Meta-analysis of the efficacy of volar plate internal fixation versus closed reduction and external fixation in the treatment of adult distal radius fractures
CHEN Jian-ge , ZHANG Hai-ning , ZHAO Hong-zhou , LIU Ming-jun , XING Jia-hui ,WANG Ping , WANG Wei-min✉
1.First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Acupuncture and Moxibustion, Tianjin 300381, China
2.Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Tianjin Hospital, Tianjin 300211, China
Keywords:
ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the efficacy of open reduction and volar locking plate internal fixation with closed reduction and external fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures by using meta analysis.Methods: The databases of CNKI, Wanfang, Weipu, Chinese biomedical literature, Pubmed, Embase, and Cochrane Library were retrieved, and the randomized controlled studies that directly compared the efficacy of plate internal fixation and closed reduction external fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures published publicly from the establishment of the database to April 2023 were collected.The two researchers independently screened the retrieved literature according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria,extracted data, used Cochrane risk bias assessment tool for quality assessment, and used RevMan 5.4 software for meta analysis.Results: A total of 10 randomized controlled trials were included, all of which were in English.There were 1042 patients in total, and 9 of them were rated as low risk.Meta analysis results showed that one year after the treatment of distal radius fracture with volar locking plate internal fixation, DASH score[MD=-5.64,95%CI(-7.21,-4.06),P<0.000 01]; One year later, PRWE score [MD=-5.90,95%CI(-8.88,-2.92),P=0.001];Palm flexion [MD=5.92,95%CI(1.29,10.55),P=0.01]; Pronation [MD=2.48,95%CI(0.59,4.3 6),P=0.01]; Postrotation[MD=4.73,95%CI(2.15,7.31),P=0.000 3]; Grip strength [MD=0.61,95%CI(0.12,1.10),P=0.02]; palmar tilt angle [MD=9.84,95%CI(5.66,14.02),P<0.000 01];Radial inclination [MD=4.33,95%CI(2.97,5.69),P<0.000 01] was superior to closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation.One year later, the European Five dimensional Health Scale(EQ-5D-5L) score[MD=0.02,95%CI(-0.01,0.05),P=0.27]; Back extension[MD=2.22,95%CI(-4.15,8.59),P=0.49]; Ulnar deviation[MD=3.49,95%CI(-0.80,7.78),P=0.11]; Radial deviation[MD=2.05,95%CI(-2.39,6.50),P=0.37]; Ulnar variance[MD=-1.14,95%CI(-3.16,0.88),P=0.27]; There was no significant difference in complications [MD=0.77,95%CI(0.54,1.10),P=0.16](P>0.05).Conclusion: Based on the current clinical data, internal fixation with volar locking plate is more conducive to mid-term DASH score and grip strength recovery than closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation, but there is no significant difference in the quality of life and complications of patients.For adult distal radius fractures, surgical indications should be carefully grasped, and non operative treatment should be given priority.
1.Introduction
Distal radius fracture refers to a fracture that occurs within 3cm of the radial wrist joint surface.This fracture is very common in emergency orthopedic trauma patients, accounting for about 16 %of systemic fractures[1].The injured population is mainly middleaged and elderly osteoporosis patients with low-energy injury and young patients with high-energy injury.Among the elderly patients over 60 years old, the incidence of women is about 80%, which is closely related to osteoporosis caused by postmenopausal bone loss in women[2].At present, the non-surgical methods for the treatment of distal radius fractures are mainly closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation.There are relatively many surgical methods,including external fixator fixation, Kirschner wire fixation and open reduction plate internal fixation.Some scholars believe that the application of closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation for most stable distal radius fractures can achieve relatively satisfactory results, and there is no significant difference between long-term efficacy and surgical treatment[3].However, most scholars believe that open reduction and plate internal fixation is superior to traditional closed reduction and conservative treatment in all aspects of data indicators, especially for complex fractures involving the radial wrist joint surface, namely AO classification, type B and type C distal radius fractures.The application of volar locking plate can fix the fracture block more stably, maintain the height of the radius and the smoothness of the radial wrist joint surface to the greatest extent, and can carry out early functional exercise of the wrist joint[4].Therefore, the best way to treat distal radius fractures has been controversial, especially for the middle-aged and elderly patients with unstable distal radius fractures[5].
In order to systematically compare the functional scores, wrist range of motion, imaging indexes and complications of volar locking plate internal fixation and closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures, this paper used Meta-analysis method to search for randomized controlled trials that directly compared the two methods for the treatment of distal radius fractures in adults before April 2023.The clinical efficacy of the two methods in the treatment of distal radius fractures was evaluated and analyzed to enrich the evidence-based medical evidence in clinical application and further guide clinical practice.
2.Data and Methods
2.1 Literature retrieval strategy
Search CNKI, Wanfang, VIP, Chinese Biomedical Literature Database, Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane Library database.The search time was from the establishment of the database to April 2023, and the ‘ Cochrane Intervention System Evaluation Manual ‘ and the list of preferred reporting items for systematic evaluation and metaanalysis in 2009 were strictly followed[6].Search terms include: “Distal radius fracture ”, “ Colles fracture ”, “ external fixator ”,”non-surgical treatment ”, “ closed reduction ”, “ plaster ”, “ volar plate ”.The combination of subject words and free words is used for retrieval.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria : (1) Research object : closed distal radius fracture (patients over 18 years old) ; (2) Research type : randomized controlled trials ; (3) Intervention methods : direct comparison of volar locking plate fixation and closed reduction plaster, splint external fixation efficacy study ; (4) Outcome indicators : The main observation indicators were DASH and PRWE.The secondary indicators were wrist activity (dorsiflexion, palmar flexion,pronation, supination, radial deviation, ulnar deviation, etc.), imaging data (palmar tilt angle, radial inclination, ulnar variance, etc.), grip strength and complications.
Exclusion criteria : (1) Re-fracture treatment ; (2) Non-randomized controlled trials ; (3) The original research design is not rigorous ;(4) Lack of important outcome indicators.
2.3 Literature screening and data extraction
After eliminating duplicate literature, two researchers independently screened the literature.First, read the title and abstract to exclude the literature that did not meet the inclusion criteria.After reading the full text one by one, the possible included studies were strictly screened according to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria.If there was a disagreement on whether a study could be included, it was resolved through discussion with the third researcher.
Data extraction included extracting the following features from the included original studies : first author name, publication year,research method, country of study, sample size, gender and age of participants, AO fracture classification, follow-up time, outcome indicators.Two researchers independently completed the data extraction according to the pre-established data extraction table,and cross-checked it.If there were differences, the third researcher judged it.
2.4 Methodological quality evaluation of literature
According to the ‘ Cochrane handbook ‘ risk bias assessment tool[7], two researchers independently completed the methodological quality evaluation of the literature included in the study.If differences arise, they will discuss with the third researcher.Evaluation indicators include : random sequence generation,allocation concealment, blinding of researchers and subjects,blinding of outcome assessment, integrity of outcome data, selective reporting, and other biases.The above seven evaluation indicators were evaluated for ‘ low risk bias ‘, ‘ unclear risk bias ‘, and ‘ high risk bias ‘ according to the bias risk assessment table made by RevMan5.4 software.
2.5 Statistical methods
The data were analyzed by RevMan5.4 software provided by Cochrane Collaboration.The outcome of dichotomous variables was expressed as relative risk (RR), and the outcome of continuous variables was expressed as mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD).95 % CI was used as the combined statistic(test level : α = 0.05).Heterogeneity test used chi-square test for qualitative (test level : α = 0.1) and I2test for quantitative.When the test results showed that there was homogeneity between the included studies (P 0.1, I250 %), the fixed effect model could be used for analysis.When the test results showed that there was heterogeneity between the included studies (P<0.1, I2>50%), the source of heterogeneity could not be determined after excluding the obvious heterogeneity, and the random effect model could be used for analysis.
Sensitivity analysis was performed on the results of the heterogeneity test P<0.1, I2>50% in this analysis using a fixed-effect model and a random-effect model conversion.Publication bias was analyzed using Stata 15.1 software, and Egger ‘s test was used to quantitatively evaluate publication bias.
