一类大转角两转动并联机构的构型分析与运动学优化设计
宋轶民,周 培,齐 杨,霍欣明
一类大转角两转动并联机构的构型分析与运动学优化设计
宋轶民1,周 培1,齐 杨2,霍欣明1
(1. 天津大学机构理论与装备设计教育部重点实验室,天津 300354; 2. 天津职业技术师范大学天津市高速切削与精密加工重点实验室,天津 300222)
面向航空航天和仿生设计等领域对大转角两转动并联机构的应用需求,围绕一类新型两自由度转动并联机构——2-RRRR&2-RSR机构的构型分析与运动学优化设计问题展开研究.首先,以投影关系为基础分析2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构在给定工作空间内实现两自由度转动运动所需满足的几何条件,并针对两种投影情况分析机构的参数特解.其次,基于闭环矢量法求解2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的位置逆解,推导机构驱动角度与动平台姿态角之间的映射关系,继而利用RRRR支链与RSR支链的运动特点,获得机构动平台姿态角的正解模型.以此为基础,借助螺旋理论建立2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的速度映射模型,构建机构的广义雅可比矩阵,并通过软件仿真验证机构位置正、逆解及速度映射模型的有效性.再次,根据2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的运动特性,以奇异性、铰链许用转角范围、连杆安全距离为约束条件,借助极限边界搜索法求解机构动平台中心点的位置工作空间,进而对应位置工作空间等效获得机构的转角工作空间.最后,借助螺旋理论中运动与力的互易积的物理含义定义可描述2-RRRR&2-RSR机构瞬时功率传递特性的无量纲运动学性能评价指标,并结合工程实际需求设定机构的约束条件,实现机构的尺度参数的运动学优化设计.研究成果可为大工作空间两自由度转动并联机构的样机设计与控制策略制定奠定理论基础.
转动并联机构;构型分析;运动学分析;工作空间;尺度综合
两自由度转动并联机构因结构紧凑、精度高等优点在工业、航空航天、医疗等领域具有重要的应用价值,例如空间5R机构、PantoScope机构等两转动并联机构已成功应用于摄像探测装备、微创手术辅助装置[1-3]等.近年来,航天测控、仿生学的发展对转动机构的工作空间提出了更高的要求[4-6],设计具有大转角、优异运动性能的两自由度转动并联机构成为研究的热点问题.
Dunlop等[7]在3-RSR并联机构的基础上添加了SS支链,提出了两转动Canterbury Tracker天线角跟踪机构,实现了大范围目标追踪.受腕关节的启发,Ross-Hime公司研发了Omni-wrist系列并联机构,该系列机构可实现半球面无奇异两转动运动[8-9].Omni-wrist系列机构的优异性能引起了国内外学者的广泛关注.文献[10-14]分别针对该类机构进行了运动学分析.研究表明,Canterbury Tracker、Omni-wrist系列机构转动轴线的方向与位置均随机构运动发生改变,且该类机构可视为零扭转机构,即机构运动的扭转角为零[15].相较于定轴两转动并联机构,零扭转机构具有实现更大工作空间的可能性.
笔者前期提出了一类新型两自由度转动并联机构2-RRRR&2-RSR,该机构具有零扭转运动特点[16].与Canterbury Tracker和Omni-wrist机构相比,2-RRRR&2-RSR机构摆脱了中间支链的约束,具有实现更大工作空间的可能性.此外,机构的4条支链呈圆周形状对称分布,可保证机构在给定工作空间内具有良好的运动学与静力学对称性.由于机构静平台转动副轴线通过静平台中心点,机构的正、逆运动学求解与控制策略将更为简便.
本文以2-RRRR&2-RSR机构为研究对象开展构型分析与优化设计研究.首先,分析2-RRRR&2-RSR机构在给定工作空间内实现两自由度转动运动所需满足的几何条件.其次,采用闭环矢量法建立机构的位置逆、正解模型,并借助螺旋理论推导机构的广义雅克比矩阵.之后,基于螺旋理论互易积的概念,定义可描述机构瞬时功率传递特性的运动学性能评价指标,并计及各种约束条件,构造尺度综合的目标函数,以实现机构运动学优化设计.
1 构型分析
在机构运动过程中,动坐标系相对于固定坐标系的姿态变换矩阵可表示为
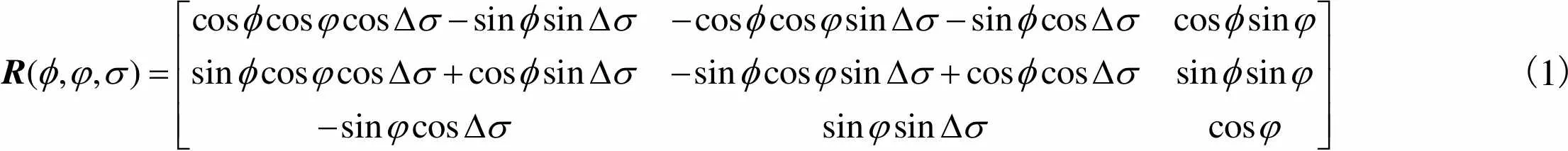
(1)

(2)
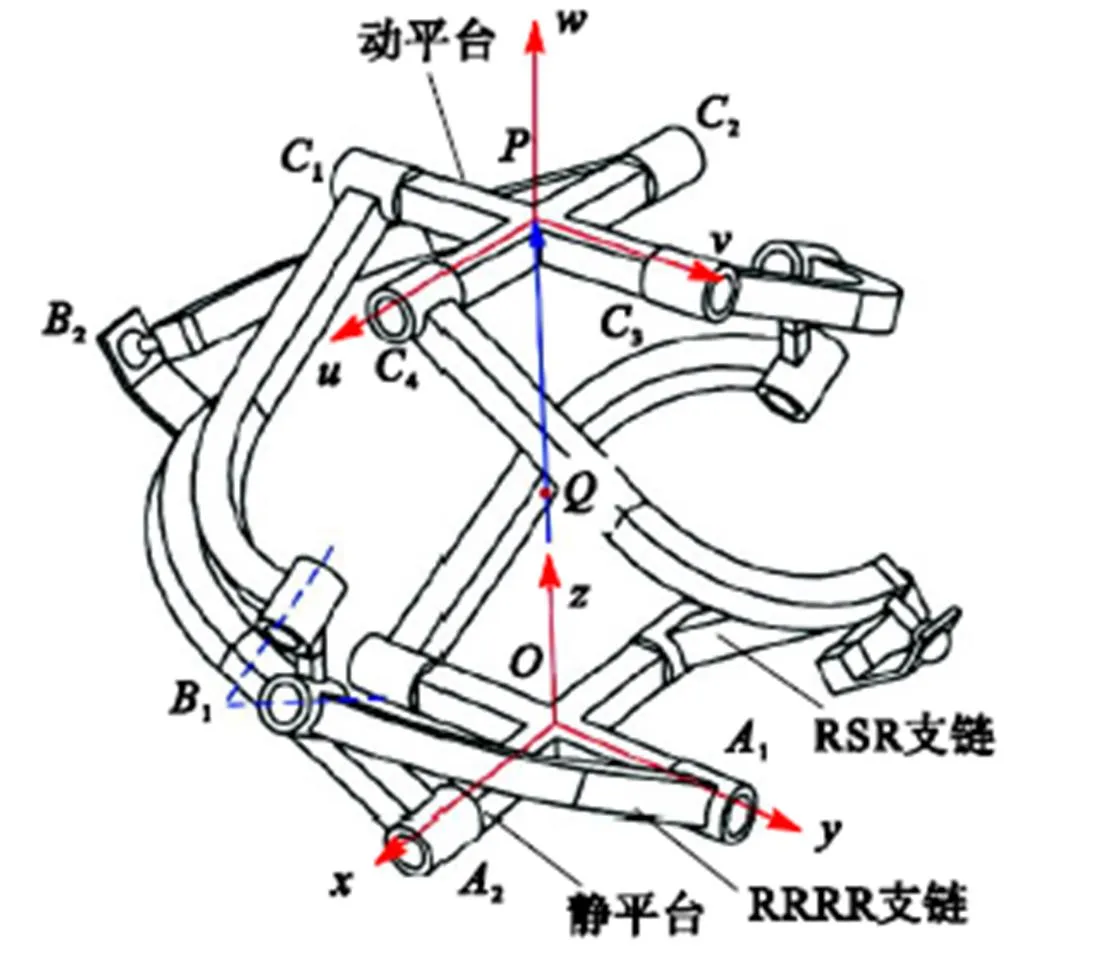
图1 2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构
零扭转两转动并联机构动平台中心点的运动可描述为

