MiR-15a-5p in neutrophil exosomes promotes macrophage apoptosis through targeted inhibition of BCL2L2
KE Qiao, HU Long-hui, RUAN Chu-jun, LI Min,3✉
1.Emergency and Trauma College of Hainan Medical University, Haikou 570311, China
2.Emergency Center of Hainan Medical University Affiliated Hainan Hospital, Haikou 570311, China
3.Key Laboratory of Emergency and Trauma, Ministry of Education, Haikou 570311, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the possible mechanism of neutrophil exosomes regulating macrophage apoptosis.Methods: neutrophils were induced by lipopolysaccharide, inflammatory factors were detected by ELISA, the morphology of exosomes was identified by electron microscope,and the expression of mir-15a-5p in exosomes was detected by RT-PCR; Raw267.4 macrophages was treated with neutrophil exosomes and mir-15a-5p mimic respectively,CCK8 to detect cell viability, flow cytometry to detect apoptosis; The binding sites of mir-15a-5p and BCL2L2 were predicted and verified by double luciferase experiment; RT-PCR and Western blot verified that mir-15a-5p regulate the expression of BCL2L2.Results:lipopolysaccharide induced neutrophil inflammatory factors IL-2, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α.The morphological characteristics of exosomes were observed by electron microscope.Mir-15a-5p was significantly overexpressed in neutrophil exosomes induced by lipopolysaccharide;Lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophil exosomes and mir-15a-5p simulants can promote raw267.4 macrophage apoptosis and inhibit its cell viability; Targetscan database predicted that mir-15a-5p and BCL2L2 had binding sites.Double-luciferase experiment verified that mir-15a-5p and BCL2L2 bound through binding sites; Mir-15a-5p mimic was transfected into raw267.4 macrophages which inhibit the expression of BCL2L2 mRNA and protein.Conclusion:inflammatory neutrophils may promote raw267.4 by secreting exosomes containing mir-15a-5p and inhibiting BCL2L2 by targeting macrophage apoptosis.This may provide a theoretical basis for further understanding the molecular mechanism of inflammatory regulation of neutrophils and macrophages.
1.Introduction
Neutrophils are the most abundant leukocytes in the human lymphatic system and play a role in innate immunity by accumulating at inflammatory and injury sites[1,2].Studies have shown that these cells can regulate macrophages through extracellular vesicles, thereby participating in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated acute lung injury[3,4], but the molecular mechanisms are not fully understood.
Extracellular vesicles are a type of cell-derived small vesicles with a lipid bilayer membrane, ranging in size from 40 to 150 nanometers, and containing DNA, RNA, and proteins[5].In recent years, they have been discovered as important mediators of specific intercellular communication[6].In particular, the role of microRNAs(miRNAs), which are approximately 22 nucleotides in length, in extracellular vesicles has attracted much interest from researchers[7,8].Studies have shown that miR-15a-5p is downregulated in various tumors and plays a role in inhibiting tumor proliferation and metastasis[9-11].Furthermore, miR-15a-5p has been found to regulate the inflammatory response of macrophages by targeting TNIP2 and participate in the occurrence and development of sepsis[12].Although it has been demonstrated that miR-15a-5p can regulate the inflammatory response of macrophages, there is currently no research on how it is transferred through extracellular vesicles in the process of neutrophil-mediated regulation of macrophages.
This study investigates the expression of miR-15a-5p in neutrophilderived extracellular vesicles, and the effects of extracellular vesicles and miR-15a-5p mimics on the proliferation and apoptosis of macrophage raw267.4, as well as the verification of the interaction between miR-15a-5p and BCL2L2.The results suggest that miR-15a-5p is highly expressed in neutrophil-derived extracellular vesicles induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and may promote the apoptosis of raw267.4 macrophages by targeting and inhibiting the expression of BCL2L2 in macrophages.This might present a novel mechanism whereby inflammation-induced neutrophils modulate macrophage apoptosis through extracellular vesicle miR-15a-5p.This is of great significance in understanding the role of neutrophils and macrophages in microenvironmental regulation, and provides new insights and directions for research and clinical treatment of related diseases.
