Effects of icariside II on hepatic cytochrome P450 expression in mice
, , , ,
(1.Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology of Ministry of Education and Joint International Research Laboratory of Ethnomedicine of Ministry of Education,Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi Guizhou 563099,China; 2.Department of Clinical Pharmacotherapeutics,School of Pharmacy,Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi Guizhou 563099,China; 3.Department of Neurology,Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi Guizhou 563099,China)
[Abstract]Objective To investigate the effects of icariside II (ICS II) on the contents of hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes and its major isoforms expressions in mice.Methods Male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into six groups:normal saline (NS),ICS II (5,10 and 20 mg/kg) groups,dexamethasone (DEX,80 mg/kg) and erythromycin (ERY,200 mg/kg) groups (n=12).Mice were treated with different doses of ICS II by gavage daily for 14 days,and the NS group was administered with volume-matched saline.To induce and inhibit selectively certain CYP3A11,mice were oral gavage with either DEX and ERY,respectively.The contents of CYP450 enzymes in liver were detected by Elisa kits.Liver injury were evaluated by analyzing the histopathological changes and the level of serum biochemical parameters was detected by hematoxylin and eosin staining and Elisa kits.Western blot assay was used to analyze the expression of major CYP450 isoforms.Results ICS II decreased the content of liver CYP450 enzymes.Furthermore,ICS II decreased CYP3A11 and induced CYP1A2 protein expression.No obvious changes in serum and liver tissue biochemical parameters were found and no significant pathological changes were observed in liver tissues after ICS II treatment.Conclusion The present study indicates that ICS II could decrease the content of liver CYP450 enzymes and decrease the expression of CYP3A11 and increase the expression of CYP1A2.
[Key words]icariside II; CYP450; flavonoids; liver toxicity
As the world’s understanding of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) broadens,the benefits of TCM in preventing and curing diseases have been focused,especially central nervous system diseases,such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD),Parkinson’s disease (PD),Stroke[1].However,evidence suggests that the adverse reactions/events of TCM limit its application in clinic at home and abroad[2].Of note,flavonoids are one of the most important classification of bioactive compounds in TCM that display many beneficial effects on human health.Whereas,the majority of flavonoids not only possesses biological activities,but also exhibit toxicity,especially hepatotoxicity[3].
Liver is the main organ responsible for drug biotransformation.Hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP450) isozymes belong to a multigene superfamily of heme-containing monoxygenases,which are responsible for the metabolism of a wide range of exogenous compounds in liver[4].Under normal physiological conditions,many of the genes encoding CYP450s involved in drug metabolism are highly polymorphic and the most important polymorphic enzymes are CYP1A1,CYP1A2,CYP2A6,CYP2B10,CYP2D6,CYP2E1 and the CYP3A4 in human being[5].A substantial body of evidence demonstrates that the difference expressions and activities of CYP450s leads to different pharmacokinetics properties of therapeutics drugs,specifically,flavonoids[6].Therefore,elucidation of the relationship between CYP450 expression and drugs is essential to reduce the adverse drug reaction.
Icariside II (ICS II),a flavonoid,derived fromHerbaEpimedii(Yin-yang-huo in Chinese),which has multiple pharmacological effects,including anti-osteoporotic,anti-aging and erectile dysfunction[7].Recently,ICS II has been drawn increasing attention due to its remarkable beneficial effects on neurological disorders[8].Of note,our previous studies have demonstrated that ICS II protects against learning and memory impairments and neuronal damage in the hippocampus induced by Aβ25-35,ibotenic acid,streptozotocin or lipopolysaccharide in rats.The protective mechanisms ICS II may be attributable to the blockade of inflammation and apoptosisviaregulation of MAPK signaling pathway,TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway or attenuated the level of Aβ in the AD brain through inhibiting Aβ production and enhancing of the Aβ degradation[9-10].Moreover,our previous finding suggested that ICS II could attenuate spatial learning and memory impairments in APP/PS1 transgenic mice.This protection appears to be due to the increased ADAM10 expression and decreased expression of both APP and BACE1,resulting in inhibition of Aβ production in the hippocampus and cortex[11].Coordinately,our preliminary investigations also have suggested that ICS II could attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury both invitroand invivo; And its possible mechanism may be related to regulating NF-κB/PPAR signaling pathway or Nrf2/SIRT3 signaling pathway[12-14].These findings suggest that ICS II,in fact,might be a promising neuroprotective agent to treat neurological disorders such as AD and stroke.
