Clinical efficacy of bushen huatan huoxue recipe in combination with acupuncture in treating patients suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome with insulin resistance
ZHANG Chu-chu, LIU He-jing, XU Xin
Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hubei Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Wuhan 430000, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To investigate the clinical efficacy and effects on sex hormone level and glucose metabolism indexes of acupuncture therapy combined with the Bushen Huatan Huoxue Recipe in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) with insulin resistance (IR).Methods:The patients with PCOS-IR admitted from December 2021 to December 2022 were randomly divided into two groups, 30 cases in each group.The comparison one and the observation one were given the relevant treatment of metformin and traditional Chinese medicine combined with acupuncture, respectively.The evidence points, sex hormone indexes and glucose metabolism indexes were compared between the two groups before and after treatment, and the insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR), glucose area under the curve (GLU-AUC) and blood insulin area under the curve (INS-AUC) were calculated.Results: The evidence points of the observation group of patients were less than the pre-treatment and comparison groups; after treatment, the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) level of patients in the observation group was more than the control and pre-treatment groups (P<0.05), and the ratio of luteinizing hormone (LH) to follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) was less than that of the comparison and pre-treatment groups (P<0.05),and the levels of LH and testosterone (T) were reduced to varying degrees in both groups around the time of treatment(P<0.05 ).The patients in the observation group had lower levels of 0.5hPG than those in the comparison group and pretreatment (both P<0.05), and the levels of 3hPG in both groups were lower than those before treatment (P<0.05).The oral OGIRT in each of the two groups after treatment was lower than that of pretreatment (P<0.05).HOMA-IR and INS-AUC of the observation group were lower than those of the control group and pre-treatment (P<0.05).Conclusion: The treatment of PCOS-IR patients with Bushen Huatan Huoxue Recipe combined with acupuncture can improve the sex hormone, glucose metabolism level and insulin resistance.
1.Introduction
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder commonly presenting in women of childbearing age associated with genetic, endocrine, psychological anxiety and metabolic abnormalities.It is mainly characterized by hyperinsulinemia,insulin resistance, and hyperandrogenemia.The probability of insulin resistance is higher in patients with PCOS; however, the sequential relationship between insulin resistance and polycystic ovary syndrome is still unclear[1].Metformin, as an insulin sensitizing agent, can inhibit intestinal glucose absorption, hepatic gluconeogenesis and output, increase the uptake and utilization of glucose by tissues, and improve insulin sensitivity, and is clinically indicated for PCOS patients with metabolic abnormalities[2].Metformin, which is commonly used clinically for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, is able to improve IR.However, for some patients with contraindications to hormonal drugs, metformin, or intolerance, such as those with severe gastrointestinal reactions,it is even more important to look for alternative medications or therapies that are proven to be effective and have fewer side effects.The Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine of our hospital has been treating PCOS for many years by using the herbal formula of tonifying the kidney, transforming phlegm and activating blood in combination with acupuncture, and the therapeutic effect is accurate[3-6].In clinical practice, it was found that the combination treatment improved the fertility function of patients while IR was significantly relieved.Therefore, in this study, the efficacy of metformin combined with acupuncture was compared and analyzed,so as to provide a basis for the clinical improvement of early glucose metabolism abnormality in patients with PCOS-IR by the combination of acupuncture and medicine.
2.Data and Methods
2.1 General information
Sixty patients with PCOS-IR from September 2021 to September 2022 in Hubei Maternal and Child Health Hospital were divided into two groups.They met the diagnostic criteria for PCOS promulgated in the Rotterdam Conference[7], and the oral glucose insulin release test (OGIRT) suggested insulin resistance; their ages ranged from 20 to 45 years old; they were examined and approved by the Ethics Committee of the hospital, and the patients were informed of the details and signed an informed consent form to enroll in the group, with the ethical approval number (XYSZYY2020-KY-008).The 60 patients were randomly divided into the needle-medicine combination group and metformin Metformin group, 30 cases in each group.
2.2 Exclusion criteria
Cushing’s syndrome, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, ovarian or adrenal hormone-secreting tumors and other diseases related to hyperandrogenism; diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, etc.; hormonal drugs taken within three months; pregnant and lactating patients.