(3)
首先,分析2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构在给定工作空间内实现两自由度转动需满足的几何条件.如图2(a)所示,在初始位形下,RRRR支链中转动副1和转动副4轴线平行,转动副1和转动副2轴线相交于静平台中心点,转动副2和转动副3轴线相交于点,转动副3和转动副4轴线相交于动平台中心点.如图2(b)所示,初始位形下,RSR支链中2个转动副轴线平行,球副中心记为点.对于RRRR支链和RSR支链,点在支链首、末转动副轴线上的投影分别记为点和点.
由闭环矢量可知
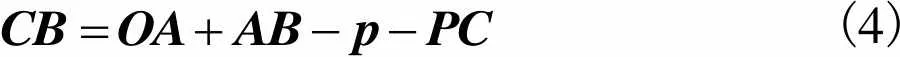
(4)
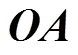
根据转动副的运动性质,可知

(5)
由式(4)可知
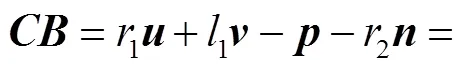

(6)

(7)
将式(6)代入式(7),可得
图2 组成支链构成
Fig.2 Construction of assembled limb
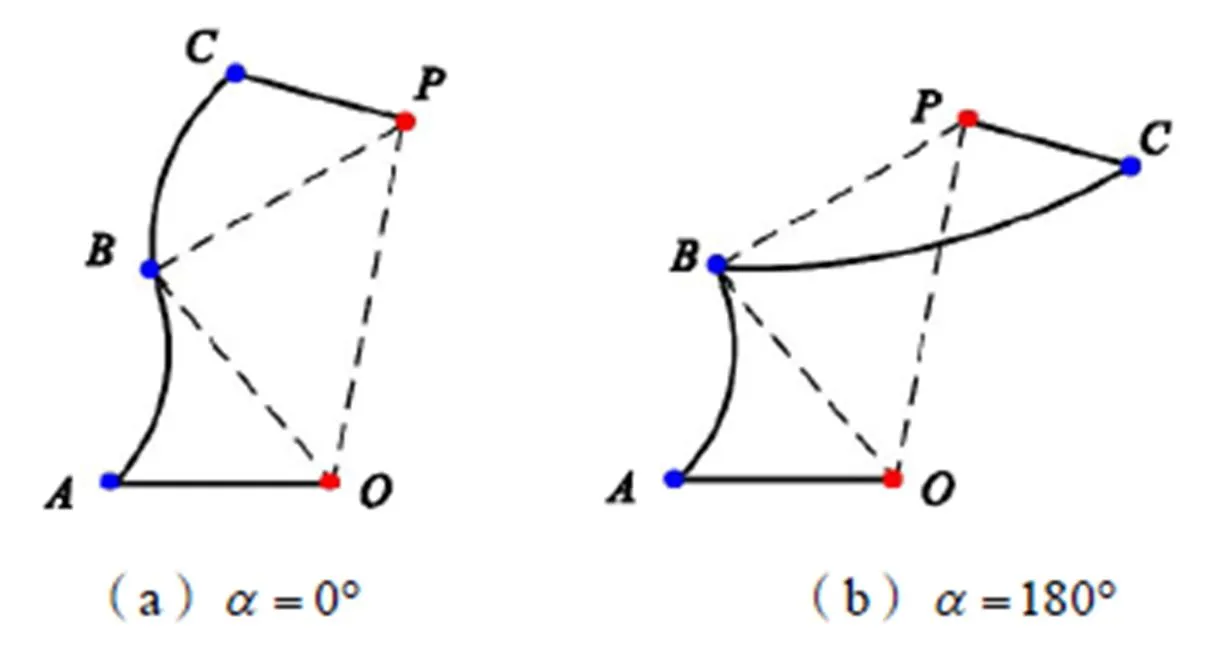
图3 支链末端点投影情况
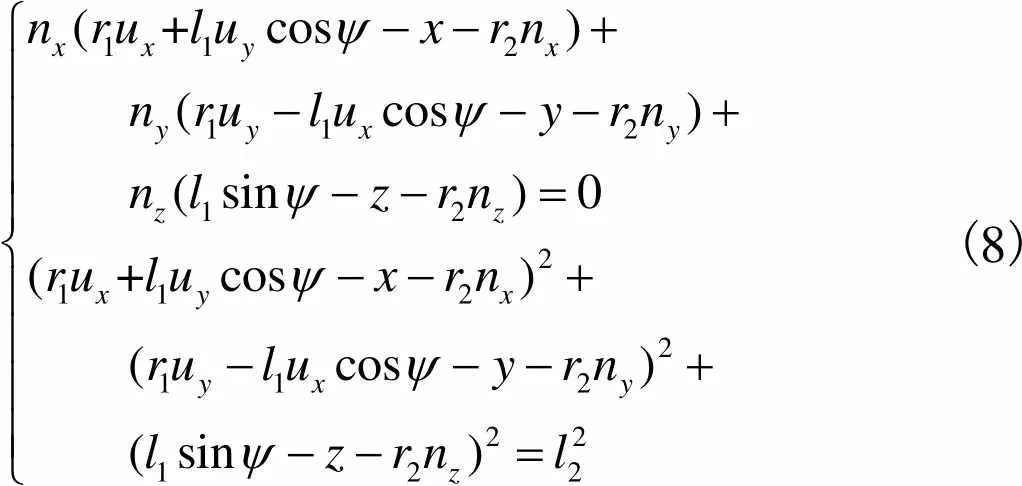
(8)
初始位形下,式(8)可简化为
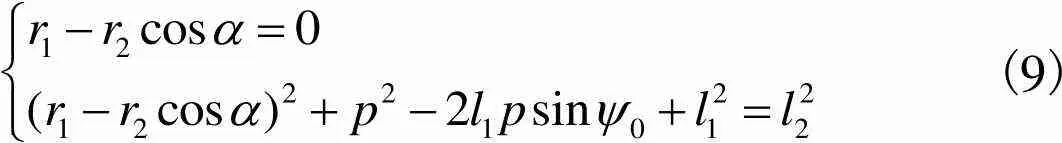
(9)
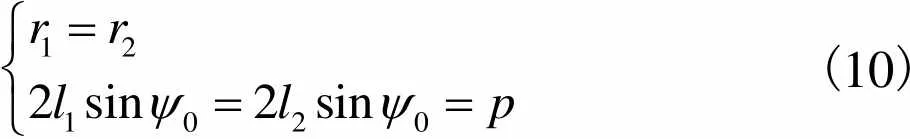
(10)