3.Results
3.1 Literature search results
A total of 1472 articles were retrieved from Chinese and English databases.According to the inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria,10 articles[8-17] were finally included for data analysis.All of them were in English.The specific screening flow chart is shown in Figure1.
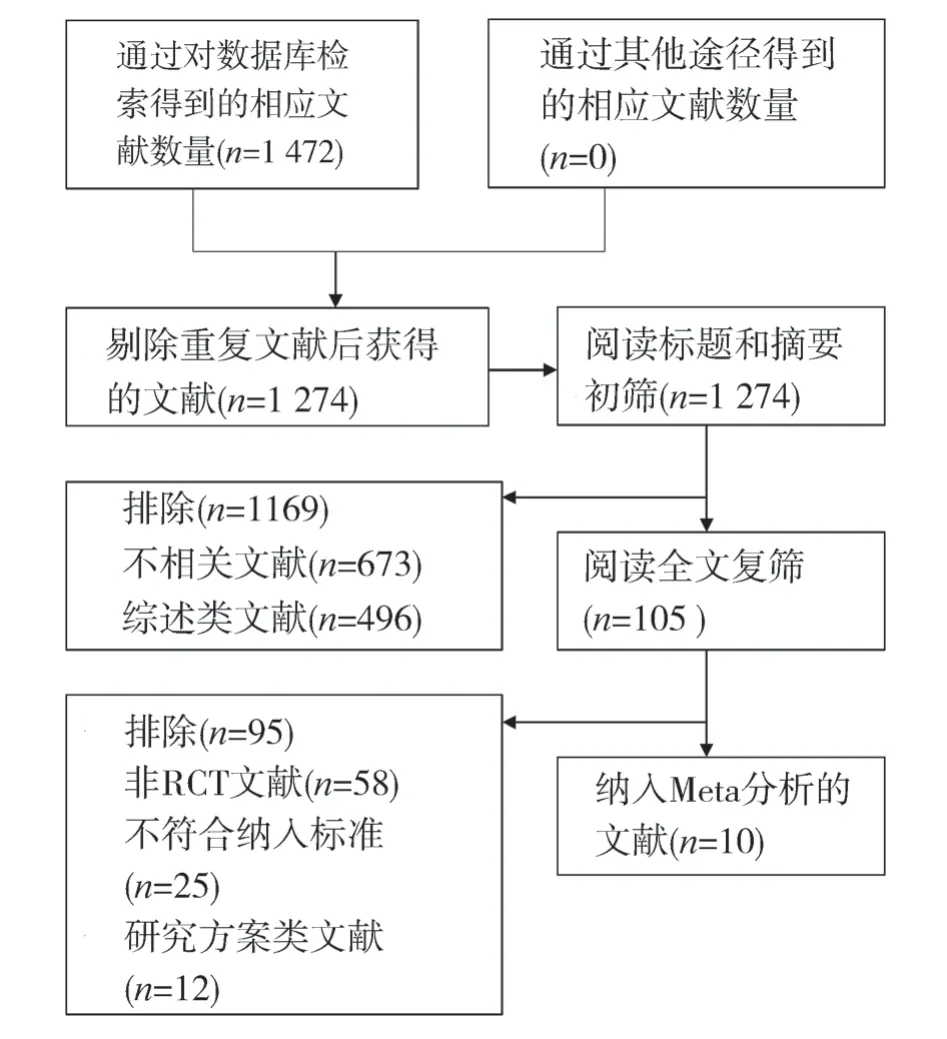
Fig 1 Literature screening process
3.2 Basic characteristics of included studies
A total of 1042 patients were included in 10 studies, of which 517 received open reduction and volar locking plate internal fixation,and 525 received closed reduction plaster ( 492 cases ) and splint( 33 cases ) external fixation conservative treatment.The total weighted average age was 70.2 years ( 70.3 years in the surgical group and 70.1 years in the non-surgical group ).This includes 173 men ( 16.6 % ) and 869 women ( 83.4 % ).The average follow-up time was 12 months to 3 years.All studies reported the upper limb dysfunction rating scale ( DASH ), 8 studies[9,11-17] reported wrist mobility, 7 studies[9,11,13-17] reported grip strength, 6 studies[8,9,11-14,16] reported imaging indicators, and 9 studies[8-11,13-17] reported complications.Each study compared the age and gender differences between the two groups, and there was no significant difference.The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
3.3 Risk of bias assessment of included studies
Nine of the 10 articles included in the study[8-12,14-17] clearly stated the random method and allocation concealment used, which could be evaluated as low-risk bias.One of the articles[13] used the oddeven grouping method, which means that allocation concealment cannot be implemented and was evaluated as high-risk bias.Due to the particularity of surgical treatment, this study could not blind the researchers and subjects, but the evaluator judged the outcome index as an objective measurement index, which was not affected by whether blinding was performed, so blinding the researchers and subjects could be evaluated as low risk bias.Among them, 4 articles[9,10,12,16] showed that the blind method was used to measure the results, and the blind method of outcome indicators could be evaluated as low risk bias.The specific bias risk assessment can be seen in Table 2, and the risk bias assessment using RevMan5.4 software can be seen in Figure 2.
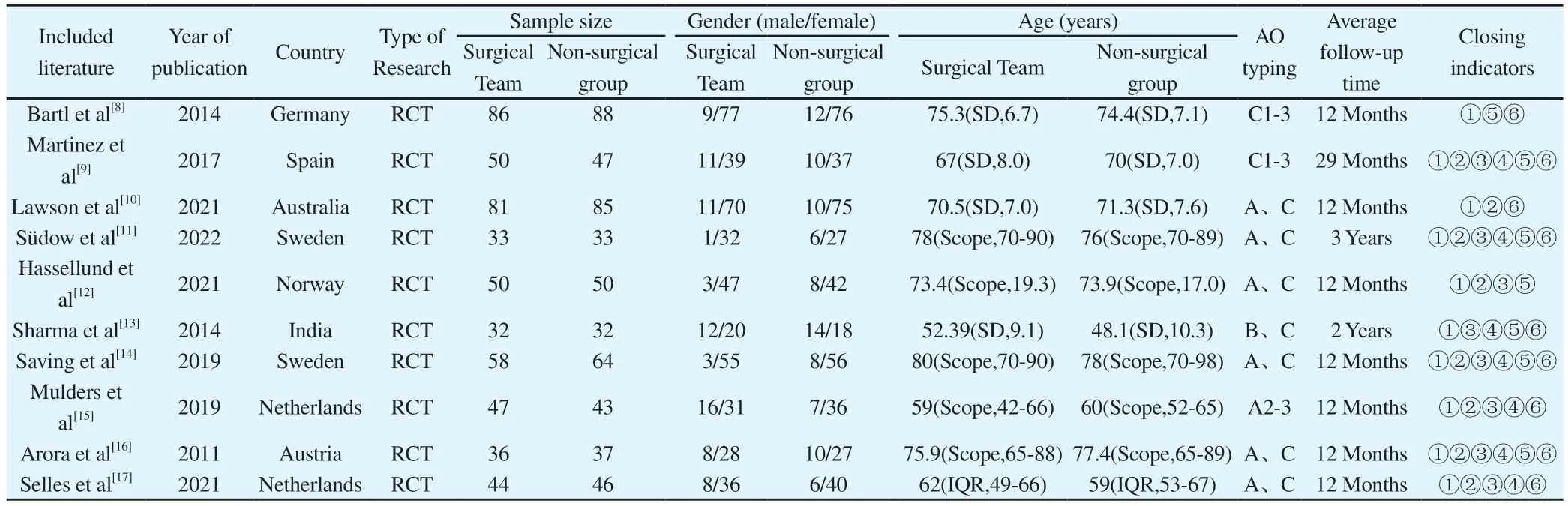
Tab 1 Basic characteristics of the included studies
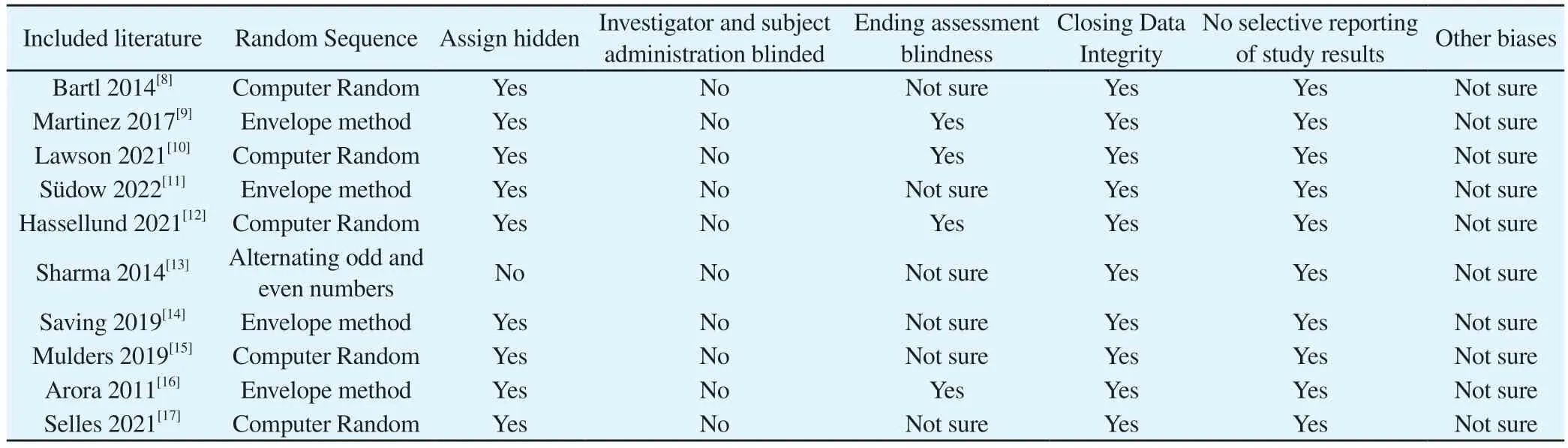
Tab 2 Methodological quality assessment of the included studies
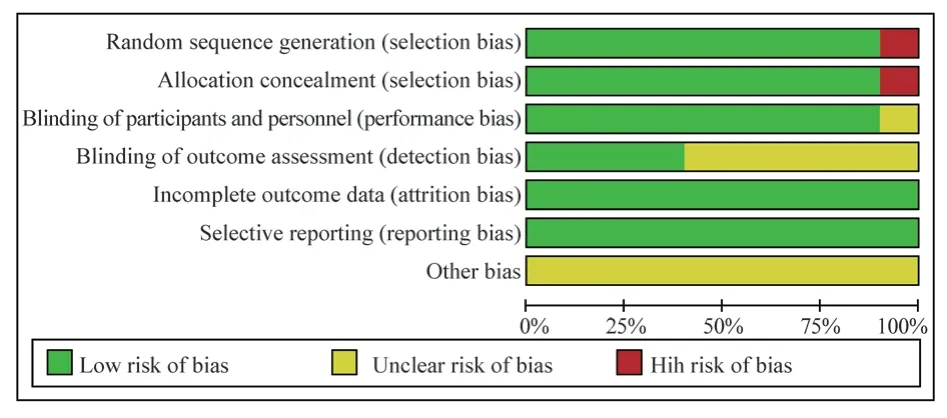
Fig 2 Publication bias of the included studies
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Upper limb dysfunction rating scale ( DASH )