However,little study has been taken to clarify whether ICS II affect CYP450s.Therefore,the present study was designed to investigate the effects of ICS II on CYP450s in C57BL/6 mice,and it will provide experimental basis to predict the relationship between ICS II and CYPs.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Reagents Icariside II (ICS II,purity ≥ 98%,Nanjing Zelang Medical Technology Corporation Ltd.,Nanjing,China),was dissolved in normal saline with 15 min ultra-sonication.Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) analysis kits were purchased from Shanghai Jianglai Biological Institute (Shanghai,China).CYP 1A1 (ab79819),CYP1A2 (ab22717),CYP2A6 (ab3570),CYP2D6 (ab230690),CYP2E1 (ab28146) and CYP3A4 (ab135813) antibodies were obtained from Abcam Inc.(Cambridge,MA,USA).CYP2B10 (sc-73546) was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology,Inc.(Santa Cruz,CA,USA).Anti-GAPDH mouse monoclonal antibody (M10523) was obtained from Beijing TransGen Biotech (Beijing,China).Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA) protein concentration analysis kits,and HRP-labeled Goat Anti-rabbit IgG were purchased from Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology (Nantong,China).Dexamethasone (DEX) and erythromycin (ERY) were purchased from Dalian Meilun Biotechnology.Co.,Ltd.Microsome Isolation Kit (K249-50) were purchased from Bio Vision (USA).Mouse Cytochrome P450 Elias Kit was obtained from Renjie Biological Institute (Shanghai,China).All related reagents were of analytical grade and commercially available.
1.2 Experimental animals and drug administration Male C57BL/6 mice weighing 20 ± 2 g were obtained from SIPEFU Biotechnology Co.Ltd (Beijing,China; certificate no.SCXK2016-0002).Before experimentation,the mice were allowed to acclimatize to the experimental conditions (25 ± 2 °C temperature,60% relative humidity,and a 12 h light/dark cycle) for a week.Laboratory chow and tap water were allowed ad libitum.Mice were randomly divided into six groups:(normal saline,NS),ICS II (5,10,20 mg/kg) groups,dexamethasone (DEX,80 mg/kg) and erythromycin (ERY,200 mg/kg) groups (n=12).ICS II (5,10,20 mg/kg) groups were treated with different doses of ICS II by gavage,once a day for 14 days,and the NS group were administered volume-matched saline.To induce and inhibit selectively certain CYP3A11,mice were oral gavage with either DEX and ERY,respectively.Mice were dosed between 8:00 a.m.and 9:00 a.m.Mice were then weighed,and euthanized after the last drug administered and the serum were withdrawn from the eye vein.Liver tissues and serum samples were store at - 80℃ until use.All of the animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics and Use Committee of Zunyi Medical University.
1.3 Liver microsome preparation,Blood biochemistry and Contents of CYP450 Liver microsomes from each mouse were prepared according to microsome isolation kit protocol.Briefly,add cold Homogenization Buffer to the thawed frozen tissue (100~200 mg),then gently homogenize tissue on ice.Centrifuge at 10,000 ×g for 15 min (4 ℃).Transfer the supernatant to a new,pre-chilled microcentrifuge tube and centrifuge at 20,000 ×g for 20 min (4 ℃).Following centrifugation,aspirate floating lipids and discard the supernatant,the light beige/pink opalescent pellet is microsomal.Aliquot the microsomal solution and store at -80 ℃.ALT,AST and contents of CYP450 were determined with Elisa kit.In brief,add serum sample (50 μl) to wells and gently mix,then add HRP-conjugate reagent 100 μl to each well.After closing plate with closure plate membrane,incubate for 60 min at 37 ℃.Washing and add chromogen solution A and B,evade the light preservation for 15 min at 37 ℃.Finally,stop the reaction and assay absorbance at 450 nm.