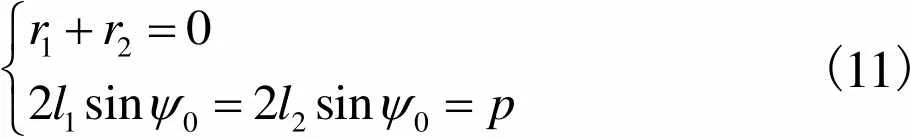
(11)
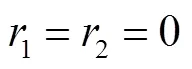
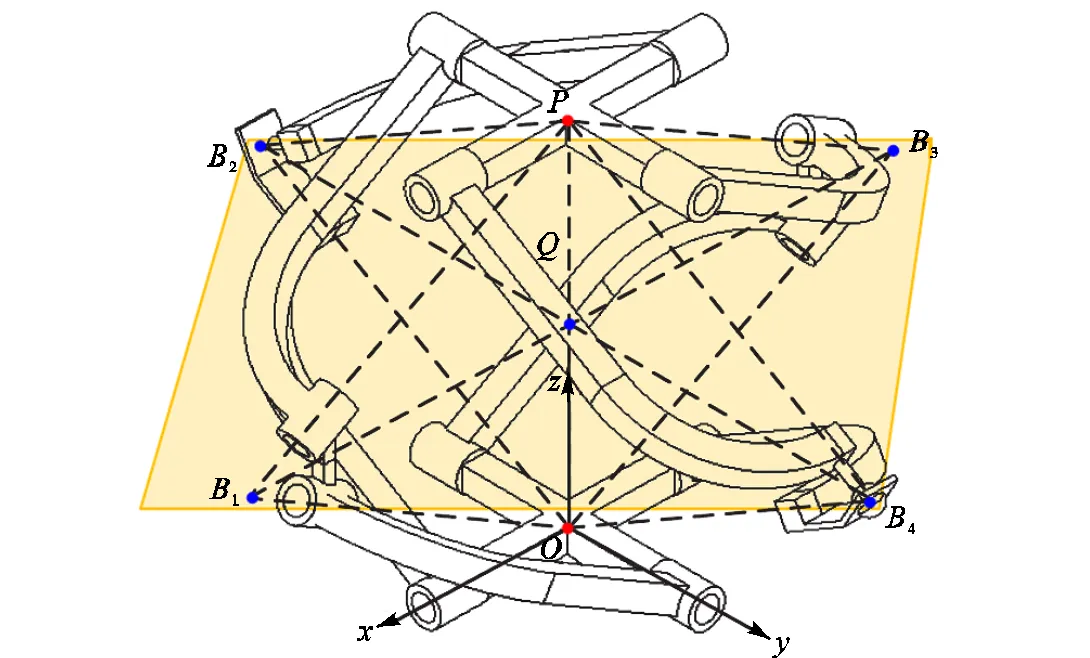
图4 2-RRRR&2-RSR机构结构示意
2 运动学分析
2.1 位置逆解
如图5所示,选择支链1与支链2的转动副1作为驱动关节.基于闭环矢量法,可建立机构的闭环矢量方程
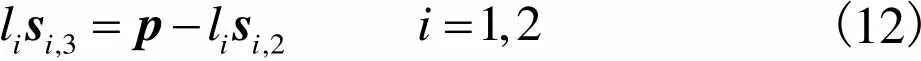
(12)
图5 机构组成支链
Fig.5 Assembled limbs of mechanism
式(12)左右两边分别与其自身做内积,得
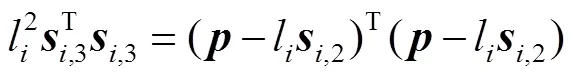
化简上式,可得
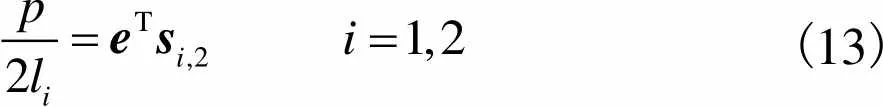
(13)
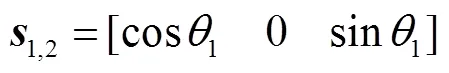
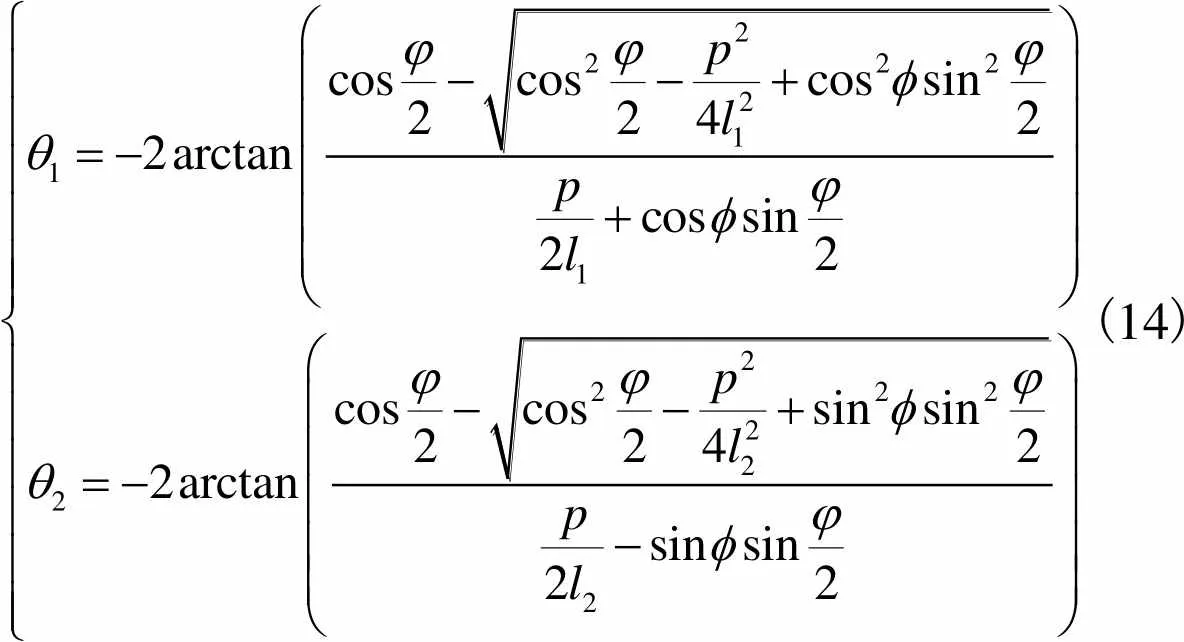
(14)
2.2 位置正解

