Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
●心电学英语
Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
The primary electric disorders responsible for polymorphic ventricular tachycardia(VT)or ventricular fibrillation are long-QT syndrome,Brugada syndrome, the short-coupled variant of torsades de pointes, short-QT syndrome,and catecholaminergic polymorphic VT(CPVT).CPVT is a rare arrhythmogenic disorder characterized by adrenergic-induced bidirectional and polymorphic VT.The prevalence of the disease is estimated to be 1:10 000 in Europe.The first case was reported in 1975.Key features include polymorphic VT reproducibly induced during exercise tests,isoproterenol infusion,or emotion and exercise.CPVT occurs in children and adolescents and causes syncope and sudden cardiac death at a young age,in the absence of structural heart disease.The resting ECG,including the QTc interval,is normal.The mortality of CPVT is extremely high,reaching 31%by the age of 30 years when untreated.The estimated 4-and 8-year cardiac event rates were 33%and 58%,respectively,in our series of patients without β-blockers.There is a clear correlation between the age of the first syncope and the severity of the disease,with a worse prognosis in the case of early occurrence.β-blockers without sympathomimetic activity are clinically effective in reducing syncope.However,arrhythmic event rate with β-blocker therapy remains significant,suggesting the need for alternate pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies.
With the advancements of molecular genetics and the identification of mutations in the genes encoding the cardiac ryanodine receptor and cardiac calsequestrin 21in patients with CPVT,the central role of the intracellular calcium dysregulation in myocardial cells is progressively better understood through expression studies and murine models.
Genetic Background
Priori et al and Laitinen et al identified the first mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor gene (RYR2)in families suffering of this type of CPVT,now known as CPVT1.Lahat et al.identified a homozygous missense mutation in the cardiac calsequestrin gene (CASQ2)as the cause of this recessive form,now known as CPVT2.RYR2 mutations are frequent, whereas CASQ2 mutations are rare;altogether,mutations are only found in 50%to 60%of patients with CPVT,which suggests that other genes are involved.
Ryanodine Receptor
The cardiac ryanodine receptors(RyR2)are calcium(Ca2+)release channels present in the sarcoplamic reticulum(SR),an intracellular vesicular network playing a major role in the regulation of Ca2+homeostasis in the heart.The mechanism of their activation is called calcium-induced calcium release because it requires that Ca2+provided by the activated L-type Ca2+channel (Cav1.2).Calcium binds to RyR2 and triggers opening of a high-conductance channel,allowing rapid Ca2+efflux from the SR.The consecutive high cytoplasmic Ca2+induces myocardial contraction,then Ca2+is reuptaken in the SR,where it is stored at high concentrations.
RYR2 Mutations
The 4967-amino acid RyR2 channel is encoded by one of the largest genes in the human genome,containing 105 exons.To date,>50 mutations have been reported,most of them for CPVT1 and unexplained or exercise-induced sudden death.Most of the RYR2 mutations are missense mutations,occurring in 3 hot-spotregions:the N-terminal region,the central region where the calstabin-21binding domain is localized,and the C-terminal domain,including the channel region.These 3 regions are well conserved among the RyR gene family and are involved in the regulation of RyR channels.
High variability of the phenotypic expression among subjects of the same family or unrelated families was demonstrated and estimates of the penetrance range from 25%to 100%.It is noteworthy that there are asymptomatic RyR2 mutation carriers with normal exercise stress tests.Some of them can further present with exercise-induced arrhythmia during a subsequent stress test,but more importantly may die suddenly as the first manifestation of the disease.
CASQ2 Mutations
The399-amino acid CASQ2 protein is encoded by a gene containing 11 exons.Twenty-one distinct CASQ2 mutations have been reported,either homozygous or compound heterozygous mutations transmitted under a recessive mode of inheritance.Half of them are missense mutations localized in different exons.The others lead to truncated proteins by various mechanisms,nonsense codon, small deletion,and abnormal splicing leading to premature stop codon.Interestingly,a synonymous c.381C>T variation in exon 3,recently identified in a family with CPVT2,was shown to induce abnormal splicing and a premature stop codon using a splicing minigene assay.
The phenotype is similar among the patients with 2 CASQ2 mutations and the patients with an RyR2 mutation.Most of the carriers of a single CASQ2 mutation are healthy.Nevertheless,several clinical investigations suggested that a single CASQ2 mutation could represent a potential susceptibility for ventricular arrhythmias in some subjects.The origin of the variability among subjects of a same family is still unknown.