The upper limb DASH score was used as the outcome index in 10 articles included in the study.Six of them[8,12,14,15-17] reported the DASH scores of the two treatments at 3 months, and the heterogeneity test had high heterogeneity ( P = 0.08, I2= 49 % ).Four[12,15-17] studies reported DASH scores at 6 months of the two treatments, and the heterogeneity test was highly heterogeneous (P = 0.10, I2= 52 % ) ; ten studies[8-17] reported the DASH scores after 1 year of the two treatments.There was no high heterogeneity in the heterogeneity test ( P = 0.46, I2= 0 % ).The random effect model was used to merge the data.Considering the different followup time points, subgroup analysis was performed to further explore the source of heterogeneity.The results showed that the DASH score of the surgical group was significantly lower than that of the non-surgical group at 3 months, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -10.45,95% CI ( -14.65, -6.25 ), P < 0.00001 ].At 6 months, the DASH score of the operation group was significantly lower than that of the non-operation group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -6.36, 95% CI ( -10.56, -2.15 ), P=0.003].After 1 year, the DASH score of the surgical group was significantly lower than that of the non-surgical group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -5.64,95% CI ( -7.21,-4.06 ), P < 0.000 01].The results showed that the DASH score of volar locking plate internal fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year was better than that of closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation, see figure 3.
3.4.2 Patient-Rated Wrist Evaluation ( PRWE )
A total of 8 articles included in the study used the wrist PRWE score as an outcome indicator.Among them, 6 studies[10,12,14-17] reported the PRWE scores of the two treatment methods at 3 months, and the heterogeneity test had high heterogeneity ( P =0.05, I2= 54 % ) ; four studies[12,15-17] reported the PRWE scores of the two treatments at 6 months, and the heterogeneity test showed no high heterogeneity ( P = 0.19, I2= 37 % ).Eight studies[9-12,14-17] reported PRWE scores after 1 year of two treatment methods.Heterogeneity test showed no high heterogeneity ( P = 0.10, I2= 42% ).Random effect model was used to merge data.Considering the different follow-up time points, subgroup analysis was performed to further explore the source of heterogeneity.The results showed that the PRWE score of the surgical group was significantly lower than that of the non-surgical group at 3 months, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -13.16,95% CI ( -18.82, -7.51 ),P < 0.000 01].At 6 months, the PRWE score of the surgical group was significantly lower than that of the non-surgical group, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -8.79,95%CI ( -14.61,-2.98 ), P = 0.003].After 1 year, the PRWE score of the surgical group was significantly lower than that of the non-surgical group,and the difference was statistically significant [MD = -5.90,95%CI ( -8.88, -2.92 ), P = 0.001 ].The results showed that the PRWE score of volar locking plate internal fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures was better than that of closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation at 3 months, 6 months and 1 year later, as shown in figure 4.