(15)
由式(15)可得动平台中心点的位置坐标为
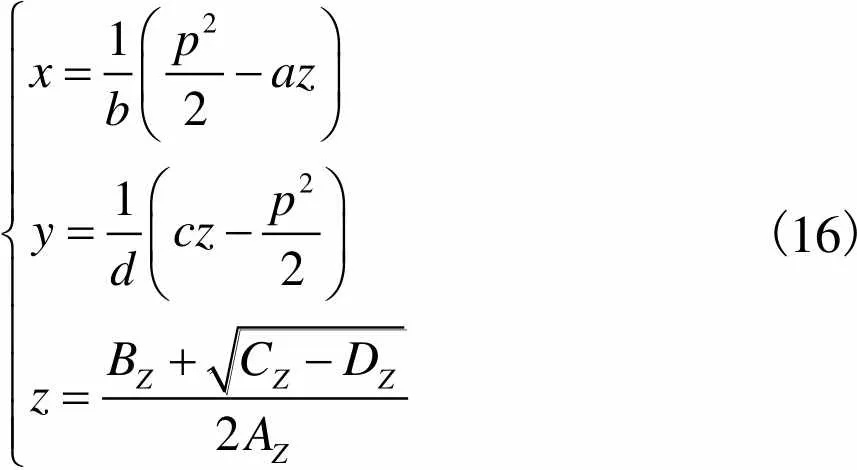
(16)
其中
以式(16)为基础,可解得机构动平台姿态角
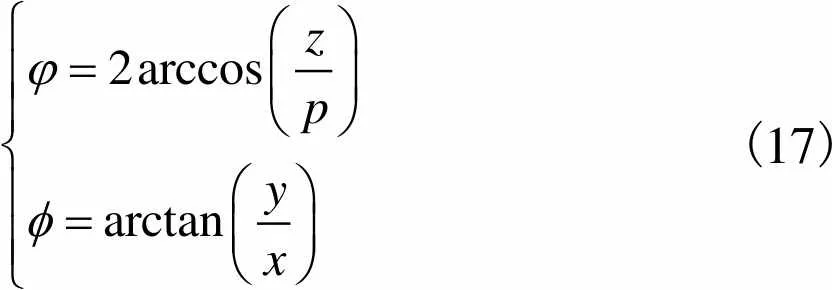
(17)
2.3 速度映射模型
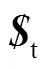
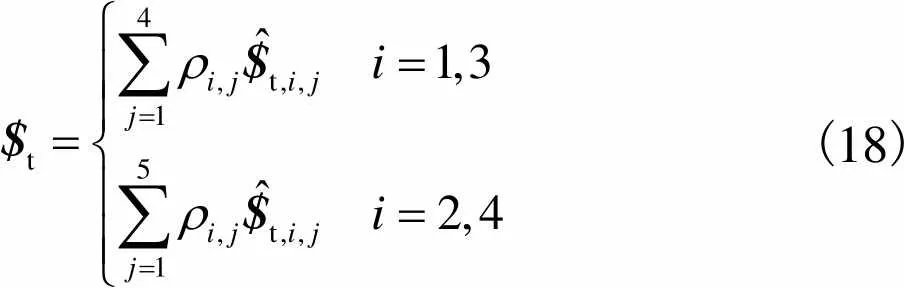
(18)
对于支链1与支链3,有
对于支链2与支链4,有
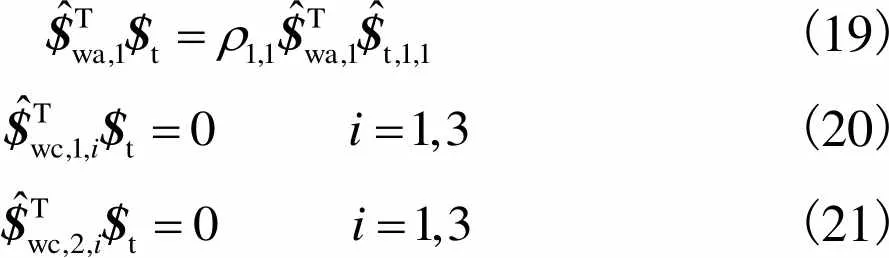
(19) (20) (21)
其中

(22)
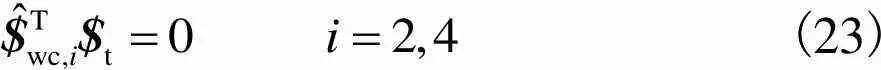
(23)
其中
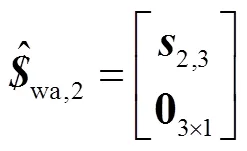
将式(19)~(23)整理为