Clinical Presentation
CVPT is extremely uncommon before the age of 2 years.The first episode of syncope usually occurs during the first or second decade of life.The symptoms are always triggered by exercise or emotional stress.Often,epilepsy is diagnosed and children are inappropriately treated with long-term antiepileptic therapy.A mean delay in diagnosis of≥2 years is usually reported in patients with syncope initially attributed to vasovagal or neurological causes.A family history of exercise-related syncope,seizure,or sudden death is reported in 30% of the patients.
Diagnosis
A history of exercise-induced or emotional stress-induced syncope with polymorphic ventricular arrhythmia in a child is highly suggestive of CPVT. The heart is structurally normal.The arrhythmia is reproducibly induced during an exercise test as well as during isoproterenol infusion.Holter monitoring or an exercise test can document CPVT by showing the ventricular arrhythmia progressively appearing after a heart rate threshold(around 120-130 beats per minute).Polymorphic VT is usually not inducible by programmed ventricular stimulation.Implantable loop recorders can be useful to record CPVT in children with adrenergically triggered,unexplained syncope.
Electrocardiographic key features in CVPT
The resting ECG is usually normal,and there is progressive ventricular ectopy as heart rate increases during exercise or isoproterenol infusion.Frequency and complexity increase as heart rate increases,first monomorphic ventricular premature beats(VPBs)followed by bidirectional VT(Figure 1).VPBs usually have a right bundle branch block pattern with alternating right and left axis deviation,suggesting a left ventricular origin.If the exercise is continued,salvos of polymorphic VT may appear and become more sustained and rapid,leading to syncope.Usually,the arrhythmia is self-terminating,but in some cases it can degenerate into ventricular fibrillation and sudden death(Figure 2). The arrhythmia disappears with the discontinuation of the exercise or after cessation of the isoproterenol infusion. The reverse heart rate-dependent sequence is usually observed during recovery.Some individuals expressing bidirectional VT during exercise may not have CPVT.Instead,clinical consideration of either Andersen-Tawil syndrome2or long-QT syndrome and appropriate genetic testing may be warranted for individuals without a RyR2 mutation but considered as patients with CPVT,particu-larly women.Careful inspection of the TU-wave morphology may assist in distinguishing between CPVT and Andersen-Tawil syndrome in a patient exhibiting exercise-induced bidirectional VT.Atrial arrhythmias,including atrial fibrillation,are not uncommon during exercise tests and have been described in some adult patients.
Current Management
β-Blockers
The first-line therapeutic option for patients with CPVT is β-blockers without sympathomimetic activity, in accordance with the arrhythmia's catecholaminergic mechanism,combined with exercise restriction.Nadolol, a long-acting drug,is preferred for prophylactic therapy and has been found to be effective clinically.In our experience,the dosage used to provide adequate prevention of CVPT and syncope is usually high(1.8 mg/kg).We reported in 2009 the long-term follow-up results of 101 patients with CPVT with an estimated 8-year cardiac event rate of 27%,even in those taking β-blockers.
The apparent discrepancy in the efficacy of β-blocker treatment between the various studies probably reflects differences in genetic background and in β-blocker dosages or a poor drug compliance.This discrepancy in β-blocker efficacy may also be because of the presence of polymorphisms influencing their metabolism.
Meanwhile,the maximal well-tolerated dosages of β-blockers should be prescribed and Holter recordings and exercise tests should be repeated periodically to ensure that the degree of sinus tachycardia that precedes the onset of arrhythmias is never reached.Furthermore, once the diagnosis is established,it is crucial to make the patients aware of the necessity of faultless compliance with the β-blocker therapy,given the number ofnoncompliance-related sudden cardiac deaths.It is strongly suggested that genetically positive family members should receive β-blockers even after a negative exercise test.