2.3 Treatment method
Patients in the observation group were treated with traditional Chinese medicine +electroacupuncture.The Chinese herbal Bushen Huatan Huoxue Recipe[4, 5] (purchased from the traditional Chinese medicine pharmacy of Hubei Provincial Maternal and Child Healthcare Hospital) was mainly composed of Epimedii Folium,Cuscutae Semen, Fluoritum, Atractlodis Rhizoma, Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium, Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum, Coicis Semen, Poria, Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Paeoniae Radix Alba, Chuanxiong Rhizoma , Persicae Semen, Carthami Flos, Cyperi Rhizoma and Aurantii Fructus made up of Chinese medicine granules from Shenzhen Sanjiu Pharmaceutical Company, China, which can be taken during menstruation.1 dose per day 200 mL/day 200 mL/times.2 times/day.Acupuncture should not be performed during menstruation, the treatment of acupuncture performed three times a week, a menstrual period for a course of treatment, a total of three courses of treatment.Electroacupuncture points: the main points are Qihai, Guanyuan, Zigong, Tianshu, Zusanli, Yinlingquan, Fenglong,Sanyinjiao, Shenshu, Pishu, Weishu and Ganshu.Operation: The back points and abdominal points were divided into two groups and each side of the points should be operated 20 min, the abdominal points were placed in the supine position, with Qihai, Guanyuan,Zigong, Tianshu, Zusanli, Taixi, Sanyinjiao, Yinlingquan, Xuehai and Fenglong being treated with 0.25 mm×40 mm disposable sterile acupuncture needles, and low-frequency electronic pulse therapy instrument (G6805-2A, Shanghai Huayi Medical Instrument) was used to treat the points, and the pulse frequency was chosen to be sparse and dense wave, the frequency was 10 times/min, the pulse width was 0.5 ms, the positive pole of the same side was connected to the Tianshu acupoint, and the negative pole was connected to the Zusanli acupoint, and the needles were retained for 20 min.The back point adopts the prone position, Shenshu, Pishu, Weishu, Ganshu points using Pingbu Pingxie, acupuncture after qi.Low frequency electronic pulse therapy device treatment frequency same as above,same side.The positive electrode was connected to Ganshu point, the negative electrode was connected to Shenshu point, and the needle was retained for 20 min.Patients in the control group were given metformin hydrochloride tablets (0.5g/tablet, Zhongmei Shanghai Schweppes Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) 0.5g/times, 2 times/d, morning and evening after meals.The treatment period was 3 months, and the patients were instructed to take regular work and rest, healthy diet and moderate exercise during the medication period.
2.4 Observation indexes
All patients had venous blood drawn on an empty stomach on the 3rd-5th day of menstruation before and after treatment, and were tested for the six sex hormones and related glucose metabolism indexes, and according to the above test values, the insulin resistance formula in the homeostasis model assessment method (HOMA-IR)= (FBG*FINS) /22.5 was used to calculate the homeostasis model’s insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR), area under the glucose curve(GLU-AUC), and area under the blood insulin curve (INS-AUC).area under the curve (GLU-AUC), and area under the blood insulin curve (INS-AUC).According to the “Clinical Guidelines for New Chinese Medicines”, before treatment and after three months of treatment, the scores were assigned using the Chinese medicine evidence scale, with the following main symptoms: obesity, duration of disease, menstrual cycle, menstrual color, menstrual quantity,and menstrual quality.The scores were categorized into 4 levels for evaluation.The scores were: 0 as normal, 2 as mild, 4 as moderate,and 6 as severe.The higher the score, the more serious the patient’s condition.Secondary symptoms: lumbar and knee pain, dizziness and tinnitus, lumbosacral pain, menstrual abdominal pain, and pain under the block.It is divided into 4 levels for score evaluation.The scores are as follows: 0 is considered normal, 1 is considered mild,2 is considered moderate, and 3 is considered severe.The higher the score, the more serious the patient’s condition.
2.5 Statistical methods
SPSS25.0 software was used for statistical analysis.Measurement data were expressed in the form of mean ± standard deviation(±s),t-test was used for comparison between groups, and paired t-test was used for comparison before and after treatment, and the difference was regarded as statistically significant at P<0.05.