(24)
其中

(25)
2.4 算 例
借助MATLAB软件,将动平台的姿态角代入机构位置逆解与速度映射模型,可得驱动副的角度与角速度变化情况,如图6与图7所示.将机构位置逆解所得驱动角变化情况代入机构位置正解模型,可得动平台姿态角变化曲线,如图8所示.由于位置正解模型所得动平台姿态角与给定姿态角相同,可验证机构位置正、逆解模型的有效性.
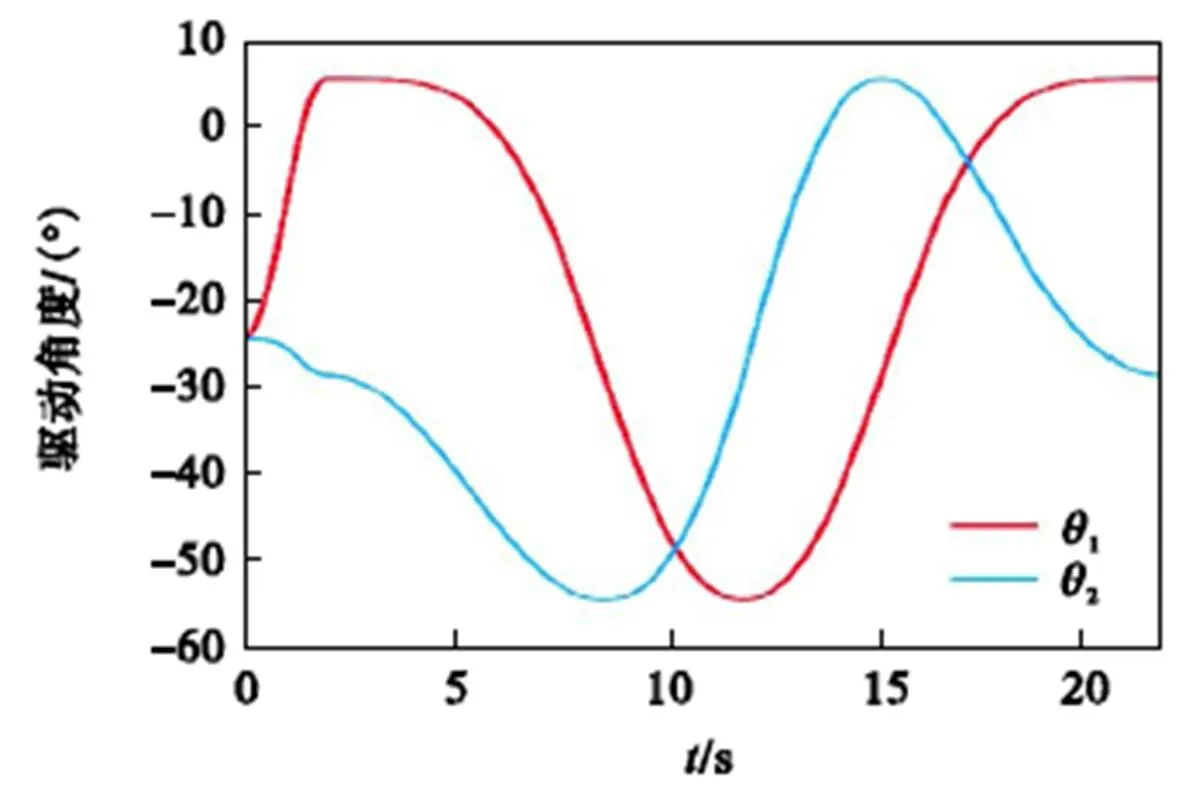
图6 驱动角度变化
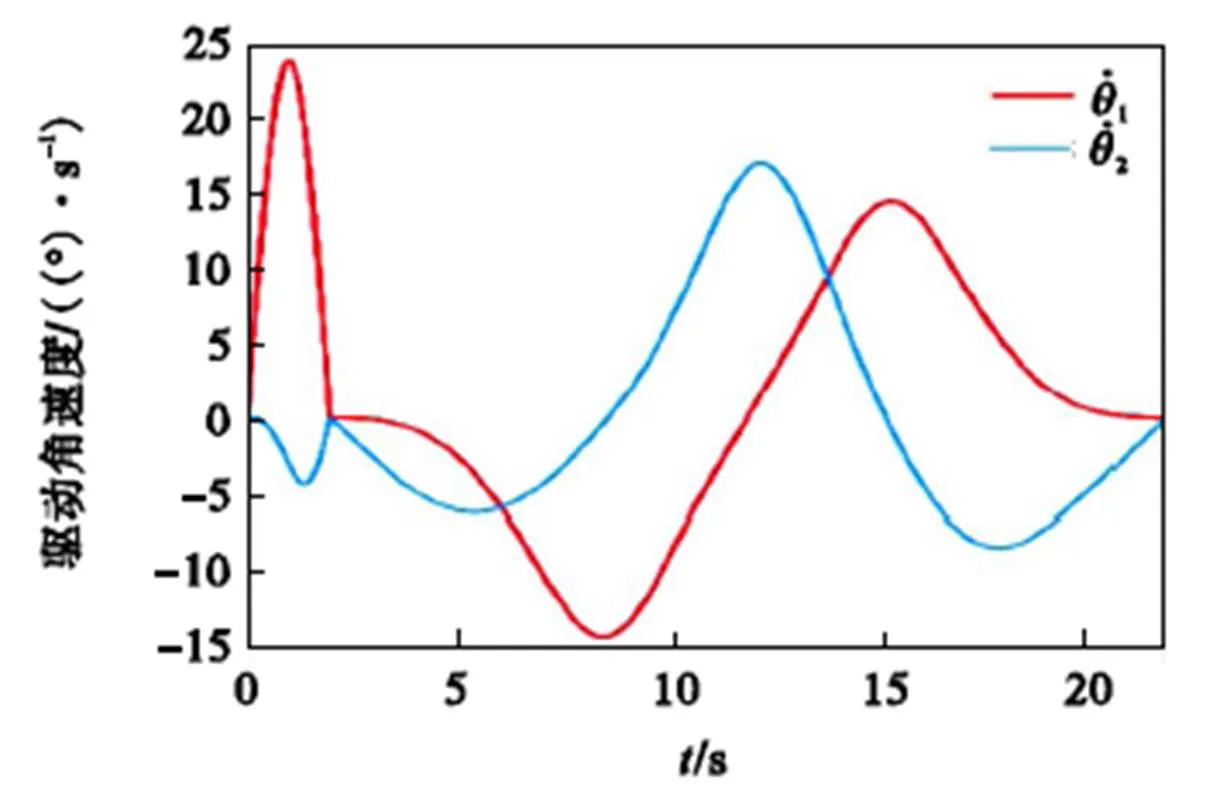
图7 驱动角速度的变化

图8 姿态角的变化
3 工作空间分析
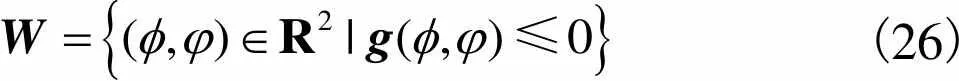
(26)
(1) 奇异性约束.
为了使机构在可达工作空间全域不出现奇异位形,需要对雅可比矩阵的行列式进行约束,即

(27)
(2) 转角范围约束.