2.Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental Animals
Male C57BL/6J mice were purchased from Shanghai Slack Laboratory Animals Co., Ltd, and were provided with sufficient water and food.They were raised in a pathogen-free environment,and the care and handling of the animals were in accordance with the animal management and ethics of Hainan Medical University.
2.2 Experimental Cells
According to the literature[13], neutrophils were induced in the abdominal cavity of 8-10-week-old C57BL/6J mice.In brief,mice received two intraperitoneal injections of a 1 ml 9% casein solution on alternate days.The mice were sacrificed 3 h after the second injection and the peritoneal lavage fluid was collected and centrifuged to obtain the cell pellet.Further, the cells were isolated using discontinuous density gradient centrifugation according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Sigma, #1119 and #10771).The isolated cells consisted of 90% neutrophils.Raw267.4 macrophages were purchased from Wuhan Pusaite Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd.(CL-0190).Following isolation, neutrophils were resuspended in complete medium (RPMI1640, containing 10%exosome-free fetal bovine serum, with the addition of 50 mg/ml penicillin/streptomycin) at a concentration of 106cells/mL, and then induced with 15μM lipopolysaccharide LPS (purchased from Sigma,SMB00610) at 37 ℃ for 12 h to activate the neutrophils.An equal volume of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) was used for 12 h as a negative control.
2.3 Isolation and Identification of Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular vesicles were extracted using ultracentrifugation.The collected samples were centrifuged at 12,000 g at 4℃ for 45 min to remove larger vesicles, followed by two centrifugations at 110,000 g at 4 ℃ for 70 min to obtain the precipitate.The extracted extracellular vesicles were fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and observed using transmission electron microscopy (JEOL, JEM-2100) at 80 kV and 10,000 times magnification.
2.4 ELISA Detection
IL-2 (ml063136), IL-6 (ml063159), IL-10 (ml037873), and TNF-α(ml002095) kits were purchased from Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd.According to the instructions provided with the kits, standard curves were plotted using standard samples, and the OD values of the samples were measured using a spectrophotometer(Shimadzu UV-1900).The corresponding concentrations of the samples were calculated using the standard curves.
2.5 RT-PCR Detection
Total RNA was extracted from cells and extracellular vesicles using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen, 15596-026), and complementary DNA was synthesized using a reverse transcription kit (Toyobo,fsq-101) according to the instructions provided.RT-PCR was performed using SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., SR1110).The expression data were normalized to the reference genes GAPDH or U6, and the relative expression levels were evaluated using the 2-ΔΔCtmethod.Primers for BCL2L2, GAPDH, miR-15a-5p, and U6 were purchased from Guangzhou Anno Biological Technology Co., Ltd.The primer sequences used in this study are as follows: miR-15a-RT: GTCG TATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTGCACTGGA TACGACCACAAAC, miR-15a-F: ATCCAGTGCGTGTCGTG,miR-15a-R: TGCTTAGCAGCACATAATG, BCL2L2-F:GGTGGGACAAGTGCAGGATT, BCL2L2-R:TCTGTTCCGTGA CCATCCAG, U6-RT: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTG CACTGGATACGACAAAATATGG, U6-F: TGCGGGTGCTCGCT TCGGCAGC, U6-R:CCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT, GAPDHF:GGTTGTCTCCTGCGACTTCA, GAPDH-R:CCCTAGGCCCCT CCTGTTAT.
2.6 Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer containing complete protease and phosphatase inhibitors (MedChemExpress, HY-K1001).Each sample loaded 30 μg of protein onto SDS-PAGE gels, which were then transferred to 0.22 μm PVDF membranes.The membranes were blocked and then incubated overnight at 4 ℃ with primary antibodies, followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies at room temperature.Finally, chemiluminescent detection was performed using Thermo-Pierce chemiluminescent substrate(Thermo, 34577), and the observation and imaging were conducted with an automated chemiluminescence imaging analysis system(Shanghai Tanon Technology Co., Ltd., Tanon 5200).The primary antibodies used in the experiment were BCL2L2 polyclonal antibody(16026-1-AP) and GAPDH monoclonal antibody (60004-1-Ig),purchased from Wuhan Sanying Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
2.7 Cell Viability Assay (CCK8)
After respective treatments, 5×103cells were seeded into each well of a 96-well plate, with three replicates per treatment group.Cell viability was evaluated using a CCK-8 assay kit (Dojindo Molecular Technologies, FC101-03) on days 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 posttreatment.Ten microliters of CCK-8 reagent were mixed with cells and incubated for 2 h.The final absorbance at 450 nm was measured in each well using a microplate reader (Shimadzu Corporation, UV-1900).
