Clinical Analysis of Early Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation in the Treatment of Acute Left Heart Failure Complicated with Respiratory Failure
Ting SUN, Tianfu GONG, Qianhui SUN, Jian ZHANG, Jiaming CAO
ICU, 98th Hospital Center, Chinese people's Liberation Army, Huzhou 313000, China
ABSTRACT:Objective To evaluate the efficacy of early and non-early non-invasive mechanical ventilation(NIV) for acute left heart failure and respiratory failure.Methods 29 cases of patients with acute left heart failure and respiratory failure treated by NIV were selected from our department from August 2016 to March 2019.According to the time of initiation of noninvasive mechanical ventilation, the patients were divided into the early treatment group(group A, treatment with NIV immediately after admission, n=15) and the non-early treatment group (group B, treatment with NIV for 2 h after admission, n=14), the improvement time, mechanical ventilation time, effective rate, intubation rate and fatality rate were compared between the two groups.Results The improvement time of patients in group A was (4.8±2.5) hours, the time of mechanical ventilation was (9.6±3.2) hours, the improvement time of group B was (6.8±2.6) hours, and the time of mechanical ventilation (12.8±4.4) hours.There were significant differences between the two groups (P<0.05).In group A, 13 patients were cured, 2 patients were intubated, 1 patient died, 10 patients in group B were cured, 4 patients were intubated, and 2 patients died.The difference in cure rate, intubation rate and mortality was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The treatment of acute left heart failure and respiratory failure is effective,and early application can improve the cure rate, reduce intubation and mortality.
KEY WORDS:Left ventricular failure; Respiratory Failure; Mechanical; Ventilation
The emphasis of oxygen therapy in patients with acute left heart failure is to obtain enough oxygen at the cell level, which is very important to prevent terminal organ insufficiency and multiple organ failure[1].In recent years, both domestic and overseas studies have shown that noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIV) is an effective auxiliary method to correct hypoxia and improve cardiac function in the treatment of respiratory failure caused by acute left heart failure complicated with pulmonary edema, and improves the success rate of rescue.In this study, the clinical efficacy of NIV in 29 patients with left heart failure was analyzed retrospectively, and the early and non-early use of NIV was compared.The report is as follows.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 General information From August 2016 to March 2019, 29 patients with acute left heart failure complicated with respiratory failure were selected.All cases met the diagnostic criteria of acute left heart failure, cardiac function grade IV (NYHA grade), and all of them met the diagnostic criteria of respiratory failure.According to the time of starting noninvasive mechanical ventilation, they were divided into early application group (group A) and non-early application group (group B,n=15, M 9, F 6, age 56-88 years).There were 9 cases of male, 5 cases of female, age 55-91 years old, There were no significant differences in sex, age,basic diseases and illness between the two groups.
1.2 Method According to the time of use of NIV, the patients were divided into two groups: group A (n=15),group A (n=14), group B (n=14), no matter whether the condition was improved or aggravated at the same time, after treatment with cardiotonic, diuretic,vasodilation, antispasmodic and sedation, there were 15 patients in group A with acute left heart failure complicated with respiratory failure.All patients were treated with oral and nasal masks for noninvasive mechanical ventilation.The improvement time,mechanical ventilation time, cure, catheterization and death were compared between the two groups.
The PB-840 ventilator was treated with its own noninvasive ventilation module.The mode of (BiPAP)ventilation was double level positive pressure airway(BiPAP) ventilation (equivalent to Psv Peep), respiratory frequency set to 12-14 times/min, inhaled oxygen concentration gradually decreased from 60%-80% to 30%-35%, inspiratory pressure (IPAP) 10-20 cm H2O,exhalation pressure (EPAP) 4-8 cm H2O.Respiratory parameters were adjusted according to ventilation,blood gas analysis, blood pressure and tolerance.
The improvement criteria[2]: (1) dyspnea was alleviated or disappeared, cardiac function was improved above grade 1; (2) wet rales and wheezing in the lungs disappeared completely; or a little wet rales had nothing to do with dyspnea; (3) chest radiography showed that the shadow of both lungs disappeared or returned to the manifestation before the onset of heart failure; (4) arterial blood gas returned to normal, or blood gas indexes improved significantly, with only mild hypoxia.
Invasive ventilation standard: patients with continuous deterioration of the disease during treatment.(1) The original consciousness disorder is worse or even coma; (2) Blood gas analysis: patients with pH<7.20 or FiO2>50%, PaO2<60mmHg, or PaO2>50 mmHg with progressive increase; (3) Those who cannot tolerate non-invasive mechanical ventilation and the condition has not improved.
1.3 Methods of statistics The statistical analysis was carried out by SPSS 13.0 software package, and the measurement data were expressed by mean standard deviation (Mean±SD).The data were tested by group T test and the counting data were measured by χ2test.The difference was statistically significant withP<0.05.
