CXCL-13通过激活PI3K-Akt信号通路对人骨髓间充质干细胞迁移的影响
沈雷 李永涛 孙石柱 姚立杰 王璐璐 刘丹阳 金海峰 张善强
[摘要] 目的 验证趋化因子-13(CXCL-13)通过激活PI3K-Akt信号通路对人骨髓间充质干细胞(hBMSC)迁移的影响。 方法 无任何刺激的hBMSCs为对照组;80 μmol/L CXCL-13刺激hBMSCs为CXCL-13组;hBMSCs先用25 nmol/L LY294002培养40 min,再添加80 μmol/L CXCL-13为PI3K抑制剂组;hBMSCs先用50 nmol/L Triciribine培养30 min,再添加80 μmol/L CXCL-13为Akt抑制剂组。细胞划痕实验和Transwell细胞迁移实验检测四组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率和细胞迁移率;酶联免疫吸附试验检测四组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白的表达。结果 CXCL-13组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率和迁移率均高于对照组,PI3K抑制剂组和Akt抑制剂组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率和迁移率均低于CXCL-13组(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);CXCL-13组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白含量均高于对照组,PI3K抑制劑组和Akt抑制剂组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白含量低于CXCL-13组(均P < 0.01)。 结论 CXCL-13激活PI3K-Akt信号通路促进hBMSCs迁移。
[关键词] 趋化因子-13;人骨髓间充质干细胞;Akt信号通路;细胞迁移;归巢
[中图分类号] R318.06 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)09(c)-0004-04
Effect of CXCL-13 on human bone marrow mesenchymal mtem cell migration by activating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway
SHEN Lei LI Yongtao SUN Shizhu YAO Lijie WANG Lulu LIU Danyang JIN Haifeng ZHANG Shanqiang
Department of Anatomy, Qiqihar Medical University, Heilongjiang Province, Qiqihaer 161006, China
[Abstract] Objective To verify C-X-C motif chemokine ligand-13 (CXCL-13) effect on human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSC) migration by activating PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Methods hBMSC without stimulation was control group. hBMSCs were stimulated with 80 μmol/L CXCL-13 as CXCL-13 group. hBMSCs were first cultured with 25 nmol/L LY294002 for 40 min, and then 80 μmol/L CXCL-13 were added as PI3K inhibitor group. hBMSCs were cultured with 50 μmol/L Triciribine for 30 min in advance and then 80 μmol/L CXCL-13 were added as Akt inhibitor group. Cell wound scratch assay and Transwell cell migration assay were used to detect the scratch area closure rate and cell migration rate of hBMSCs in four groups. The expression of human PI3K, Akt and P-Akt proteins in hBMSCs of four groups were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Results The hBMSCs scratch area closure rate and cell migration rate in CXCL-13 group were higher than those in control group, the hBMSCs scratch area closure rate and cell migration rate in PI3K inhibitor group and Akt inhibitor group were lower than those in CXCL-13 group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). The protein contents of human PI3K, Akt and P-Akt in CXCL-13 group were higher than those in control group, the protein contents of human PI3K, Akt and P-Akt in PI3K inhibitor group and Akt inhibitor group were lower than those in CXCL-13 group(all P < 0.01). Conclusion CXCL-13 activates the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway to promote the migration of hBMSCs.