1.4 Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining Liver tissues were fixed with 4% formaldehyde at 4 ℃ for 48 h (pH 7.4),then dehydrated and embedded in paraffin.Subsequently,3.5 μm thick sections were prepared and H&E staining at room temperature.Images of the histopathological examination were observed using a light microscope.Three mice per group were used for H&E staining.
1.5 Western blot analysis Briefly,the liver microsomes were homogenized and lysed in RIPA lysis buffer supplemented with proteinase inhibitors phenyl methyl sulfonyl fluoride.After the mixed liquid were incubated on ice for 30 min and then centrifuged at 12,000 ×g for 10 min,the supernatant was obtained and the total protein levels were quantified by BCA assay kit.Equal amounts of total protein (30 μg) were separated on 8% SDS-PAGE gel by electrophoresis and then transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes.Membranes were blocked with 5% non-fat milk and incubated with primary antibodies and GAPDH at 1∶1 000-5 000 dilution followed by the secondary antibody (1∶5 000) incubation.The immunoreactive bands were visualized with ECL detection reagents.Western blot quantifications were performed using ChemiDoc.MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories,Inc.,Hercules,cA,USA).
1.6 Statistical analysis All values are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and analyzed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS,Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance and differences among means were analyzed using LSD (equal variance assumed) and Dunnett’s T3(equal variance not assumed).P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically difference andP<0.01 indicate the difference was significant.
2 Results
2.1 Effects of ICS II on mouse body weight and liver weight After ICS II,DEX and ERY administered for two weeks,the liver weight of mice in ICS II(5,10,20 mg/kg) group were significantly decreased and DEX group increased significantly (P<0.01).Furthermore,mouse body weight significantly decreased compared with control group (P<0.01) as shown in Fig 1.
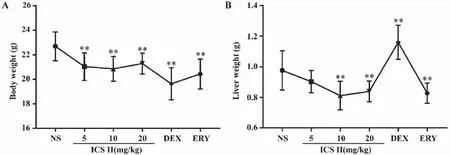
A: Body weight; B:Liver weight.**:P <0.01 versus NS;NS (normal saline),ICS II (icariside II),DEX (dexamethasone),ERY (erythromycin) (n=10-12).Fig 1 Effects of ICS II on mouse body weight and liver weight
2.2 Effects of ICS II on mouse CYP450 enzymes The contents of CYP450 enzymes in liver were detected by Elisa kit and the result is shown in Fig 2.After ICS II,DEX and ERY administered for two weeks,ICS II 10 mg/kg (P<0.05),20 (P<0.01) mg/kg,DEX and ERY (P<0.01) group decreased the content of liver CYP450 enzymes.
2.3 Effects of ICS II on mouse ALT and AST Serum AST and ALT levels were tested using Elias kit.As shown in Fig 3,administered with ERY decreased ALT levels (P<0.01) and ICS II,DEX had no effect on serum ALT and AST levels in mice.
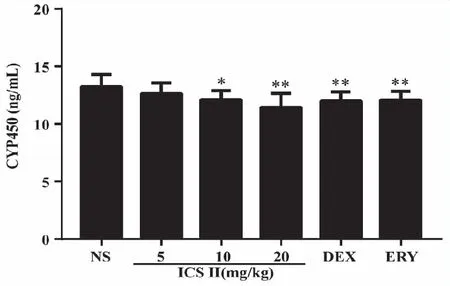
*:P<0.05,**:P <0.01 versus NS;NS (normal saline),ICS II (icariside II),DEX (dexamethasone),ERY (erythromycin) (n=7).Fig 2 Effects of ICS II on mouse liver CYP450 enzymes
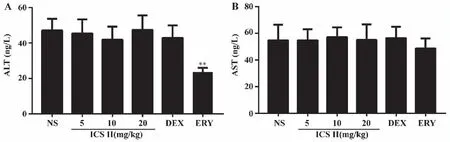
A: ALT; B: AST.**:P <0.01 versus NS;NS (normal saline),ICS II (icariside II),DEX (dexamethasone),ERY (erythromycin) (n=6).Fig 3 Effects of ICS II on ALT and AST
2.4 Liver histopathology Histopathological examination exhibited that DEX and ERY group extensive edema and transparent parts around the cell nuclei and ICS II did not affect the morphological architecture of live tissue on the HE staining Fig 4.