(28)
(3) 连杆干涉约束.
机构中的支链杆件具有一定的几何尺寸,在运动过程中两连杆可能发生干涉.为避免影响机构性能,需设定连杆干涉约束条件为

(29)
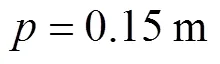
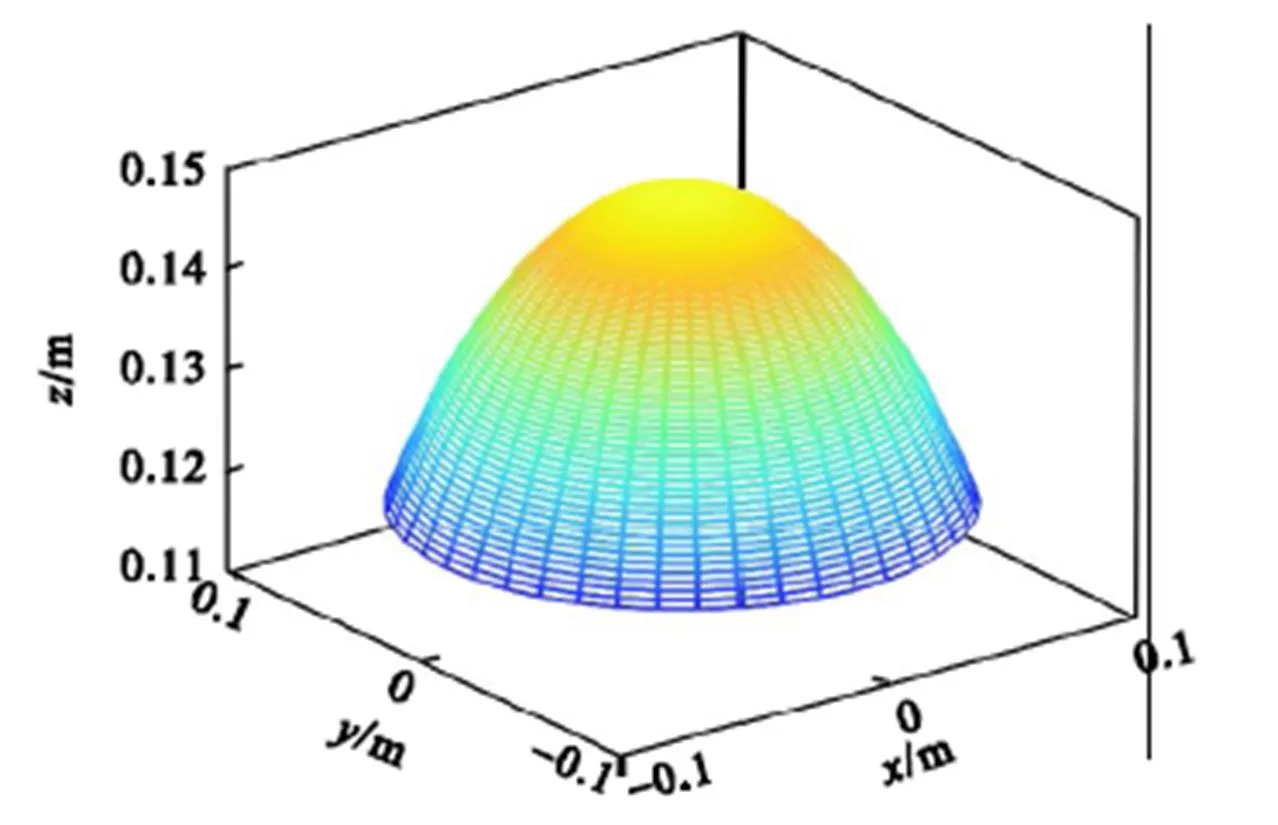
图9 动平台中心点位置工作空间
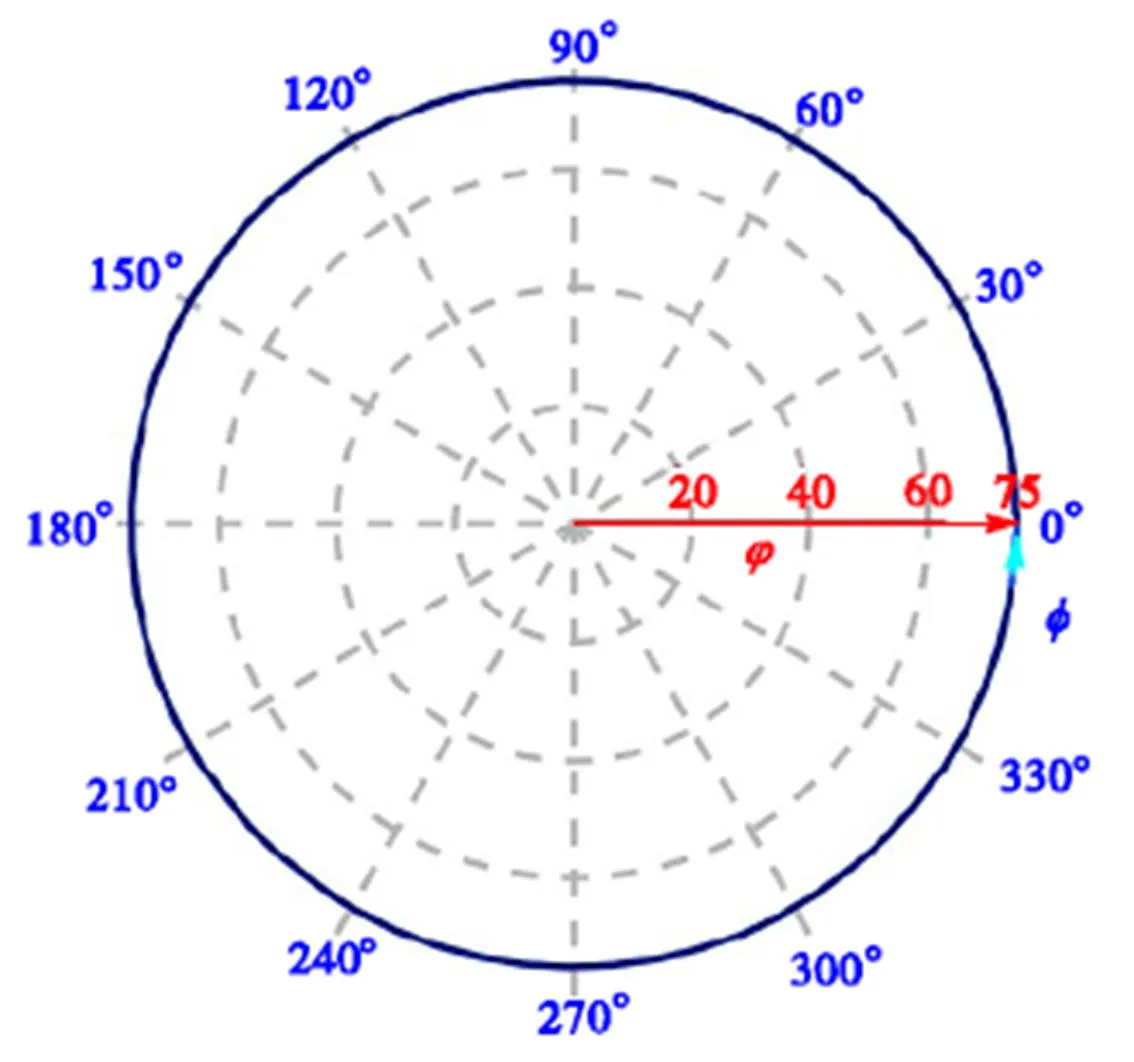
图10 角度工作空间
4 优化设计
4.1 尺度参数
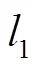
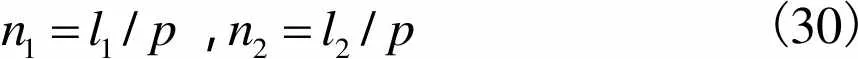
,(30)
4.2 评价指标
借助螺旋理论运动/力互易积的物理含义,定义可描述2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构瞬时功率传递特性的无量纲运动学性能评价指标
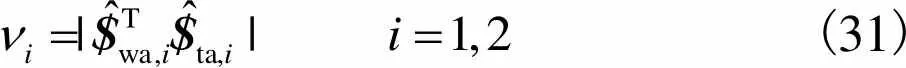
(31)
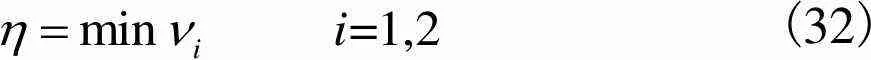
(32)
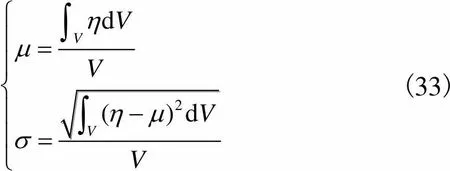
(33)
式中为机构工作空间的体积.
为综合考虑2-RRRR&2-RSR机构在工作空间内的运动学性能评价指标均值与波动,可构建机构全域性能评价指标为