3.4.3 European five-dimensional health scale ( EQ-5D-5L )
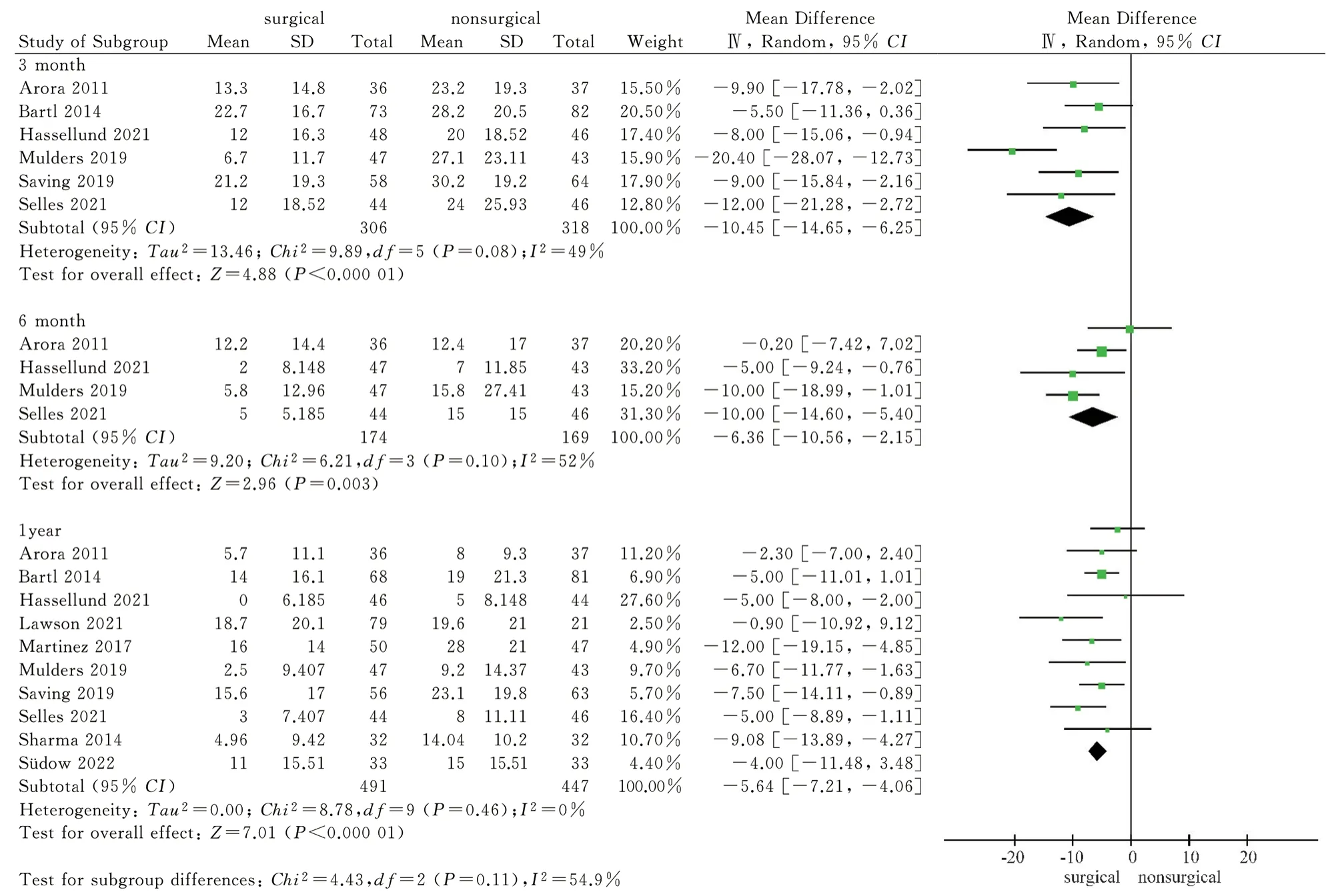
Fig 3 Meta analysis of DASH scores after two treatments
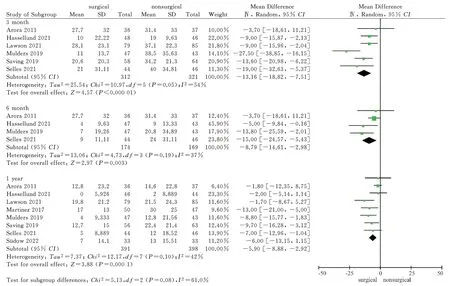
Fig 4 Meta analysis of PRWE scores after two treatments
A total of 5 articles included in the study used the European five-dimensional health scale as an outcome indicator.Four of them [8,9,12,14] reported the scores of the scale at 3 months after 2 treatments, and the heterogeneity test showed no high heterogeneity( P = 0.74, I2= 0 % ).Five studies[8,9,11,12,14] reported the scores of the scale after one year of two treatment methods.The heterogeneity test showed no high heterogeneity ( P = 0.20, I2= 33 % ).The fixed effect model was used for data merging.Considering the different follow-up time points, the results of subgroup analysis showed that the EQ-5D-5L scale score of the surgical group was higher than that of the non-surgical group at 3 months, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 0.05, 95%CI ( 0.02,0.08 ), P =0.001 ].After 1 year, the EQ-5D-5L score of the surgical group was higher than that of the non-surgical group, but the difference was not statistically significant [MD = 0.02, 95%CI ( -0.01,0.05 ), P = 0.27].The results showed that the EQ-5D-5L score of volar locking plate internal fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures was better than that of closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation at 3 months, but there was no significant difference between the two scores after 1 year, see figure 5.
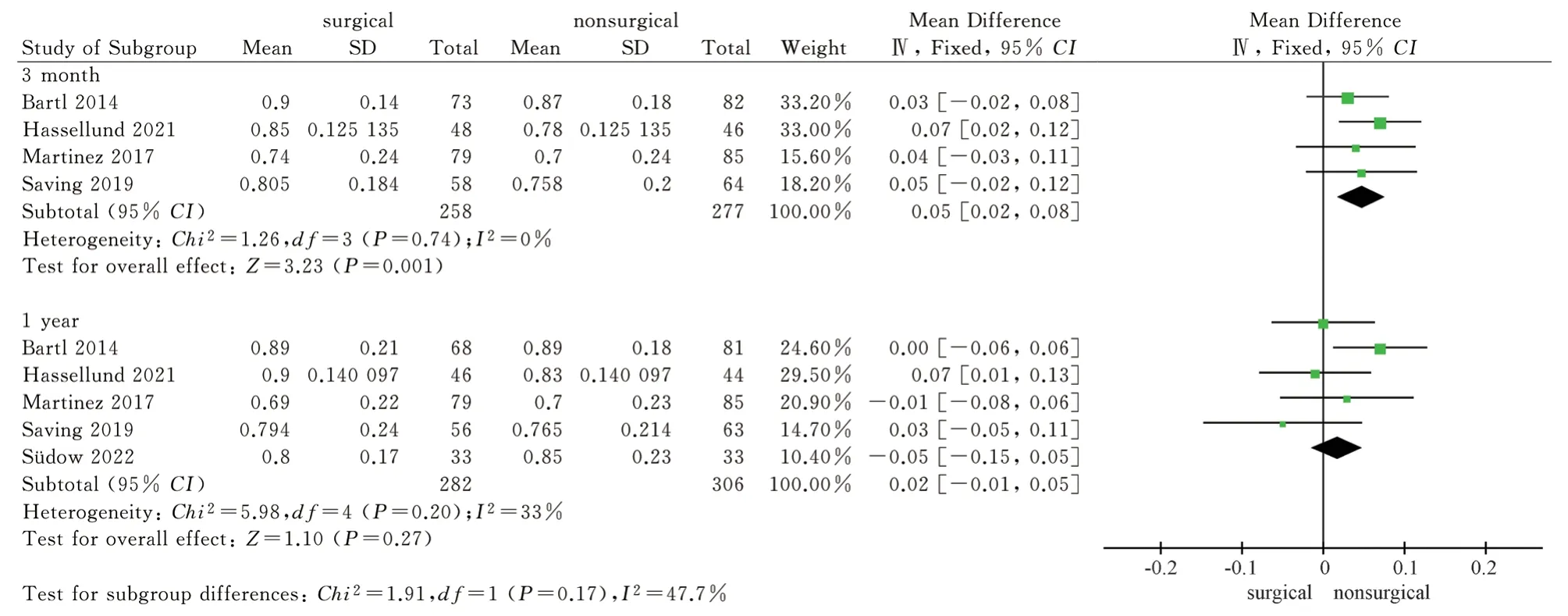
Fig 5 Meta analysis of the European Five dimensional Health Scale after two treatments
3.4.4 Wrist joint activity
A total of 8 articles[9,11-17] included wrist dorsiflexion, palmar flexion, pronation and supination as outcome indicators, and 7 articles[11-17] included ulnar deviation and radial deviation as outcome indicators.The wrist joint activity after 1 year of the two treatment methods was reported.The results of heterogeneity test showed that there was significant heterogeneity (P<0.1, I2>50%)among the studies, so the random effect model was used to analyze the above six wrist activity outcome indicators.The results showed that the surgical group was superior to the non-surgical group in palmar flexion, pronation and supination after 1 year, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 5.92, 95%CI ( 1.29,10.55 ), P = 0.01 ; MD = 2.48, 95%CI ( 0.59,4.36 ), P = 0.01 ; MD= 4.73,95%CI ( 2.15,7.31 ), P = 0.0003 ).There was no significant difference in dorsal extension, ulnar deviation and radial deviation between the surgical group and the non-surgical group after 1 year[MD = 2.22, 95%CI ( -4.15, 8.59 ), P = 0.49 ; MD = 3.49,95%CI (-0.80,7.78 ), P = 0.11 ; MD = 2.05, 95%CI ( -2.39,6.50 ), P = 0.37).The results showed that volar locking plate internal fixation was superior to closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation in palmar flexion, pronation and supination after 1 year of treatment of distal radius fracture, but there was no significant difference between the two in dorsal extension, ulnar deviation and radial deviation, as shown in Fig.6-Fig.11.