3.Results
3.1 Comparison of age, BMI, duration of PCOS and other data of the two groups before treatment
Before treatment, there were 30 cases in the control group with age (27.80±4.13), BMI (22.97±4.81) kg/m2and disease duration(4.3±1.58) years.In the observation group 30 cases age (26.43±3.48)years, BMI (22.99±4.23) kg/m2,disease duration (3.67±1.88) years.Comparison of age, BMI and disease duration between the two groups showed no statistically significant difference (P>0.05), and were comparable, see Table 1.
Tab 1 Comparison of Age, BMI, and PCOS Course between two group before treatment (±s)
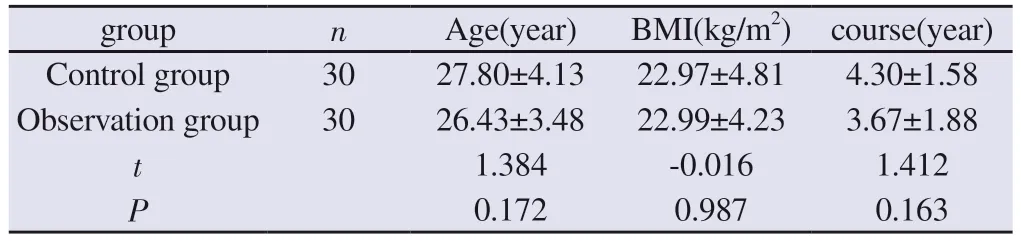
Tab 1 Comparison of Age, BMI, and PCOS Course between two group before treatment (±s)
group n Age(year) BMI(kg/m2) course(year)Control group 30 27.80±4.13 22.97±4.81 4.30±1.58 Observation group 30 26.43±3.48 22.99±4.23 3.67±1.88 t 1.384 -0.016 1.412 P 0.172 0.987 0.163
3.2Comparisonofsyndrome points between two groups before andaftertreatment (points,±s)
Before treatment, the comparison of the two groups of evidence points, the difference between the two groups of data is not statistically significant (P>0.05), is comparable.After treatment,the evidence points of the observation group were lower than those of the pre-treatment and control groups, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), see Table 2.
Tab 2 Comparison of syndrome points between two groups before and after treatment(points, ±s)
group n before after t P Control group 30 19.90±6.39 16.86±3.45 3.085 0.004 Observation group 30 22.40±6.89 13.56±4.59 9.022 <0.001 t-1.494 3.143 P 0.141 0.003
3.3 Comparison of serum levels of sex hormones before and after treatment between the two groups of patients
In the control group of 30 cases, before treatment, FSH (6.13±1.58)mIU/mL; LH (12.81±4.74) mIU/mL; E2 (53.34±15.35) pg/mL; T(0.52±0.33) ng/mL; P (0.48±0.84) ng/mL; PRL (15.42±6.39) ng/mL.LH/FSH (2.21±1.07).In the observation group of 30 cases,before treatment, FSH (6.68±3.02) mIU/mL; LH (12.54±3.81) mIU/mL; E2 (52.31±27.48) pg/mL; T (0.61±0.31) ng/mL; P (0.36±0.32)ng/mL; RPL (17.67±10.92) ng/mL ; LH/FSH (2.03±0.59).The levels of follicle-stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone,estrogen, testosterone, progesterone, and prolactin before treatment in the two groups were not statistically significant (P>0.05), and were comparable.After treatment, the FSH level of patients in the observation group was higher than that of the control group and before treatment (P<0.05), and LH/FSH was lower than that of the control group and before treatment (P<0.05), and the LH and T levels of the two groups before and after treatment were reduced to different degrees (P<0.05), but the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05), and the differences in the levels of E2, P, and RPL of the two groups before and after treatment were not statistically significant (both P>0.05), and the differences in the levels of E2,P, and RPL of the two groups before and after treatment were not statistically significant (both P>0.05), and the differences were not statistically significant (both P>0.05).statistical significance (all P>0.05).See Table 3 and Table 4.