(34)
4.3 约束条件
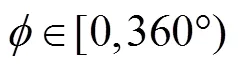

(35)
4.4 优化设计
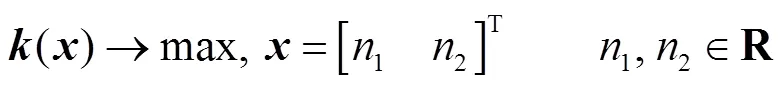
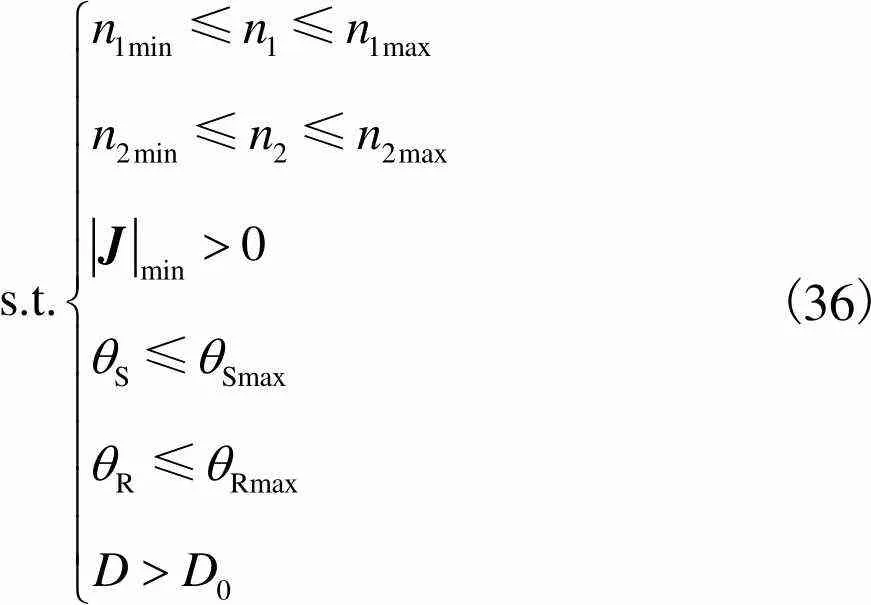
(36)
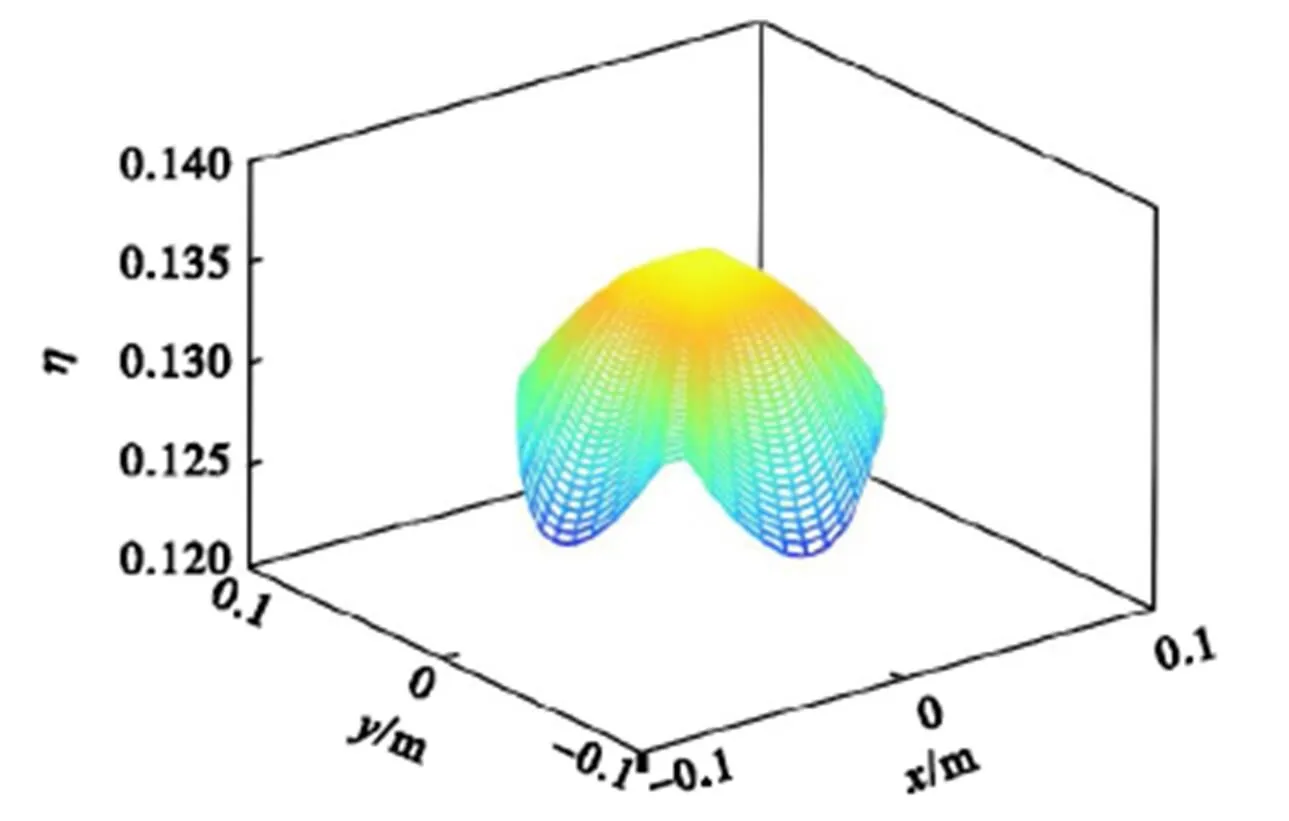
图11 运动学性能评价指标的分布情况
5 结 论
针对航空航天和仿生领域对大转角两转动并联机构的应用需求,本文以2-RRRR&2-RSR机构为研究对象,开展了构型分析与运动学优化设计.所得主要结论如下.
(1) 基于投影关系分析了2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构在给定工作空间内实现两自由度转动所需满足的几何条件,获得了机构参数特解.
(2) 以闭环矢量法为基础,开展了2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的位置逆解分析,推导了机构驱动角度与动平台姿态角间的映射关系;利用RRRR支链与RSR支链的运动特点,建立了机构动平台姿态角的正解模型,并基于软件仿真验证了正、逆解模型的有效性.
(3) 借助螺旋理论建立了2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的速度映射模型,构建了机构的广义雅可比矩阵,结合机构位置逆解,考虑工程实际经验,利用极限边界搜索法求解了机构工作空间.
(4) 定义了可描述并联机构瞬时功率传递特性的无量纲运动学性能评价指标,构造了尺度综合的目标函数,完成了2-RRRR&2-RSR并联机构的运动学优化设计.
[1] Gosselin C M,Caron F. Two Degree-of-Freedom Spherical Orienting Device:US 09/064553[P]. 1999-10-19.
[2] Lum M J H,Rosen J,Sinanan M N,et al. Kinematic optimization of a spherical mechanism for a minimally invasive surgical robot[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New Orleans,USA,2004:829-834.
[3] Baumann R,Maeder W,Glauser D,et al. The pantoscope:A spherical remote-center-of-motion parallel manipulator for force reflection[C]// IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Albuquerque,USA,1997:718723.
[4] 刘海涛,熊 坤,贾昕胤,等. 3 自由度冗余驱动下肢康复并联机构的运动学优化设计[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版,2018,51(4):357-366.
Liu Haitao,Xiong Kun,Jia Xinyin,et al. Kinematic optimization of a redundantly actuated 3-DOF parallel mechanism for lower-limb rehabilitation[J]. Journal of Tianjin University:Science and Technology,2018,51(4):357-366(in Chinese).
[5] 赵 庆,王攀峰,黄 田. 考虑链间耦合的高速并联机器人惯性参数预估方法[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版,2017,50(8):868-876.
Zhao Qing,Wang Panfeng,Huang Tian. An inertial parameter estimation method for high-speed parallel robots by considering inter-chain coupling[J]. Journal of Tianjin University:Science and Technology,2017,50(8):868-876(in Chinese).
[6] 谢胜龙,梅江平,刘海涛. 足底驱动型下肢康复机器人的运动学建模与轨迹跟踪控制研究[J]. 天津大学学报:自然科学与工程技术版,2018,51(5):443-452.
Xie Shenglong,Mei Jiangping,Liu Haitao. Kinematics modeling and simulation of trajectory tracking control of a foot-plate-based lower-limb rehabilitation robot[J]. Journal of Tianjin University:Science and Technology,2018,51(5):443-452(in Chinese).
[7] Dunlop G R,Jones T P. Position analysis of a two DOF parallel mechanism:The canterbury tracker[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory,1999,34(4):599-614.
[8] Rosheim M E. New high-angulation omnidirectional sensor mount[C]//International Symposium on Optical Science & Technology. USA,2002,4281:163-174.
[9] Sofka J,Nikulin V V,Skormin V A,et al. Laser communication between mobile platforms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,2009,45(1):336-346.
[10] Sofka J,Skormin V,Nikulin V,et al. Omni-wrist Ⅲ—A new generation of pointing devices,part Ⅰ:Laser beam steering devices—Mathematical modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems,2006,42(2):718-725.
[11] Sofka J,Skormin V. Integrated approach to electro-mechanical design of a digitally controlled high precision actuator for aerospace applications[C]//IEEE International Conference on Control Applications. Munich,Germany,2006:261-265.
[12] Wu Y Q,Li Z X,Shi J B. Geometric properties of zero-torsion parallel kinematics machines[C]//IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Taipei,China,2010:18-22.
[13] Yu J J,Dong X,Xu P,et al. Mobility and singularity analysis of a class of two degrees of freedom rotational parallel mechanisms using a visual graphic approach[C]// ASME International Design Engineering Technical Conferences & Computers & Information in Engineering Conference. Chicago,USA,2012,4(4):1027-1036.
[14] Wu K,Yu J J,Zong G H,et al. Type synthesis of 2- DOF rotational parallel manipulators with an equal-diameter spherical pure rolling motion[C]//ASME 2013 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference,Portland. Oregon,USA,2013,6A:V06AT07A042.