3.4.5 Grip strength
A total of 7 articles[9,11,13-17] included in the study used grip strength as an outcome indicator, and reported the grip strength of the two treatments after 1 year.Because the data unit system was not uniform, the standard mean difference ( SMD ) was used as a statistical indicator.The heterogeneity test had high heterogeneity( P < 0.00001, I2= 88 % ), so the random effect model was used for combined analysis.The results showed that the grip strength of the non-surgical group was lower than that of the surgical group after 1 year, and the difference was statistically significant [SMD =0.61,95%CI( 0.12,1.10 ), P = 0.02].The results showed that the grip strength of volar locking plate internal fixation for the treatment of distal radius fractures after 1 year was better than that of closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation, see figure 12.
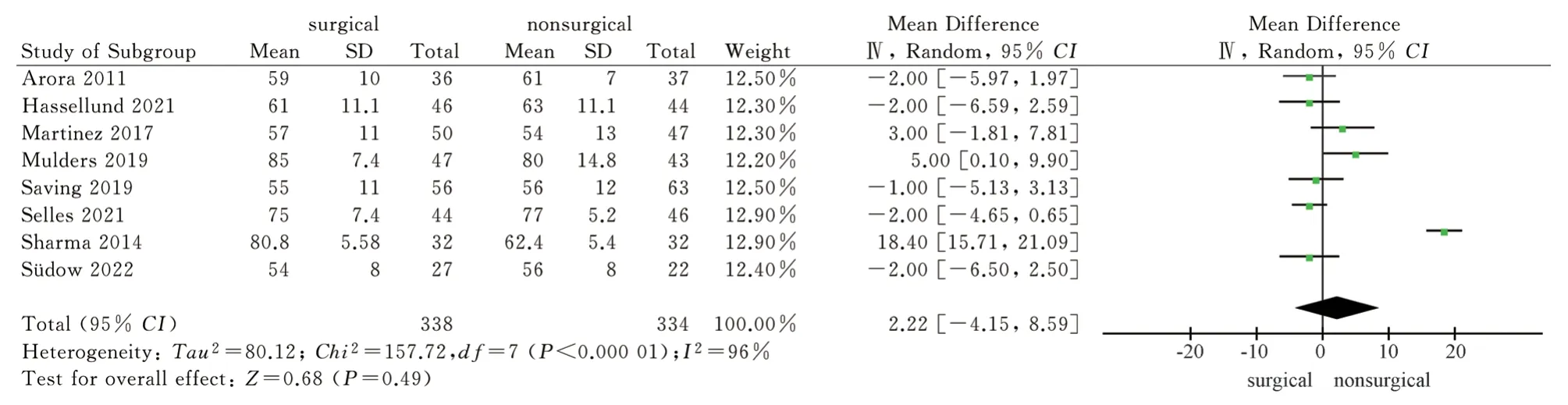
Fig 6 Meta analysis of wrist dorsiflexion after two treatments
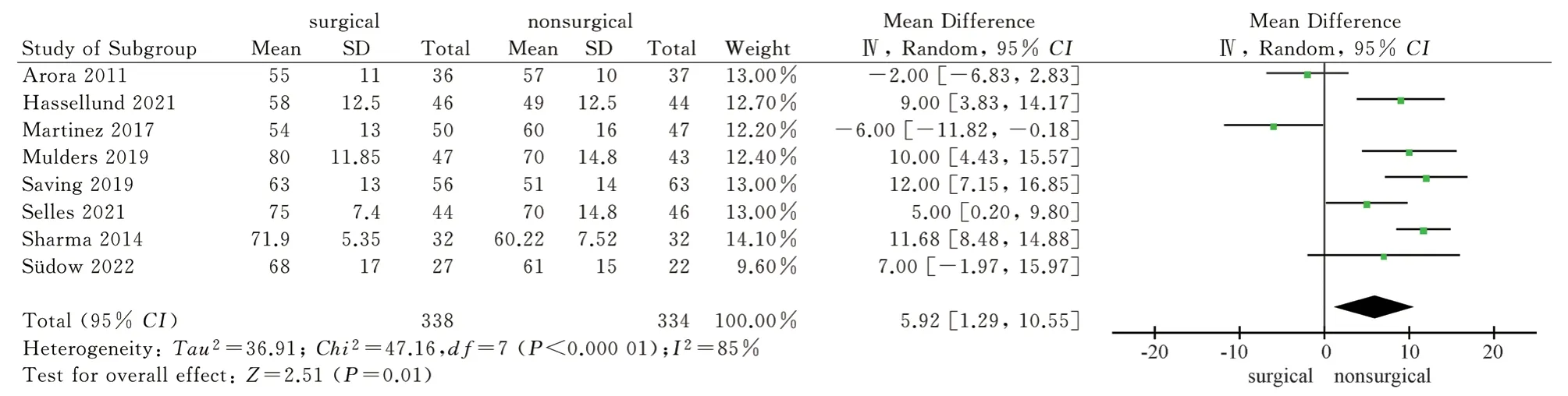
Fig 7 Meta analysis of wrist flexion after two treatments
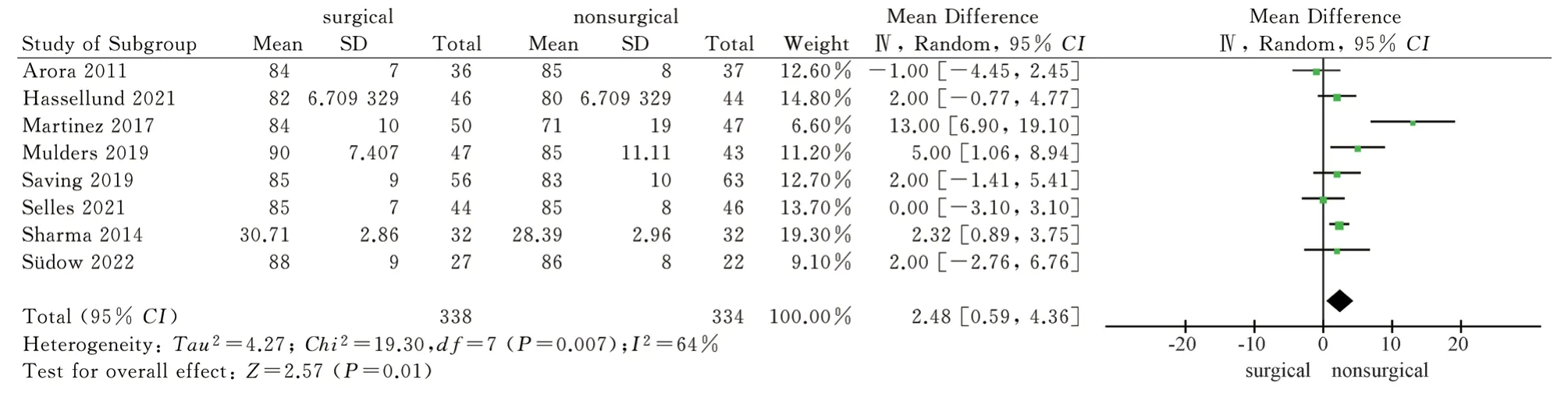
Fig 8 Meta analysis of forearm pronation after two treatments
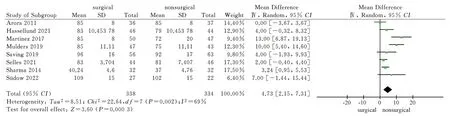
Fig 9 Meta analysis of forearm supination after two treatments

Fig 10 Meta analysis of ulnar deviation of wrist joint after two treatments
3.4.6 Imaging indicators
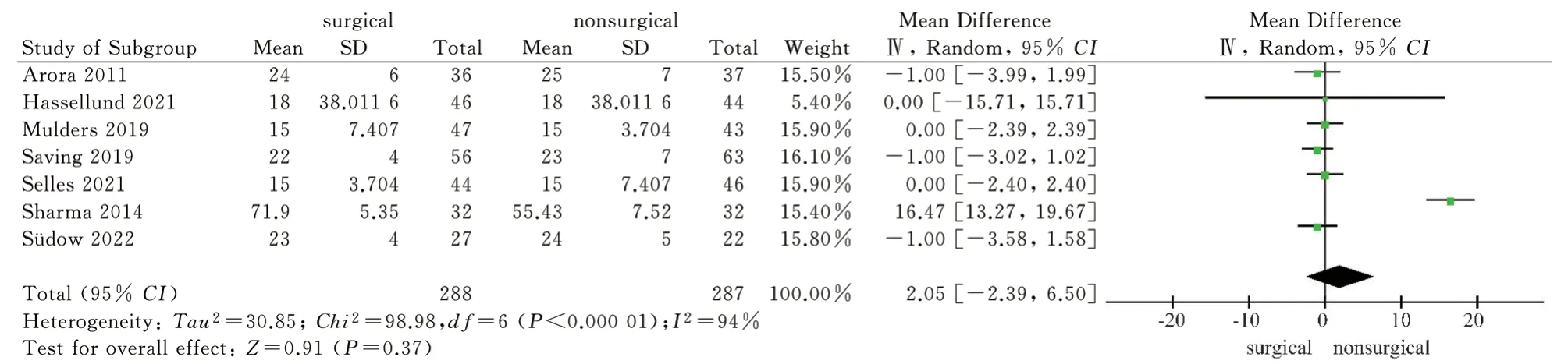
Fig 11 Meta analysis of wrist radial deviation after two treatments
A total of 7 literatures[8,9,11-14,16] included in the study used imaging analysis as an outcome indicator.Among them, 7 literatures[8,9,11-14,16] reported palmar tilt angle and radial inclination after 1 year of two treatment methods, and 5 literatures[8,9,11,12,16] reported ulnar variance.Heterogeneity tests showed high heterogeneity (P<0.1, I2>50%), so the random effect model was used to analyze the above three imaging indicators.The results showed that the palmar tilt angle and radial inclination of the surgical group were greater than those of the non-surgical group after 1 year, and the difference was statistically significant [MD = 9.84, 95%CI ( 