Tab 3 Comparison of serum levels of sex hormones between two groups before and after treatment (±s)
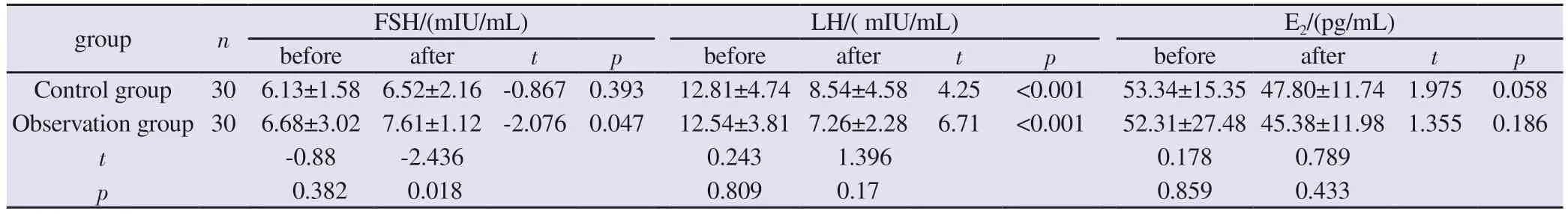
Tab 3 Comparison of serum levels of sex hormones between two groups before and after treatment (±s)
group n FSH/(mIU/mL) LH/( mIU/mL) E2/(pg/mL)before after t p before after t p before after t p Control group 30 6.13±1.58 6.52±2.16 -0.867 0.393 12.81±4.74 8.54±4.58 4.25 <0.001 53.34±15.35 47.80±11.74 1.975 0.058 Observation group 30 6.68±3.02 7.61±1.12 -2.076 0.047 12.54±3.81 7.26±2.28 6.71 <0.001 52.31±27.48 45.38±11.98 1.355 0.186 t-0.88 -2.436 0.243 1.396 0.178 0.789 p 0.382 0.018 0.809 0.17 0.859 0.433
Tab 4 Comparison of serum levels of sex hormones between two groups before and after treatment (±s)

Tab 4 Comparison of serum levels of sex hormones between two groups before and after treatment (±s)
group n PRL/(ng/mL) T/(ng/mL) P/(ng/mL) LH/FSH before after t p before after t p before after t p before after t p Control group 30 15.42±6.39 18.22±9.79 -1.318 0.198 0.52±0.33 0.34±0.16 2.9 0.007 0.48±0.84 0.45±0.82 0.644 0.524 2.21±1.07 1.31±0.59 4.21 <0.001 Observation group 30 17.67±10.92 18.64±6.32 -0.47 0.642 0.61±0.31 0.31±0.12 5.226 <0.001 0.36±0.32 0.32±0.18 0.661 0.514 2.03±0.59 0.98±0.29 8.96 <0.001 t-0.975 -0.196 -1.155 0.99 0.73 0.798 0.806 2.93 p 0.334 0.845 0.253 0.326 0.468 0.428 0.424 0.005
3.4 Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) Comparison of FPG,0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG, 3hPG levels
Before treatment, there was no statistical significance in the comparison of FPG, 0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG and 3hPG levels between the two groups (P>0.05).After treatment, the 0.5hPG level of patients in the observation group was lower than that of the control group and before treatment (both P<0.05),and the 3hPG level of patients in the two groups was lower than that of the pre-treatment group(P<0.05),but the difference between the groups was not statistically significant (P>0.05).,The FPG level of the observation group was lower than that of the control group after treatment (P<0.05), but the difference between the FPG levels of the two groups before and after treatment was not statistically significant (P>0.05).The difference between the serum levels of 1hPG and 2hPG of the two groups of patients was not statistically significant (P>0.05).See Table 5 and Table 6.