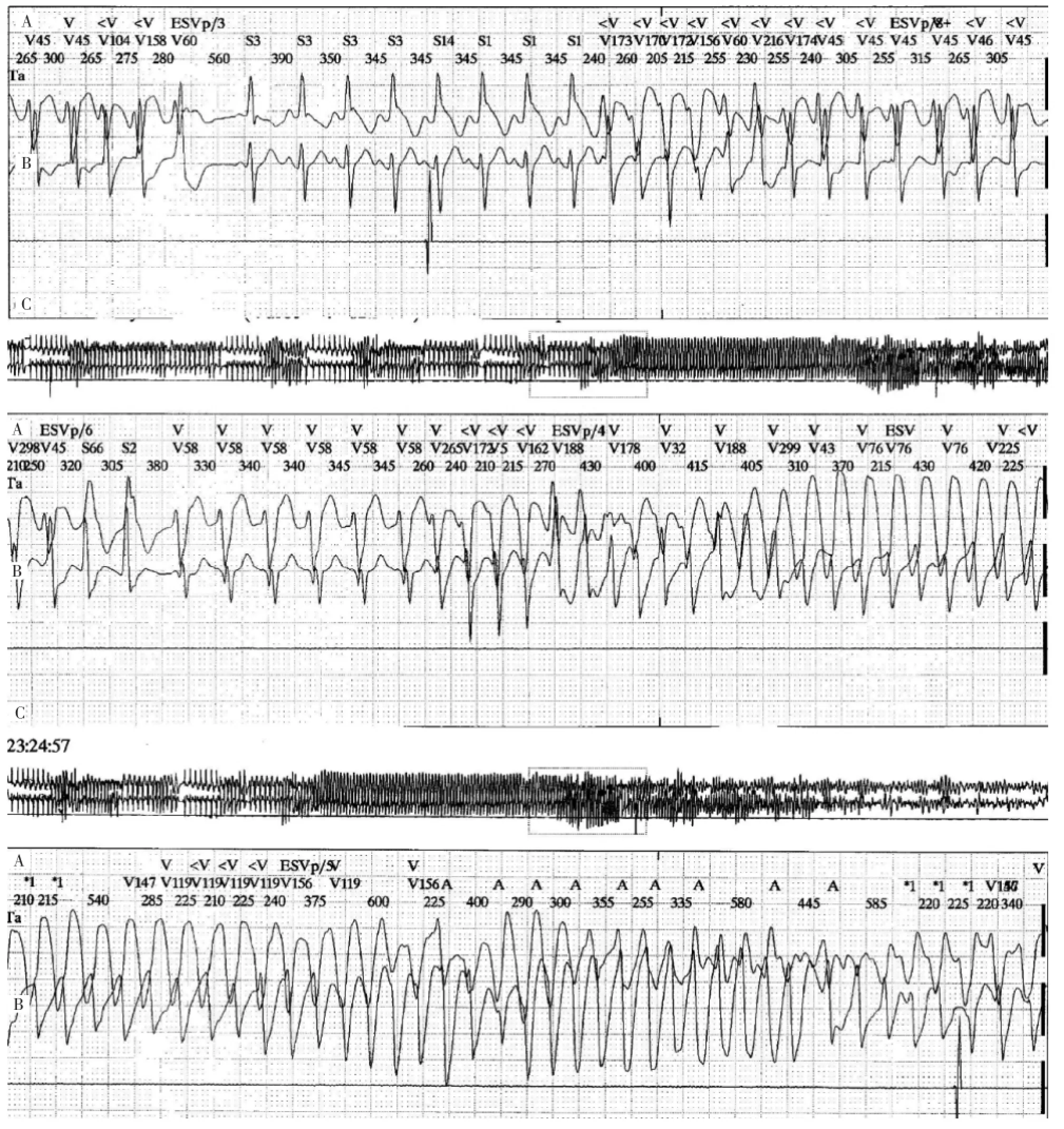
Figure 2 Holter tracings showing pleiomorphic and polymorphic ventricular tachycardia preceding the occurrence of ventricular fibrillation in a patient with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator(ICD)implantation is recommended in patients with CPVT and syncope or documented sustained VT,despite β-blocker therapy.Nevertheless,ICDs can potentially have proarrhythmic effects in patients with CPVT because stress caused by appropriate or inappropriate discharges could prove disastrous by evoking a self-induced vicious circle.However,a combination therapy involving both an ICD and an optimized dosage of β-blocker should safeguard against any such adverse effects and provide ultimate protection in nonresponsive patients.
Left Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation
The first publication reported the efficacy of LCSD in 3 young patients with CPVT,with a long follow-up in 2(aged 20 and 10 years)in whom ventricular arrhythmias were not controlled by β-blocker therapy.The following series reported results of LCSD in patients with resistant and symptomatic ventricular arrhythmias, despite optimal pharmacological therapy.Although the short-term results seem encouraging,more data from a long-term follow-up are needed.LCSD is not available in many centers worldwide because it requires well-trained surgeons and dedicated techniques.
