护理风险管理在心血管内科临床护理干预中的应用效果分析
纪鹏
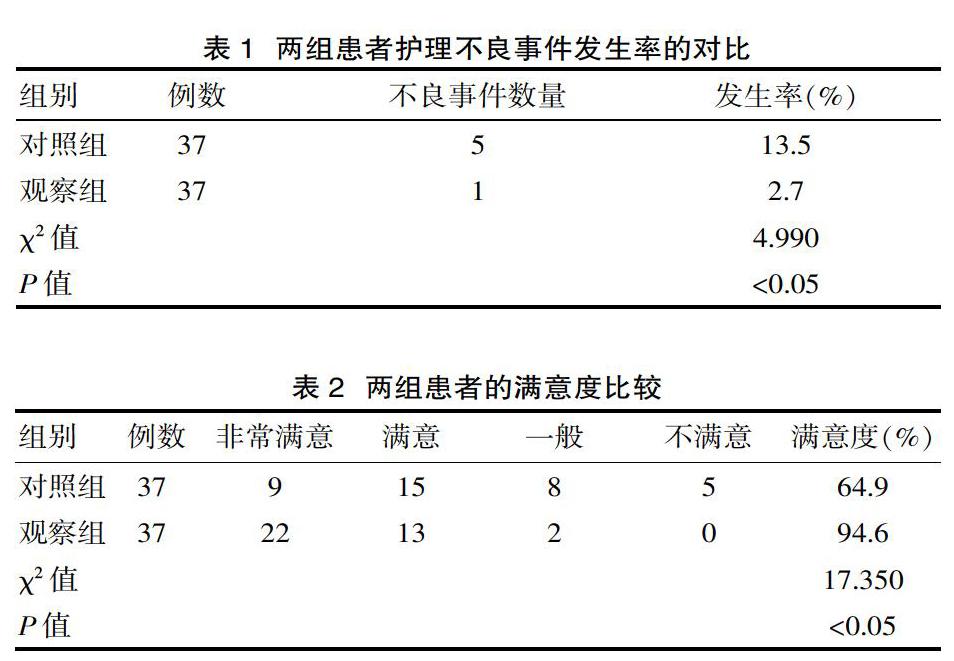
[摘要] 目的 探讨护理风险管理在心血管内科临床护理干预中的应用与价值。方法 该文随机选择该院心血管内科2018年11月—2019年11月收治的74例患者作为该次研究的对象,将其分为对照组和观察组,观察组进行在常规护理的基础上增加护理风险管理,通过完善各方面的制度、加强护理人员培训力度、做好风险防控工作等促进心血管内科临床护理工作顺利进行,而对照组37例患者采取常规护理管理,通过观察与比较两组的不良事件发生率及护理满意度得出结论。结果 观察组发生的不良事件的概率较低,为2.7%,而对照组的不良事件发生概率较高,为13.5%(P<0.05)。并且观察组的患者对于护理人员的工作满意程度更高,医患矛盾较少(P<0.05)。结论 护理风险管理有助于提升患者的护理效果,缓解医患之间的矛盾,同时促进医院各项管理制度不断趋于完善。
[关键词] 护理风险管理;心血管内科;护理干预;应用效果
[中图分类号] R271.1 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-5654(2020)09(b)-0100-03
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application and value of nursing risk management in clinical nursing intervention of cardiovascular medicine, and to understand whether nursing risk management is worth applying to clinical nursing intervention of cardiovascular medicine. Methods This article randomly selected 74 patients from the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine in the hospital from November 2018 to November 2019 as the subjects of this study. They were divided into a control group and an observation group. The observation group with nursing risk management on the basis of routine care, and the smooth progress of cardiovascular clinical care was promoted by improving various systems, strengthening the training of nursing staff, and doing a good job in risk prevention and control. The 37 patients in the control group adopted routine care management, observing and comparing the incidence of adverse events and nursing satisfaction between the two groups. Results The probability of adverse events in the observation group was low, 2.7%, while the probability of adverse events in the control group was higher, 13.5%(P<0.05). In addition, patients in the observation group were more satisfied with the work of nursing staff and had fewer doctor-patient conflicts(P<0.05). Conclusion Nursing risk management helps improve the nursing effect of patients, alleviate the contradiction between doctors and patients, and at the same time promote the continuous improvement of various management systems in the hospital.
[Key words] Nursing risk management; Cardiovascular medical; Nursing intervention; Application effect
心血管疾病又稱为人体内的循环系统疾病,不仅仅可以分为急性和慢性,还会因为动脉硬化而加速心血管疾病发作,这些病都有着一些相似的病因,并且在发病的过程中也会有相似之处,采取治疗的方法也有相同点,一旦发病会直接威胁到人们的生命健康安全[1]。相关人员通过实验发现[2],护理风险管理在心血管内科临床护理干预中的应用能够提高护理人员的护理能力水平与增强护理风险防范意识,有利于减少临床事故的发生,为了进一步了解实施风险管理在心血管内科临床护理干预工作中的效果,该院对2018年11月—2019年11月实施护理风险管理的74例患者进行了简要的分析。现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
随机选择该院74例患者作为该次的研究对象,该次研究通过伦理委员会批准并且征得患者意见。将其分为对照组和观察组,观察组37例患者,男21例,女16例;年龄在42~77岁之间;治疗时间为2个月~10年。对照组37例患者,男28例,女9例;年龄在42~78岁之间;治疗时间在3个月~11年。该次研究对象排除有过往病史、精神压抑不正常等患者。两组患者的性别、年龄、治疗时间等一般资料差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。具有可比性。