Tab 5 Comparison of FPG, 0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG, and 3hPG Levels(±s)
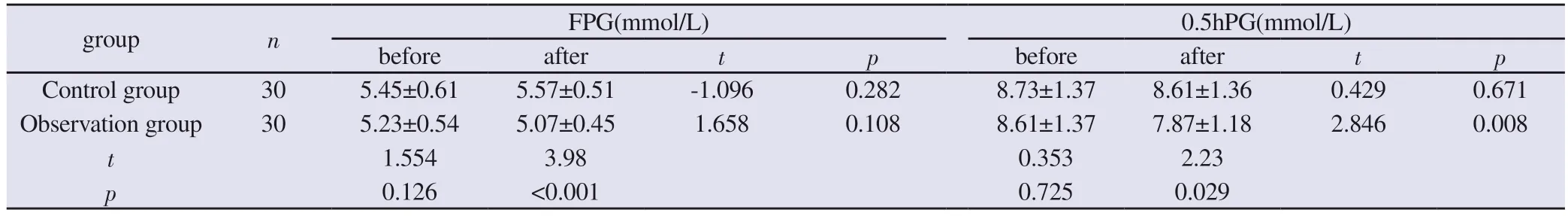
Tab 5 Comparison of FPG, 0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG, and 3hPG Levels(±s)
group n FPG(mmol/L) 0.5hPG(mmol/L)before after t p before after t p Control group 30 5.45±0.61 5.57±0.51 -1.096 0.282 8.73±1.37 8.61±1.36 0.429 0.671 Observation group 30 5.23±0.54 5.07±0.45 1.658 0.108 8.61±1.37 7.87±1.18 2.846 0.008 t 1.554 3.98 0.353 2.23 p 0.126 <0.001 0.725 0.029
Tab 6 Comparison of FPG, 0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG, and 3hPG Levels(±s)

Tab 6 Comparison of FPG, 0.5hPG, 1hPG, 2hPG, and 3hPG Levels(±s)
group n 1hPG(mmol/L) 2hPG(mmol/L) 3hPG(mmol/L)before after t p before after t p before after t p Control group 30 8.95±2.42 8.12±2.07 1.849 0.075 7.38±2.35 6.99±1.84 1.059 0.298 6.00±1.58 5.21±0.94 3.195 0.003 Observation group 30 8.61±2.29 7.50±1.67 2.56 0.016 7.18±1.67 6.27±1.31 2.604 0.014 5.56±1.04 5.14±0.97 2.18 0.038 t 0.552 1.278 0.38 1.73 1.07 0.238 p 0.583 0.206 0.705 0.088 0.287 0.813
3.5 Oral glucose insulin release test (OGIRT) Comparison of Fins, 0.5 h Ins, 1hIns, 2 h Ins, 3 h Ins levels
Before treatment, there was no statistically significant difference in the levels of Fins, 0.5hIns, 1hIns, 2hIns and 3hIns between the two groups (P>0.05) After treatment, all the items in the oral glucose insulin release test of the two groups were lower than those before treatment (P<0.05), but the degree of improvement of the observation group was higher than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05), as shown in Table 7 and Table 8.
Tab 7 Comparison of Fins, 0.5hIns, 1hIns, 2hIns and 3hIns levels(±s)
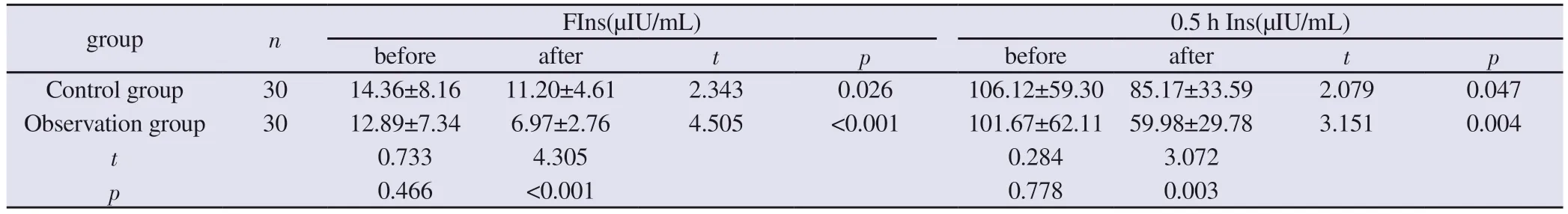
Tab 7 Comparison of Fins, 0.5hIns, 1hIns, 2hIns and 3hIns levels(±s)
group n FIns(μIU/mL) 0.5 h Ins(μIU/mL)before after t p before after t p Control group 30 14.36±8.16 11.20±4.61 2.343 0.026 106.12±59.30 85.17±33.59 2.079 0.047 Observation group 30 12.89±7.34 6.97±2.76 4.505 <0.001 101.67±62.11 59.98±29.78 3.151 0.004 t 0.733 4.305 0.284 3.072 p 0.466 <0.001 0.778 0.003
Tab 8 Comparison of Fins, 0.5hIns, 1hIns, 2hIns and 3hIns levels(±s)

Tab 8 Comparison of Fins, 0.5hIns, 1hIns, 2hIns and 3hIns levels(±s)
group n 1 h Ins(μIU/mL) 2 h Ins(μIU/mL) 3 h Ins(μIU/mL)before after t P before after t P before after t P Control group 30 130.07±75.91 90.67±45.07 3.328 0.002 102.89±62.81 77.72±49.37 2.267 0.031 56.97±45.90 32.40±27.21 3.536 0.001 Observation group 30 108.77±74.61 63.24±27.18 3.216 0.003 101.69±70.08 44.00±21.81 4.408 <0.001 41.40±40.60 16.23±16.08 3.133 0.004 t 1.096 2.854 0.07 3.421 1.392 2.801 p 0.278 0.006 0.944 0.001 0.169 0.007
3.6 Comparison of HOMA-IR, GLU-AUC, INS-AUC before and after treatment between the two groups
Before the treatment, there was no statistically significant difference between the levels of insulin resistance index, area under the blood insulin curve and area under the blood glucose curve in the two groups (P>0.05).After treatment, the insulin resistance index and the area under the blood insulin curve of the observation group were lower than those of the control group and before treatment, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05).The GAUC(GLU) of the area under the blood glucose curve of the observation group was smaller than that before treatment, but the difference with the control group after treatment was not statistically significant(P>0.05),see Table 9.
Tab 9 Comparison of HOMA-IR, GLU-AUC, INS-AUC Levels (±s)