词汇
Murine n.&adj.鼠;鼠的
Calsequestrin n.集钙蛋白
Salvo n.&v.一阵,一片,爆发,齐射;齐射
Exon n.外显子
Truncate v.截去,删节
Codon n.密码子
Faultless adj.无错误的,完美的
Disastrous adj.灾难性的,灾难性,极坏的
注释
1.Calstabin-2是一种小的调节蛋白即FKBP12.6,能与RyR2结合并稳定其,阻止这种结合会增加室性心律失常危险。
2.Andersen-Tawil syndrome又称长QT综合征7,是一种罕见的常染色体显性遗传疾病,60%与KCNJ2基因有关,除长Q-T间期,室性心律失常外,合并存在发作性或持续性肌无力及躯体异常,如小下颌、低耳位、指弯曲等。
参考译文
第59课儿茶酚胺源性多形性室性心动过速
与多形性室性心动过速(VT)或心室颤动相关的原发性电子病有长QT综合征、Brugada综合征、短偶联间期尖端扭转型室性心动过速、短QT综合征和儿茶酚胺源性多形性室性心动过速(CPVT)。CPVT是一种罕见的致心律失常疾病,特征表现为肾上腺素诱发的双向性和多形性VT。在欧洲该疾病发病率估计为1:10 000。1975年首次报道。关键特征包括运动试验、滴注异丙肾上腺素、情绪激动和运动能重复诱发多形性VT。CPVT发生于儿童和青少年,导致无结构性心脏病的少年晕厥和心脏性猝死。静息心电图包括Q-TC间期正常。CPVT死亡率极高,如不治疗,到30岁时可达31%。本文作者报道系列患者非β受体阻滞剂治疗下4年和8年的心脏事件发生率分别达33%和58%。首次晕厥发作的年龄与疾病严重性之间存在明确的相关性,早发者预后差。临床上,无拟交感活性的β受体阻滞剂能有效减少晕厥发生。然而,β受体阻滞剂治疗下心律失常事件仍然明显,提示需要更换药物和非药物治疗。
随着分子遗传学的进展和CPVT患者编码ryanodine受体和心脏集钙蛋白2(calsequestrin 2)基因突变的发现,通过表达研究和小鼠模型,更进一步了解了心肌细胞胞内钙调节异常的中心作用。
遗传性背景
Priori和Laitinen等在罹患CPVT的家族首次发现心脏ryanodine受体基因(RYR2)突变,现称作CPVT1。Lahat等发现心脏集钙蛋白基因(CASQ2)的纯合子错义突变为隐性形式的原因,现称作CPVT2。RYR2突变常见,而CASQ2突变罕见;合计只有50%~60%的CPVT患者发现突变,提示其他基因受累。
Ryanodine受体
心脏ryanodine受体(RyR2)是肌质网上的钙释放通道,这是一种细胞内囊状网络,在心脏的钙离子稳态调节中起重要作用。激活机制需要活化的L型钙离子通道(Cav1.2)提供钙离子,因此称为钙诱导钙释放。钙结合到RyR2并促发开放高通量通道,使得钙离子快速从肌质网流出。连续的胞浆内高钙离子诱发心肌收缩,随后,钙离子被重新摄回到肌质网中以高浓度存储其中。
RYR2突变
有4 967个氨基酸的RyR2通道由人体基因组中最大基因之一编码,该基因包含105个外显子。至今,已报道>50个突变,其中多数与CPVT1和不明原因或运动诱发的猝死有关。多数RYR2突变为错义突变,发生在3个热点区域:N-端区域;中心区域,钙活动调节蛋白2(calstabin-2)结合域位于此区域;C-端区域,包含通道区域。这3个区域在RyR基因家族中是极保守的,涉及RyR通道的调节。
已证实同一家族或不同家族个体之间的表型表达高度易变,估计外显率为25%~100%。值得注意的是存在运动试验正常的无症状RyR2突变携带者。他们中的一些人在随后的负荷试验中进一步表现出运动诱发的心律失常,但更重要的是首次表现可为猝死。
CASQ2突变
有399个氨基酸的CASQ2蛋白由包含11个外显子的基因编码。已报道21个明确的CASQ2突变,系纯合子突变或隐性遗传的复合杂合子突变。其中半数为位于不同外显子的错义突变。其他的通过各种机制,无义密码子,小缺失,异常剪接致提前中止密码子,导致截短蛋白。令人感兴趣的是,使用剪接小基因检测显示,最近在一CPVT2家族中发现的外显子3上的同义c.381C>T变异诱发出异常剪接和提前中止密码子。
两种CASQ2突变的患者与RyR2突变的患者的表型是相类似的。多数单一CASQ2突变携带者是健康的。然而,数个临床研究表明某些单一CASQ2突变患者表现出发生室性心律失常的潜在易感性。同一家族不同个体之间变异的根源尚不清楚。
