effects of different drugs on PHGDHmRNA transcription and protein expression in Huh7 cells
4.Discussion
Sorafenib, as a first-line targeted therapy for advanced liver cancer,has shown effectiveness in prolonging patient survival and improving quality of life.However, the development of drug resistance and the occurrence of toxic side effects limit the therapeutic outcomes of sorafenib[14].Therefore, there is considerable research focused on enhancing the sensitivity to sorafenib or reversing sorafenib resistance[15, 16].Some studies have demonstrated that the combination of traditional Chinese medicine with sorafenib can improve its sensitivity and hold promise for liver cancer treatment[17].Our research team has also conducted studies on the therapeutic effects of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicine on HCC, as well as enhancing the sensitivity to sorafenib and reversing drug resistance.One of our studies isolated and extracted the active component DMDD from the roots of the star fruit plant, which has shown effective anticancer properties in hepatocellular carcinoma and has been applied for a patent[12].Additionally, Wang L found that DMDD can regulate the cell cycle to inhibit the growth of lung cancer cells[18].Zhou X discovered that DMDD can inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway[19].In this study, we further explored whether the combination of DMDD and sorafenib has a synergistic effect and investigated their impact on the malignant biological behavior of liver cancer cells, providing experimental evidence for the improved therapeutic efficacy of DMDD in combination with sorafenib for HCC.The results demonstrated that both DMDD and sorafenib, when used alone or in combination, exhibited inhibitory effects on Huh7 cells, with the combination treatment showing greater inhibition compared to individual drug treatments.According to the Kim’s formula method, the combination of DMDD and sorafenib exhibited synergistic or additive effects, and the combination of low-dose DMDD and low-dose sorafenib showed particularly significant synergistic effects, indicating that DMDD can enhance the sensitivity of hepatoma cells to sorafenib.The colony formation assay results showed that both DMDD and sorafenib alone could reduce the number of colonies formed by Huh7 cells,while the combination treatment significantly decreased the number of colonies, indicating a stronger inhibitory effect on Huh7 cells.The scratch wound healing assay and Transwell assay demonstrated that both DMDD and sorafenib alone could inhibit the migration and invasion abilities of Huh7 cells, with the combination treatment showing a more pronounced inhibitory effect.The cell cycle assay results revealed that both DMDD and sorafenib alone, as well as the combination treatment, led to G2/M phase cell cycle arrest in Huh7 cells.The G2 phase is the period between the S phase and the M phase, during which cells undergo organelle replication and prepare the necessary substances for mitosis[20].G2/M checkpoint blockade is an effective approach for many cytotoxic drugs to kill tumor cells[21].The combination treatment showed a significantly higher G2/M phase arrest in Huh7 cells compared to sorafenib alone, but there was no statistical significance when compared to DMDD alone.This suggests that DMDD alone possesses strong G2/M phase cell cycle arrest capability.
The serine synthesis pathway converts glucose metabolism product 3-phosphoglycerate through a three-step enzymatic reaction into serine.Intermediate metabolites participate in cellular processes such as one-carbon metabolism and antioxidant capacity.In cancer cells, abnormal activation of serine metabolism is considered to be an important mechanism for tumor growth and development[22].Mechanistically, we found that DMDD, sorafenib alone, and their combination could downregulate the expression level of PHGDH in Huh7 cells, with the combination treatment showing a more significant downregulation.PHGDH is the first rate-limiting enzyme in the serine synthesis pathway.Elevated expression of PHGDH has been detected in colon cancer, Ewing’s sarcoma, and breast cancer,and the expression level of PHGDH is positively correlated with the proliferation, invasion, and migration capabilities of these tumors[23].Montrose found that restricting serine activation could reverse 5-fluorouracil resistance in colon cancer and improve the therapeutic efficacy of 5-fluorouracil[24].These studies suggest that inhibiting the excessive activation of the serine synthesis pathway is an effective approach to inhibit the malignant biological behavior of cancer cells,enhance the effectiveness of drug treatment, and overcome tumor cell resistance.
In conclusion, the combination of DMDD and sorafenib exhibits a significantly superior inhibitory effect on the proliferation,migration, and invasion of Huh7 cells compared to their individual applications.This enhanced effect may be attributed to the synergistic downregulation of the serine synthesis pathway by DMDD and sorafenib.This study provides a new strategy to improve the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib, reduce its dosage to delay resistance, and mitigate toxic side effects.
Author contributions statement:
Yingdan Nong: conceived and designed the research, conducted experiments, analyzed data, and drafted the manuscript.PHAM THI Thai Hoa: extracted DMDD monomers.Xiao Han, Yongfei He,Tianyi Liang: designed the experimental protocols and provided technical guidance.Chunmiao Lu: involved in cell culture.Libo Tang: involved in the Transwell experiment.Ziye Yang: involved in the RT-PCR experiment.Chuangye Han, Xiaoling Luo: contributed to the research concept, experimental design and technical guidance,research funding, and manuscript revisions.
There is no conflict of interest in this article.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年13期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年13期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- A comparative study of two methods for establishing a chronic non-bacterial prostatitis model in rats
- Relationship between microRNA-29c expression and clinicopathological features of gastric cancer
- Effect of small interference RNA on expression of the Skp2 in human chondrocytes cell
- Regulation of Quan Du Zhong capsule on VEGF/bFGF and expression of Bcl-2/Bax and Caspase-3 protein in the repairing process of canine femoral head necrosis
- Association of novel and legacy PFAS with reproductive hormones in women of child-bearing age
- Meta-analysis of influencing factors associating with treatment outcome of multidrug resistant tuberculosis