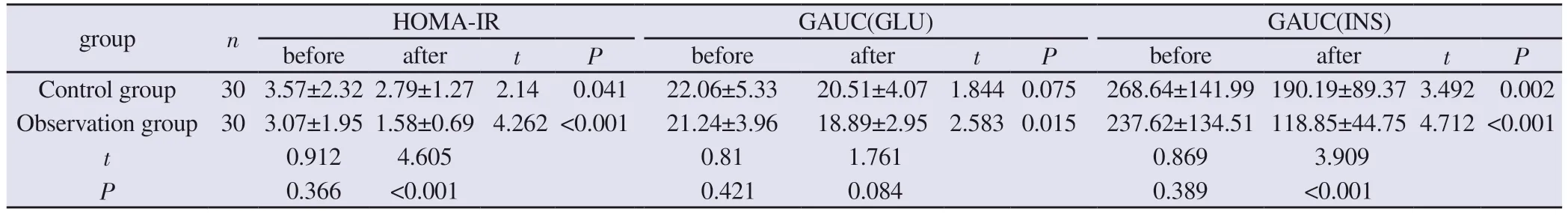
Tab 9 Comparison of HOMA-IR, GLU-AUC, INS-AUC Levels (±s)
group n HOMA-IR GAUC(GLU) GAUC(INS)before after t P before after t P before after t P Control group 30 3.57±2.32 2.79±1.27 2.14 0.041 22.06±5.33 20.51±4.07 1.844 0.075 268.64±141.99 190.19±89.37 3.492 0.002 Observation group 30 3.07±1.95 1.58±0.69 4.262 <0.001 21.24±3.96 18.89±2.95 2.583 0.015 237.62±134.51 118.85±44.75 4.712 <0.001 t 0.912 4.605 0.81 1.761 0.869 3.909 P 0.366 <0.001 0.421 0.084 0.389 <0.001
4.Discussion
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), as a complex disease highly prevalent in women of childbearing age, is often clinically characterized by sparse ovulation or anovulation, scanty menstruation, hyperandrogenemia, and hyperinsulinemia.In patients with PCOS, insulin resistance (IR) contributes to compensatory hyperinsulinemia, and higher insulin levels increase luteinizing hormone (LH)-induced androgen production and decrease hepatic synthesis of sex hormone binding globulin[8, 9].In women with PCOS, excess androgens aggravate IR and lead to compensatory increase in serum insulin levels, which further enhances androgen secretion from ovarian membrane cells[10-12].IR plays a key role in the pathogenesis of PCOS, and improving IR and insulin sensitivity is of great significance in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS).Insulin sensitizers are often used in combination with anti-androgen drugs to improve sex hormones, menstrual cycle,hyperinsulinemia, insulin resistance, glucose and lipid metabolism in order to increase the ovulation rate to promote the return of the menstrual cycle to normal[13-16].Metformin acts mainly by inhibiting hepatic glucose production and enhancing insulin sensitivity[17].Improvement of insulin sensitivity by metformin has been demonstrated in nondiabetic women with polycystic disease,and metformin often plays a corresponding role in modifying the menstrual cycle, ovulation-promoting therapy, and lowering androgen levels[13, 18].A relationship between changes in the HOMA-IR index and the level of menstrual cycle disorders has also been demonstrated[19], and menstrual dysfunction in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome is more related to the dynamic state of insulin resistance than to hyperandrogenemia[9].However, for some patients with contraindications or intolerance to hormonal drugs and metformin, such as those with severe gastrointestinal reactions, it is especially important to find alternative drugs or therapies that are effective and have fewer side effects.There is no name for polycystic ovary syndrome in Chinese medicine, and the disease belongs to the categories of infertility, late menstruation, amenorrhea, and Abdominal Mass in Chinese medicine.A woman’s menstruation is the result of the joint action of the Tian Gui, qi and blood, Zang Fu Viscera and Meridian and Collateral in the uterus.In recent years,traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has broadly divided polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) into three types: kidney deficiency, blood stasis and phlegm-dampness.Kidney deficiency is the fundamental etiology of PCOS, so tonifying the kidneys is usually carried out throughout the whole treatment[20], and clinically, symptoms such as enlarged ovaries, increased follicles, thickened lining and elevated blood glucose and blood lipids belong to the category of phlegmdampness and blood stasis, so tonifying the kidneys is the basic treatment for