2.5 Protein expression of the major cytochrome P450s Protein expression of CYP1A1,CYP1A2,CYP2A6,CYP2B10,CYP2D6,CYP2E1 and CYP3A11 were detected using western blot in Fig 5.The results suggested that ICS II noteworthily decreased CYP3A11 and significantly induced CYP1A2.No effects were observed on the other tested P450s isoforms.And DEX group significantly induced CYP3A11 (P<0.05) and decreased CYP2E1,CYP1A1,CYP1A2,CYP2B10 protein expression (P<0.01).ERY group significantly decreased CYP1A1,CYP1A2,CYP2B10 (P<0.01) and CYP2E1 (P<0.05).
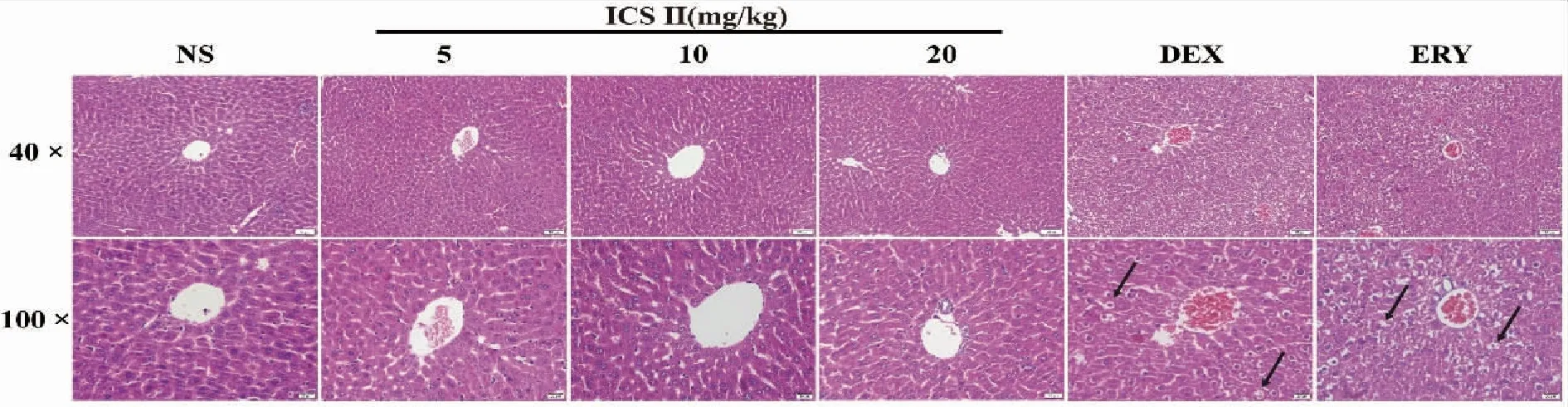
NS (normal saline),ICS II (icariside II),DEX (dexamethasone),ERY (erythromycin);(100×,scale bar=50 μm,400×,scale bar=20 μm;The arrows indicate cellular edema,and transparent parts around the cell nuclei.Fig 4 Effects of ICS II on mouse liver histopathology
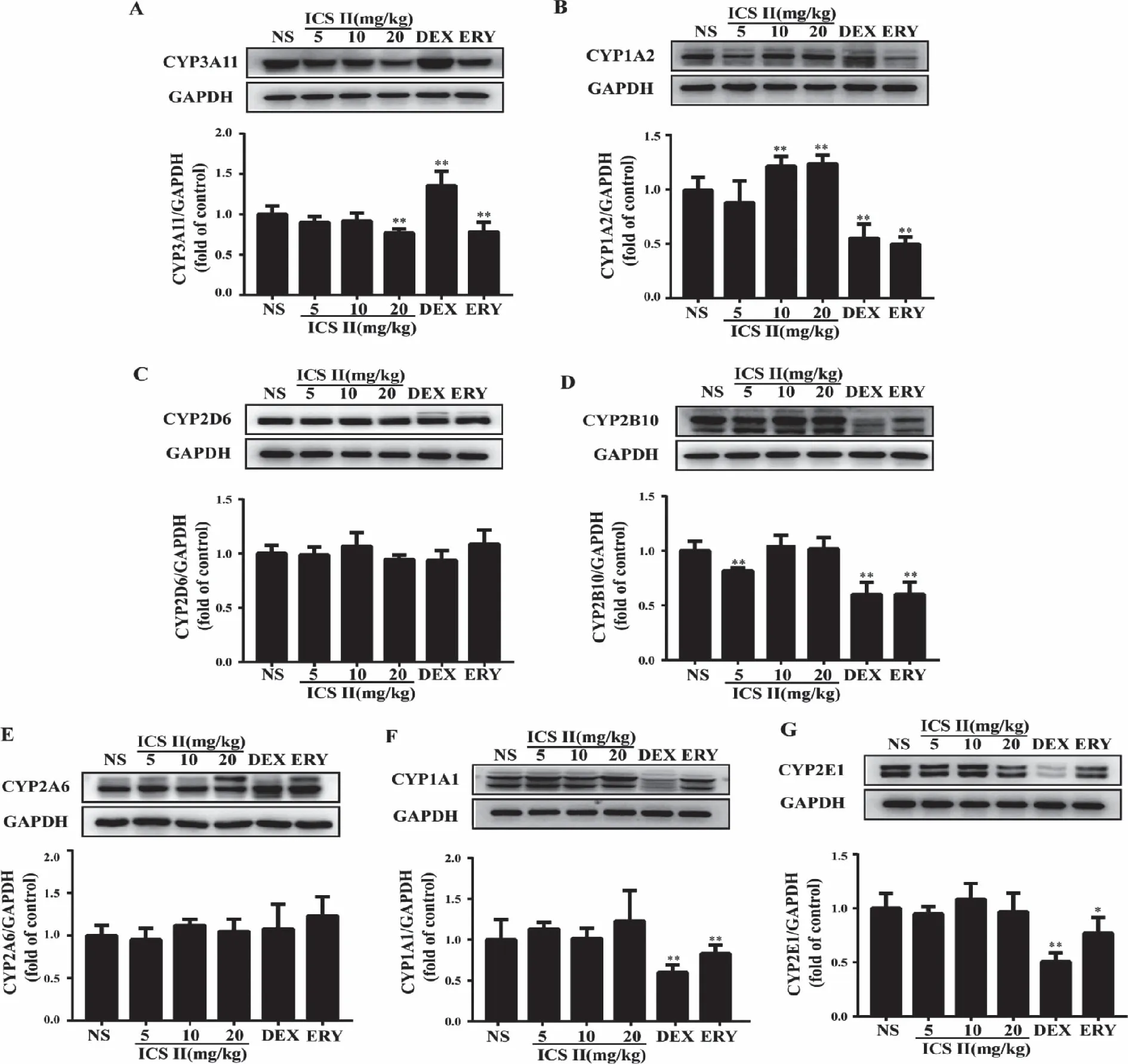
A:Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP3A11; B:Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP1A2; C:Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP2D6; D:Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP2B10; E: Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP2A6; F:Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP1A1; G: Representative and quantification Western blots of CYP2E1;*:P<0.05,**:P <0.01 versus NS;NS (normal saline),ICS II (icariside II),DEX (dexamethasone),ERY (erythromycin) (n=5).Fig 5 Effect of ICS II on major cytochrome P450s isoforms expression
3 Discussion
To date,considerable evidences indicate that the co-administration of Herbal products and drugs will lead to adverse reactions,specifically those that affect CYP450s invivo[15].The neuroprotective properties of ICS II are attracting increasing interests in searching for promising agents to neurodegenerative diseases’ treatment.Nevertheless,further studies may be warranted to clarify the effects of ICS II on the expressions of CYP450s.
In the present study,we first measured the levels of two liver-specific enzymes,ALT and AST,which are most commonly used as markers of hepatotoxicity.Hence,the analysis of these biomarkers is significant for the identification of drug-induced liver damage.The results showed that DEX and ERY group induced liver injury,consistent with previous study[16].Of note,although ICS II decreased body weight in mice may be due to gastrointestinal reaction,there were no obvious liver damage was triggered with different doses of ICS II for 14 days as evidenced by ALT,AST and liver histopathology.These findings implied that ICS II has no obvious liver damage in mice.