2.8 Flow Cytometry Analysis of Cell Apoptosis
After 48 h of culture, all treated cells were collected, and apoptosis rate was measured using an Annexin V-FITC apoptosis detection kit(Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd., E-CK-A211).The harvested cells were centrifuged and washed in ice-cold PBS buffer (purchased from Absin Biotechnology Co., Ltd., abs961).Subsequently, the cells were prepared as a suspension in binding buffer (100 μL)containing Annexin V-FITC (5 μL) and propidium iodide solution(5 μL), and incubated in the dark for 15 min.Apoptosis proportions were determined on a flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, FACSAria).
2.9 Dual-Luciferase Assay
The potential binding sites of miR-15a-5p and BCL2L2 were predicted through the Targetscan database (http://www.targetscan.org/).BCL2L2 3’ UTR wild-type and mutant sequences were synthesized and constructed into the luciferase plasmid.They were then co-transfected with miR-15a-5p mimic and renal plasmid into 293T cells.Firefly and Renilla luciferase expressions were detected using an enzyme marker (Shanghai Biospec Biotechnology Co.,Ltd., ReadMax 1200).
2.10 Statistical Analysis
The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to check for normal data distribution.Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation (±s) for normally distributed data.Student’s t-test was used for the comparison between two groups.One-way ANOVA was applied for comparing multiple groups, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test and plotting using GraphPad Prism 8 software.Values of P<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1 miR-15a-5p is significantly overexpressed in exosomes from neutrophils in an inflamed state
Following treatment of neutrophils with lipopolysaccharides(LPS) and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) respectively, ELISA results showed that the concentrations of inflammation factors IL-2,IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α in the LPS-treated group (LPS group)were 190.66±6.94 pg/mL, 66.61±2.46 pg/mL, 18.80±0.88 pg/mL, 180.73±3.00 pg/mL, respectively.These were significantly higher than those in the PBS-treated group (PBS group), where the concentrations of IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α were 15.69±0.76 pg/mL (t= 43.38, P<0.001), 6.29±2.18 pg/mL (t= 31.81, P<0.001),3.39±0.10 pg/mL (t= 30.12, P<0.001), and 77.05±1.06 pg/mL(t=56.46, p<0.001), respectively, as shown in Figure 1A.These results suggest that LPS successfully induced an inflamed state in neutrophils.
Extractions of exosome in the supernatant from inflamed neutrophils were observed under a transmission electron microscope.Results suggested the structures of exosomes with a double-layer membrane, a recessed center, and a “persimmon cake” shape, as shown in Figure 1C.This indicates that our method of separating exosomes is feasible and successful.
Exosomal RNA was extracted and the expression of miR-15a-5p in the exosomes was detected by RT-PCR.The results showed that the relative expression of miR-15a-5p in the LPS group was 3.23±0.20,significantly higher than the 0.97±0.06 in the PBS group (t=18.59,P<0.001), as shown in Figure 1B.This suggests that miR-15a-5p is significantly overexpressed in exosomes from neutrophils in an inflamed state.
3.2 Exosomes from Neutrophils in the Inflammatory State Promote Apoptosis in raw267.4 Macrophages via miR-15a-5p
Flow cytometry analysis revealed that the apoptosis rate in the exosome group derived from neutrophils treated with LPS (LPSexo) (8.79±0.30) % was significantly higher than that in the exosome group derived from neutrophils treated with PBS (PBSexo) (4.53±0.11) % (t=23.25, P<0.001).The apoptosis rate in the miR-15a-5p mimic transfection group (miR-15a-5p mimic)(10.57±0.59) % was significantly higher than that in the negative control transfection group (NC) (4.51±0.13) % (t=17.43, P<0.001),as shown in Figure 2A and Figure 2B.
CCK-8 assay results showed that the cell viability in the LPSexo group was significantly lower than that in the PBS-exo group(t=15.52, P<0.001).The cell viability in the miR-15a-5p mimic transfection group (miR-15a-5p mimic) was significantly lower than that in the negative control transfection group (NC) (t=10.28,P<0.001), as shown in Figure 2C.