the disease, and also for treating the symptoms with the treatment of phlegm-dampness and blood stasis.Experimental studies have shown that Bushen Huoxue Recipe, Bushen Huatan Recipe, and acupuncture have better overall efficacy in treating patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, improving the endometrial environment, enhancing the ovulation rate, and improving the glucose and lipid metabolism[21-24].This is corroborated with the results of this experimental study that the TCM scores of the observation group were lower than those of the control group and the pre-treatment results.This formula consists of Epimedii Folium,Cuscutae Semen, Fluoritum, Atractlodis Rhizoma, Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium, Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum, Coicis Semen, Poria, Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Paeoniae Radix Alba, Chuanxiong Rhizoma, Persicae Semen, Carthami Flos, Cyperi Rhizoma and Aurantii Fructus, and it emphasizes on the kidney-nourishing drugs such as Epimedii Folium, Cuscutae Semen and Fluoritum.The combination of the three drugs takes its effect of tonifying the kidney and nourishing the liver and benefiting the essence, as the main drug,and its tonic effect is gentle and not stagnant; Atractlodis Rhizoma,Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium and Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum are aiming at drying dampness , resolving phlegm and strengthening the spleen and stomach; Coicis Semen and Poria are adept in diuresis and removing dampness; Chuanxiong Rhizoma is often used with Coicis Semen, which is a thick, downward-facing and sinking drug to check the upward-facing nature of the Chuanxiong Rhizoma Ligustici, which is a combination of both drugs, enhancing the effect of fluency; Angelicae Sinensis Radix, Paeoniae Radix Alba, Persicae Semen,and Carthami Flos are proficient in promoting blood circulation for removing blood Stasis; Cyperi Rhizoma and Aurantii Fructus detach the liver to relieve depression and promote the circulation of qi to harmonize stomach.The whole formula tonifies the Kidney and strengthens the Spleen, induces diuresis and dries dampness, and promotes Blood and Qi.Selecting the main acupoints of the Conception Vessel, Kidney, Spleen, Stomach, and Bladder meridians to tonify the kidney and benefit the vital essence and regulate the Chong Ren, supplemented by drying dampness ,removing phlegm, activating blood circulation and removing blood stasis, which is aimed at regulating patients’ symptoms of kidney deficiency.It indicated that the combination of the acupuncture and medicine program could significantly reduce the level of Chinese medicine symptom score of the patients with kidney deficiency and blood stasis type of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
The study conducted by our group on the mechanism of needle and drug combination to regulate the PI3K/AKT pathway to improve PCOS-IR rats, and the results showed that the combination of acupuncture and moxibustion could improve the morphology and structure of the ovary, insulin resistance, and sex hormone level of PCOS-IR rats; and the combination of needle and drug could significantly up-regulate p-PI3K, p-AKT, p-AKT and p-PI3K in the ovarian tissues of PCOS-IR rats.PI3K, p-AKT and GLUT4 protein expression in ovarian tissues of PCOS-IR rats, suggesting that its mechanism of action may be related to the improvement of the transduction of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in