5.66, 14.02 ), P <0.00001 ; MD = 4.33,95%CI ( 2.97,5.69 ), P < 0.00001 ).One year later, there was no significant difference in ulnar variance between the surgical group and the non-surgical group [MD = -1.14, 95%CI( -3.16, 0.88 ), P = 0.27 ].The results showed that the volar locking plate internal fixation for the treatment of distal radius fractures after 1 years of imaging indicators palmar tilt angle, radial inclination is better than the closed reduction plaster, splint external fixation, but the difference between the two ulnar variance was not statistically significant, see Figure 13-15.
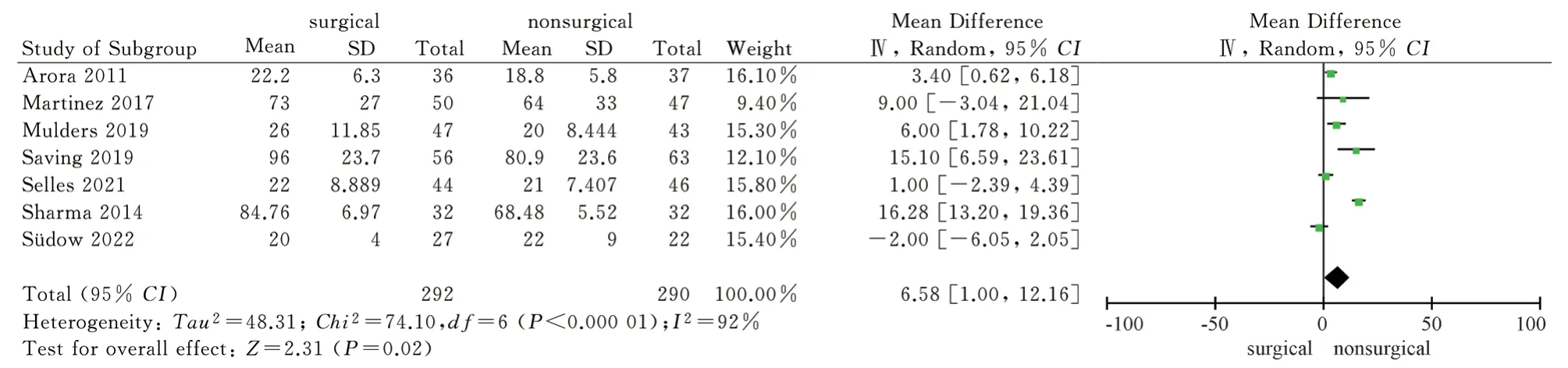
Fig 12 Meta analysis of grip strength after two treatments
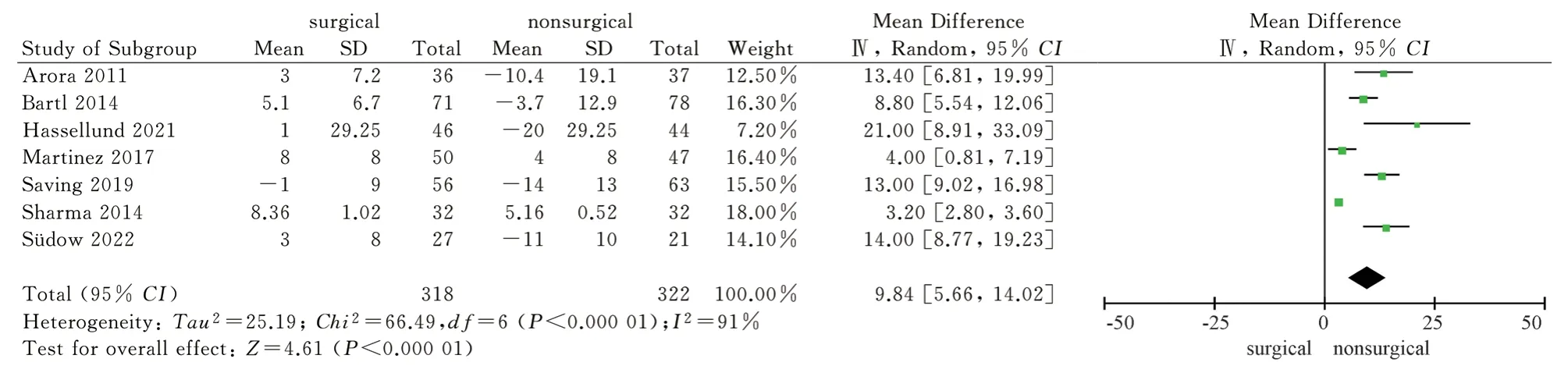
Fig 13 Meta analysis of palmar tilt angle after two treatments
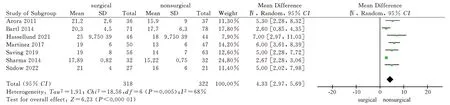
Fig 14 Meta analysis of radial inclination after two treatments
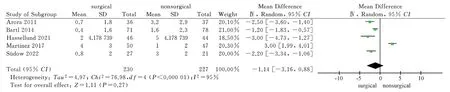
Fig 15 Meta analysis of ulnar variance after two treatments
3.4.7 Complications
A total of 9 articles[8-11,13-17] included in the study used the occurrence of complications as an outcome indicator, and reported the occurrence of complications in the two treatment methods.The heterogeneity test had high heterogeneity ( P = 0.008, I2= 61 % ), so the random effect model was used for combined analysis.The results showed that there was no significant difference in complications between the two treatment methods [RR = 0.77,95%CI( 0.54,1.10), P = 0.16].Six articles[8,11,14-17] reported the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome in the two treatment methods.There was no high heterogeneity in the heterogeneity test ( P = 0.41, I2= 1%), so the fixed effect model was used for combined analysis.The results showed that there was no significant difference in the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome between the two treatment methods [RR =0.49, 95%CI( 0.24,1.02 ), P = 0.06 ].The results showed that there was no significant difference in complications between palmar locking plate internal fixation and closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures, as shown in Figure 16-17.