CYP450 enzymes play an important role in the biotransformation of most xenobiotic compounds and difference expressions and activities of CYP450s lead to different pharmacokinetics properties of therapeutics drugs and even exhibit toxicity.And researches have noted that there are currently several suitable animal models which are widely used to predict the kinetics and toxicity of xenobiotics during Phase I metabolism studies in humans.For example,mouse CYP3A11 are the most similar to human CYP3A4 and both have approximately 72% amino acid similarity with human CYP3A4.CYP2E1 is conserved in mice and has approximately 80% identity with human CYP2E1.Studies have characterized that at least nine mouse Cyp2d genes are proposed orthologs to human[17].Notably,ICS II is the active metabolite compound of icarrin which decreased the content of liver microsomal CYP450 in mice in previous study[18]; whereas,to the best of our knowledge,there are few studies investigate the effects of ICS II on hepatic CYP450 expression.Hence,we designed this experiment in mice.
In the present study,we measured the content of liver CYP450 enzymes in mice.The results suggested that ICS II 10 and 20 mg/kg decreased the content of liver CYP450 enzymes.However,ICS II had no effect on the content of liver CYP450 enzymes at a dose of 5 mg/kg,probably due to ICS II absorbed into the liver did not reach the threshold dose.Hence,caution needs to be exercised when ICS II is used alongside other drugs that reducing the risks associated with its clinical treatment.
CYP3As are considered to be the most important and abundantly expressed P450 subfamily; responsible for the phase I metabolism of approximately 30% of clinically administered drugs.CYP3A11 in mice are homologs of human CYP3A4 which accounts for up to 50% of the total hepatic CYP protein.CYP1A2,a member of the CYP1A superfamily and accounts for approximately 15% of total hepatic P450,which is the main enzyme involved in the metabolism of many clinically important drugs,including caffeine,phenacetin,clozapine,theophylline,tacrine,and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons[19].It is highly inducible by 3-methylcholanthrene-like inducers (e.g.,heterocyclic aromatic amines,and dioxins) through the aryl hydrocarbon receptor induction mechanism.Our results suggested that ICS II noteworthily decreased the expression of CYP3A11 at a dose of 20 mg/kg and induced the expression of CYP1A2 enzymes at 10 and 20 mg/kg.Hence,when ICS II is combined with other drugs which were metabolized by CYP3A11,it might prolong the metabolic time and increase the curative effect,or argument the incidence of drug adverse reactions,etc.Therefore,caution needs to be exercised when ICS II is used alongside drugs that are metabolized by CYP3A11 and CYP1A2.
CYP1A1 is primarily found in the respiratory system,which is involved in the metabolism of multiple pro-carcinogens including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from tobacco and environmental exposure.CYP2D6 participates in the metabolism of more than 25% of clinically used drugs,including debrisoquine,propafenone,and amitriptyline.CYP2E1 participates in the metabolic activation process of many pre-carcinogen and poisons[20].CYP2A6 responds to the metabolism of nicotine and to the metabolic activation of a number of procarcinogens,which can ultimately lead to development of lung cancer.CYP2B10 is a monooxygenase with testosterone and bile acid hydroxylation activity in mouse liver[21].However,ICS II at a dose of 20 mg/kg also had no effect on the expression of CYP1A1,2A6,2B10 and 2E1.
Additionally,the effects of DEX and ERY on the expression of some CYP450 enzymes were observed.Intriguingly,the expression of CYP1A1,1A2,2B10 and 2E1 were decreased by DEX and ERY in mice,consistent with previous study and probably dur to liver injury was induced.These results indicated that DEX and ERY have the potential to cause clinical drug-drug interactions based on CYP1A1,1A2,2B10 and 2E1 metabolism.Likewise,caution needs to be exercised when DEX and ERY were used.
In summary,the present study revealed that ICS II significantly decreased the content of liver CYP450 enzymes and noteworthily decreased the expression of CYP3A11 and induced CYP1A2.Hence,caution needs to be exercised when ICS II is used alongside drugs particular that are metabolized by CYP3A11 and CYP1A2.