PCOS-IR rats[25,26].It has been demonstrated that impairment of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is one of the important causes of insulin resistance and development of type 2 diabetes in peripheral tissues[27].OGTT, OGIRT, INS, etc.are indicators for assessing insulin sensitivity, and in this experiment HOMA-IR, INS, OGIRT and other glycolipid metabolism indicators were reduced to different degrees,which also suggested that Kidney tonic formula combined with electroacupuncture could improve glycolipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity.PCOS patients are often accompanied by endocrine disorders, and the clinic often manifests the symptoms of multiple follicles, sparse LH and FSH are both glycoprotein hormones produced by gonadotrophoblasts in the anterior pituitary gland,which mainly act on the ovary and promote the growth, development,maturation and ovulation of follicular cells, and the value of LH is often significantly higher than that of normal females in patients with PCOS, resulting in a rise in LH/FSH[28].It has been proved that the kidney tonic formula can significantly reduce the levels of LH, T,LH/FSH, and its obvious effect in correcting sex hormone disorders has been confirmed[29, 30], and in the present study, the values of LH,T, LH/FSH were reduced after treatment, and the value of FSH was slightly increased, and the difference was statistically significant,which is in line with the results of the previous related studies.
The results of this study show that the observation group can significantly reduce serum LH, T, LH/FSH levels and increase FSH levels in PCOS patients; 0.5 h PG and 3 h PG as well as OGIRT are all reduced, and at the same time, the HOMA-IR, area under the insulin curve, and Chinese medicine evidence score are lower than those of the pre-treatment and the control group, which indicates that the traditional Chinese medicine prescription combined with electroacupuncture treatment used in this study can more obviously It shows that the combination of Chinese medicine prescription and electroacupuncture treatment in this study can more obviously improve the clinical symptoms of the patients and improve the clinical efficacy, and it is effective in improving insulin sensitivity,insulin resistance, and correcting endocrine disorders, and there is a convergence between the improvement of the evidence points and the changes of the insulin resistance index and sex hormones, but the mechanism of its action still needs to be further researched.
Authors’ Contributions
Xin Xu, Chu Chu Zhang, Hejing Liu, Research implementation:Chu Chu Zhang, Hejing Liu, Xin Xu, Data collection and organization: Chu Chu Zhang, Hejing Liu, Xin Xu, Paper writing:Chu Chu Zhang, Revision of the paper by Hejing Liu, Xin Xu,Reviewer: Xin Xu
All authors agree that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on the in vitro anti ovarian cancer effect and mechanism of quinazoline derivative (N111)
- m6A modification promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer and regulates the expression of PD-L1
- Expression and correlation of pyroptosis-related markers and PI3K/AKT pathway in endometriosis
- Meta-analysis of the efficacy of volar plate internal fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation in the treatment of adult distal radius fractures
- A review of the epidemic and clinical study on scrub typhus in China(2010-2020)
- MiR-15a-5p in neutrophil exosomes promotes macrophage apoptosis through targeted inhibition of BCL2L2