[Key words] C-X-C motif chemokine ligand-13; Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell; Akt signaling pathway; Cell migration; Homing
慢性疾病会引起人体多种器官出现慢性组织损伤[1]。人骨髓间充质干细胞(hBMSCs)是再生修复作用理想的细胞[2-3]。趋化因子-13(CXCL-13)对乳腺癌等肿瘤细胞具有很好的逃避免疫效果[4]。MSCs具有逃避宿主免疫系统监视的能力[5],MSCs可表达CXCL-13等多种趋化因子[6],CXCL-13可促进MSCs分化为成骨细胞[7],MSCs迁移到损伤组织能力与肿瘤细胞转移过程相类似[8-9],但CXCL-13是否促进hBMSCs运动还需验证。
1 材料与方法
1.1 细胞
hBMSCs(No.CP-H166)购于武汉普诺赛科技有限公司。
1.2 主要仪器与试剂
人CXCL-13重组蛋白(No.801-CX-025)购于美国R&D公司;人磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K,No.ab207 484)、Akt(No.ab126433)、P-Akt(No.ab207452)酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒均购于Abcam公司;LY294002(No.S1105)、Triciribine(No.S1117)购于Selleck公司;550型酶标仪购于Bio-Rad公司。
1.3 实验分组与方法
1.3.1 细胞培养 hBMSCs用含10% FBS的α-MEM培养基培养。
1.3.2 实验分组 无任何刺激的hBMSCs为对照组;80 μmol/L CXCL-13刺激为CXCL-13组;hBMSCs先用25 nmol/L LY294002培养40 min,再添加80 μmol/L CXCL-13为PI3K抑制剂组;hBMSCs先用50 nmol/L Triciribine培养30 min,再添加80 μmol/L CXCL-13为Akt抑制剂组。
1.3.3 细胞划痕实验 6.5×105个/孔hBMSCs置于6孔板,1000 μL枪头划痕;按“1.3.2”添加不同试剂,培养12 h后,4%多聚甲醛溶液室温固定60 min。Image-Pro Plus 6.0.1(IPP 6.0.1)软件计算hBMSCs细胞数目,随后计算hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率。