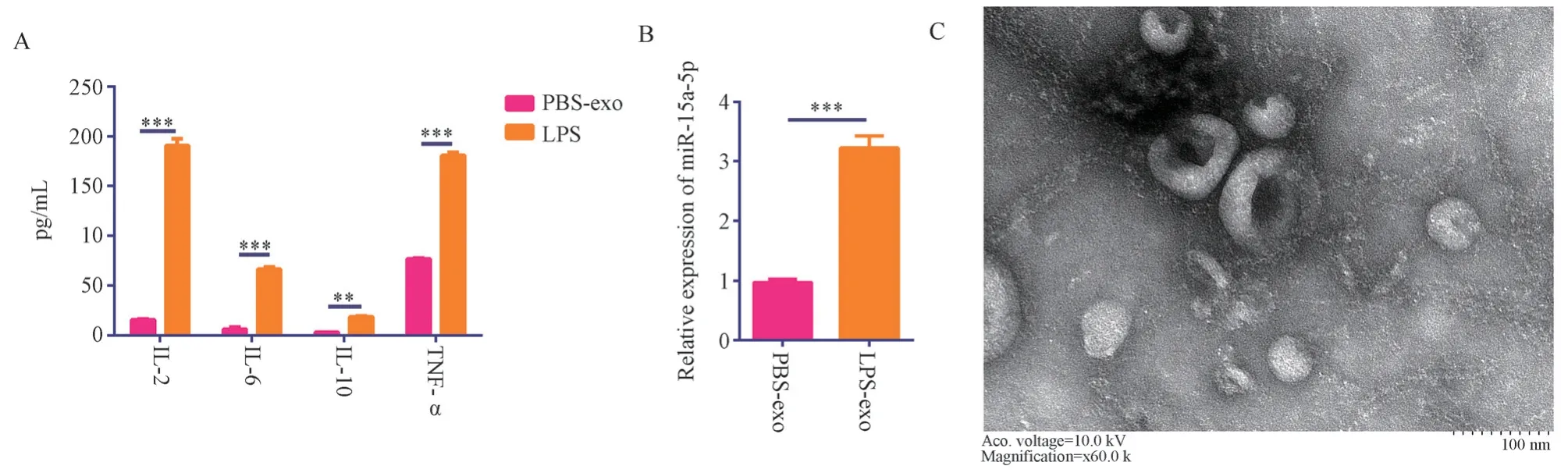
Fig 1 mir-15a-5p is significantly overexpressed in the exosomes of inflammatory neutrophils.
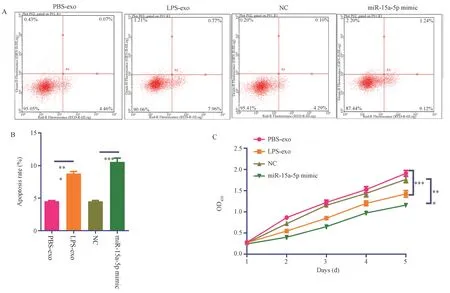
Fig 2 Exosomes of inflammatory neutrophils and mir-15a-5p promote raw267.4 macrophage apoptosis.
3.3 Database Prediction and Dual-Luciferase Assay Validation of miR-15a-5p Targeting BCL2L2
Using the Targetscan database to predict miR-15a-5p target genes,the apoptosis-related target gene BCL2L2 was identified.The 3’UTR of BCL2L2 mRNA was found to have binding sites for miR-15a-5p, as shown in Figure 3A.Based on the binding sites, wild-type and mutant sequences of the 3’UTR of BCL2L2 mRNA were designed,as shown in Figure 3A.The dual-luciferase assay results showed that the relative luciferase activity in the BCL2L2 wild-type and miR-15a-5p co-transfection group (BCL2L2-WT+miR-15a-5p group)was 0.50±0.06, significantly lower than that in the BCL2L2 wildtype and miRNA control co-transfection group (BCL2L2-WT+miRNC group) with a relative luciferase activity of 1.00±0.06 (t=9.26,P<0.001).The relative luciferase activity in the BCL2L2 mutant and miR-15a-5p co-transfection group (BCL2L2-MUT+miR-15a-5p group) was 1.00±0.10, showing no significant difference compared to the BCL2L2 mutant and miRNA control co-transfection group(BCL2L2-MUT+miR-NC group) with a relative luciferase activity of 1.05±0.05 (t=0.83, P=0.45>0.05), as shown in Figure 3B.