2 Results
The improvement time of group A was (4.8±2.5) h, the time of mechanical ventilation was (9.6±3.2) h, and that of group B was (6.8±2.6) h and (12.8±4.4) h.There was significant difference between the two groups (P<0.05).13 cases were cured, 2 cases were intubated, 1 case died in group A.In group B, 10 cases were cured, 4 cases were inserted, 2 cases died and 3 cases died of multiple organ failure caused by severe heart failure.There were significant differences in cure rate, catheterization rate and mortality between the two groups (P<0.05).Results were shown in Table 1.
3 Discussion
At present, noninvasive positive pressure ventilation is recommended for the treatment of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema as follows: after active drug treatment and oxygen therapy there were still dyspnea and hypoxia, respiratory frequency>30 times/min, pulse oxygen saturation-90% (oxygen uptake flow 4 L/min), strong spontaneous respiration,stable hemodynamics and good wearing cooperation ability[3,4].Fang Baominget al[5].Suggested that the application of noninvasive mechanical ventilation in the treatment of acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema should be relaxed and that noninvasive mechanical ventilation should be used as soon as it was diagnosed in routine.In this study, noninvasive mechanical ventilation was compared between early(immediately after routine treatment) and non-early (2 hours after routine treatment).The results showed that the improvement time, mechanical ventilation time,intubation rate and mortality of patients treated with NIV were significantly shortened, which were basically consistent with those of Fang Baoming.Consider the possibility of early application of noninvasive mechanical ventilation to correct hypoxia, reduce pulmonary edema, prevent respiratory muscle fatigue,prevent the further deterioration of the condition is related.Therefore, we suggest that once acute left heart failure and respiratory failure are diagnosed,noninvasive ventilation should be carried out as soon as possible to avoid deterioration of the disease and reduce intubation and mortality.
In the process of practical use, we have the following experience: (1) it is necessary to pay close attention to the tightness of the mask, such as the loosening of the mask, which can lead to excessive air leakage, lead to false trigger or bad trigger of ventilator,and affect ventilation effect and oxygenation.If the mask is too tight, the ventilation time is too long, it is easy to cause facial injury and patient discomfort,compliance decreases.(2) strengthen respiratory tract management, maintain a certain ability of spontaneous sputum excretion, timely removal of respiratory secretions, close observation of tidal volume, heart rate, blood pressure, consciousness and other changes,once the condition deteriorate, mental confusion,weak spontaneous breathing, more sputum and weak expectoration,etc., should be treated with invasive mechanical ventilation in time and strictly Grasp the indication of invasive ventilation in order to avoid the delay of the condition.(3) Non-invasive ventilation should be used in patients with severe pulmonary underlying disease or hypotension.(4) During thetreatment, the change of heart work enzyme should be monitored, and the patients with severe chest pain should be used with caution.When the pulmonary edema is improved, the ventilation pressure should be moderately reduced to reduce the suppression of the cardiac function by excessive positive pressure ventilation.
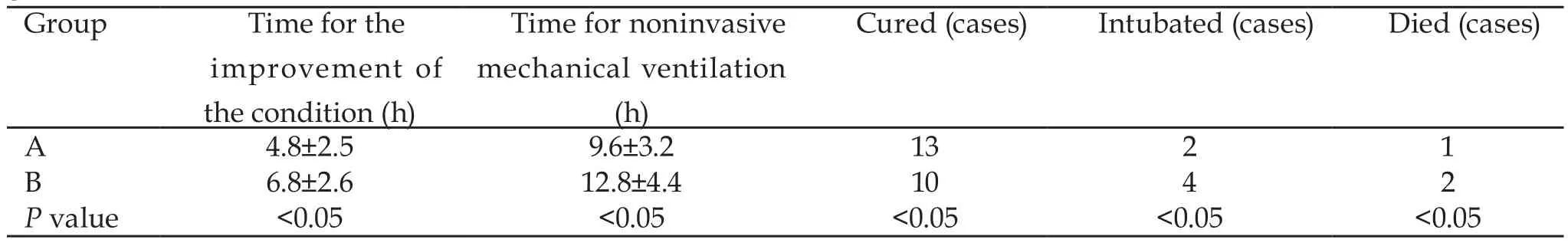
Table 1 Comparison of improvement time, mechanical ventilation time, effective, intubation and death between the two groups
The results show that NIV treatment of acute left heart failure is effective, and the application of NIV can correct hypoxia in time, increase the cure rate, reduce intubation and mortality.Therefore, the non-invasive mechanical ventilation indication should be relaxed properly.Once the diagnosis is conducted at the same time of routine treatment, non-invasive mechanical ventilation should be used immediately.However,the indication of invasive ventilation shall be strictly controlled, and those who cannot tolerate non-invasive ventilation or the patients with worse conditions after treatment shall be given invasive ventilation treatment in time.