1.3.4 Transwell细胞迁移实验 1.2×104个hBMSCs置于Transwell细胞小室内,下层腔室加入无血清的α-MEM培养基或相关试剂。37℃,5%CO2培养10 h。收集下室液体,800 g离心5 min,收集细胞并计数;擦除Transwell细胞小室内hBMSCs,4%多聚甲醛溶液室温固定60 min,0.5%结晶紫染色。IPP 6.0.1软件计算hBMSCs细胞数目[10],随后计算hBMSCs迁移率。
1.3.5 蛋白含量检测 RIPA细胞裂解液裂解各组hBMSCs,4℃,12 000 g离心5 min;BCA法测定蛋白浓度。人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt的ELISA试剂盒检测蛋白含量。所有实验均重复3次。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料用均数±标准差(x±s)表示,多组比较采用方差分析,两两比较采用q检验;计数资料用百分率表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
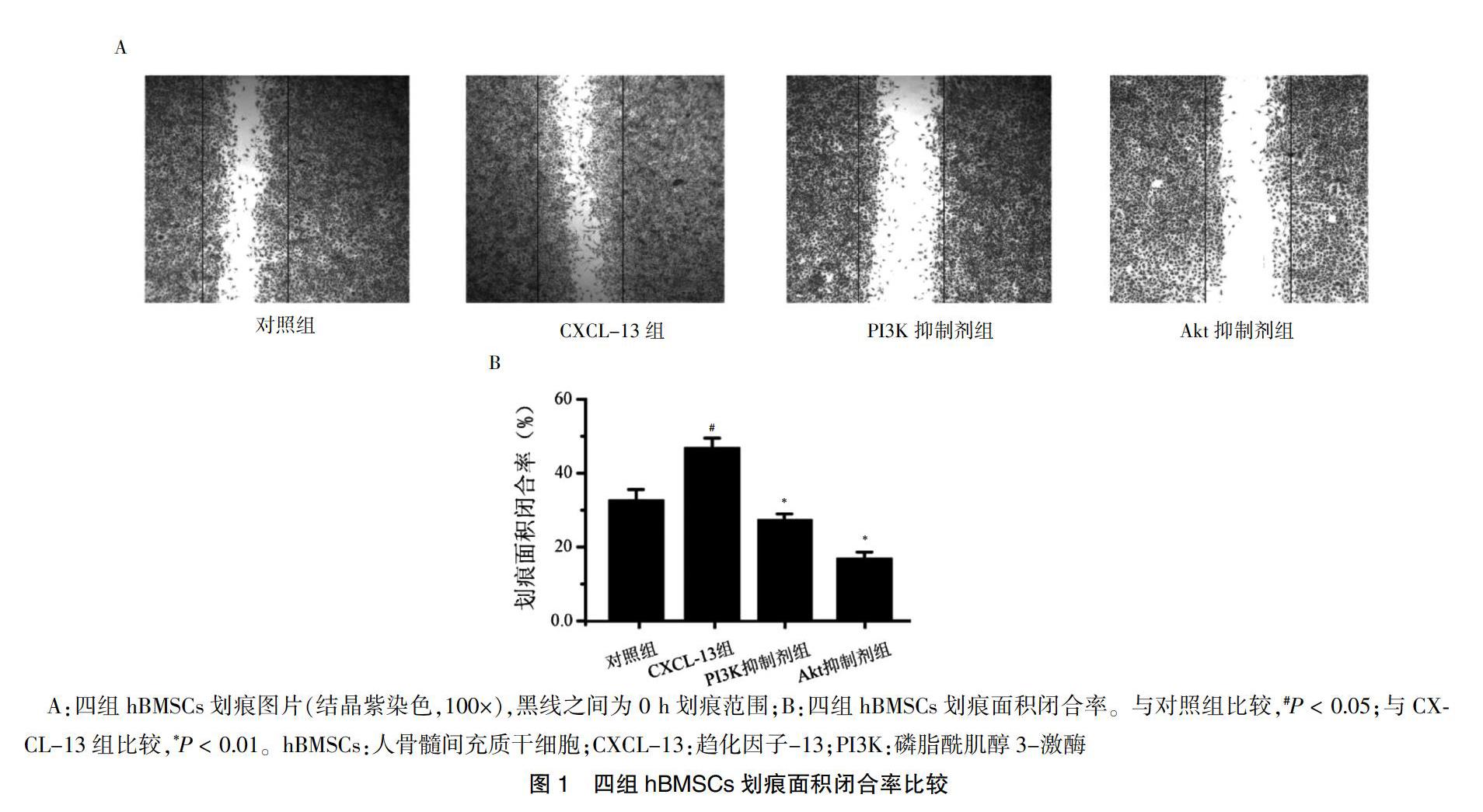
2.1 四组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率比较
CXCL-13组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率高于对照组,PI3K抑制剂组和Akt抑制剂组hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率低于CXCL-13组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。见图1。
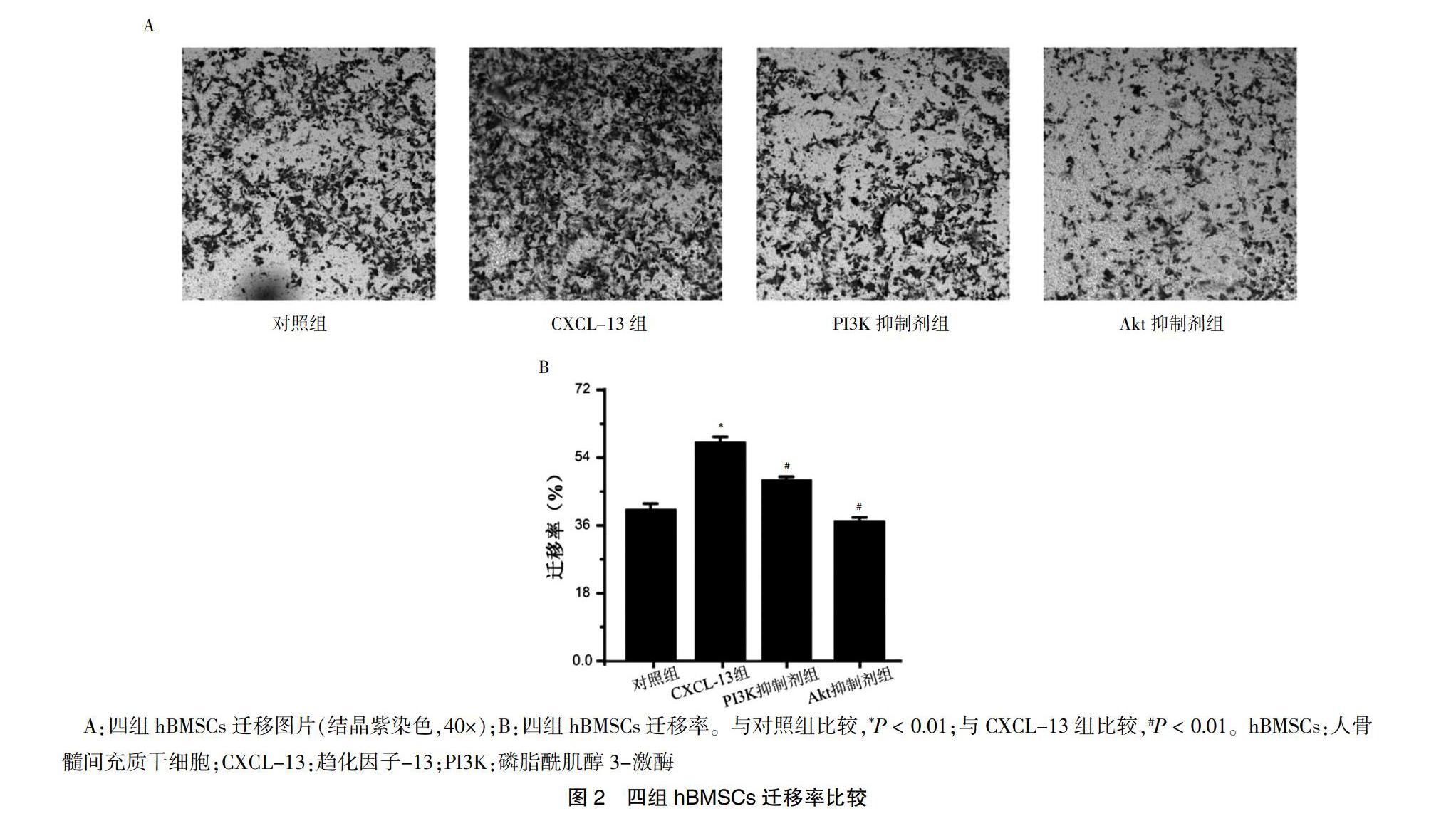
2.2 四组hBMSCs迁移率比较
CXCL-13组hBMSCs迁移率高于对照组,PI3K抑制剂和Akt抑制剂组hBMSCs迁移率低于CXCL-13组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见图2。
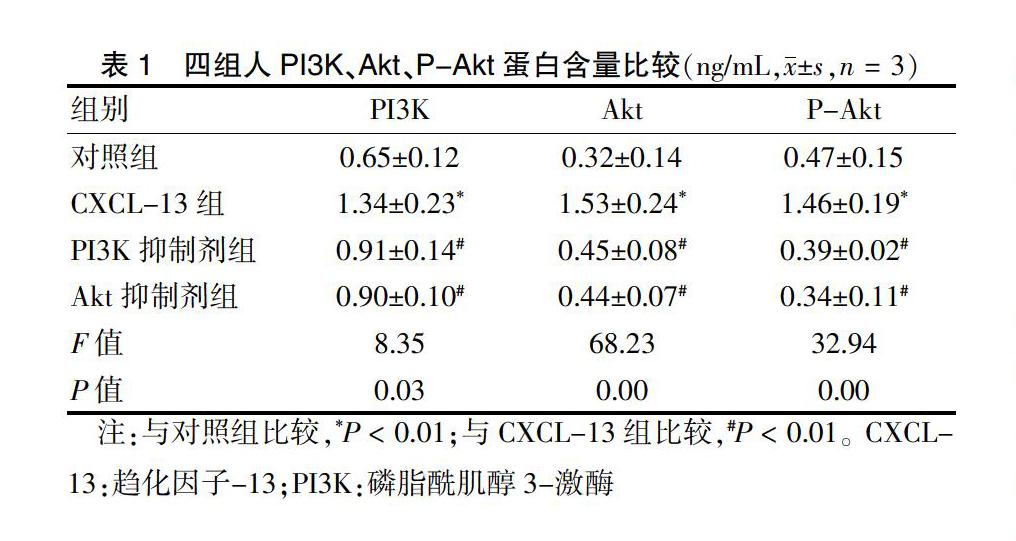
2.3 四组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白含量比较
CXCL-13组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白含量高于对照组,PI3K抑制剂组和Akt抑制剂组人PI3K、Akt、P-Akt蛋白含量低于CXCL-13组,差异均有高度统计学意义(均P < 0.01)。见表1。
3 讨论