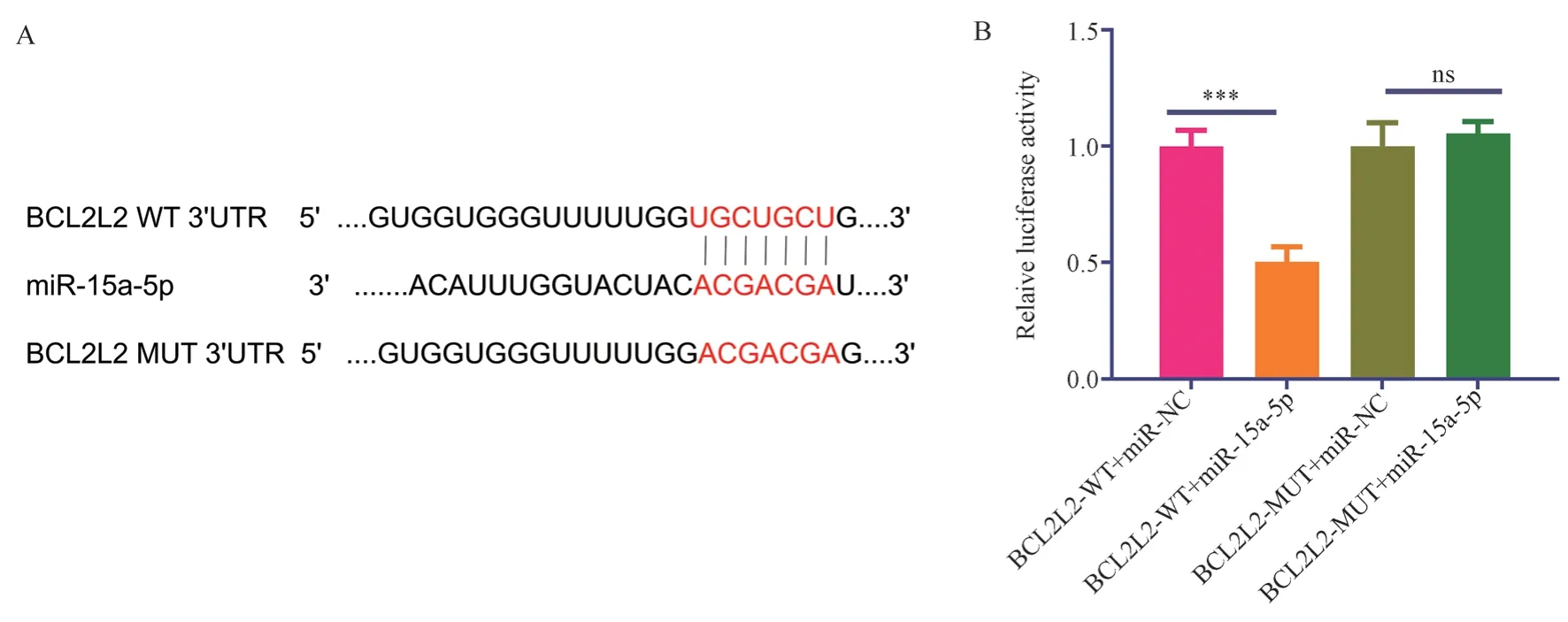
Fig 3 Database prediction and double-luciferase experiment to verify the targeted binding of mir-15a-5p to BCLCL2.*** means P <0.001
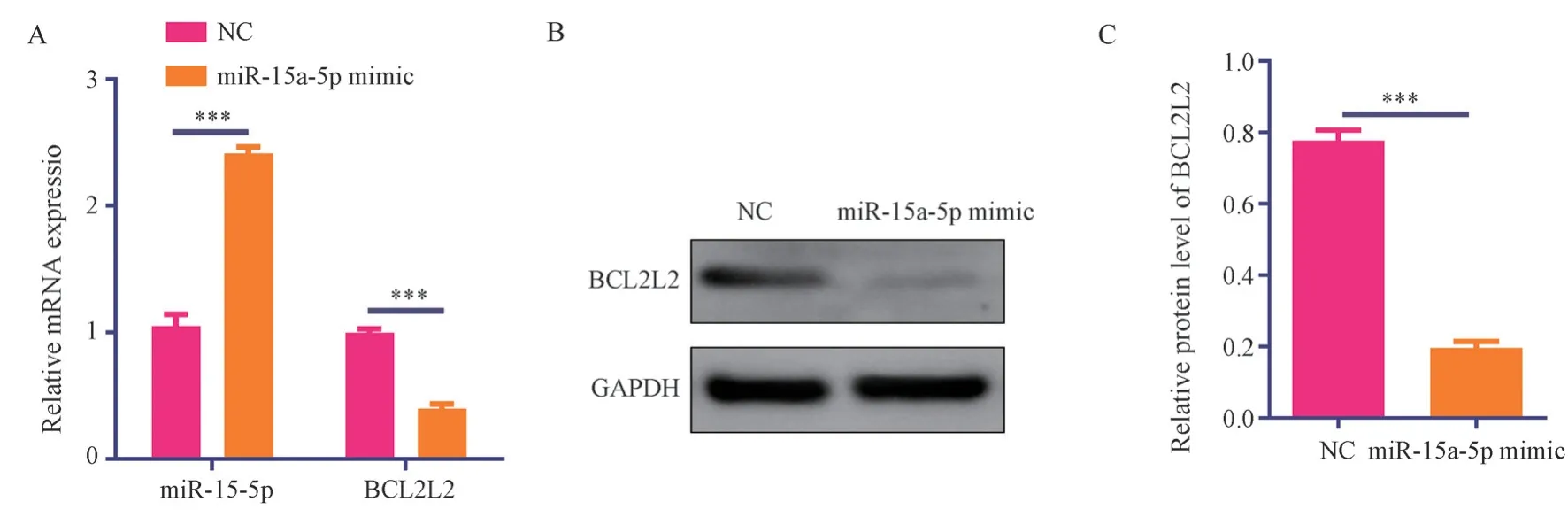
Fig 4 miR-15a-5p inhibits BCLCL2 mRNA and protein expression in raw267.4 macrophages.
3.4 miR-15a-5p Suppresses BCLCL2 mRNA and Protein Expression in Raw267.4 Macrophages
The RT-PCR results showed that the relative expression of miR-15a-5p in the miR-15a-5p mimic transfection group was 2.41±0.05,which was significantly higher than the relative expression of miR-15a-5p (1.05±0.09) in the negative control group (t=22.33, P<0.001).The relative expression of BCLCL2 mRNA in the miR-15a-5p mimic transfection group was 0.40±0.04, significantly lower than that in the negative control group (0.99±0.03) (t=21.52, P<0.001),see Figure 4A.
Western blot results showed that the relative expression of BCLCL2 protein in the miR-15a-5p mimic transfection group was 0.40±0.04, significantly lower than that in the negative control group(0.78±0.20) (t=29.47,P<0.001), see Figure 4B and 4C.
4.Discussion
During the early stages of sepsis, neutrophils are considered to be the primary innate immune cells causing host tissue injury[14].In addition to releasing crucial cytokines, chemoattractants, and ROS, neutrophil-derived exosomes can be key to the neutrophildriven inflammation and tissue injury[15].Our research results showed that after neutrophils were induced by lipopolysaccharide(LPS), the release of inflammatory factors IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α significantly increased.Simultaneously, the expression of miR-15a-5p in neutrophil exosomes significantly increased.Lipopolysaccharide LPS as a common drug for cell inflammation modeling can promote the inflammatory state of cells after treatment[16].This suggests that neutrophil exosomes under inflammatory conditions enhance the release of miR-15a-5p.This could be a crucial molecular mechanism for neutrophils under inflammatory conditions to regulate other cells or the microenvironment.