[15] Bonev I A. Geometric Analysis of Parallel Mechanisms[D]. Quebec:Department de Genie Mecanique,Universite Laval,2002.
[16] Qi Y,Sun T,Song Y M. Type synthesis of parallel tracking mechanism with varied axes by modeling its finite motions algebraically[J]. ASME Transactions,Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics,2017,9(5):054504.
[17] 黄 真,赵永生,赵铁石. 高等空间机构学[M]. 北京:高等教育出社,2006.
Huang Zhen,Zhao Yongsheng,Zhao Tieshi. Advanced Spatial Mechanism[M]. Beijing:Higher Education Press,2006(in Chinese).
[18] 赵延治,梁博文,曹亚超,等. 恒定雅可比3-PRRR移动并联机构及其传递性能研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(1):333-338.
Zhao Yanzhi,Liang Bowen,Cao Yachao,et al. 3-PRRR translational parallel mechanism with constant Jacobian matrix and its transfer performance analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2017,48(1):333-338(in Chinese).
[19] 杨继东,万彪刚,高俊东,等. Tripod并联机器人运动学分析与样机实验[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(10):390-397.
Yang Jidong,Wan Biaogang,Gao Jundong,et al. Kinematic analysis and experiment of Tripod parallel robot[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2016,47(10):390-397(in Chinese).
Topology Analysis and Kinematic Optimization of a 2-DoF Rotational Parallel Mechanism with Large Workspace
Song Yimin1,Zhou Pei1,Qi Yang2,Huo Xinming1
(1. Key Laboratory of Mechanism Theory and Equipment Design of Ministry of Education,Tianjin University,Tianjin 300354,China;2. Tianjin Key Laboratory of High Sepeed Cutting and Precision Machining, Tianjin University of Technology and Education,Tianjin 300222,China)
This work focuses on topology analysis and kinematic optimization of a new type of two degree-of-freedom(2-DoF)rotational parallel mechanism 2-RRRR&2-RSR to meet application requirements for 2-DoF rotational parallel mechanisms with large workspaces in the fields of aerospace and bionic design. First,geometric conditions necessary for the 2-RRRR&2-RSR parallel mechanism to realize 2-DoF rotations in a given workspace are analyzed on the basis of the projection relation of revolute joint axis,and specific parameter solutions of the mechanism for two projection cases are formulated. Second,the 2-RRRR&2-RSR parallel mechanism is subjected to inverse position analysis via closed-loop vector method,and mapping relation between actuated angles and attitude angles of the moving platform of the mechanism is derived. Then,forward solution of the attitude angles is obtained in accordance with motion characteristics of RRRR and RSR limbs. Accordingly,velocity mapping model of the 2-RRRR&2-RSR parallel mechanism is established based on screw theory,and generalized Jacobian matrix of the mechanism is constructed. The validity of the inverse/forward position mapping model and velocity mapping model of the mechanism is verified through software simulation. Third,in accordance with the kinematic characteristics of the 2-RRRR&2-RSR parallel mechanism,position workspace of the center point of the moving platform of the mechanism is solved using the limit boundary search method under constraints of singularity,allowable rotational angle range of hinges,and safe distance of connecting rods. The corresponding rotational workspace is obtained by transforming the aforementioned position workspace. Finally,dimensionless kinematic performance evaluation index of the 2-RRRR&2-RSR mechanism is defined as per the physical meaning of reciprocal product of motion and force screws in screw theory. Constraints of the mechanism are formed and optimal design of the scale parameters of the mechanism is completed. The results of this work can lay a theoretical foundation for prototype design and control strategy of rotational parallel mechanisms with large workspaces.
rotational parallel mechanisms;topology analysis;kinematics analysis;workspace;dimensional synthesis
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.51475321).
TH112.1
A
0493-2137(2019)09-0908-09
2018-10-23;
2018-11-30.
宋轶民(1971—),男,博士,教授.
宋轶民,ymsong@tju.edu.cn.
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51475321)
10.11784/tdxbz201810039
(责任编辑:金顺爱)