BMSC具有较强迁移到损伤组织的能力[8]。MSCs分泌活性因子可帮助MSCs避免免疫排斥[6]。星形胶质瘤细胞分泌CXCL-13在抗免疫中起重要作用[9]。CXCL-13具有召集细胞归巢能力[10]。趋化因子是能促进细胞归巢能力的肽类家族[11]。CXCL-13属于趋化因子家族中的CXC亞科[12],CXCL-13与MSCs表面CXCR5受体结合,促进MSC成骨分化[13],还具有促进MSCs等干细胞分泌血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)等功能[14]。
本研究结果显示,添加CXCL-13后,hBMSCs划痕面积闭合率和细胞迁移率升高,提示CXCL-13能够结合hBMSCs表面CXCR5受体,促进细胞运动,对招募MSCs等细胞定向趋化具有积极意义。CXCL-13在慢性关节炎的关节囊滑膜层结缔组织中会明显高表达,同时在滑膜层结缔组织中发现嗜酸性粒细胞等免疫细胞大量集中,说明CXCL-13能够招集淋巴细胞或白细胞等免疫性细胞归巢[15]。乳腺癌等恶性肿瘤细胞分泌CXCL-13,可促进肿瘤细胞迁移[16-17]。本研究结果显示,与CXCL-13组比较,PI3K抑制剂组、Akt抑制剂组hBMSCs运动能力降低,提示PI3K-Akt信号通路与CXCL-13对hBMSCs的作用有关。抑制PI3K抑制蛋白后,PI3K下游Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达明显降低,而Akt抑制剂组与PI3K抑制剂组hBMSCs的PI3K蛋白表达比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),提示PI3K是CXCL-13作用于MSCs过程中Akt蛋白上游信号蛋白。CXCL-13与hBMSCs表面CXCR5受体结合,激活了PI3K蛋白激酶,上调Akt激酶,再依次活化下游雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)等 [18],最后引起微丝、微管收缩,启动细胞运动[16,18]。CXCL-13能激活Erk通路,促进小鼠MCF-7乳腺癌移植瘤增殖和血管新生,加速乳腺癌血管转移[19]。因此,不排除CXCL-13还会激活核因子(NF)-κβ、Erk、NIK信号通路[20],CXCL-13的分子机制还需要进行深入研究,关于CXCL-13能否对hBMSCs自噬发挥效应,还需要在细胞水平和分子水平进行深入验证。
[参考文献]
[1] Eid S,Sas KM,Abcouwer SF,et al. New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic complications:role of lipids and lipid metabolism [J]. Diabetologia,2019,62(9):1539-1549.