Sepsis is a leading cause of mortality worldwide and is characterized by an excessive inflammatory response to infection[17].During septic inflammatory reactions, neutrophils and monocytes are recruited to the peritoneal cavity, with the latter differentiating into inflammatory macrophages[18].Macrophages are immune cells within tissues that, during sepsis-induced lung injury, cause pulmonary vascular and bronchial constriction,systemic vasodilation, increased capillary permeability, as well as activation of macrophages and neutrophils to produce higher levels of inflammatory mediators, ultimately leading to septic lung injury[19,20].The interaction between neutrophil-derived exosomes and macrophages is considered an important factor in regulating posttraumatic inflammation, hemorrhagic shock, endotoxemia, and other pathological conditions[21,22].For example, exosomes released by alveolar macrophages activated during hemorrhagic shock promote neutrophil necrotic apoptosis in the lungs[21].Additionally,neutrophil-derived exosomes promote inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis by inducing cytokine production in macrophages[22].However, the role and potential mechanisms of interaction between neutrophils and macrophages in the context of sepsis and the development of inflammation remain unclear.Our research results indicate that in an inflammatory state, neutrophils may deliver miR-15a-5p through exosomes, thereby suppressing BCL2L2 protein expression in macrophages and promoting their apoptosis.This may be a key mechanism by which inflammatory neutrophils regulate macrophage apoptosis.
MicroRNAs (miRNA), approximately 22 nucleotides in length,are non-encoding single-stranded RNA molecules.They exert their biological function mainly by targeting and binding the 3’UTR end of mRNA, inhibiting protein translation[23].Previous studies have found that miR-15a-5p can inhibit tumor progression by directly targeting MYCN in neuroblastoma[24].miR-15a-5p can also regulate the expression of multiple proteins in the GPVI signaling pathway of megakaryocytes[25].The miR-15a-5p-XISTCUL3 axis can regulate sepsis-induced acute kidney injury[26].Circular RNA circFADS2 promotes the development of sepsis by inhibiting the maturation of miR-15a-5p and thereby inhibiting lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary cell apoptosis[27].Several reports have mentioned the regulatory effect associated with miR-15a-5p and BCL2L2.For instance, miR-15a induces apoptosis of HPV-positive hypopharyngeal squamous cells by targeting BCL2L2 and BCL2[28] ; miR-15a induces apoptosis and inhibits metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting BCL2L2[29] ; miR-15a suppresses the invasiveness of melanoma cells by targeting BCL2L2 and other target genes[30].All these suggest that miR-15a-5p promotes apoptosis and can bind with BCL2L2.However, there has been no report on miR-15a-5p regulating macrophage BCL2L2 through neutrophil exosomes.Our study results reveal that miR-15a-5p can target and bind the 3’UTR end of BCL2L2, suppress BCL2L2 mRNA and protein expression, thereby promoting the apoptosis of Raw267.4 macrophages, consistent with the literature.Naturally, our study has certain limitations.First of all, our research lacks clinical validation between sepsis and normal controls.Furthermore, we have not conducted investigations at the level of in vivo animals.Additionally, we did not perform experiments verifying the combined intervention of miR-15a-5p and BCL2L2 along with co-culture of neutrophils and macrophages.
In conclusion, our study suggests that in the inflammatory state induced by lipopolysaccharide LPS, neutrophils may secrete exosomes containing miR-15a-5p, targeting and binding the 3’UTR end of BCL2L2, inhibiting BCL2L2 mRNA and protein expression,and thereby promoting the apoptosis of Raw267.4 macrophages.This may provide a theoretical basis for further understanding the molecular mechanism of inflammation regulation between neutrophils and macrophages.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors have confirmed that there are no conflicts of interest in this manuscript.
Authors’contributions

Author contribution degree of contribution Li Min Experiment and writing Main Hu Longhui ELISA testing Assistance Ke Qiao RT-PCR and WB detection Assistance Ruan Chujun proliferation and apoptosis detection Assistance Liu Xiaoran Statistical Analysis, Article Review Main
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on the in vitro anti ovarian cancer effect and mechanism of quinazoline derivative (N111)
- m6A modification promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer and regulates the expression of PD-L1
- Expression and correlation of pyroptosis-related markers and PI3K/AKT pathway in endometriosis
- Meta-analysis of the efficacy of volar plate internal fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation in the treatment of adult distal radius fractures
- A review of the epidemic and clinical study on scrub typhus in China(2010-2020)
- Clinical efficacy of bushen huatan huoxue recipe in combination with acupuncture in treating patients suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome with insulin resistance