临床表现
CVPT 2岁前极少发生。首次晕厥通常发生在10岁前或20岁前。症状总是由运动或情绪压力所触发。儿童常被诊断癫痫发作,而长期不适当地接受抗癫痫治疗。对于最初将晕厥归因于血管迷走或神经源性的患者,诊断上通常平均延后2年或以上。据报道,30%患者有运动相关晕厥、癫痫发作或猝死的家族史。
诊断
儿童有运动诱发或情绪压力诱发晕厥伴多形性室性心律失常病史高度提示CVPT。心脏结构正常。运动试验及异丙肾上腺素滴注可重复诱发这种心律失常。动态心电记录或运动试验通过显示当心率达到临界值(约120~130次/min)后室性心律失常逐渐出现而印证CVPT。程序心室刺激通常不能诱发多形性VT。对于肾上腺素触发、不明原因晕厥的儿童植入型记录器是有用的。
CPVT心电图关键特征
静息心电图通常正常,运动或异丙肾上腺素滴注过程随着心率增加室性异位搏动逐渐增加。随着心率增加,频率及复杂性增加,首先为单形性室性期前收缩,接着为双向性VT(图1)。室性期前搏动通常呈右束支传导阻滞图形伴心电轴右偏和左偏交替,提示为左心室起源。如果运动持续,可出现阵发多形VT,并变得更持久更快,导致晕厥。通常,心律失常呈自限性,但有时蜕化为心室颤动和猝死(图2)。心律失常随着运动的中止或异丙肾上腺素滴注结束而消失。恢复期可见到反向心率依赖变化过程。某些个体运动中表现为双向性VT而不发生CPVT。反之,临床应考虑Andersen-Tawil综合症或长QT综合征,对于无RyR2突变但认为是CPVT患者,特别是女性,应做恰当的基因测试。对于运动诱发双向性VT的患者,仔细检查TU波形态有助于鉴别CPVT和Andersen-Tawil综合征。运动中房性心律失常,包括心房颤动并非少见,已报道见于某些成年患者。
现行治疗方法
β受体阻滞剂
基于该心律失常的儿茶酚胺源性机制,CPVT患者一线治疗应选择无拟交感活性的β受体阻滞剂,结合运动限制。纳多洛尔(Nadolol),一种长效制剂,适合预防治疗,并证实临床有效。根据本文作者经验,为保证充分预防CPVT和晕厥的发生,通常需给大剂量(1.8 mg/kg)。2009年本文作者报道101例CPVT患者长期随访结果,即使那些服用β受体阻滞剂者,8年心脏事件为27%。
不同研究之间β受体阻滞剂治疗疗效的明显不一致可能反映遗传背景或β受体阻滞剂剂量不同或服药依从性差。β受体阻滞剂疗效明显不一也可因存在影响其代谢的多态性。
同时,应予以最大良好耐受剂量的β受体阻滞剂,并定期重复动态心电图和运动试验检查,以确保绝不达到(室性)心律失常发作前窦性心动过速的速率。此外,鉴于一些因缺乏依从性而导致的心脏性猝死,一旦诊断明确,至关重要的是让患者意识到完全遵医嘱服用β受体阻滞剂治疗的必要性。强烈建议基因阳性家族成员接受β受体阻滞剂治疗,即使运动试验阴性。
植入性心律转复除颤器
CPVT和晕厥或记录到持续性VT患者,除了β受体阻滞剂治疗外,建议植入心律转复除颤器(ICD)。不过,ICD对CPVT患者有致心律失常作用,因为恰当或不恰当放电所致的压力可引起自-诱发恶性循环而导致灾难性后果。然而,联合ICD和最佳剂量β受体阻滞剂治疗应能防范任何这类不良反应,并能对无反应者提供根本保护。
心脏左交感神经去除术
首篇文章报道了3例年轻CPVT患者心脏左交感神经去除术(LCSD)的疗效,长期随访的2例(年龄分别为20岁和10岁)为β受体阻滞剂不能控制室性心律失常的患者。其后系列报道了优化药物治疗下顽固性症状性室性心律失常患者的LCSD结果。虽然短期结果令人鼓舞,但需更多的长期随访资料。LCSD在世界上许多中心无法实行,因其需要良好训练的外科医生和专用的技术。
图1负荷试验中12导联心电图显示典型的双向性VT,特征为QRS电轴每搏呈180°交替,伴随右束支传导阻滞图形提示左心室起源。
图2动态心电图记录显示一例儿茶酚胺源性室性心动过速患者心室颤动发生前多种形态的VT。
[1]Leenhardt A,Denjoy I,Guicheney P.Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia[J].Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol,2012,5:1044-1052.
(童鸿)