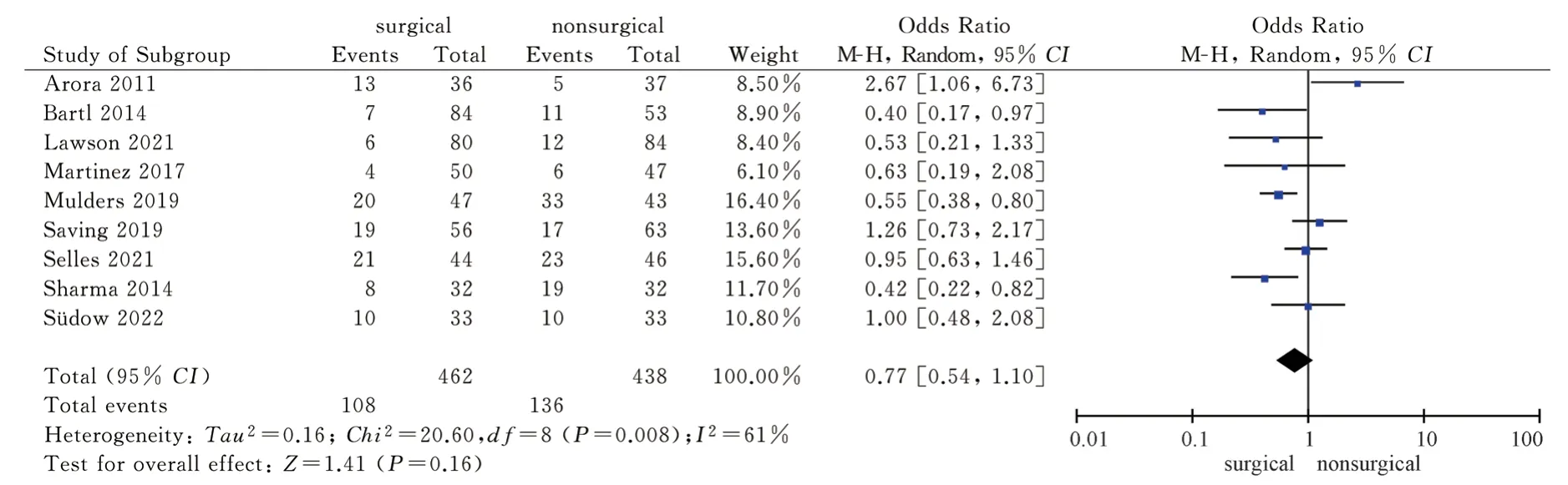
Fig 16 Meta analysis of the total number of complications after two treatments
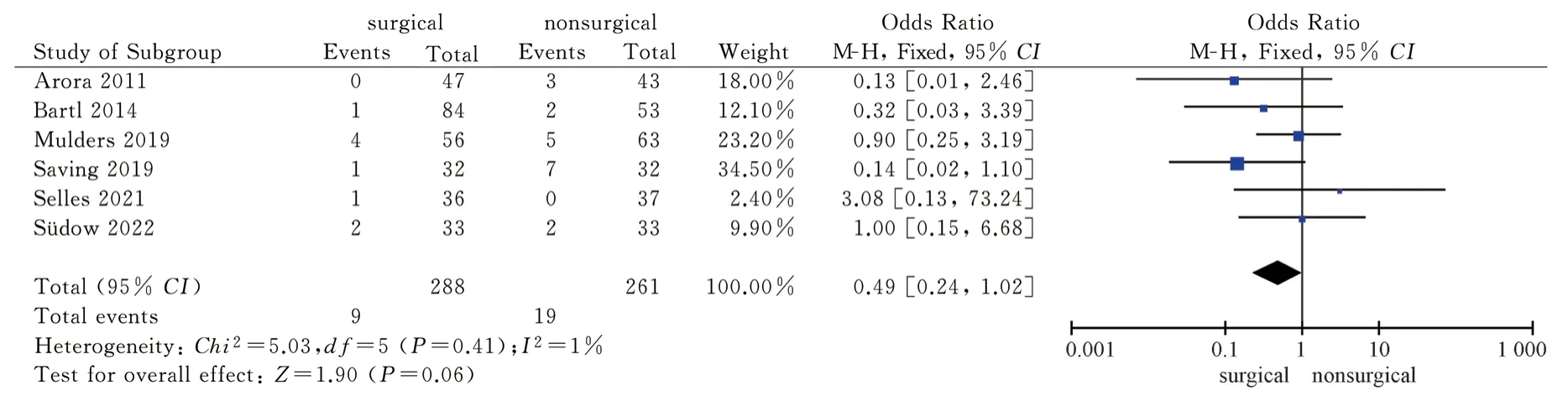
Fig 17 Meta analysis of carpal tunnel syndrome after two treatments
3.5 Sensitivity analysis and publication bias
3.5.1 Sensitivity analysis
The results of heterogeneity test P<0.1, I2>50% in this study (DASH score at 3 months and 6 months, PRWE score at 3 months,wrist joint activity, grip strength, imaging indicators, complications) were analyzed by fixed effect model and random effect model.The results were consistent with the results of meta-analysis of fixed effect model and random effect model except dorsal extension, radial deviation, ulnar deviation, ulnar variance and complications, as shown in table 3.
3.5.2 Publication bias
The results of DASH score after 1 year, PRWE score after 1 year, dorsal extension, palmar flexion, pronation, supination, grip strength and complications showed P > 0.05 and 95%CI contained 0,indicating that the included original study was not published bias, as shown in Table 4.
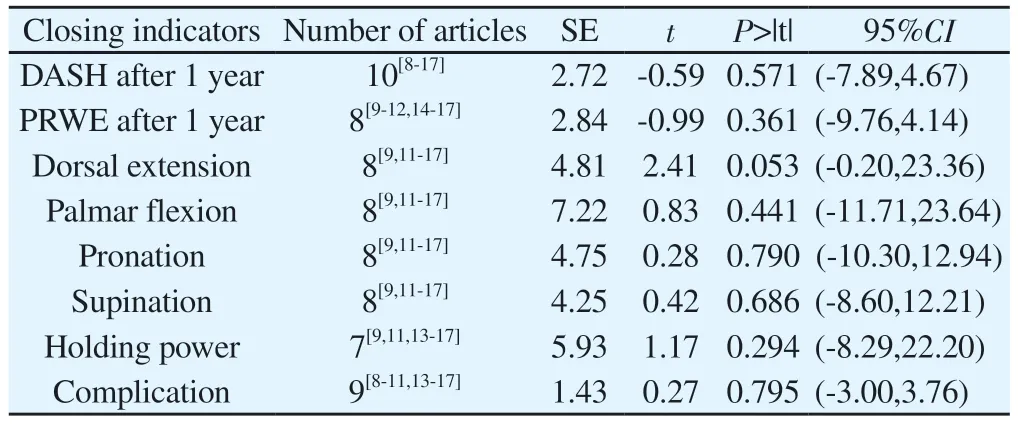
Tab 4 Publication bias of the included studies
4.Discussions
This study analyzed and evaluated the results of volar locking plate internal fixation and closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation in the treatment of distal radius fractures in terms of function, imaging indicators and complications.The results showed that the two treatment methods had similar results in the European five-dimensional health scale ( EQ-5 D-5 L ) score and complications after 1 year.The DASH score, PRWE score and grip strength of the volar locking plate internal fixation were better than the closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation.In the range of motion of the wrist joint, the results of the two were equivalent in the direction of dorsal extension, ulnar deviation and radial deviation.In the direction of palmar flexion, pronation and supination, the volar locking plate internal fixation was better than the closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation.In terms of imaging indicators, volar locking plate internal fixation is superior to closed reduction plaster and splint external fixation in palmar tilt angle and radial inclination after treatment, but the results of ulnar variance are similar.