[2] Nagaishi K,Mizue Y,Chikenji T,et al. Umbilical cord extracts improve diabetic abnormalities in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and increase their therapeutic effects on diabetic nephropathy [J]. Sci Rep,2017, 7(1):8484.
[3] Debnath T,Chelluri LK. Standardization and quality assessment for clinical grade mesenchymal stem cells from human adipose tissue[J]. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther,2019,41(1):7-16.
[4] Jenh CH,Cox MA,Hipkin W,et al. Human B cell-attracting chemokine 1(BCA-1;CXCL13)is an agonist for the human CXCR3 receptor [J]. Cytokine,2001,15(3):113-121.
[5] Wang S,Zhu R,Li H,et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and immune disorders:from basic science to clinical transition [J]. Front Med,2019,13(2):138-151.
[6] Ahmadian Kia N,Bahrami AR,Ebrahimi M,et al. Comparative Analysis of Chemokine Receptor′s Expression in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from Human Bone Marrow and Adipose Tissue [J]. J Mol Neurosci,2011,44(3):178-185.
[7] Tian F,Ji XL,Xiao WA,et al. CXCL13 Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Inhibiting miR-23a Expression [J]. Stem Cells Int,2015,2015:632305.
[8] 李培蕾,林明.骨髓间充质干细胞归巢研究进展[J].中国心血管病研究,2010,8(1):65-67.
[9] 卜慧莲,郭海明,焦鵬飞,等.趋化因子CXCL13通过诱导星形胶质细胞活化参与骨癌痛的发生[J].肿瘤基础与临床,2019,32(3):185-189.
[10] 李永涛,王璐璐,姚立杰,等.缺氧条件下CXCL13通过MAPK信号通路促进人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和自噬[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2019,35(3):23-28.
[11] Donà E,Barry JD,Valentin G,et al. Directional tissue migration through a self-generated chemokine gradient [J]. Nature,2013,503(7475):285-289.
[12] Ponte AL,Marais E,Gallay N,et al. The In Vitro Migration Capacity of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells:Comparison of Chemokine and Growth Factor Chemotactic Activities [J]. Stem Cell,2007,25(7):1737-1745.
[13] Li ZW,Zhao L,Han QC,et al. CXCL13 inhibits micro RNA-23a through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2016,83:876-880.
[14] Viallard C,Larrivée B. Tumor angiogenesis and vascular normalization:alternative therapeutic targets [J]. Angiogenesis,2017,20(4):409-426.
[15] Armas-González E,Domínguez-Luis MJ,Díaz-Martín A,et al. Role of CXCL13 and CCL20 in the recruitment of B cells to inflammatory foci in chronic arthritis [J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2018,20(1):114.
[16] Biswas S,Sengupta S,Roy Chowdhury S,et al. CXCL13-CXCR5 co-expression regulates epithelial to mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells during lymph node metastasis[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat,2014,143(2):265-276.
[17] Wei YC,Lin C,Li H,et al. CXCL13 expression is prognostic and predictive for postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy benefit in patients with gastric cancer [J]. Cancer Immunol Immunother,2018,67(2):261-269.
[18] Xu L,Liang Z,Li S,et al. Signaling via the CXCR5 /ERK pathway is mediated by CXCL13 in mice with breast cancer [J]. Oncol Lett,2018,15(6):9293-9298.
[19] Garg R,Blando JM,Perez CJ,et al. Protein kinase C epsilon cooperates with PTEN loss for prostate tumorigenesis through the CXCL13-CXCR5 pathway[J]. Cell Rep,2017,19(2):375-388.
[20] Wang X,Shaalan A,Liefers S,et al. Dysregulation of NF-κβ in glandular epithelial cells results in Sj?觟gren′s-like features [J]. PLoS One,2018,13(8):e0200212.
(收稿日期:2020-02-26)