The optimal treatment of distal radius fractures has been controversial for a long time.Egol et al[18] compared the difference between surgical and non-surgical treatment of distal radius fractures showed that there was no significant difference in DASH score,VAS score and complications between the two groups.Only the grip strength and imaging indexes of the surgical group were better than those of the non-surgical group.Martinez et al[9] found that the quality of life and functional indicators of patients after plate fixation were significantly improved, and 25% of non-surgical treatment patients had significant reduction loss.Hammer et al[19] showed that volar plate internal fixation was superior to external fixation in DASH score, wrist range of motion and grip strength.The cost of closed reduction and plaster or splint external fixation is lower than that of plate internal fixation, but it is not easy to maintain the anatomical position for complex intra-articular fractures, and the risk of fracture re-displacement is higher[20].Open reduction and internal fixation can be operated under direct vision, which is easy to achieve anatomical reduction, and stable fixation can be used for early functional exercise.However, when the fracture displacement is large, the complex intra-articular fracture or the bone defect of the broken end is obvious, the open reduction needs to fully expose the surgical field, which has a great damage to the blood supply and soft tissue of the broken end of the fracture, and increases the risk of complications such as nerve and tendon injury[21,22].The factors affecting the efficacy of closed reduction and external fixation come from many aspects, mainly reflected in the professional level differences of closed reduction physicians and the self-management of external fixation after closed reduction.Due to the particularity of closed reduction technology, it is controversial with surgical treatment.
In recent years, some scholars have systematically evaluated the difference between surgical and non-surgical treatment of distal radius fractures, but they have not reached a consensus due to the relative diversity of treatment methods.Handoll et al[23] reported that there is not enough evidence to confirm that surgical treatment of distal radius fractures is superior to non-surgical treatment in functional recovery.Peng et al[24] studied the difference between surgical and non-surgical treatment of complex intra-articular distal radius fractures, and the results showed that surgical treatment was superior to non-surgical treatment.Due to the small sample size of each study and the obvious differences among the studies, the systematic evaluation and Meta-analysis of the efficacy of surgical and non-surgical treatment of distal radius fractures are quite different.
In this study, it was shown that volar locking plate internal fixation was superior to closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation in DASH score after 1 year, which was not the same as the previous meta-analysis results.Ju et al[25] reported a meta-analysis of 6 studies with a total of 577 patients that showed no difference in DASH scores.Chen et al[26] evaluated 7 studies with a total of 600 patients and found no difference in DASH scores between surgical and nonsurgical groups.It has been reported that the DASH score after treatment of distal radius fractures tends to be stable after 1 year.The DASH score obtained by long-term follow-up is susceptible to other events and patient factors, so the mid-term functional score ( 1 year later ) is identified as the most relevant to the efficacy[27,28].Ju et al [25] and Chen et al[26] did not distinguish the mid-term and longterm DASH scores.In this study, 10 items were included in a total of 1042 patients, which exceeded the sample size of the previous meta-analysis.The results showed that the DASH score, PRWE score, wrist flexion, pronation and supination directions after 1 year suggested that the volar locking plate internal fixation group had certain advantages, but after 1 year, the European five-dimensional health scale ( EQ-5D-5L ) score, wrist extension, ulnar deviation and radial deviation were not significantly different from the nonsurgical group.It may be related to the fact that the weighted average age of the patients included in this study is more than 70 years old,the requirement for limb function is not high, and there is no need to bear high-intensity physical labor.Therefore, the difference in functional scores after the two treatment methods has no significant effect on the quality of life and overall health of the patients.
In this study, when comparing the differences in imaging indicators between the two treatment methods, it was found that the palmar tilt angle and radial inclination of the volar plate internal fixation group were better than those of the closed reduction plaster or splint fixation group, which was consistent with the Meta-analysis results of Ochen et al[29] and He et al[30].In recent years, studies have shown that the imaging indexes of unstable complex distal radius fractures after treatment are inconsistent with the clinical outcome function [31,32], and the correlation between subjective and objective functional outcome indexes and anatomical reduction is insufficient[33].In this study, the European five-dimensional health scale ( EQ-5D-5L) score and the range of motion of some wrist joints after two treatments were not significantly different, so it was impossible to prove the relationship between imaging indicators and patients’quality of life and health status.
This study shows that volar locking plate internal fixation is more conducive to the recovery of grip strength, which is different from the previous two Meta-analysis results.Ju et al[25] reported 4 Meta-analyses of 337 patients in total, and the results showed that there was no significant difference in grip strength between the two treatment methods.Song et al[34] reported 2 Meta-analyses of 133 patients at 12 months, and the results showed that there was no significant difference in grip strength between the two groups.However, the results of the above two meta-analyses may be limited by the number of patients included in the study.In contrast, Ochen et al[29] reported 13 meta-analyses of 971 patients, which showed that surgical treatment was superior to non-surgical treatment for grip strength recovery.In this study, 7 items were included in a total of 582 patients.Meta-analysis showed that the grip strength was significantly greater after volar locking plate internal fixation.
This study showed that there was no significant difference in the incidence of complications between the two treatment methods,which was consistent with the results of Song et al[34] and Yu et al[35].However, due to the limited information on the manifestations and treatment of complications in the included studies, it is impossible to accurately compare the main complications and secondary complications, and it is impossible to determine whether they are simple symptoms or nerve damage.Therefore, it is still difficult to evaluate the complications of the two treatment methods.Volar plate internal fixation can significantly improve the midterm DASH score, PRWE score, imaging indicators and grip strength of patients with distal radius fractures.These results may make clinicians more inclined to surgical treatment of distal radius fractures.However, we must always consider the special factors of the patient, such as the patient ‘s age, habits, occupation and complications.Although surgical treatment has the above advantages, there is no significant difference in the quality of life,the range of motion of some wrist joints and complications after the two treatments.Therefore, the author believes that the indications for open reduction and internal fixation for the treatment of distal radius fractures should be carefully grasped, and non-surgical treatment should be given priority.
5.Limitations and deficiencies
The follow-up time of the original literature included in this study has certain differences.Although some outcome indicators have been analyzed in subgroups, there is still some heterogeneity.Although this study showed no publication bias, due to the lack of literature on some outcome indicators, publication bias cannot be completely ruled out.
Meta-analysis of this topic is mostly limited to people over 60 years old.Studies have shown that the incidence of distal radius fractures in people aged 17~64 is increasing[36].Therefore, for people under 60 years old who still need to work and work, the best treatment for distal radius fractures needs further research and discussion.In addition to studying traditional outcome indicators, we can further observe the situation of sports activities and labor work.
This study contains a variety of fracture types, most of which include AO type A and C fractures.It has been reported that different injury methods will lead to differences in fracture classification,and there are some differences in wrist function after treatment in patients with different types of distal radius fractures[37,38].However,due to data limitations, subgroup analysis cannot be performed to compare the differences in outcome indicators between different types of fractures, and more detailed individual patient data is needed for meta-analysis.
In conclusion, this study shows that compared with closed reduction plaster or splint external fixation, volar locking plate internal fixation is beneficial to medium-term DASH score and grip strength, but there is no significant difference in patients ‘ quality of life and complications.For adult distal radius fractures, surgical indications should be carefully grasped, and non-surgical treatment should be given priority.More detailed research and analysis are needed for young people under 60 years old.
Author’s contribution
Chen Jiange conceptualized, designed, and wrote the article; Chen Jiange and Zhang Haining searched and screened relevant literature,while Zhao Hongzhou and Chen Jiange extracted data and conducted quality evaluation; Liu Mingjun and Xing Jiahui conducted data processing and used RevMan 5.4, Stata 15.1, and Word software to draw relevant charts; Wang Weimin and Wang Ping control and proofread the quality of the article, and are responsible for the overall quality of the article.
All authors of this article declare that they have no conflict of interest.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2023年19期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study on the in vitro anti ovarian cancer effect and mechanism of quinazoline derivative (N111)
- m6A modification promotes the proliferation and migration of cervical cancer and regulates the expression of PD-L1
- Expression and correlation of pyroptosis-related markers and PI3K/AKT pathway in endometriosis
- A review of the epidemic and clinical study on scrub typhus in China(2010-2020)
- MiR-15a-5p in neutrophil exosomes promotes macrophage apoptosis through targeted inhibition of BCL2L2
- Clinical efficacy of bushen huatan huoxue recipe in combination with acupuncture in treating patients suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome with insulin resistance
